Optimal Inspired Fraction of Oxygen in the Delivery Room for Preterm Infants
Abstract
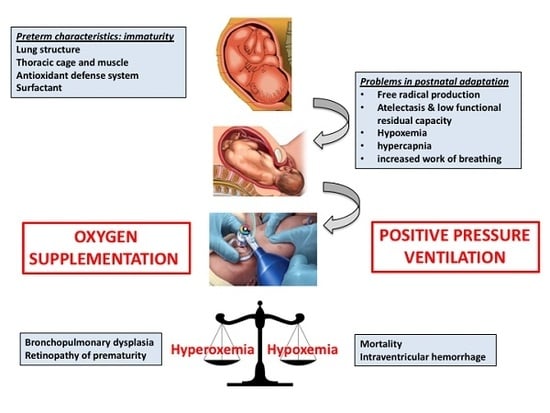
:1. Introduction
2. Oxygen in the Fetal to Neonatal Transition
3. Initial FiO2 in the Delivery Room
4. Target Oxygen Saturation during Stabilization
5. Heart Rate
6. Follow-Up
7. Clinical Practice
8. Seeking an Answer: Forthcoming Trials
9. Conclusions
Author contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alphonse, R.S.; Rajabali, S.; Thébaud, B. Lung injury in preterm neonates: The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1013–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, M.; Aguar, M.; Escobar, J.; Arduini, A.; Escrig, R.; Brugada, M.; Izquierdo, I.; Asensi, M.A.; Sastre, J.; Saenz, P.; et al. Antenatal steroids and antioxidant enzyme activity in preterm infants: Influence of gender and timing. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, D.G.; Carnielli, V.; Greisen, G.; Hallman, M.; Ozek, E.; Plavka, R.; Saugstad, O.D.; Simeoni, U.; Speer, C.P.; Vento, M.; et al. European consensus guidelines on the management of respiratory distress syndrome—2016 Update. Neonatology 2017, 111, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Cuevas, I.; Cernada, M.; Nuñez, A.; Escobar, J.; Kuligowski, J.; Chafer-Pericas, C.; Vento, M. Oxygen supplementation to stabilize preterm infants in the fetal to neonatal transition: No satisfactory answer. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento, M.; Teramo, K. Evaluating the fetus at risk for cardiopulmonary compromise. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vali, P.; Lakshminrusimha, S. The fetus can teach us: Oxygen and the pulmonary vasculature. Children 2017, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Raj, J.U. Regulation of the pulmonary circulation in the fetus and newborn. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1291–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.A.; Kamlin, C.O.; Vento, M.; Wong, C.; Cole, T.J.; Donath, S.M.; Davis, P.G.; Morley, C.J. Defining the reference range for oxygen saturation for infants after birth. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e1340–e1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, M.H.; Aziz, K.; Escobedo, M.B.; Kapadia, V.S.; Kattwinkel, J.; Perlman, J.M.; Simon, W.M.; Weiner, G.M.; Zaichkin, J.G. Part 13: Neonatal resuscitation: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2015, 132, S543–S560, Suppl. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento, M.; Escobar, J.; Cernada, M.; Escrig, R.; Aguar, M. The use and misuse of oxygen during the neonatal period. Clin Perinatol. 2012, 39, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento, M.; Cubells, E.; Escobar, J.J.; Escrig, R.; Aguar, M.; Brugada, M.; Cernada, M.; Saénz, P.; Izquierdo, I. Oxygen saturation after birth in preterm infants treated with continuous positive airway pressure and air: Assessment of gender differences and comparison with a published nomogram. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F228–F232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, J.L.; Ghadge, A.; Coates, E.; Wright, I.M.; Saugstad, O.D.; Vento, M.; Buonocore, G.; Nagashima, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hosono, S.; et al. Clinicians in 25 countries prefer to use lower levels of oxygen to resuscitate preterm infants at birth. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, O.; Jordan, H.; Rabe, H. Strategies for implementing placental transfusion at birth: A systematic review. Birth 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katheria, A.; Hosono, S.; El-Naggar, W. A new wrinkle: Umbilical cord management (how, when, who). Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, J.M.; Wyllie, J.; Kattwinkel, J.; Wyckoff, M.H.; Aziz, K.; Guinsburg, R.; Kim, H.S.; Liley, H.G.; Mildenhall, L.; Simon, W.M.; et al. Part 7: Neonatal resuscitation: 2015 International consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Circulation 2015, 132, S204–S241, Suppl. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, J.; Bruinenberg, J.; Roehr, C.C.; Rüdiger, M.; Trevisanuto, D.; Urlesberger, B. European Resuscitation Council guidelines for resuscitation 2015: Section 7. Resuscitation and support of transition of babies at birth. Resuscitation 2015, 95, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, M.; Schmölzer, G.; Cheung, P.Y.; Finer, N.; Solevåg, A.L.; Oei, J.L.; Saugstad, O.D. What initial oxygen is best for preterm infants in the delivery room?-A response to the 2015 neonatal resuscitation guidelines. Resuscitation 2016, 101, e7–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugstad, O.D.; Aune, D.; Aguar, M.; Kapadia, V.; Finer, N.; Vento, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of optimal initial fraction of oxygen levels in the delivery room at ≤32 weeks. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, J.L.; Saugstad, O.D.; Lui, K.; Wright, I.M.; Smyth, J.P.; Craven, P.; Wang, Y.A.; McMullan, R.; Coates, E.; Ward, M.; et al. Targeted oxygen in the resuscitation of preterm infants, a randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20161452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, Y.; Lodha, A.; Soraisham, A.; Singhal, N.; Barrington, K.; Shah, P.S. Outcomes of preterm infants following the introduction of room air resuscitation. Resuscitation 2015, 96, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsford, M.; Nishiyama, C.; Shortt, C.; Weiner, G.; Roehr, C.C.; Isayama, T.; Dawson, J.A.; Wyckoff, M.H.; Rabi, Y. International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation Neonatal Life Support Task Force. Initial oxygen use for preterm newborn resuscitation: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20181828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, K.; Jones, L.J.; Foster, J.P.; Davis, P.G.; Ching, S.K.; Oei, J.L.; Osborn, D.A. Lower versus higher oxygen concentrations titrated to target oxygen saturations during resuscitation of preterm infants at birth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, CD010239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, P.; Rawat, M.; Gugino, S.F.; Koenigsknecht, C.; Helman, J.; Nair, J.; Vali, P.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Effect of various inspired oxygen concentrations on pulmonary and systemic hemodynamics and oxygenation during resuscitation in a transitioning preterm model. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, G.; Urlesberger, B.; Balk, N.; Schwaberger, B.; Binder-Heschl, C.; Avian, A.; Pansy, J.; Cheung, P.Y.; Schmölzer, G.M. Cerebral oxygen saturation to guide oxygen delivery in preterm neonates for the immediate transition after birth: A 2-center randomized controlled pilot feasibility trial. J. Pediatr. 2016, 170, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, G.; Schmölzer, G.M.; Urlesberger, B. Cerebral tissue oxygenation during immediate neonatal transition and resuscitation. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüdiger, M.; Braun, N.; Aranda, J.; Aguar, M.; Bergert, R.; Bystricka, A.; Dimitriou, G.; El-Atawi, K.; Ifflaender, S.; Jung, P.; et al. Neonatal assessment in the delivery room--Trial to evaluate a specified type of apgar (TEST-Apgar). BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, J.L.; Finer, N.N.; Saugstad, O.D.; Wright, I.M.; Rabi, Y.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Rich, W.; Kapadia, V.; Rook, D.; Smyth, J.P.; et al. Outcomes of oxygen saturation targeting during delivery room stabilisation of preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 103, F446–F454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamrin, V.; Saugstad, O.D.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Wang, Y.A.; Lui, K.; Wright, I.M.; De Waal, K.; Travadi, J.; Smyth, J.O.; Craven, P.; et al. Preterm infant outcomes after randomization to initial resuscitation with FiO2 0.21 or 1.0. J. Pediatr. 2018, 201, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwill, A.G.; Dick, G.M.; Kiel, A.M.; Tune, J.D. Regulation of coronary blood flow. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 321–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, V.S.; Oei, J.L.; Saugstad, O.D.; Rabi, Y.; Finer, N.N.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Rich, W.; Rook, D.; Vermeulen, M.; Smyth, J.; et al. BradyPrem study: Heart rate is the most vital signs during resuscitation of preterms. 2019; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Saugstad, O.D.; Oei, J.L.; Lakshminrusimha, S.; Vento, M. Oxygen therapy of the newborn from molecular understanding to clinical practice. Pediatr. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soraisham, A.S.; Rabi, Y.; Shah, P.S.; Singhal, N.; Synnes, A.; Yang, J.; Lee, S.K.; Lodha, A.K. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants resuscitated with different oxygen concentration at birth. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, V.S.; Lal, C.V.; Kakkilaya, V.; Heyne, R.; Savani, R.C.; Wyckoff, M.H. Impact of the neonatal resuscitation program-Recommended low oxygen strategy on outcomes of infants born preterm. J. Pediatr. 2017, 191, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronat, N.; Aguar, M.; Rook, D.; Iriondo, M.; Brugada, M.; Cernada, M.; Nuñez, A.; Izquierdo, M.; Cubells, E.; Martinez, M.; et al. Survival and neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterms resuscitated with different oxygen fractions. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, V.S.; Chalak, L.F.; Sparks, J.E.; Allen, J.R.; Savani, R.C.; Wyckoff, M.H. Resuscitation of preterm neonates with limited versus high oxygen strategy. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e1488–e1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente-Pozo, S.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Núñez-Ramiro, A.; Cernada, M.; Hervás, D.; Boronat, N.; Sandoval, J.; Vento, M. The oxygen load supplied during delivery room stabilization of preterm infants modifies the DNA methylation profile. J. Pediatr. 2018, 202, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.A.; Vento, M.; Finer, N.N.; Rich, W.; Saugstad, O.D.; Morley, C.J.; Davis, P.G. Managing oxygen therapy during delivery room stabilization of preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Vento, M.; Shah, P.S.; Saugstad, O.; Finer, N.; Rich, W.; Morton, R.L.; Rabi, Y.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Suzuki, K.; et al. A review of international clinical practice guidelines for the use of oxygen in the delivery room resuscitation of preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, C.M.; Kofa, E.W.; Slutsky, J.R. Clinicians' attitudes to clinical practice guidelines: A systematic review. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 502–506. [Google Scholar]
- Iriondo, M.; Thió, M.; Burón, E.; Salguero, E.; Aguayo, J.; Vento, M. Neonatal Resuscitation Group of the Spanish Neonatal Society. A survey of neonatal resuscitation in Spain: Gaps between guidelines and practice. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gestational Age | Initial FiO2 | Target SpO2 at 5 min |
|---|---|---|
| <37 weeks | 0.21 | 85–90% |
| 33+0 to 36+6 weeks | 0.21 | 85% |
| 29+0 to 32+6 weeks | 0.21-0.30* | 80–85% |
| ≤28 weeks | 0.3 | 80% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara-Cantón, I.; Solaz, A.; Parra-Llorca, A.; García-Robles, A.; Vento, M. Optimal Inspired Fraction of Oxygen in the Delivery Room for Preterm Infants. Children 2019, 6, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020029
Lara-Cantón I, Solaz A, Parra-Llorca A, García-Robles A, Vento M. Optimal Inspired Fraction of Oxygen in the Delivery Room for Preterm Infants. Children. 2019; 6(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara-Cantón, Inmaculada, Alvaro Solaz, Anna Parra-Llorca, Ana García-Robles, and Máximo Vento. 2019. "Optimal Inspired Fraction of Oxygen in the Delivery Room for Preterm Infants" Children 6, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020029
APA StyleLara-Cantón, I., Solaz, A., Parra-Llorca, A., García-Robles, A., & Vento, M. (2019). Optimal Inspired Fraction of Oxygen in the Delivery Room for Preterm Infants. Children, 6(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020029