Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identifies Dysbiosis in Triplet Sibling with Gastrointestinal Symptoms and ASD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
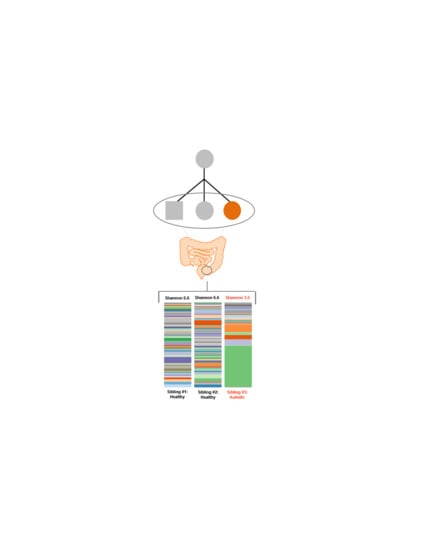
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, J.B.; Johansen, L.J.; Powell, L.D.; Quig, D.W.; A Rubin, R. Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism—Comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuong, H.E.; Hsiao, E.Y. Emerging Roles for the Gut Microbiome in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, H.K.; Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. The Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, B. Targeting gut microbiome: A novel and potential therapy for autism. Life Sci. 2018, 194, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, H. Altered composition and function of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.K.H.; Tong, V.J.W.; Syn, N.; Nagarajan, N.; Tham, E.H.; Tay, S.K.; Shorey, S.; Tambyah, P.A.; Law, E.C.N. Gut microbiota changes in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cussotto, S.; Strain, C.R.; Fouhy, F.; Strain, R.G.; Peterson, V.L.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Differential effects of psychotropic drugs on microbiome composition and gastrointestinal function. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1671–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Bercik, P. The Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and the Central Nervous System in Normal Gastrointestinal Function and Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Gregory, A.C.; Borody, T.; Chittick, L.; Fasano, A.; Khoruts, A.; Geis, E.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; et al. Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: An open-label study. Microbiome 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-W.; Adams, J.B.; Coleman, D.M.; Pollard, E.L.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; Caporaso, J.G.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitschke, A.; Deonandan, R.; Konkle, A.T. The link between autism spectrum disorder and gut microbiota: A scoping review. Autism 2020, 24, 1328–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Relative Abundance (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother | Sibling #1 | Sibling #2 | Sibling #3 | ||
| Healthy | Healthy | Healthy | ASD | ||
| Phylum | Actinobacteria | 10.32 | 16.50 | 9.48 | 0.79 |
| Bacteroidetes | 17.07 | 12.39 | 12.90 | 39.33 | |
| Firmicutes | 72.59 | 70.38 | 77.48 | 58.82 | |
| Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.67 | |
| Genus | Bacteroides | 13.84 | 3.14 | 10.76 | 34.57 |
| Eubacterium | 12.47 | 9.00 | 2.79 | 1.86 | |
| Bifidobacterium | 9.88 | 15.44 | 8.70 | 0.70 | |
| Blautia | 5.33 | 2.68 | 3.38 | 14.30 | |
| Species | Bacteroides uniformis | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 16.86 |
| Bacteroides plebius | 11.72 | 0.00 | 1.01 | 17.71 | |
| Bacteroides vulgatus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.55 | 0.00 | |
| Roseburia faecis | 11.06 | 1.04 | 1.61 | 0.00 | |
| Bifidobacterium longum | 9.87 | 3.96 | 5.08 | 0.47 | |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | 0.00 | 11.48 | 3.62 | <0.01 | |
| Clostridiales bacterium | 2.32 | 2.73 | 11.56 | 0.00 | |
| Escherichia coli | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hazan, S.; Spradling-Reeves, K.D.; Papoutsis, A.; Walker, S.J. Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identifies Dysbiosis in Triplet Sibling with Gastrointestinal Symptoms and ASD. Children 2020, 7, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7120255
Hazan S, Spradling-Reeves KD, Papoutsis A, Walker SJ. Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identifies Dysbiosis in Triplet Sibling with Gastrointestinal Symptoms and ASD. Children. 2020; 7(12):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7120255
Chicago/Turabian StyleHazan, Sabine, Kimberly D. Spradling-Reeves, Andreas Papoutsis, and Stephen J. Walker. 2020. "Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identifies Dysbiosis in Triplet Sibling with Gastrointestinal Symptoms and ASD" Children 7, no. 12: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7120255
APA StyleHazan, S., Spradling-Reeves, K. D., Papoutsis, A., & Walker, S. J. (2020). Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identifies Dysbiosis in Triplet Sibling with Gastrointestinal Symptoms and ASD. Children, 7(12), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7120255