Relationships between Dietary Patterns and Indices of Arterial Stiffness and Central Arterial Wave Reflection in 9–11-Year-Old Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Description
2.2. Sample Size Estimation
2.3. Study Variables
2.3.1. Dietary Intake and Dietary Pattern Derivation
2.3.2. Arterial Stiffness (PWV) and Wave Reflection (AIx)
2.4. Study Covariates
2.4.1. Socio-Demographic, Anthropometric Factors and Body Composition
2.4.2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness
2.4.3. Physical Activity
2.5. Data Handling and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
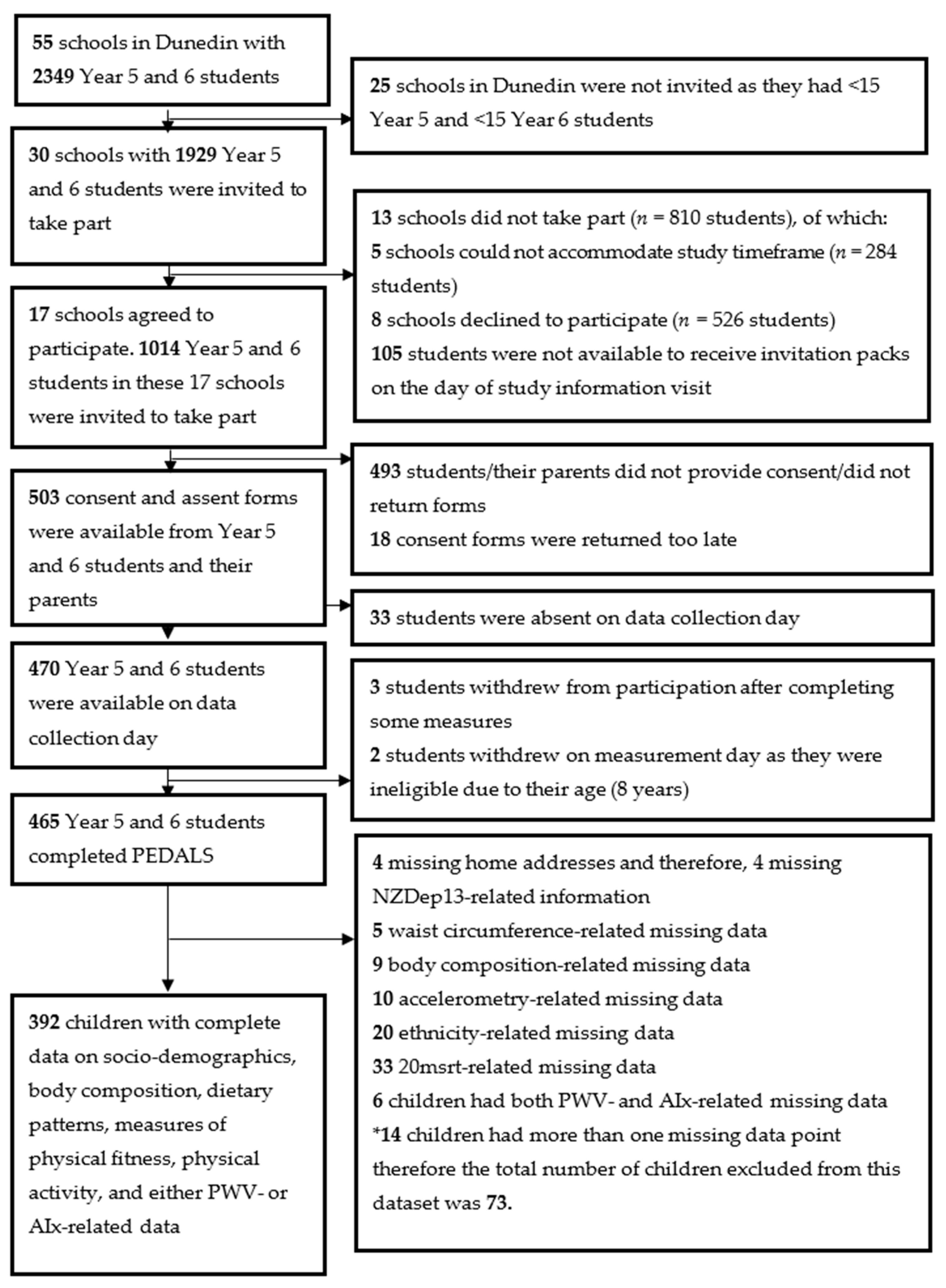
3.1. Participants
3.2. Characteristics of Participants
3.3. Dietary Patterns Identification
3.4. Bivariable Analyses
3.5. Association between Dietary Pattern Scores and PWV and AIx
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/nmh/countries/en/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Disease. 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Hardy, R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Kuh, D. A life course approach to cardiovascular aging. Future Cardiol. 2015, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggoun, Y.; Szezepanski, I.; Bonnet, D. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events in children. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattace-Raso, F.U.S.; van der Cammen, T.J.M.; Hofman, A.; van Popele, N.M.; Bos, M.L.; Schalekamp, M.A.D.H.; Asmar, R.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P.G.; Breteler, M.M.B.; et al. Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: The Rotterdam Study. Circulation 2006, 113, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, J.A.; Babyak, M.A.; Hinderliter, A.; Watkins, L.L.; Craighead, L.; Lin, P.-H.; Caccia, C.; Johnson, J.; Waugh, R.; Sherwood, A. Effects of the DASH diet alone and in combination with exercise and weight loss on blood pressure and cardiovascular biomarkers in men and women with high blood pressure: The ENCORE study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Vergnaud, A.-C.; Fezeu, L.; Zureik, M.; Blacher, J.; Péneau, S.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Czernichow, S. Associations between dietary patterns and arterial stiffness, carotid artery intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2010, 17, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyama, S.; Minami, K.; Yano, M.; Okumura, M.; Hayashi, S.; Takayama, H.; Yorimoto, A. Relationship between dietary patterns and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity among middle-aged adults in Japan. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 26, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Pase, M.P.; Grima, N.A.; Sarris, J. The effects of dietary and nutrient interventions on arterial stiffness: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, A.; Carubelli, V.; Sciatti, E.; Bonadei, I.; Gorga, E.; Cani, D.; Vizzardi, E.; Metra, M.; Lombardi, C. Nutrition and Cardiovascular Disease: Finding the Perfect Recipe for Cardiovascular Health. Nutrients 2016, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, Y.-F. Arterial stiffness in the young: Assessment, determinants, and implications. Korean Circ. J. 2010, 40, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.N.; Abreu, G.R.; Resende, R.S.; Goncalves, W.L.; Gouvea, S.A. Cardiovascular risk factor investigation: A pediatric issue. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2013, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purath, J.; Lansinger, T.; Ragheb, C. Cardiac risk evaluation for elementary school children. Public Health Nurs. 1995, 12, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Black, K.; Haszard, J.; Skeaff, S.; Stoner, L.; Davidson, B.; Harrex, H.A.L.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Quigg, R.; Wong, J.E.; et al. Dietary Patterns, Cardiorespiratory and Muscular Fitness in 9–11-Year-Old Children from Dunedin, New Zealand. Nutrients 2018, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Skeaff, S.; Wong, J.; Skidmore, P. Reproducibility and relative validity of a short food frequency questionnaire in 9–10 year-old children. Nutrients 2016, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Hoffmann, K.; Kroke, A.; Boeing, H. An approach to construct simplified measures of dietary patterns from exploratory factor analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, B.; Saeedi, P.; Black, K.; Harrex, H.; Haszard, J.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Quigg, R.; Skeaff, S.; Stoner, L.; Wong, J.E.; et al. The Association between Parent Diet Quality and Child Dietary Patterns in Nine- to Eleven-Year-Old Children from Dunedin, New Zealand. Nutrients 2017, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Duprez, D.; Starmans-Kool, M.J.; Safar, M.E.; Giannattasio, C.; Cockcroft, J.; Kaiser, D.R.; Thuillez, C. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness, Task Force III: Recommendations for user procedures. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Pauca, A.; Jiang, X.-J. Pulse wave analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Cruickshank, J.K.; De Backer, T.; Filipovsky, J.; Huybrechts, S.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.S.; Protogerou, A.D.; et al. European Network for Noninvasive Investigation of Large Arteries. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; Salmond, C.; Crampton, P. NZDep2013 Index of Deprivation; University of Otago: Dunedin, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, J.J.; Penpraze, V.; Hislop, J.; Davies, G.; Grant, S.; Paton, J.Y. Objective measurement of physical activity and sedentary behaviour: Review with new data. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.L.; Brazendale, K.; Beets, M.W.; Mealing, B.A. Classification of physical activity intensities using a wrist-worn accelerometer in 8–12-year-old children. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrex, H.A.L.; Skeaff, S.A.; Black, K.E.; Davison, B.K.; Haszard, J.J.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Quigg, R.; Saeedi, P.; Stoner, L.; Wong, J.E.; et al. Sleep timing is associated with diet and physical activity levels in 9–11-year-old children from Dunedin, New Zealand: The PEDALS study. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 27, e12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Shavandi, A.; Skidmore, P. What Do We Know about Diet and Markers of Cardiovascular Health in Children: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, A.P.; Liese, A.D.; Urbina, E.M.; Crandell, J.L.; Jaacks, L.M.; Dabelea, D.; Black, M.H.; Merchant, A.T.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Associations of dietary intake patterns identified using reduced rank regression with markers of arterial stiffness among youth with type 1 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lydakis, C.; Stefanaki, E.; Stefanaki, S.; Thalassinos, E.; Kavousanaki, M.; Lydaki, D. Correlation of blood pressure, obesity, and adherence to the Mediterranean diet with indices of arterial stiffness in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giontella, A.; Bonafini, S.; Tagetti, A.; Bresadola, I.; Minuz, P.; Gaudino, R.; Cavarzere, P.; Ramaroli, D.A.; Marcon, D.; Branz, L.; et al. Relation between Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Anthropometric and Vascular Parameters in Children Attending the Primary School in the Verona South District. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.A.; Crespo, N.C.; Sallis, J.F.; Patterson, R.E.; Elder, J.P. Dietary-Related and Physical Activity-Related Predictors of Obesity in Children: A 2-Year Prospective Study. Child. Obes. 2012, 8, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Poursafa, P. A review on the genetic, environmental, and lifestyle aspects of the early-life origins of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2014, 44, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials Research Unit and Synovate. A National Survey of Children and Young People’s Physical Activity and Dietary Behaviours in New Zealand: 2008/09; Technical Report; Ministry of Health: Wellington, New Zealand, 2010.
- Parnell, W.; Scragg, R.; Wilson, N.; Schaaf, D.; Fitzgerald, E. NZ Food NZ Children: Key Results of the 2002 National Children’s Nutrition Survey; Ministry of Health: Wellington, New Zealand, 2003.
- Avogaro, A.; Albiero, M.; Menegazzo, L.; de Kreutzenberg, S.; Fadini, G.P. Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes: The role of reparatory mechanisms. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. 2), S285–S290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauslund, J.; Jørgensen, T.M.M.; Nybo, M.; Green, A.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Sjølie, A.K. Risk factors for mortality and ischemic heart disease in patients with long-term type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2010, 24, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, E.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Davis, C.; Snively, B.M.; Dolan, L.M.; Daniels, S.R.; Hamman, R.F.; Dabelea, D. Prevalence of increased arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus differs by measurement site and sex: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bussel, B.C.T.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.S.; Henry, R.M.A.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Ferreira, I.; Chaturvedi, N.; Toeller, M.; Fuller, J.H.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group. Unhealthy dietary patterns associated with inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: The EURODIAB study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juonala, M.; Jarvisalo, M.J.; Maki-Torkko, N.; Kahonen, M.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Raitakari, O.T. Risk factors identified in childhood and decreased carotid artery elasticity in adulthood: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation 2005, 112, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogaro, A.; de Kreutzenberg, S.V. Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 360, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEniery, C.M.; Wallace, S.; Mackenzie, I.S.; McDonnell, B.; Yasmin Newby, D.E.; Wilkinson, I.B. Endothelial Function Is Associated With Pulse Pressure, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Augmentation Index in Healthy Humans. Hypertension 2006, 48, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic Variable 1 | Children with PWV Data n = 389 | SD | Children with AIx Data n = 337 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 9.7 | 0.7 | 9.7 | 0.7 |
| Sex | ||||
| Boys | 194 (49.9) | - | 166 (49.3) | - |
| Girls | 195 (50.1) | - | 171 (50.7) | - |
| School year | ||||
| Year 5 | 222 (57.1) | - | 195 (57.9) | - |
| Year 6 | 167 (42.9) | - | 142 (42.1) | - |
| Ethnicity 2 | ||||
| Māori | 44 (11.3) | - | 42 (12.5) | - |
| Non-Māori | 345 (88.7) | - | 295 (87.5) | - |
| NZDep13 3 | ||||
| Low deprivation | 172 (44.2) | - | 149 (44.2) | - |
| Middle deprivation | 148 (38.1) | - | 131 (38.9) | - |
| High deprivation | 69 (17.7) | - | 57 (16.9) | - |
| Weight status 4 | ||||
| Underweight | 20 (5.1) | - | 19 (5.6) | - |
| Normal weight | 296 (76.1) | - | 257 (76.2) | - |
| Overweight | 55 (14.2) | - | 45 (13.4) | - |
| Obese | 18 (4.6) | - | 16 (4.8) | - |
| Variable 1 | Children with PWV Data n = 389 | SD | Children with AIx Data n = 337 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWV (m/s) | 5.8 | 0.8 | - | - |
| AIx (%) | - | - | −2.1 | 14.1 |
| AIx@HR75 2 (%) | - | - | −1.4 | 14.9 |
| PP | 43.0 | 6.5 | 42.8 | 6.3 |
| cPP | 26.5 | 4.5 | 26.4 | 4.3 |
| PP/cPP ratio | 1.6 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 0.1 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 74.6 | 10.0 | 76.7 | 9.7 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 82.8 | 8.1 | 82.4 | 7.3 |
| VO2max (ml/kg/min) | 48.8 | 4.8 | 48.9 | 4.8 |
| FMI (kg/m2) | 3.4 (3.2, 3.5) | - | 3.3 (3.2, 3.5) | - |
| FFMI (kg/m2) | 14.1 | 1.2 | 14.1 | 1.1 |
| BMI Z-score 3 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| MVPA (h/d) | 2.2 (2.0, 2.4) | - | 2.2 (2.0, 2.5) | - |
| Snacks score | −0.0 | 1.0 | −0.0 | 1.0 |
| Fruit and Vegetables score | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Variable 1 | Snacks Score | Fruit and Vegetables Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β 2 | 95% CI | p Value | β 2 | 95% CI | p Value | |
| PWV (m/s) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 0.02 | −0.05, 0.09 | 0.61 | −0.00 | −0.09, 0.08 | 0.93 |
| Model 2 | 0.00 | −0.06, 0.06 | 0.97 | −0.01 | −0.10, 0.08 | 0.77 |
| Model 3 | −0.02 | −0.08, 0.05 | 0.61 | −0.05 | −0.13, 0.04 | 0.31 |
| AIx (%) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.05 | −2.00, 1.91 | 0.96 | −0.85 | −1.77, 0.08 | 0.07 |
| Model 2 | 0.46 | −1.46, 2.39 | 0.64 | −0.57 | −1.50, 0.35 | 0.23 |
| Model 3 | 0.32 | −1.28, 1.93 | 0.70 | −0.37 | −1.26, 0.52 | 0.41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeedi, P.; Haszard, J.; Stoner, L.; Skeaff, S.; Black, K.E.; Davison, B.; Harrex, H.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Quigg, R.; Wong, J.E.; et al. Relationships between Dietary Patterns and Indices of Arterial Stiffness and Central Arterial Wave Reflection in 9–11-Year-Old Children. Children 2020, 7, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7060066
Saeedi P, Haszard J, Stoner L, Skeaff S, Black KE, Davison B, Harrex H, Meredith-Jones K, Quigg R, Wong JE, et al. Relationships between Dietary Patterns and Indices of Arterial Stiffness and Central Arterial Wave Reflection in 9–11-Year-Old Children. Children. 2020; 7(6):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7060066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeedi, Pouya, Jillian Haszard, Lee Stoner, Sheila Skeaff, Katherine E. Black, Brittany Davison, Harriet Harrex, Kim Meredith-Jones, Robin Quigg, Jyh Eiin Wong, and et al. 2020. "Relationships between Dietary Patterns and Indices of Arterial Stiffness and Central Arterial Wave Reflection in 9–11-Year-Old Children" Children 7, no. 6: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7060066
APA StyleSaeedi, P., Haszard, J., Stoner, L., Skeaff, S., Black, K. E., Davison, B., Harrex, H., Meredith-Jones, K., Quigg, R., Wong, J. E., & Skidmore, P. M. L. (2020). Relationships between Dietary Patterns and Indices of Arterial Stiffness and Central Arterial Wave Reflection in 9–11-Year-Old Children. Children, 7(6), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7060066








