Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnea
3. Deciding to Use Positive Airway Pressure
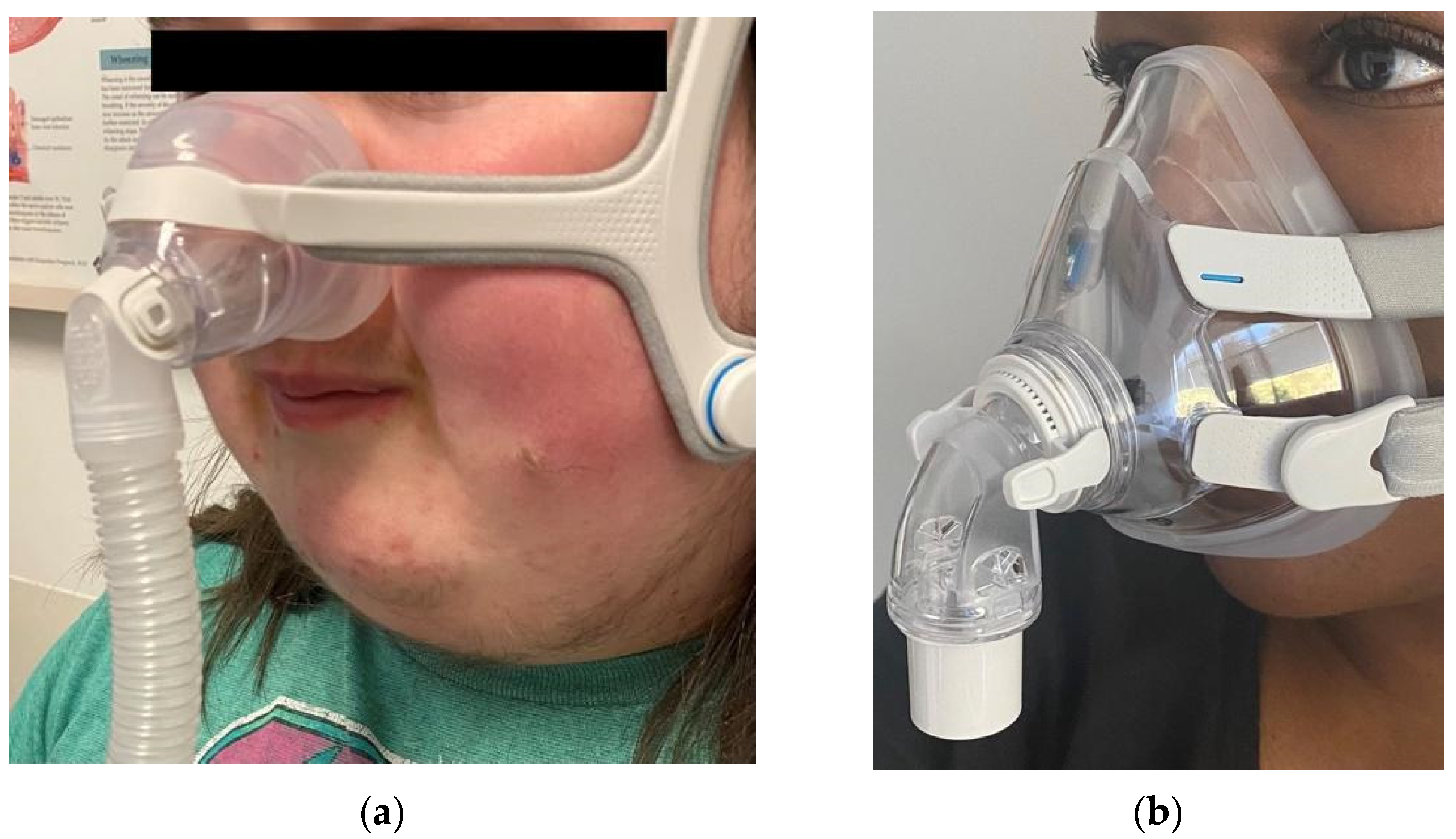
4. What Is Positive Airway Pressure?
5. Preparing for PAP Initiation
6. Choosing the Right Pressures/Settings
7. Monitoring Patients after PAP Initiation
8. Positive Airway Pressure Adherence
9. Auto-Titration CPAP in Pediatric Patients
10. Positive Airway Pressure Cessation
11. In Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition (ICSD-3); American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, C.L.; Keens, T.G.; Bautista, D.B.; von Pechmann, W.S.; Ward, S.L. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome. Pediatrics 1991, 88, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Lin, S.-P.; Lin, C.-C.; Tsai, L.-P.; Chen, M.-R.; Chuang, C.-K.; Huang, C.-Y. Polysomnographic Characteristics in Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2007, 42, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.C.W.; Sedaghat, A.R.; McGinley, B.M.; Redett, R.J.; Boss, E.F.; Ishman, S.L. Prevalence and Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring in Infants with Pierre Robin Sequence. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2011, 48, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, O.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Dayyat, E.; Gozal, D. Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Complications, Management, and Long-Term Outcomes. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Lee, J.H.; Chan, A. Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2005, 159, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.H.; Spruyt, K.; Ward, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Childhood Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, K.; Roberts, K.; Manning, P.; Manley, C.; Hill, N.S. OSA and Pulmonary Hypertension: Time for a New Look. Chest 2015, 147, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattimore, J.-D.L.; Wilcox, I.; Adams, M.R.; Kilian, J.G.; Celermajer, D.S. Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Leads to Enhanced Pulmonary Vascular Nitric Oxide Release. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 126, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamness, J.A. Taking a Pediatric Sleep History. Pediatr. Ann. 2008, 37, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, N.A.; Abramowitz, T.; Weedon, J.; Koliskor, B.; Turner, S.; Taioli, E. Racial/ethnic Differences in the Prevalence of Snoring and Sleep Disordered Breathing in Young Children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.B.; Harrison, H.C.; Waters, K.A.; Sullivan, C.E. Snoring and Stertor Are Associated with More Sleep Disturbance than Apneas and Hypopneas in Pediatric SDB. Sleep Breath. 2019, 23, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.C.; Elkins, T.P.; Keech, D.; Wauquier, A.; Hubbard, D. Accuracy of Clinical Evaluation in Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1998, 118, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, A.; Maul, J.; Rosenheim, E.; O’Donnell, A.; Wilson, A.; Stick, P.S. Comparison of Home Ambulatory Type 2 Polysomnography with a Portable Monitoring Device and in-Laboratory Type 1 Polysomnography for the Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Quan, S.F.; Abreu, A.R.; Bibbs, M.L.; DelRosso, L.; Harding, S.M.; Mao, M.-M.; Plante, D.T.; Pressman, M.R.; Troester, M.M.; et al. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.E.; Marcus, C.L. Pediatric Polysomnography. Sleep Med. Clin. 2009, 4, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, V.; Baughn, J.; D’Andrea, L.; Friedman, N.; Galion, A.; Garetz, S.; Hassan, F.; Wrede, J.; Harrod, C.G.; Malhotra, R.K. American Academy of Sleep Medicine Position Paper for the Use of a Home Sleep Apnea Test for the Diagnosis of OSA in Children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehlink, E.; Tan, H.-L. Update on Paediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 224–235. [Google Scholar]
- Gipson, K.; Lu, M.; Kinane, T.B. Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Children. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 40, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.; Werkhaven, J.A. Cost-Effectiveness of Polysomnography in the Management of Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prévost, A.-S.; Hylands, M.; Gervais, M.; Praud, J.-P.; Battista, M.-C.; Déziel-Malouin, S.; Lachance, M.; Lamontagne, F. Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Compared with Systematic Adenotonsillectomy in the Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.; Emani, J.; Suskind, D.L.; Baroody, F.M. Predictors of Persistent Sleep Apnea after Surgery in Children Younger than 3 Years. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Spruyt, K.; Mitchell, R.B.; Promchiarak, J.; Simakajornboon, N.; Kaditis, A.G.; Splaingard, D.; Splaingard, M.; Brooks, L.J.; et al. Adenotonsillectomy Outcomes in Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Caples, S.M.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Somers, V.K. Interactions between Obesity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Implications for Treatment. Chest 2010, 137, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsch, I.A.; Schahin, S.P.; Radespiel-Tröger, M.; Weintz, O.; Jahreiss, H.; Fuchs, F.S.; Wiest, G.H.; Hahn, E.G.; Lohmann, T.; Konturek, P.C.; et al. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment Rapidly Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.L.; Kirk, V.G.; MacLean, J.E.; Bendiak, G.N.; Harrison, M.-A.; Barrowman, N.; Hoey, L.; Horwood, L.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Legault, L.; et al. Factors Related to Positive Airway Pressure Therapy Adherence in Children with Obesity and Sleep-Disordered Breathing. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.L.; MacLean, J.E.; Hoey, L.; Horwood, L.; Barrowman, N.; Foster, B.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Legault, L.; Bendiak, G.N.; Kirk, V.G.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Hypertension in Obese Youth with Sleep-Disordered Breathing Treated with Positive Airway Pressure: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.L.; Radcliffe, J.; Konstantinopoulou, S.; Beck, S.E.; Cornaglia, M.A.; Traylor, J.; DiFeo, N.; Karamessinis, L.R.; Gallagher, P.R.; Meltzer, L.J. Effects of Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Neurobehavioral Outcomes in Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, S.J.; Tardif, H.P.; Barry, R.J.; Sands, T. Nasal Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure Therapy in Children with a Sleep-Related Breathing Disorder and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Effects on Electrophysiological Measures of Brain Function. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, A.; Baker, A.; Narang, I. Positive Airway Pressure in Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2019, 31, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, T.J.; Teets, S.; Lehman, E.B.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Zwillich, C. Nasal Congestion Secondary to Allergic Rhinitis as a Cause of Sleep Disturbance and Daytime Fatigue and the Response to Topical Nasal Corticosteroids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Guilleminault, C.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Sullivan, S.S. Mouth Breathing, “Nasal Disuse,” and Pediatric Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liming, B.J.; Ryan, M.; Mack, D.; Ahmad, I.; Camacho, M. Montelukast and Nasal Corticosteroids to Treat Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Bandla, H.P.R.; Gozal, D. Montelukast for Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Ann. ATS 2016, 13, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupak, H.D.; Park, S.Y. Gravitational Forces, Negative Pressure and Facial Structure in the Genesis of Airway Dysfunction during Sleep: A Review of the Paradigm. Sleep Med. 2018, 51, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Guilleminault, C. Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea and the Critical Role of Oral-Facial Growth: Evidences. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.-S. From Oral Facial Dysfunction to Dysmorphism and the Onset of Pediatric OSA. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloia, M.S.; Arnedt, J.T.; Stanchina, M.; Millman, R.P. How Early in Treatment Is PAP Adherence Established? Revisiting Night-to-Night Variability. Behav. Sleep Med. 2007, 5, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.S.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Marcus, C.L. Improving Positive Airway Pressure Adherence in Children. Sleep Med. Clin. 2014, 9, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, V.G.; O’Donnell, A.R. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Children: A Discussion on How to Maximize Compliance. Sleep Med. Rev. 2006, 10, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbower, A.C. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. In UpToDate; Chervin, R.D., Eichler, A.F., Eds.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2020; (accessed on 13 September 2021). [Google Scholar]
- Koontz, K.L.; Slifer, K.J.; Cataldo, M.D.; Marcus, C.L. Improving Pediatric Compliance with Positive Airway Pressure Therapy: The Impact of Behavioral Intervention. Sleep 2003, 26, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibra, M.N.; Berry, R.B.; Wagner, M.H. Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Choosing the Best Interface. Sleep Med. Clin. 2017, 12, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, M.P.; Pagani, J.; Ambrosio, R.; Ronchetti, R.; Bernkopf, E. Mid-Face Hypoplasia after Long-Term Nasal Ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1142–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.D.; Kapadia, H.; Greenlee, G.; Chen, M.L. Midfacial and Dental Changes Associated with Nasal Positive Airway Pressure in Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Craniofacial Conditions. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariani, R.C.B.; Guimarães, T.M.; Cappellette, M.; Moreira, G.; Fujita, R.R. The Impact of Positive Airway Pressure on Midface Growth: A Literature Review. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.M.; Dassanayake, D.U.N.; Weichard, A.J.; Davey, M.J.; Nixon, G.M.; Horne, R.S.C. Back to Sleep or Not: The Effect of the Supine Position on Pediatric OSA: Sleeping Position in Children with OSA. Sleep Med. 2017, 37, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholen, K.; Meier, M.; Kloor, J.; Friedman, N. Persistent OSA in Obese Children: Does Body Position Matter? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSharry, D.G.; Saboisky, J.P.; Deyoung, P.; Jordan, A.S.; Trinder, J.; Smales, E.; Hess, L.; Chamberlin, N.L.; Malhotra, A. Physiological Mechanisms of Upper Airway Hypotonia during REM Sleep. Sleep 2014, 37, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, C.A.; Chediak, A.; Berry, R.B.; Brown, L.K.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; Rowley, J.A.; Positive Airway Pressure Titration Task Force; et al. Clinical Guidelines for the Manual Titration of Positive Airway Pressure in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.; Al-Halawani, M.D.; Kreinin, I.; Kryger, M. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Positive Airway Pressure Adherence Criteria May Limit Treatment to Many Medicare Beneficiaries. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watach, A.J.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Afolabi-Brown, O.; Saconi, B.; Fox, K.A.; Qiu, M.; Sawyer, A.M. Positive Airway Pressure Adherence in Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Scoping Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 51, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, R.; Vandeleur, M.; Pecoraro, S.; Davey, M.J.; Nixon, G.M. Autotitrating CPAP as a Tool for CPAP Initiation for Children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebraheem, Z.; Toulany, A.; Baker, A.; Christian, J.; Narang, I. Facilitators and Barriers to Positive Airway Pressure Adherence for Adolescents. A Qualitative Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, A.; Messiha, S.; Baker, A.; Zweerink, A.; Toulany, A.; Narang, I. Caregiver Support and Positive Airway Pressure Therapy Adherence among Adolescents with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 25, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.M.M.; Jensen, E.L.; Simon, S.L.; Friedman, N.R. Correlates of Pediatric CPAP Adherence. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Blechner, M.; Chang, M.-Y.; Menello, M.K.; Brown, C.; Matthews, E.; Weaver, T.E.; Shults, J.; Marcus, C.L. Self-Efficacy and Short-Term Adherence to Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment in Children. Sleep 2017, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashad, P.S.; Marcus, C.L.; Maggs, J.; Stettler, N.; Cornaglia, M.A.; Costa, P.; Puzino, K.; Xanthopoulos, M.; Bradford, R.; Barg, F.K. Investigating Reasons for CPAP Adherence in Adolescents: A Qualitative Approach. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puri, P.; Ross, K.R.; Mehra, R.; Spilsbury, J.C.; Li, H.; Levers-Landis, C.E.; Rosen, C.L. Pediatric Positive Airway Pressure Adherence in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Enhanced by Family Member Positive Airway Pressure Usage. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, E.B.; Fieldston, E.S.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Beck, S.E.; Menello, M.K.; Matthews, E.; Marcus, C.L. Financial Analysis of an Intensive Pediatric Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Program. Sleep 2017, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.M.; Gooneratne, N.S.; Marcus, C.L.; Ofer, D.; Richards, K.C.; Weaver, T.E. A Systematic Review of CPAP Adherence across Age Groups: Clinical and Empiric Insights for Developing CPAP Adherence Interventions. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Grunstein, R.R. Clinical Side Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Respirology 2020, 25, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egesi, A.; Davis, M.D.P. Irritant Contact Dermatitis due to the Use of a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Nasal Mask: 2 Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Cutis 2012, 90, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, K.A.; Doghramji, K. Does Transition From Cpap To Bipap Improve Symptoms Of Aerophagia? Sleep 2018, 41, A203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaytin, I.; Tapia, I.E.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Cielo, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Smith, J.; Matthews, E.C.; Beck, S.E. Auto-Titrating CPAP for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim-Uzzaman, Q.A.; Bae, C.J.; Ehsan, Z.; Setty, A.R.; Devine, M.; Dhankikar, S.; Donskoy, I.; Fields, B.; Hearn, H.; Hwang, D.; et al. The Use of Telemedicine for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Sleep Disorders: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Update. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.G.; Sullivan, S.S.; Nti, A.; Rastegar, V.; Gurubhagavatula, I. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Sleep Medicine Practices. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Z.; Josee-Leclerc, M.; Wales, P.; Masters, I.B.; Kapur, N. Can CPAP Therapy in Pediatric OSA Ever Be Stopped? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hady, K.K.; Okorie, C.U.A. Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Children 2021, 8, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8110979
Hady KK, Okorie CUA. Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Children. 2021; 8(11):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8110979
Chicago/Turabian StyleHady, Kelly K., and Caroline U. A. Okorie. 2021. "Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Children 8, no. 11: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8110979
APA StyleHady, K. K., & Okorie, C. U. A. (2021). Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Children, 8(11), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8110979





