Outcomes of Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discontinued Devices
2.1. King and Mill’s Device
2.2. Rashkind’s Devices
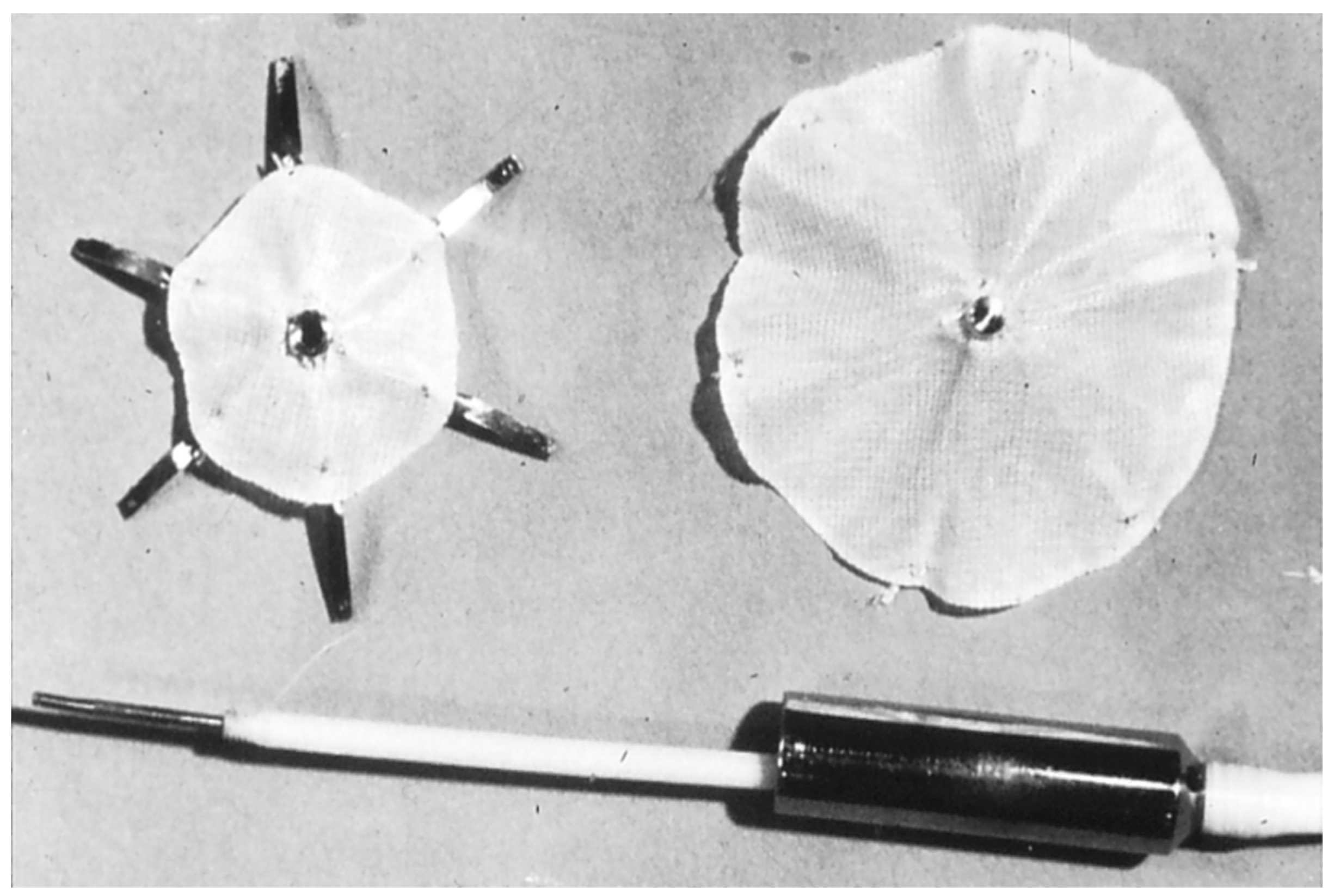
2.3. Clamshell Occluder
2.4. Buttoned Device
2.5. Atrial Septal Defect Occluding System (ASDOS)
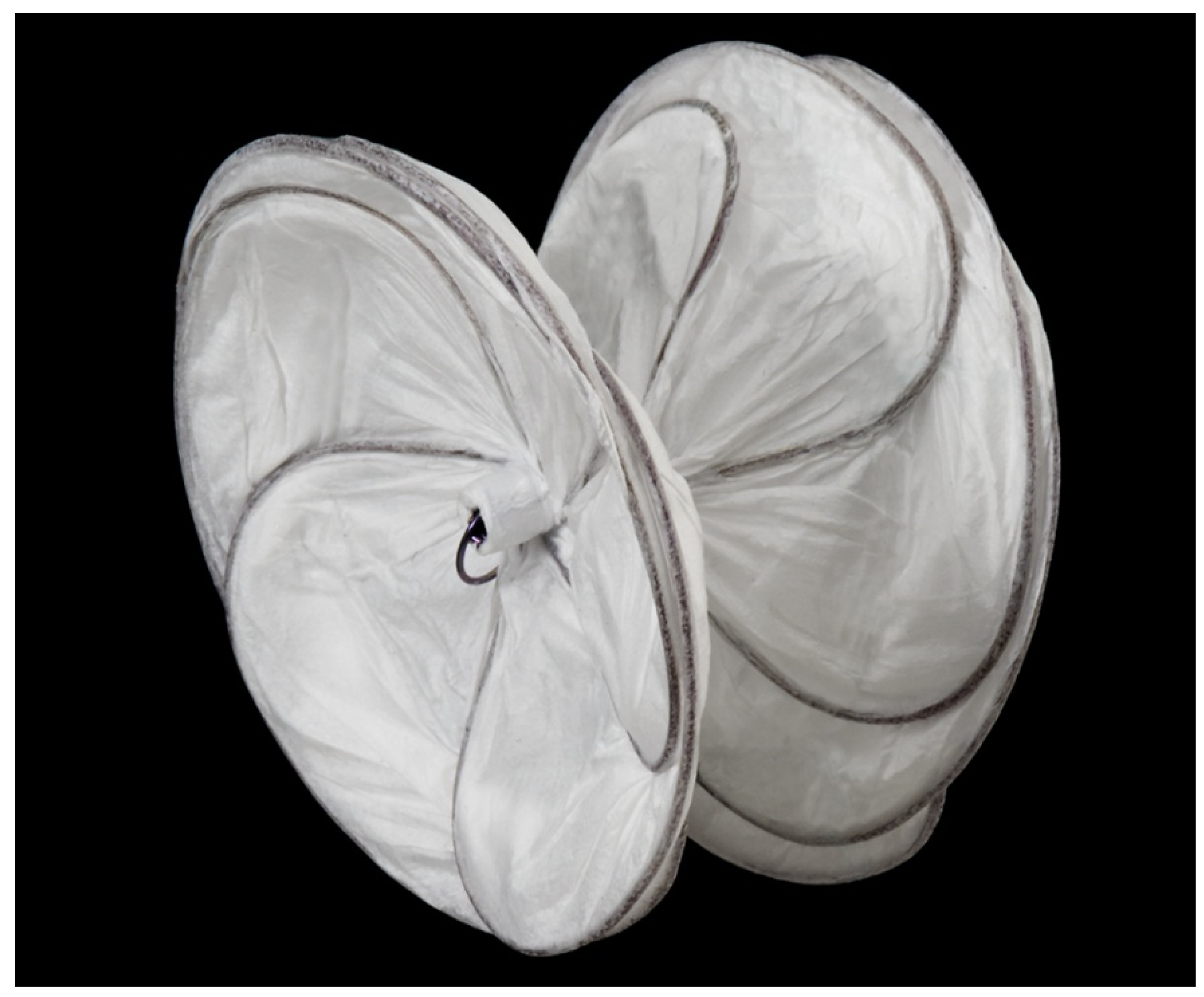
2.6. Das Angel Wing Device
3. Devices Not Yet Approved by FDA
4. Devices Currently in Use
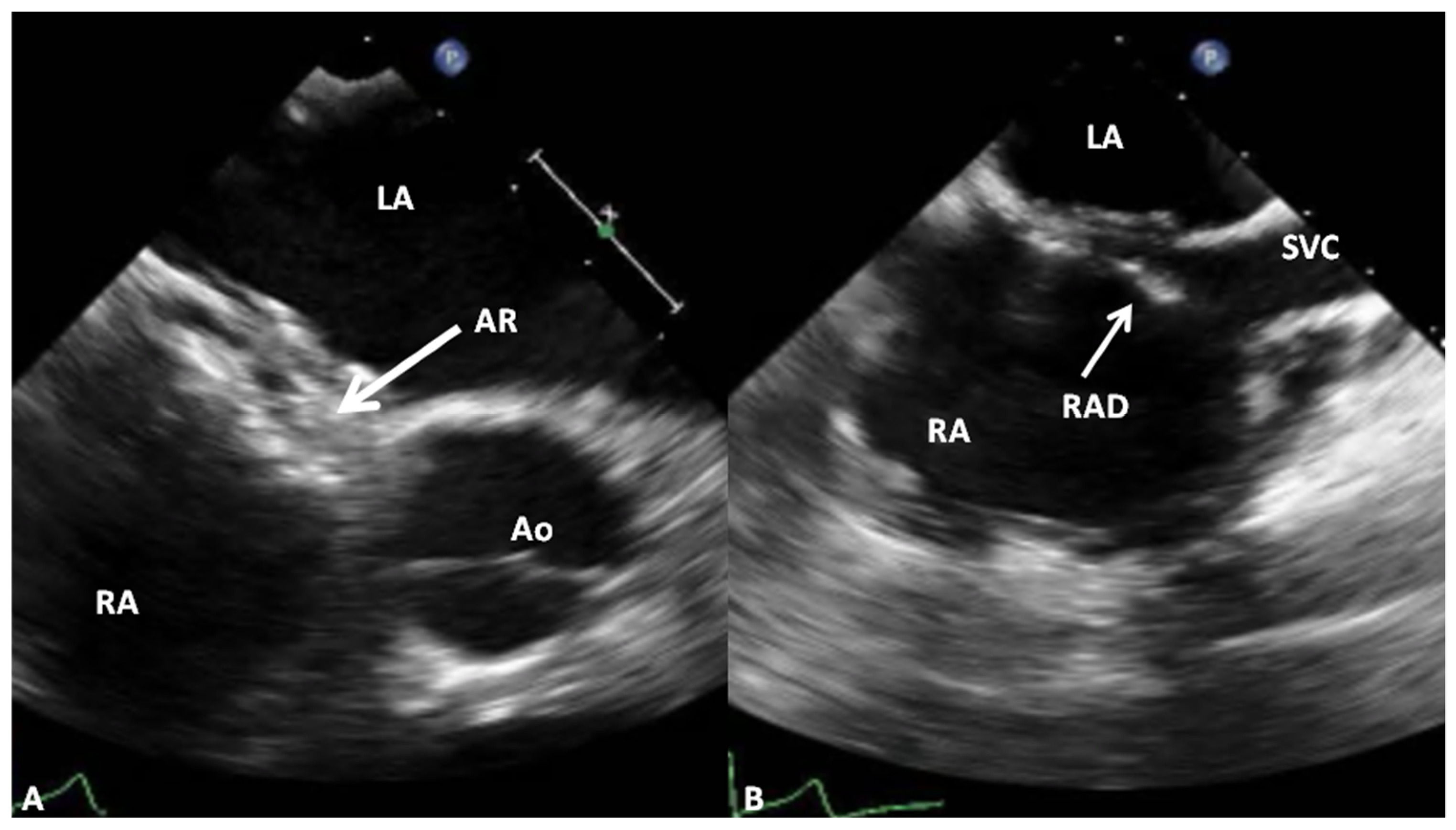
4.1. Amplatzer Septal Occluder
Advantages and Limitations
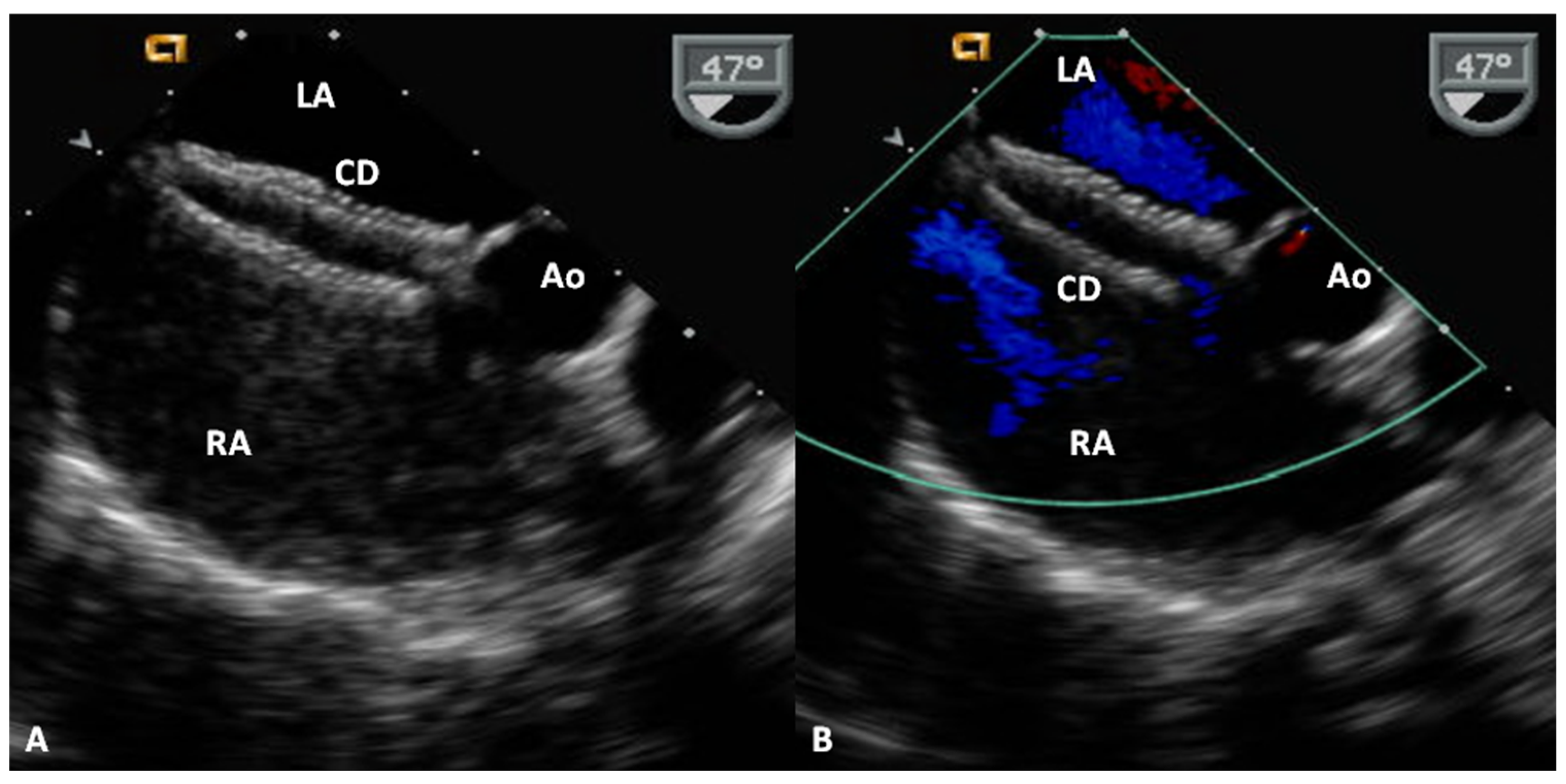
4.2. Amplatzer Cribriform Device
Advantages and Limitations
4.3. Gore HELEX® Device
Advantages and Limitations
4.4. GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD Occluder
Advantages and Limitations
5. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirklin, J.W.; Swan, H.J.; Wood, E.H.; Burchell, H.B.; Edwards, J.E. Anatomic, physiologic, and surgical considerations in repair of interatrial communications in man. J. Thorac. Surg. 1955, 29, 37–49; discussion, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S. Present status of surgery in congenital heart disease. Indian J. Pediatr. 1981, 49, 349–463. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, P.S.; Rao, P.S. Surgical management of congenital heart disease: Current trends. Indian J. Pediatr. 1991, 58, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, M.O.; Wobst, A.; Halees, Z.; Hatle, L.; Schmaltz, A.A.; Khougeer, F.; De Vol, E.; Fawzy, M.E.; Abbag, F.; Fadley, F.; et al. Perioperative complications following surgical closure of atrial septal defect type II in 232 patients—A baseline study. Eur. Heart J. 1994, 15, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorek, J.S.; Allen, H.D.; Davis, J.T. Current outcomes of surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.D.; Mills, N.L. Nonoperative closure of atrial septal defects. Surgery 1974, 75, 383–388. [Google Scholar]
- King, T.D.; Thompson, S.L.; Steiner, C.; Mills, N.L. Secundum atrial septal defect: Nonoperative closure during cardiac catheterization. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1976, 235, 2506–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.L.; King, T.D. Nonoperative closure of left-to-right shunts. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1976, 72, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkind, W.J. Experimental transvenous closure of atrial and ventricular septal defects. Circulation 1975, 52, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkind, W.J.; Cuaso, C.E. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in children. Eur. J. Cardiol. 1977, 8, 119–120. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkind, W.J. Transcatheter treatment of congenital heart disease. Circulation 1983, 67, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chopra, P.S.; Rao, P.S. History of the development of atrial septal occlusion devices. Curr. Interv. Cardiol. Rep. 2000, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S. History of atrial septal occlusion devices. In Catheter Based Devices in the Treatment of Non-Coronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alapati, S.; Rao, P.S. Historical aspects of trans-catheter occlusion of atrial septal defects. In Atrial Septal Defect; Rao, P.S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 57–84. ISBN 978-953-51-0531-2. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, F.; Vogel, M.; Alexi-Meskishvili, V.; Lange, P.E. Comparison of results and complications of surgical and Amplatzer device closure of atrial septal defects. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 118, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.D.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Kleinman, C.S.; Silverman, N.H.; Larntz, K.; Amplatzer Investigators. Comparison between transcatheter and surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect in children and adults: Results of multicenter nonrandomized trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.J.; Hijazi, Z.M. Clinical outcomes and costs of Amplatzer transcatheter closure as compared with surgical closure of ostium secundum atrial septal defects. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 12, CR787–CR791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettencourt, N.; Salome, N.; Carneiro, F.; Gonçalves, M.; Ribeiro, J.; Braga, J.P.; Fonseca, C.; Correia, D.M.; Vouga, L.; Ribeiro, V.G. Atrial septal closure in adults: Surgery versus Amplatzer—Comparison of results. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2003, 22, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.S. Catheter closure of atrial septal defects. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2003, 15, 398–400. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.S. Non-surgical closure of atrial septal defects in children. In Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects: Molecular Determinants, Impact of Environmental Factors and Non-Surgical Interventions; Larkin, S.A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-62618-326-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.S.; Harris, A.D. Recent advances in managing septal defects: Atrial septal defects. Fac. Rev. 2017, 2042, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.S. Management of congenital heart disease: State of the art—Part I—Acyanotic heart defects. Children 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, T.D.; Mills, N.L. Historical perspectives on ASD device closure. In Transcatheter Closure of ASDs and PFOs: A Comprehensive Assessment; Hijazi, Z.M., Feldman, T., Abdullah, M.H., Al-Qbandi, A., Sievert, H., Eds.; Cardiotext: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2010; pp. 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.S. Atrial septal defects. In Pediatric Cardiology: How It Has Evolved Over the Last 50 Years; Rao, P.S., Ed.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2020; pp. 321–386. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkind, W.J.; Tait, M.A.; Gibson, R.J., Jr. Interventional cardiac catheterization in congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 1985, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkind, W.J.; Mullins, C.E.; Hellenbrand, W.E.; Tait, M.A. Non-surgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus: Clinical applications of the Rashkind PDA occluder system. Circulation 1987, 75, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lock, J.E.; Rome, J.J.; Davis, R.; Van Praagh, S.; Perry, S.B.; Van Praagh, R.; Keane, J.F. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects: Experimental studies. Circulation 1989, 79, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rome, J.J.; Keane, J.F.; Perry, S.B.; Spevak, P.J.; Lock, J.E. Double-umbrella closure of atrial defects: Initial clinical applications. Circulation 1990, 82, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perry, S.B.; Van der Velde, M.E.; Bridges, N.D.; Keane, J.F.; Lock, J.E. Transcatheter closure of atrial and ventricular septal defects. Herz 1993, 18, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Justo, R.N.; Nykanen, D.G.; Boutin, C.; McCrindle, B.W.; Freedom, R.M.; Benson, L.N. Clinical impact of transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects with double umbrella device. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 77, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, L.R.; Foreman, C.K.; Cheatham, J.P.; Latson, L.A. Intermediate-term outcome of transcatheter secundum atrial septal defect closure using Bard clamshell septal umbrella. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 78, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, E.B.; Sideris, S.E.; Fowlkes, J.P.; Ehly, R.L.; Smith, J.E.; Gulde, R.E. Transvenous atrial septal defect occlusion in piglets with a buttoned double disc device. Circulation 1990, 81, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sideris, E.B.; Sideris, S.E.; Thanopoulos, B.D.; Ehly, R.L.; Fowlkes, J.P. Transvenous atrial septal defect occlusion by the buttoned device. Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 1524–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Sideris, E.B.; Chopra, P.S. Catheter closure of atrial septal defect: Successful use in a 3.6 kg infant. Am. Heart J. 1991, 121, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Wilson, A.D.; Levy, J.M.; Chopra, P.S. Role of “buttoned” double-disk device in the management of atrial septal defects. Am. Heart J. 1992, 123, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Wilson, A.D.; Chopra, P.S. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect by “buttoned” devices. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 69, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Ende, D.J.; Wilson, A.D.; Smith, P.A. Follow-up results of trans-catheter occlusion of atrial septal defect with buttoned device. Canad. J. Cardiol. 1995, 11, 695–701. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, R.; Trehan, V.K.; Karla, G.S.; Chawla, R.; Jhamb, U.; Nigam, M.; Kenchaiah, K.S.; Bhardwaj, S.; Khalilullah, M. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect using buttoned device: Indian experience. Indian. Heart J. 1996, 48, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haddad, J.; Secches, A.; Finzi, L.; Nazzetta, H.; Wanderley, M.; Wanderley, R.; Correa, M.; Freitas, J.; Kajita, L.; Carvalho, S.; et al. Atrial septal defect: Percutaneous transvenous occlusion with the buttoned device. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 1996, 67, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Worms, A.M.; Rey, C.; Bourlon, F.; Losay, I.; Marçon, F.; Godart, F.; Coullet, J.M. French experience in the closure of atrial septal defects of the ostium secundum type with Sideris buttoned occluder. Arch. Mal. Coeur. Vaiss. 1996, 89, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, T.R.; Rao, P.S.; Beekman, R.H., III; Mendelsohn, A.M.; Sideris, E.B. Atrial septal defect occlusion with the buttoned device: A multi-institutional U.S. trial. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 73, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamora, R.; Rao, P.S.; Lloyd, T.R.; Beekman, R.H.; Sideris, E.B. Intermediate-term results of Phase I FDA Trials of buttoned device occlusion of secundum atrial septal defect. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Sideris, E.B.; Hausdort, G.; Ray, C.; Loyd, T.R.; Beekman, R.H.; Worms, A.M.; Bourlon, F.; Onorato, E.; Khalilullah, M.; et al. International experience with secundum atrial septal defect occlusion by the buttoned device. Am. Heart J. 1994, 128, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.S.; Sideris, E.B. Buttoned device closure of the atrial septal defect. J. Interv. Cardiol. 1998, 11, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Berger, F.; Rey, C.; Haddad, J.; Meier, B.; Walsh, K.P.; Chandar, J.S.; Lloyd, T.R.; Suarez de Lezo, J.; Zamora, R.; et al. Results of transvenous occlusion of secundum atrial septal defects with 4th generation buttoned device: Comparison with 1st, 2nd and 3rd generation devices. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.S.; Sideris, E.B. Centering-on-demand buttoned device: Its role in trans-catheter occlusion of atrial septal defects. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2001, 14, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S.; Sideris, E.B. Buttoned device modifications: Influence on feasibility, safety and effectiveness. In Proceedings of the Poster Presentation at the 26th Annual Scientific Sessions of the Society of Cardiac Angiography and Interventions, Westin Copley Place, Boston, MA, USA, 7–10 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Babic, U.U.; Grujicic, S.; Popovic, Z.; Djurisic, Z.; Vucinic, M.; Pejcic, P. Double-umbrella device for transvenous closure of patent ductus arteriosus and atrial septal defect: First clinical experience. J. Interv. Cardiol. 1991, 4, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babic, U.; Sievert, H.; Schneider, M.; Babic, M. ASDOS-atrial septal defect occluder system. In Catheter Based Devices for Treatment of Noncoronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott: Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Babic, U.; Thomsen-Bloch, A. Das ASDOS-implantat: Tierexperimentelle erprobung. Z. Kardiol. 1995, 84, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen-Bloch, A. Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Catheter Technique: An Animal Experimental Study. Diploma Thesis, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorf, G.; Schneider, M.; Franzbach, B.; Kampmann, C.; Kargus, K.; Goeldner, B. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects with the atrial septal defect occlusion system (ASDOS): Initial experience in children. Heart 1996, 75, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sievert, H.; Babic, U.U.; Ensslen, R.; Scherer, D.; Spies, H.; Wiederspahn, T.; Zeplin, H.E. Transcatheter closure of large atrial septal defects with the Babic system. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 1995, 36, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, H.; Babic, U.U.; Hausdorf, G.; Schneider, M.; Höpp, H.W.; Pfeiffer, D.; Pfisterer, M.; Friedli, B.; Urbanet, P. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale with ASDOS device, a multi-institutional European trial. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.S.; Voss, G.; Jarvis, G.; Wyche, K.; Gunther, R.; Wilson, R.F. Experimental atrial septal defect closure with a new, transcatheter, self-centering device. Circulation 1993, 88, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, A.; Bengur, A.R.; Li, J.S.; Homans, D.C.; Toher, C.; Bank, A.J.; Marx, G.R.; Rhodes, J.; Das, G.S. Echocardiographic characteristics of successful deployment of the Das Angel Wings atrial septal defect closure device: Initial multicenter experience in the United States. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.D.; O’Laughlin, M.P.; Ito, K.; Wang, A.; Bashore, T.M.; Harrison, J.K. Five-year clinical and echocardiographic evaluation of the Das AngelWings atrial septal occluder. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.S.; Harrison, J.K.; O’Laughlin, M.P. Catheter Based Devices for Treatment of Noncoronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rickers, C.; Hamm, C.; Stern, H.; Hofmann, T.; Franzen, O.; Schrader, R.; Sievert, H.; Schranz, D.; Michel-Behnke, I.; Vogt, J.; et al. Percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defect with a new self centering device (“angel wings”). Heart 1998, 80, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafuddin, M.J.; Gu, X.; Titus, J.L.; Urness, M.; Cervera-Ceballos, J.J.; Amplatz, K. Transvenous closure of secundum atrial septal defects: Preliminary results with a new self-expanding Nitinol prosthesis in a swine model. Circulation 1997, 95, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masura, J.; Gavora, P.; Formanek, A.; Hijazi, Z.M. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the new self-centering Amplatzer Septal Occluder: Initial human experience. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 1997, 42, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.P.; Tofeig, M.; Kitchiner, D.J.; Peart, I.; Arnold, R. Comparison of the Sideris and Amplatzer septal occlusion devices. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanopoulos, B.D.; Laskari, C.V.; Tsaousis, G.S.; Zarayelyan, A.; Vekiou, A.; Papadopoulos, G.S. Closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer occlusion device: Preliminary Results. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Goh, T.H. Early clinical experience with use of the Amplatzer septal occluder device for atrial septal defect. Cardiol. Young 1998, 8, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Berger, F.; Dähnert, I.; Ewert, P.; Lange, P.E. Treatment of atrial septal defects in symptomatic children aged less than 2 years of age using the Amplatzer septal occluder. Cardiol. Young 2000, 10, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartakian, S.; Fagan, T.E.; Schaffer, M.S.; Darst, J.R. Device closure of secundum atrial septal defects in children <15 kg: Complication rates and indications for referral. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmouz, S.; Kenny, D.; Cao, Q.L.; Kavinski, C.J.; Hijazi, Z.M. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2013, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.H.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, J.K.; Kao, F.Y.; Huang, S.K. Paradigm shift in the intervention for secundum atrial septal defect in an era of transcatheter closure: A national birth cohort study. Am. Heart J. 2015, 170, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal, M.A.; Vincent, J.A. Atrial septal defect device closure in the pediatric population: A current review. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. 2015, 3, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, J.; Lucia, M.; Claire, D.; Godart, F.; Dauphin, C.; Lefort, B.; Lachaud, M.; Piot, D.; Dinet, M.L.; Levy, Y.; et al. Long-term outcome following percutaneous closure of isolated secundum atrial septal defects in children: A French nationwide series of 1000 consecutive patients (Abstract). Circulation 2016, 134, A17866. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, F.; Ewert, P.; Björnstad, P.G.; Dähnert, I.; Krings, G.; Brilla-Austenat, I.; Vogel, M.; Lange, P.E. Transcatheter closure as standard treatment for most interatrial defects: Experience in 200 patients treated with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder. Cardiol. Young 1999, 9, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, R.; Thanopoulos, B.; Tsaousis, G.; Triposkiadis, F.; Kyriakidis, M.; Redington, A. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in adults with the Amplatzer septal occluder. Heart 1999, 82, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Lopez, K.; Banerjee, A.; Joseph, A.; Cao, Q.-L.; Hijazi, Z.M. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in adults > or =40 years of age: Immediate and follow-up results. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2007, 20, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.C.; Suttorp, M.J.; Jaarsma, W.; Plokker, W.H.T. Comparison of outcome and complications using different types of devices for percutaneous closure of a secundum atrial septal defect in adults: A single-center experience. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2006, 67, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströker, E.; Van De Bruaene, A.; De Meester, P.; Van Deyck, K.; Gewillig, M.; Budts, W. Transcatheter device closure of atrial septal defects in patients above age 60. Acta Cardiol. 2013, 68, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshershari, H.; Cao, Q.-L.; Hijazi, Z.M. Transcatheter device closure of atrial septal defects in patients older than 60 years of age: Immediate and follow-up results. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2008, 20, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Jategaonkar, S.; Scholtz, W.; Schmidt, H.; Horstkotte, D. Percutaneous closure of atrial septal defects: Echocardiographic and functional results in patients older than 60 years. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 2, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.A.; Tan, J.L.; Li, W.; Dimopoulos, K.; Spence, M.S.; Chow, P.; Mullen, M.J. The impact of transcatheter atrial septal defect closure in the older population: A prospective study. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akagi, T. Atrial septal closure in geriatric patients. In Atrial Septal Defect; Rao, P.S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 139–152. ISBN 978-953-51-0531-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hijazi, Z.M.; Radtke, W.; Ebeid, M.R. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the Amplatzer septal occluder: Results of Phase II US multicenter clinical trial. Circulation 1999, 100, 804. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.C.; Godman, M.J.; Walsh, K.; Wilson, N.; Redington, A.; Gibbs, J.L. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect and interatrial communications with a new self expanding Nitinol double disc device (Amplatzer septal occluder): Multicentre UK experience. Heart 1999, 82, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamdan, M.A.; Cao, Q.; Hijazi, Z.M. Amplatzer septal occluder. In Catheter Based Devices for Treatment of Noncoronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott, William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Masura, J.; Gavora, P.; Podnar, T. Long-term outcome of transcatheter secundum-type atrial septal defect closure using Amplatzer septal occluders. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartas, G.A.; Balaguru, D.; Brown, M.; Rao, P.S. Intermediate follow-up results of Amplatzer device occlusion of secundum atrial septal defects. Poster presentation at the 19th PICS-AICS 2015, Los Vegas, NV, 2015. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 574. [Google Scholar]
- Aggoun, Y.; Gallet, B.; Acar, P.; Pulik, M.; Czitrom, D.; Lagier, A.; Laborde, F. Perforation of the aorta after percutaneous closure of an atrial septal defect with an Amplatzer prosthesis with acute severe hemolysis. Arch. Mal. Coeur. Vaiss. 2002, 95, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, D.S.; Turrentine, M.W.; Moustapha, A.; Hoyer, M.H. Development of aorta-to-right atrial fistula following closure of secundum atrial septal defect using the Amplatzer septal occluder. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2003, 58, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, Z.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Bass, J.L.; Cheatham, J.P.; Hellenbrand, W.E.; Kleinman, C.S. Erosion of Amplatzer septal occluder device after closure of secundum atrial septal defect: Review of registry of complications and recommendations to minimize future risk. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2004, 63, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S. When and how should atrial septal defects be closed in adults. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2009, 21, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hijazi, Z.M.; Cao, Q.-L. Transcatheter closure of multi-fenestrated atrial septal defects using the new Amplatzer cribriform device. Congenit. Cardiol. Today 2003, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetta, M.; Rigatelli, G.; Pedon, L.; Zennaro, M.; Carrozza, A.; Onorato, E. Catheter closure of perforated secundum atrial septal defect under intracardiac echocardiographic guidance using a single Amplatzer device: Feasibility of a new method. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2005, 17, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Numan, M.; El Sisi, A.; Tofeig, M.; Gendi, S.; Tohami, T.; El-Said, H.G. Cribriform Amplatzer device closure of fenestrated atrial septal defects: Feasibility and technical aspects. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2008, 29, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhaj, Z.; Hongxin, L.; Wenbin, G.; Zhang, W.-L.; Liang, F.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Yuan, G.-D.; Zou, C.-W. Device closure of diverse layout of multi-hole secundum atrial septal defect: Different techniques and long-term follow-up. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.K.; Hsiung, M.C.; Wei, J.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yu, H.-P.; Ou, C.-H.; Yin, W.-H. Transesophageal echocardiography for incremental value of Amplatzer cribriform septal occluder for percutaneous transcatheter closure of complex septal defects: Case series. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musto, C.; Cifarelli, A.; Pandolfi, C.; De Felice, F.; Fiorilli, R.; Caferri, G.; Violini, R. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale associated with atrial septal aneurysm with Amplatzer Cribriform septal occluder. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2009, 21, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’avvocata, F.; Cardaioli, P.; Braggion, G.; Giordan, M.; Mazza, A.; Fraccaro, C.; Chinaglia, M.; Chen, J.P. Long-term results of the Amplatzer cribriform occluder for patent foramen ovale with associated atrial septal aneurysm: Impact on occlusion rate and left atrial functional remodeling. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 2, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestry, F.E.; Naseer, N.; Wiegers, S.E.; Hirshfeld, J.W., Jr.; Herrmann, H.C. Percutaneous transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale with the Amplatzer Cribriform septal occluder. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 71, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.I.; Cavendish, J.J. Percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale via left axillary vein approach with the Amplatzer Cribriform septal occluder. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2008, 21, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’Avvocata, F.; Ronco, F.; Giordan, M. Patent oval foramen transcatheter closure: Results of a strategy based on tailoring the device to the specific patient’s anatomy. Cardiol. Young 2010, 20, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białkowski, J.; Wawrzyńczyk, M.; Karwot, B.; Fiszer, R.; Knop, M.; Szkutnik, M. Medium-term results of transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale (PFO) with Amplatzer PFO and Cribriform occluders. Kardiol. Pol. 2012, 70, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, E.; Cheatham, J.; Latson, L.; Wilson, N. Results of in vivo testing of a new Nitinol ePTTEF septal occlusion device. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Intervent. 1999, 47, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, E.; Wilson, N.; Cutright, W.; Latson, L. Development and testing of the HELEX septal occluder, a new expanded polytetraflouroethylene atrial septal defect occlusion system. Circulation 2001, 104, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latson, L.; Zahn, E.; Wilson, N. HELEX septal occluder for closure of atrial septal defects. Curr Interv. Cardiol. Rep. 2000, 2, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latson, L.A.; Wilson, N.; Zahn, E.M. Helex septal occluder. In Catheter Based Devices for Treatment of Noncoronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.K.; Latson, L.A.; Zahn, E.; Fleishman, C.E.; Jacobson, J.; Vincent, R.; Kanter, K. Multicenter Pivotal Study of the HELEX Septal Occluder Investigators. Results of the U.S. multicenter pivotal study of the HELEX septal occluder for percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhodes, J.F., Jr.; Goble, J. Combined prospective United States clinical study data for the GORE® HELEX® septal occluder device. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 83, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyboe, C.; Hjortdal, V.E.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E. First experiences with the Gore ® Septal Occluder in children and adults with atrial Septal defects. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 82, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freixa, X.; Ibrahim, R.; Chan, J.; Garceau, P.; Dore, A.; Marcotte, F.; Mercier, L.-A.; Mongeon, F.-P.; Basmadjian, A.; Khairy, P.; et al. Initial clinical experience with the GORE septal occluder for the treatment of atrial septal defects and patent foramen ovale. Eur. Interv. 2013, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, J.; Hohn, R.; Fleck, T.; Schmoor, C.; Stiller, B. Transcatheter closure of atrial Septal defects in children and adolescents. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 84, E51–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hemptinne, Q.; Horlick, E.M.; Osten, M.D.; Millan, X.; Tadros, V.-X.; Pighi, M.; Barlatey, F.G.; Alnasser, M.; Miró, J.; Asgar, A.; et al. Initial clinical experience with the GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD occluder for transcatheter atrial septal defect closure. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Thomson, J.; Crossland, D.; Spence, M.S.; Morgan, G.J. UK multicenter experience using the Gore Septal Occluder® for atrial Septal defect closure in children and adults. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 83, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, J.; Wildberg, C.; Zartner, P.; Abu-Tair, T.; Tarusinov, G.; Kitzmüller, E.; Schmoor, C.; Stiller, B.; Kampmann, C. Multicenter midterm follow-up results using the Gore Septal Occluder for atrial Septal defect closure in pediatric patients. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 89, E226–E232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, M.J.; Javois, A.J.; Moore, P.; Forbes, T.; Paolillo, J.A.; for GSO Investigator Group. Use of the GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder for percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects: Results of the multicenter U.S. IDE Trial. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]















| Devices/Studies | Sample Selection | Type of Study | Number of Patients | Age (Years) | Size of Delivery Sheath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplatzer Septal Occluder * | |||||
| Masura et al. [61] | Random sample | Cohort | 30 | Median-6.1 | 7F |
| Hartas et al. [84] | Random sample | Cohort | 65 | Mean-7.9 | 7F |
| Amplatzer Cribriform Device # | |||||
| Zanchetta et al. [90] | Random sample | Cohort | 13 | All adults | 6 to 7 F |
| Numan et al. [91] | Random sample | Cohort | 16 | Median-12.5 | 6 to 7 F |
| Gore HELEX® Device ! | |||||
| Jones et al. [104] | Random sample | Cohort | 143 | Mean-14 | 8F |
| Rhodes et al. [105] | Pivotal, continued access and post-approval cases | Cohort | 435 | Median-6.5 | 8F |
| GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD Occluder @ | |||||
| Nyboe et al. [106] | Random sample | Cohort | 22 | Mean-25.8 | 10F |
| Gillespie et al. [112] | Pivotal and continued access | Cohort | 400 | Median-6.9 | 10F |
| Devices/Studies | Size of the ASD (mm) | Implantation Feasibility | Complete Closure at Implantation | Complications/Adverse Events | Complete Closure at 6 to 12 mo after Implantation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplatzer Septal Occluder * | |||||
| Masura et al. [61] | TEE −5 to 21 BS −7 to 19 | 100% | 57% | None | 80% |
| Hartas et al. [84] | TEE −6 to 30 BS −10 to 26 | 94% | 90% | 1.6% | 98% |
| Amplatzer Cribriform Device # | |||||
| Zanchetta et al. [90] | NA | 100% | 67% | None | 96% |
| Numan et al. [91] | NA | 81% | 77% | None | 92% |
| Gore HELEX ® Device ! | |||||
| Jones et al. [104] | TEE −13 to 25 | 88% | 73% | 5.9% | 98% |
| Rhodes et al. [105] | TEE −1.7 to 25 | - | 84% | 4.8% | 98% |
| GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD Occluder @ | |||||
| Nyboe et al. [106] | TEE −11 ± 0.5 | 100% | 100% | None | 100% |
| Gillespie et al. [112] | TEE −9.7 ± 3 BS −12 ± 3 | 93.5% | 77% | 1.7% | 86% |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, P.S. Outcomes of Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects. Children 2020, 7, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7090111
Rao PS. Outcomes of Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects. Children. 2020; 7(9):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7090111
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, P. Syamasundar. 2020. "Outcomes of Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects" Children 7, no. 9: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7090111
APA StyleRao, P. S. (2020). Outcomes of Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects. Children, 7(9), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7090111





