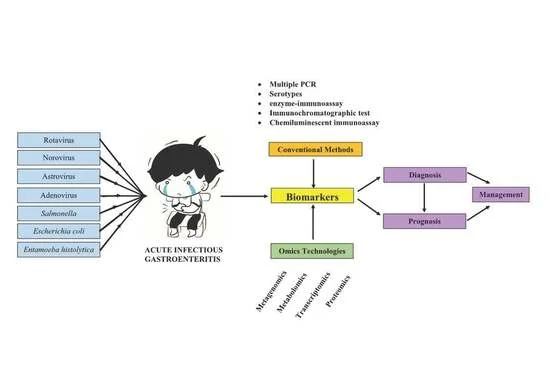
Acute Infectious Gastroenteritis: The Causative Agents, Omics-Based Detection of Antigens and Novel Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Causative Agents of AGE
2.1. Rotavirus
2.2. Norovirus
2.3. Astrovirus
2.4. Enteric Adenovirus Serotypes 40 and 41
2.5. Salmonella
2.6. Escherichia coli
2.7. Entamoeba histolytica
3. Biomarkers in the Detection of Common Aetiological Agents of AGE
3.1. Rotavirus
3.2. Norovirus
3.3. Astrovirus
3.4. Enteric Adenovirus Serotypes 40 and 41
3.5. Salmonella
3.6. Escherichia coli
3.7. Entamoeba histolytica
| Agent | Biomarker | Detection Method | Brand | Sensitivity | Specificity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotavirus | Rotavirus antigen | ELISA | Rota Antigen Test Device, Cambridge | 86–98% | 92–96% | [28] |
| EIA | Premier Rotaclone, Meridian Bioscience Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA | 76.8–77.8% | 100% | [93,94] | ||
| RIDASCREEN® Rotavirus | 82.1–97.8% | 99.1–100% | [93] | |||
| ProSpect Rotavirus Test, Oxoid Ltd., UK | 75% | 100% | [93] | |||
| Rotavirus RNA | RT-PCR | Primerdesign Genesig® Kit | 100% | 100% | [97] | |
| Real-time RT-PCR | GeneAmp EZ rTth RNA PCR kit (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Foster City, CA, USA) | 98.8–100% | 99.7–100% | [98] | ||
| Norovirus | Norovirus antigen | ICT | RIDA®QUICK Norovirus N1402 | 72.8–87% | 97–99.5% | [117,118] |
| QuickNaviTM Norovirus 2 | 27.5% | 97.7% | [120] | |||
| ELISA | RIDASCREEN® Norovirus 3rd Generation | 84.6–85.7% | >96% | [121,122] | ||
| FIA | AFIAS-Noro | 66% | 97.6% | [95] | ||
| Norovirus RNA | Real-time RT-PCR | Cepheid Xpert® Norovirus | 100% | 100% | [114] | |
| Real-time PCR | RIDA®GENE Norovirus | 98% | 98% | [102] | ||
| Astrovirus | ORF2 gene | RT-PCR | RT-PCR Luminex Assay | 100% | 100% | [123] |
| rRTLAMP Assay | 94% | 100% | [124,125] | |||
| Enteric Adenovirus Serotypes 40 and 41 | Adenovirus antigen | ICT | BioNexia RotaAdeno | 60% | 98.8% | [126] |
| RIDA Quick Rota-Adeno-Combi R-Biopharm AG | 72.7% | 98.2% | [127] | |||
| CLIA | LIAISON Adenovirus | 77% | 98.8% | [126] | ||
| Hexon-coding gene | RT-PCR | TaqMan Array Card | 100% | 100% | [129] | |
| Salmonella | Salmonella virulence genes | Multiplex PCR | RIDA®GENE-gastrointestinal kits | 25% | 99.7% | [103,104,105] |
| EntericBio real-time Gastro Panel I | 100% | 97.8% | [104] | |||
| Seeplex Diarrhea ACE | 40–100% | 96–100% | [103,106,107] | |||
| Shiga Toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) | Shiga toxins (stx) serotypes | Multiplex PCR | Seeplex Diarrhea ACE | 100% | 99.6–100% | [110] |
| Real-time PCR | TaqMan™ STEC | 100% | 100% | |||
| Culture medium | CHROMagar STEC | 84.6–85.7% | 87–95.8% | |||
| Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) | eae gene | Real-time PCR | RIDA®GENE EHEC/EPEC | 84% | 97% | [112] |
| Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) | elt and estA genes | RIDA®GENE ETEC/EIEC | 83% | 100% | ||
| Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) | aatA and aggR genes | RIDA®GENE EAEC | 69% | 100% | ||
| Entamoeba histolytica | Entamoeba histolytica antigen | ELISA | Techlab II Entamoeba histolytica | 19.2% | 100% | [131,132,133] |
| Multiplex PCR | Performed on Mx3005P detection system | 100% | 95.8% | [134] | ||
| microRNA (miRNA) | RT-PCR | Taqman Low-Density Arrays | 92% | 100% | [135] |
4. Omics-Based Technologies for AGE Diagnosis and Management
| Omics | Platform | Infectious Agents Detected | Potential Biomarkers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metagenomics | Next Generation Sequencing | Rotavirus |
| [135] |
| [135,138] | |||
| [137] | |||
| [137] | |||
| [139,140] | |||
| Norovirus |
| [135,144,145] | ||
| [137] | |||
| Astrovirus |
| [142] | ||
| [141] | |||
| Adenovirus |
| [130] | ||
| E. histolytica |
| [144] | ||
| Transcriptomics |
| Salmonella enterica | nadA gene | [155,156,157] |
| Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli | EHEC EDL933 | [146,147,148] | ||
| Proteomics | Fourier transform mass spectrometer | Salmonella enteritidis |
| [150] |
| Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF MS) | Escherichia coli | Mass peaks ranged from approximately 3000 to 15,000 m/z for different strains of E.coli (EPEC, EIEC and DAEC strains). | [151] | |
| Metabolomics |
| Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium | 22 metabolites were identified in greater abundance and these metabolites triggered oxidative stress. | [148,154,155] |
| Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) | Higher levels of histamine and lower levels of ornithine in DEC samples than in the healthy group. | [156] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartman, S.; Brown, E.; Loomis, E.; Russell, H.A. Gastroenteritis in Children. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 99, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Gharbi-Khelifi, H.; de Rougemont, A.; Hassine, M.; Chouchane, S.; Sakly, N.; Pothier, P.; Guédiche, M.N.; Aouni, M.; Ambert-Balay, K. Molecular Epidemiology of Human Astrovirus and Adenovirus Serotypes 40/41 Strains Related to Acute Diarrhea in Tunisian Children. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; Jenkins, H.; Whyte, L. Pathophysiology of Diarrhoea. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 28, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, L.A.; Jenkins, H.R. Pathophysiology of Diarrhoea. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 22, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M.; Salam, M.A.; Lindberg, G.; Dite, P.; Khalif, I.; Salazar-Lindo, E.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Goh, K.-L.; Thomson, A.; Khan, A.G.; et al. Acute Diarrhea in Adults and Children. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, C. Role of Antidiarrhoeal Drugs as Adjunctive Therapies for Acute Diarrhoea in Children. Int. J. Pediatrics 2013, 2013, 612403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, U.D.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Kang, G. Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Children. BMJ 2013, 347, f7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, T.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, K.F.; Jit, M.; Ng, C.W. Household catastrophic healthcare expenditure and impoverishment due to rotavirus gastroenteritis requiring hospitalization in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125878. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, F.; Vetter, V.; Conforti, G.; Esposito, S.; Bonanni, P. Parents’ insights after pediatric hospitalization due to rotavirus gastroenteritis in Italy. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Chaudhary, S.; Bubber, P.; Ray, P. Epidemiology and Genetic Diversity of Group A Rotavirus in Acute Diarrhea Patients in Pre-Vaccination Era in Himachal Pradesh, India. Vaccine 2019, 37, 5350–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Nair, N.P.; Mathew, A.; Manohar, B.; Simon, A.; Singh, T.; Suresh Kumar, S.; Mathew, M.A.; Babji, S.; Arora, R.; et al. Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Indian Children. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalkrishna, V.; Joshi, M.S.; Chavan, N.A.; Shinde, M.S.; Walimbe, A.M.; Sawant, P.M.; Kalrao, V.R.; Dhongade, R.K.; Bavdekar, A.R. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Gastroenteritis Viruses in Hospitalized Children. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4805–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanyevic, B.; Sepich, M.; Biondi, S.; Baroncelli, G.I.; Peroni, D.; Di Cicco, M. The Evolving Epidemiology of Acute Gastroenteritis in Hospitalized Children in Italy. Eur. J. Pediatrics 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.A.B.M.; Naik, D.G.; Fuad, M.D.F. Prevalence of Rotavirus Diarrhea in Children of Perak, Malaysia. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2017, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojobor, C.D.; Olovo, C.V.; Onah, L.O.; Ike, A.C. Prevalence and Associated Factors to Rotavirus Infection in Children Less than 5 Years in Enugu State, Nigeria. VirusDisease 2020, 31, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Sai, L. Clinical and Molecular Epidemiological Characterization of Rotavirus Infections in Children under Five Years Old in Shandong Province, China. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, V.; Nayak, M.K.; Misra, N.; Kumar, R.; Reddy, N.S.; Mohakud, N.K. Surveillance and Molecular Characterization of Rotavirus Strains Circulating in Odisha, India after Introduction of Rotavac. Indian J. Pediatrics 2021, 88, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-D.; Hu, W.-G. Spontaneous Remission of Infantile Spasms Following Rotavirus Gastroenteritis. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 42, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, L.N.; Mori, D.; John, J.L.; Chin, A.Z.; Mosiun, A.K.; Jeffree, M.S.; Ahmed, K. Emergence of Equine-like G3 Strains as the Dominant Rotavirus among Children under Five with Diarrhea in Sabah, Malaysia during 2018–2019. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Thakali, O.; Raya, S.; Shrestha, L.; Parajuli, K.; Sherchand, J.B. Acute Gastroenteritis Associated with Rotavirus A among Children Less than 5 Years of Age in Nepal. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, N.; Ngangas, S.M.T.; Bonkoungou, I.J.O.; Tiendrebeogo, A.B.; Traore, K.A.; Sanou, I.; Traore, A.S.; Barro, N. Temporal Distribution of Gastroenteritis Viruses in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso: Seasonality of Rotavirus. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkoshi, S.I.M.; Miftah, A.; Ernst, K.; Nagib, S. Frequency of Rotavirus Infection among Children in North-Eastern Region of Libya: A Hospital-Based Study from Almarj. Libyan J. Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A. Role of rotavirus as the cause of acute pediatric diarrhea in Al-Diwaniyah, Iraq. Al-Qadisiyah J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 18, 1125. [Google Scholar]
- Elnady, H.G.; Samie, O.M.A.; Saleh, M.T.; Sherif, L.S.; Abdalmoneam, N.; Kholoussi, N.M.; Kholoussi, S.M.; EL-Taweel, A.N. ABO Blood Grouping in Egyptian Children with Rotavirus Gastroenteritis. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2017, 3, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortín, R.; Vila-Vicent, S.; Carmona-Vicente, N.; Santiso-Bellón, C.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Buesa, J. Histo-Blood Group Antigens in Children with Symptomatic Rotavirus Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegering, V.; Kaiser, J.; Tappe, D.; Weißbrich, B.; Morbach, H.; Girschick, H.J. Gastroenteritis in Childhood: A Retrospective Study of 650 Hospitalized Pediatric Patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e401–e407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akelma, A.Z.; Kütükoğlu, I.; Köksal, T.; Çizmeci, M.N.; Kanburoglu, M.K.; Çatal, F.; Mete, E.; Bozkaya, D.; Namuslu, M. Serum Transaminase Elevation in Children with Rotavirus Gastroenteritis: Seven Years’ Experience. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 45, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S. Serum Transaminase Elevation in Patients with Rotavirus Gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Anal. Med. 2017, 8, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyen, D.T.T.; Hong, D.T.; Trung, N.T.; Hoa, T.T.N.; Oanh, N.K.; Thang, H.V.; Thao, N.T.T.; Hung, D.M.; Iijima, M.; Fox, K.; et al. Epidemiology of Acute Diarrhea Caused by Rotavirus in Sentinel Surveillance Sites of Vietnam, 2012–2015. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7894–7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Srivastva, G. Clinical Profile of Children (0–5 Years) with RotaVirus Diarrhea. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatrics 2017, 4, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haddadin, Z.; Batarseh, E.; Hamdan, L.; Stewart, L.S.; Piya, B.; Rahman, H.; Spieker, A.J.; Chappell, J.; Wikswo, M.E.; Dunn, J.R.; et al. Characteristics of GII.4 Norovirus Versus Other Genotypes in Sporadic Pediatric Infections in Davidson County, Tennessee, USA. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1525–e1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Phan, K.; Teng, I.; Pu, J.; Watanabe, T. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Norovirus in Cases of Gastroenteritis in Developing Countries. Medicine 2017, 96, e8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopman, B.A.; Steele, D.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Parashar, U.D. The Vast and Varied Global Burden of Norovirus: Prospects for Prevention and Control. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, M.; Moghoofei, M.; Dorost, A.; Shoja, Z.; Ghorbani, S.; Kiani, S.J.; Khales, P.; Esteghamati, A.; Sayyahfar, S.; Jafarzadeh, M.; et al. Global Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of Norovirus Infection in Children with Gastroenteritis: A Meta-analysis on 6 Years of Research from 2015 to 2020. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, e2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global Prevalence of Norovirus in Cases of Gastroenteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hou, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. Molecular Epidemiology and Genetic Diversity of Norovirus among Hospitalized Children with Acute Gastroenteritis in Tianjin, China, 2018–2020. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.-R.; Ma, X.-Z.; Li, W.-Y.; Wang, B.-N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.-R.; Kuang, Y.; You, J.-Z.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Ren, M.; et al. Epidemiology of Norovirus Gastroenteritis in Hospitalized Children under Five Years Old in Western China, 2015–2019. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikounou Louya, V.; Nguekeng Tsague, B.; Ntoumi, F.; Vouvoungui, C.; Kobawila, S.C. High Prevalence of Norovirus and Rotavirus Co-infection in Children with Acute Gastroenteritis Hospitalised in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Liu, N.; Humphries, E.M.; Yu, J.M.; Li, S.; Lindsay, B.R.; Stine, O.C.; Duan, Z.J. Aetiology of Diarrhoeal Disease and Evaluation of Viral–Bacterial Coinfection in Children under 5 Years Old in China: A Matched Case–Control Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 381.e9–381.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, Z. Pediatric Norovirus Gastroenteritis in Ireland: Seasonal Trends, Correlation with Disease Severity, Nosocomial Acquisition and Viral Co-Infection. Indian J. Pediatrics 2020, 88, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnelid, Y.; Bonkoungou, I.J.O.; Ouedraogo, N.; Barro, N.; Svensson, L.; Nordgren, J. Norovirus and Rotavirus in Children Hospitalised with Diarrhoea after Rotavirus Vaccine Introduction in Burkina Faso. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucardo, F.; Kindberg, E.; Paniagua, M.; Vildevall, M.; Svensson, L. Genetic Susceptibility to Symptomatic Norovirus Infection in Nicaragua. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, M.; Lindesmith, L.; Graham, R.; Baric, R. GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucardo, F.; Reyes, Y.; Becker-Dreps, S.; Bowman, N.; Gruber, J.F.; Vinjé, J.; Espinoza, F.; Paniagua, M.; Balmaseda, A.; Svensson, L.; et al. Pediatric Norovirus GII.4 Infections in Nicaragua, 1999–2015. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Dony, J.J.F.; Mori, D.; Haw, L.Y.; Giloi, N.; Jeffree, M.S.; Iha, H. An Outbreak of Gastroenteritis by Emerging Norovirus GII.2[P16] in a Kindergarten in Kota Kinabalu, Malaysian Borneo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikswo, M.E.; Desai, R.; Edwards, K.M.; Staat, M.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Weinberg, G.A.; Curns, A.T.; Lopman, B.; Vinjé, J.; Parashar, U.D.; et al. Clinical Profile of Children with Norovirus Disease in Rotavirus Vaccine Era. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arowolo, K.O.; Ayolabi, C.I.; Adeleye, I.A.; Lapinski, B.; Santos, J.S.; Raboni, S.M. Molecular Epidemiology of Astrovirus in Children with Gastroenteritis in Southwestern Nigeria. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhong, H.; Xu, M.; Su, L.; Cao, L.; Jia, R.; Xu, J. Molecular and Epidemiological Characterization of Human Adenovirus and Classic Human Astrovirus in Children with Acute Diarrhea in Shanghai, 2017–2018. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhgani, S.H.R.; Samarbafzadeh, A.R.; Makvandi, M.; Shamsizadeh, A.; Parsanahad, M. Jalilian, S.H. Relative Frequency of Astrovirus in Children Suffering from Gastroenteritis Referred to Aboozar Hospital, Ahvaz. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2011, 4, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Alsuwaidi, A.R.; Al Dhaheri, K.; Al Hamad, S.; George, J.; Ibrahim, J.; Ghatasheh, G.; Issa, M.; Al-Hammadi, S.; Narchi, H. Etiology of Diarrhea by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction among Young Children in the United Arab Emirates: A Case-Control Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.J.; Hanevik, K.; Blomberg, B.; Kommedal, O.; Nordbø, S.A.; Maselle, S.; Langeland, N. Prevalence and Molecular Characterisation of Human Adenovirus in Diarrhoeic Children in Tanzania; a Case Control Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Della Libera, S.; Petricca, S.; Iaconelli, M.; Donia, D.; Saccucci, P.; Cenko, F.; Xhelilaj, G.; Divizia, M. Genetic Diversity of Human Adenovirus in Children with Acute Gastroenteritis, Albania, 2013–2015. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 142912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, S.; Akter, T.; Sultana, H.; Akter, A.; Sarkar, O.; Ahmed, M.; Talukder, A.; Ahmed, F.; Dey, S. A Retrospective Analysis of Viral Gastroenteritis in Asia. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. 2015, 9, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabbaraju, K.; Tellier, R.; Pang, X.-L.; Xie, J.; Lee, B.E.; Chui, L.; Zhuo, R.; Vanderkooi, O.G.; Ali, S.; Tarr, P.I.; et al. A Clinical Epidemiology and Molecular Attribution Evaluation of Adenoviruses in Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, e02287-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, O.J.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, M.-K. Fecal Respiratory Viruses in Acute Viral Respiratory Infection and Nasopharyngeal Diarrheal Viruses in Acute Viral Gastroenteritis: Clinical Impact of Ectopic Viruses Is Questionable. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Ferreira, N.; Van Dycke, J.; Neyts, J.; Rocha-Pereira, J. Current and Future Antiviral Strategies to Tackle Gastrointestinal Viral Infections. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajon, A.; Lynch, J., III. Adenovirus: Epidemiology, Global Spread of Novel Serotypes, and Advances in Treatment and Prevention. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Im, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, H.J.; Mogeni, O.D.; Kim, J.H.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Baker, S.; Marks, F. The Global Burden and Epidemiology of Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Infections. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 15, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.F.; Wong, W.C.; Chai, L.C.; Tunung, R.; Jyaletchuemi, P.; Noor Hidayah, M.S.; Ubong, A.; Farinazleen, M.G.; Cheah, Y.K.; Son, R. Salmonella: A Foodborne Pathogen. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, N.; Wang, S.-M.; Shen, C.-F.; Kuo, F.-C.; Ho, T.-S.; Hsiung, C.A.; Mu, J.-J.; Wu, F.-T.; Huang, L.-M.; Huang, Y.-C.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics in Hospitalized Young Children with Acute Gastroenteritis in Southern Taiwan: According to Major Pathogens. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, Z. Antibiotic Resistance in Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infection. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.C.; Best, E.; Nourse, C. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Infections in Children: Review of Literature and Recommendations for Management. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivas, G.; Lagousi, T.; Mandilara, G. Epidemiological Data, Serovar Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella Species in Children, Greece 2011-2017: A Retrospective Study. Acta Med. Acad. 2021, 49, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.; Fhogartaigh, C.N. Bacterial Gastroenteritis. Medicine 2017, 45, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Chowdhury, G.; Samajpati, S.; Basak, S.; Ganai, A.; Samanta, S.; Okamoto, K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Dutta, S. Characterization of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Isolates from Children with Acute Gastroenteritis, Kolkata, India, during 2000–2016. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Yadav, A.S.; Tripathi, V.; Singh, R.P. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella Present in Poultry and Poultry Environment in North India. Food Control 2013, 33, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ran, L.; Wu, S.; Ke, B.; He, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, C.; Klena, J.D.; Yan, M.; et al. Laboratory-Based Surveillance of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Infections in Guangdong Province, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hou, H.; Lu, Y.; Yu, J.; Mao, L.; Mao, L.; Sun, Z. Characteristics of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli among Children under 5 Years of Age with Acute Diarrhea: A Hospital Based Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GebreSilasie, Y.M.; Tullu, K.D.; Yeshanew, A.G. Resistance Pattern and Maternal Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Suspected Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli among Children under 5 Years of Age in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Cross Sectional Study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, H.K.; Dabo, N.T.; Muhammad, B.; García-Soto, S.; Ugarte-Ruiz, M.; Alvarez, J. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes From Children Younger Than 5 Years in Kano State, Nigeria. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, A.; Man, A.; Toma, F.; Ciurea, C.N.; Coșeriu, R.L.; Vintilă, C.; Maier, A.C. Hemolysin-Producing Strains among Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Children under 2 Years Old with Diarrheal Disease. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisano, G.; Fornasero, S.; Migliaretti, G.; Caramello, S.; Tarasco, V.; Savino, F. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in acute gastroenteritis in infants in North-West Italy. New Microbiol. 2011, 34, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kargar, M.; Homayoon, M. Prevalence of Shiga Toxins (Stx1, Stx2), EaeA and Hly Genes of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Strains among Children with Acute Gastroenteritis in Southern of Iran. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.D. Prevalence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Children with Bloody Diarrhea Referring to Abuzar Teaching Hospital, Ahvaz, Iran. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2018, 10, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokh, C.; Jordan, K.; Auvray, F.; Glass, K.; Oppegaard, H.; Raynaud, S.; Thevenot, D.; Condron, R.; De Reu, K.; Govaris, A.; et al. Review of Shiga-Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and Their Significance in Dairy Production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Corrales, C.; Leandro-Sandí, K. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Costa Rican Children: A 9-Year Retrospective Study. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shunmugam, P.; Kanapathy, S.; Chan, S.-E.; Singh, K.-K.B. Long-Term Trends in the Epidemiology of Human Enteropathogens in Malaysia. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konaté, A.; Dembélé, R.; Guessennd, N.K.; Kouadio, F.K.; Kouadio, I.K.; Ouattara, M.B.; Kaboré, W.A.D.; Kagambèga, A.; Cissé, H.; Ibrahim, H.B.; et al. Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance Phenotypes of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Responsible for Infantile Gastroenteritis in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi Broujerdi, S.; Roayaei Ardakani, M.; Rezatofighi, S.E. Characterization of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Strains Associated with Diarrhea in Children, Khouzestan, Iran. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T.; Guler, E.; Atas Berksoy, E.; Sorguc, Y.; Arslan, N. Mean Platelet Volume in Children with Acute Gastroenteritis Caused by Entamoeba histolytica. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2015, 39, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dib, N.A. Entamoeba histolytica: An Overview. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2017, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, F. Etiology and Clinical Manifestations of Infectious Bloody Diarrhea in Children Welfare Teaching Hospital. Iraqi Postgrad. Med. J. 2016, 15, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, G.; Rebolledo, M.; White, A.C.; Crannell, Z.; Richards-Kortum, R.R.; Pinilla, A.E.; Ramírez, J.D.; López, M.C.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A. Detection of Entamoeba histolytica by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazi, M.A.; Patel, T.A.; El-Deek, B.S. Prevalence and Characters of Entamoeba histolytica Infection in Saudi Infants and Children Admitted with Diarrhea at 2 Main Hospitals at South Jeddah: A Re-Emerging Serious Infection with Unusual Presentation. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naous, A.; Naja, Z.; Zaatari, N.; Kamel, R.; Rajab, M. Intestinal Amebiasis: A Concerning Cause of Acute Gastroenteritis among Hospitalized Lebanese Children. North Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.; Afshan, K.; Firasat, S.; Qayyum, M. Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Entamoeba histolytica Infection among Gastroenteritis Patients Visited in Public Healthcare System, Pakistan. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enogiomwan, I.E.; Ikponmwosa, E.O.; Chinyere, O.-A.; Christopher, A.B. Evaluation of Vegetable Contamination with Medically Important Helminths and Protozoans in Calabar, Nigeria. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yones, D.; Othman, R.; Hassan, T.; Kotb, S.; Mohamed, A. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Parasites and its Predictors among Rural Egyptian School Children. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrul Anuar, T.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Abdul Ghani, M.K.; Osman, E.; Mohd Yasin, A.; Nordin, A.; Nor Azreen, S.; Md Salleh, F.; Ghazali, N.; Bernadus, M.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Entamoeba histolytica/Dispar/Moshkovskii Infection among Three Orang Asli Ethnic Groups in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maçin, S.; Kaya, F.; Ergüven, S.; Akyön, Y. Akut Gastroenterit Salgınının Mikrobiyolojik Değerlendirmesi. Cukurova Med. J. 2017, 42, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simon Oke, I.A.; Ogunleye, E. Prevalence of Entamoeba histolytica among Primary School Children in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.A.; Raboni, S.M.; Nogueira, M.B.; Vidal, L.R.; de Almeida, S.M.; Debur, M.C.; Cruz, C. Rotavirus Infection in a Tertiary Hospital: Laboratory Diagnosis and Impact of Immunization on Pediatric Hospitalization. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gautam, R.; Lyde, F.; Esona, M.D.; Quaye, O.; Bowen, M.D. Comparison of PremierTM Rotaclone®, ProSpecTTM, and RIDASCREEN® Rotavirus Enzyme Immunoassay Kits for Detection of Rotavirus Antigen in Stool Specimens. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, C.O.; Koech, M.; Kipkemoi, N.; Kirera, R.; Ndonye, J.; Ombogo, A.; Kirui, M.; Kipkirui, E.; Danboise, B.; Hulseberg, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Performance of a Multiplex Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Kit as a Potential Diagnostic and Surveillance Kit for Rotavirus in Kenya. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.; Yoo, I.Y.; Yun, S.A.; Chung, Y.N.; Huh, H.J.; Lee, N.Y. Performance Evaluation of Automated Fluorescent Immunoassay System ROTA and NORO for Detection of Rotavirus and Norovirus: A Comparative Study of Assay Performance with RIDASCREEN® Rotavirus and Norovirus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 35, e23585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ageery, S.M.; Ali, R.; Abou El-Khier, N.T.; Rakha, S.A.; Zeid, M.S. Comparison of Enzyme Immunoassay, Latex Agglutination and Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Diagnosis of Rotavirus in Children. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutelíková, R.; Sauer, P.; Dvořáková Heroldová, M.; Holá, V.; Prodělalová, J. Emergence of Rare Bovine–Human Reassortant DS-1-Like Rotavirus A Strains with G8P[8] Genotype in Human Patients in the Czech Republic. Viruses 2019, 11, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Mijatovic-Rustempasic, S.; Esona, M.D.; Tam, K.I.; Quaye, O.; Bowen, M.D. One-Step Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Detecting and Genotyping Wild-Type Group A Rotavirus Strains and Vaccine Strains (Rotarix® and RotaTeq®) in Stool Samples. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norovirus Laboratory Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/lab/diagnosis.html (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Wong, R.S.-L.; Yeo, F.; Chia, W.T.; Lee, C.K.; Leong, M.H.; Ng, C.W.-S.; Poon, K.S.; Yan, G.Z.; Chiu, L.-L.; Yan, B.J.; et al. Performance Evaluation of Cepheid Xpert Norovirus Kit with a User-Modified Protocol. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 90, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.D.; Langley, L.C.; Buchan, B.W.; Faron, M.L.; Maier, M.; Templeton, K.; Walker, K.; Popowitch, E.B.; Miller, M.B.; Rao, A.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the Xpert Norovirus Assay for Detection of Norovirus Genogroups I and II in Fecal Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, N.L.; Bruggink, L.D.; Marshall, J.A. Evaluation of the RIDAGENE Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection of GI and GII Norovirus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumthip, K.; Khamrin, P.; Saikruang, W.; Supadej, K.; Ushijima, H.; Maneekarn, N. Comparative Evaluation of Norovirus Infection in Children with Acute Gastroenteritis by Rapid Immunochromatographic Test, RT-PCR and Real-Time RT-PCR. J. Trop. Pediatrics 2017, 63, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere, S.; Botteldoorn, N.; Vandecandelaere, P.; Frans, J.; Laffut, W.; Coppens, G.; Vankeerberghen, A.; De Beenhouwer, H. Multicenter Evaluation of the Revised RIDA® QUICK Test (N1402) for Rapid Detection of Norovirus in a Diagnostic Laboratory Setting. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 88, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruggink, L.D.; Dunbar, N.L.; Marshall, J.A. Evaluation of the Updated RIDA®QUICK (Version N1402) Immunochromatographic Assay for the Detection of Norovirus in Clinical Specimens. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 223, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranuh, R.G.; Athiyyah, A.F.; Pa, D.A.; Darma, A.; Rahardjo, D.; Shirakawa, T.; Sudarmo, S.M. Assessment of the Rapid Immunochromatographic Test as a Diagnostic Tool for Norovirus Related Diarrhea in Children. Folia Med. Indones. 2019, 55, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thangjui, S.; Sripirom, N.; Titichoatrattana, S.; Mekmullica, J. Accuracy and Cross-Reactivity of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Norovirus and Rotavirus in a Real Clinical Setting. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 52, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geginat, G.; Kaiser, D.; Schrempf, S. Evaluation of Third-Generation ELISA and a Rapid Immunochromatographic Assay for the Detection of Norovirus Infection in Fecal Samples from Inpatients of a German Tertiary Care Hospital. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 31, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, A.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Dove, W.; Vieira, S.C.F.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Cuevas, L.E. An Evaluation of the RIDASCREEN and IDEIA Enzyme Immunoassays and the RIDAQUICK Immunochromatographic Test for the Detection of Norovirus in Faecal Specimens. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kibiki, G.; Maro, V.; Maro, A.; Kumburu, H.; Swai, N.; Taniuchi, M.; Gratz, J.; Toney, D.; Kang, G.; et al. Multiplex Reverse Transcription PCR Luminex Assay for Detection and Quantitation of Viral Agents of Gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 50, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Liu, X.-L.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wang, J.-Q.; He, X.-Q.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Z.-J. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Human Astrovirus in Water Samples by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue Dye. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zeng, J.; Deng, C.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, D.; Yi, Y. A Novel Method of Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Developed for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Human Astrovirus. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 188, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonura, F.; Mascarella, C.; Filizzolo, C.; Bonura, C.; Ferraro, D.; Di Bernardo, F.; Collura, A.; Martella, V.; Giammanco, G.M.; De Grazia, S. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performances of Two Commercially Available Assays for the Detection of Enteric Adenovirus Antigens. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 101, 115459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, N.; Yanik, K.; Aydogdu, S.; Eroglu, C.; Gunaydin, M.; Hokelek, M. An Evaluation of Rotavirus and Adenovirus Antigens by the Immunochromatographic Method in Samples with an Initial Diagnosis of Acute Gastroenteritis. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Gratz, J.; Amour, C.; Nshama, R.; Walongo, T.; Maro, A.; Mduma, E.; Platts-Mills, J.; Boisen, N.; Nataro, J.; et al. Optimization of Quantitative PCR Methods for Enteropathogen Detection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gratz, J.; Amour, C.; Kibiki, G.; Becker, S.; Janaki, L.; Verweij, J.J.; Taniuchi, M.; Sobuz, S.U.; Haque, R.; et al. A Laboratory-Developed TaqMan Array Card for Simultaneous Detection of 19 Enteropathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 51, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, B.; Anburajan, L.; Selvaganapathi, K.; Vinithkumar, N.V.; Dharani, G. Characteristics and Dynamics of Salmonella Diversity and Prevalence of Biomarker Genes in Port Blair Bays, South Andaman, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddington, K.; Tuite, N.; Minogue, E.; Barry, T. A Current Overview of Commercially Available Nucleic Acid Diagnostics Approaches to Detect and Identify Human Gastroenteritis Pathogens. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2014, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, M. An Overview of the Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8135724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Garza, H.J.; Garza-González, E.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Flores-Treviño, S. Diagnostic Syndromic Multiplex Approaches for Gastrointestinal Infections. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, J.S.; Al-Ali, A.; Rajput, P.; Smith, D.; Goldenberg, S.D. A Parallel Diagnostic Accuracy Study of Three Molecular Panels for the Detection of Bacterial Gastroenteritis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboromyrska, Y.; Vila, J. Advanced PCR-Based Molecular Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Infections: Challenges and Opportunities. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Morrison, S.; Tang, Y.-W. Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Tests for Detection of Pathogens Associated with Gastroenteritis. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 461–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézquita-López, B.A.; Soto-Beltrán, M.; Lee, B.G.; Yambao, J.C.; Quiñones, B. Isolation, Genotyping and Antimicrobial Resistance of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, L.H. Update: Recommendations for Diagnosis of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Infections by Clinical Laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2012, 34, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B.D.; Zelyas, N.; Berenger, B.M.; Chui, L. Detection, Characterization, and Typing of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.; Perry, N.T.; Godbole, G.; Gharbia, S. Evaluation of Chromogenic Selective Agar (CHROMagar STEC) for the Direct Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli from Faecal Specimens. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.; Luetgehetmann, M.; Landt, O.; Schwarz, N.G.; Frickmann, H. Comparison of One Commercial and Two In-House TaqMan Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection of Enteropathogenic, Enterotoxigenic and Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2017, 22, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khteer Al-Hadraawy, S.; Hussein Abod Al-Khafaji, K.; Deqeem, F.M.; Jawad Kadhim, N. Study Role of Hematological and Leptin Biomarkers in Human Infected with Entamoeba histolytica Parasite. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 062032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khteer Al-Hadraawy, S.; AL-Shebly, F.H.; Abood, A.H.; Khadim, N.J. Correlation Study Between Biological Markers In Patients With Entamoeba histolytica Parasite. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2019, 19, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Saidin, S.; Yunus, M.H.; Othman, N.; Lim, Y.A.-L.; Mohamed, Z.; Zakaria, N.Z.; Noordin, R. Development and Initial Evaluation of a Lateral Flow Dipstick Test for Antigen Detection Of Entamoeba histolyticain Stool Sample. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, S.; Kirveskari, J.; Antikainen, J.; Ursing, J.; Rombo, L.; Kofoed, P.-E.; Kantele, A. Multiplex PCR Detection Of Cryptosporidium sp, Giardia Lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica Directly from Dried Stool Samples from Guinea-Bissauan Children with Diarrhoea. Infect. Dis. 2017, 49, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rosas, I.; López-Camarillo, C.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N.; Palma-Flores, C.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Resendis-Antonio, O.; Guillen, N.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, M.E.; et al. Entamoeba histolytica Up-Regulates MicroRNA-643 to Promote Apoptosis by Targeting XIAP in Human Epithelial Colon Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappan, R.; Henry, R.; Chown, S.L.; Luby, S.P.; Higginson, E.E.; Bata, L.; Jirapanjawat, T.; Schang, C.; Openshaw, J.J.; O’Toole, J.; et al. TaqMan Array Cards Enable Monitoring of Diverse Enteric Pathogens across Environmental and Host Reservoirs; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakagomi, T.; Nakagomi, O.; Katayama, K. Study of Complete Genome Sequences of Rotavirus A Epidemics and Evolution in Japan in 2012–2014. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.A.; Madi, N.M.; Al-Nakib, W. Analysis of Viral Diversity in Stool Samples from Infants and Children with Acute Gastroenteritis in Kuwait Using Metagenomics Approach. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, T.; Wahyuni, R.M.; Doan, Y.H.; Dinana, Z.; Soegijanto, S.; Fujii, Y.; Juniastuti; Yamani, L.N.; Matsui, C.; Deng, L.; et al. Equine-like G3 Rotavirus Strains as Predominant Strains among Children in Indonesia in 2015–2016. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xiong, P.; Ji, F.; Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tao, Z.; Xu, A. Genetic Diversity and Molecular Epidemiological Characterization of Group A Rotaviruses in Raw Sewage in Jinan by next Generation Sequencing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 91, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagomi, T.; Doan, Y.H.; Dove, W.; Ngwira, B.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Nakagomi, O.; Cunliffe, N.A. G8 Rotaviruses with Conserved Genotype Constellations Detected in Malawi over 10 Years (1997–2007) Display Frequent Gene Reassortment among Strains Co-Circulating in Humans. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1273–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkänen, O. Rotavirus Whole Genome Sequencing with Next-Generation Sequencing. Master’s Thesis, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Strubbia, S.; Schaeffer, J.; Besnard, A.; Wacrenier, C.; Le Mennec, C.; Garry, P.; Desdouits, M.; Le Guyader, F.S. Metagenomic to Evaluate Norovirus Genomic Diversity in Oysters: Impact on Hexamer Selection and Targeted Capture-Based Enrichment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 323, 108588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronella, N.; Ronholm, J.; Suresh, M.; Harlow, J.; Mykytczuk, O.; Corneau, N.; Bidawid, S.; Nasheri, N. Genetic Characterization of Norovirus GII.4 Variants Circulating in Canada Using a Metagenomic Technique. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, A.M.; Adler, A.L.; Makhsous, N.; Crawford, K.; Qin, X.; Kuypers, J.M.; Huang, M.-L.; Zerr, D.M.; Greninger, A.L. Prospective, Real-Time Metagenomic Sequencing During Norovirus Outbreak Reveals Discrete Transmission Clusters. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelaar, H.H.J.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Zoll, J.; Melchers, W.J.G. Whole Genome Sequencing of Fecal Samples as a Tool for the Diagnosis and Genetic Characterization of Norovirus. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 70, S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Roy, S.; Ruis, C.; Yara Romero, E.; Shah, D.; Williams, R.; Breuer, J. Norovirus Whole-Genome Sequencing by SureSelect Target Enrichment: A Robust and Sensitive Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2530–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.-P.; Teng, J.L.L.; Yeong, K.-Y.; You, Z.-Q.; Liu, H.; Wong, S.S.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Metagenomic Analysis of Sichuan Takin Fecal Sample Viromes Reveals Novel Enterovirus and Astrovirus. Virology 2018, 521, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Martínez-Puchol, S.; Silva-Sales, M.; Cornejo, T.; Bartolome, R.; Bofill-Mas, S.; Girones, R. Unveiling Viruses Associated with Gastroenteritis Using a Metagenomics Approach. Viruses 2020, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, R.; Luchs, A.; Tardy, K.; Hefford, P.M.; Tinker, R.J.; Eilami, O.; de Padua Milagres, F.A.; Brustulin, R.; da Aparecida Rodrigues Teles, M.; dos Santos Morais, V.; et al. Viral Gastroenteritis in Tocantins, Brazil: Characterizing the Diversity of Human Adenovirus F through next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Sato-Ebine, E.; Escueta-de Cadiz, A.; Ji, D.; Tomii, K.; Kuroda, M.; Nozaki, T. AIG1 Affects in Vitro and in Vivo Virulence in Clinical Isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannoodt, R.; Saelens, W.; Saeys, Y. Computational Methods for Trajectory Inference from Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assisi, C.; Forauer, E.; Oliver, H.F.; Etter, A.J. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation in Persistent and Transient Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from the Retail Deli Environment Does Not Yield Insight into Persistence Mechanisms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, S.I.; Park, S.; Nam, E.; Yoon, H. Understanding Comprehensive Transcriptional Response of Salmonella enterica Spp. in Contact with Cabbage and Napa Cabbage. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1896–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, A.; Bertoni, M.; Auffret, P.; Klopp, C.; Bouchez, O.; Genthon, C.; Durand, A.; Bertin, Y.; Forano, E. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Specific Metabolic Pathways of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Bovine Digestive Contents. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de OliveiraVieira, K.C.; da Silva, H.R.A.; Rocha, I.P.M.; Barboza, E.; Eller, L.K.W. Foodborne Pathogens in the Omics Era. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsa, D.; Baiwir, D.; La Rocca, R.; Zimmerman, T.A.; Hanozin, E.; Grifnée, E.; Longuespée, R.; Meuwis, M.-A.; Smargiasso, N.; Pauw, E.D.; et al. Multi-Enzymatic Limited Digestion: The Next-Generation Sequencing for Proteomics? J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2501–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunima, A.; Yelamanchi, S.D.; Padhi, C.; Jaiswal, S.; Ryan, D.; Gupta, B.; Sathe, G.; Advani, J.; Gowda, H.; Prasad, T.S.K.; et al. “Omics” of Food-Borne Gastroenteritis: Global Proteomic and Mutagenic Analysis OfSalmonella EntericaSerovar Enteritidis. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2017, 21, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallagassa, C.B.; Huergo, L.F.; Stets, M.I.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Cruz, L.M.; Assis, F.E.A.; Wolf, S.; Volanski, W.; Picheth, G.; et al. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Escherichia coli Categories. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychert, J. Benefits and Limitations of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for the Identification of Microorganisms. J. Infect. 2019, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagoyen, M.; Pazos, F. Tools for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomic Experiments. Brief. Bioinform. 2012, 14, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Malachová, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R. Challenges and Future Directions in LC-MS-Based Multiclass Method Development for the Quantification of Food Contaminants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 413, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratburd, J.R.; Keller, C.; Vivas, E.; Gemperline, E.; Li, L.; Rey, F.E.; Currie, C.R. Gut Microbial and Metabolic Responses to Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium and Candida albicans. mBio 2018, 9, e02032-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, P.; Izquierdo, M.; Vidal, R.M.; Soto, F.; Ossa, J.C.; Farfan, M.J. Gut Microbiota-Metabolome Changes in Children With Diarrhea by Diarrheagenic E. Coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, H.; Nasirudeen, N.A.; Ruzlan, M.A.F.; Mohd Jamil, M.A.; Ismail, N.A.S.; Wahab, A.A.; Ali, A. Acute Infectious Gastroenteritis: The Causative Agents, Omics-Based Detection of Antigens and Novel Biomarkers. Children 2021, 8, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121112
Hasan H, Nasirudeen NA, Ruzlan MAF, Mohd Jamil MA, Ismail NAS, Wahab AA, Ali A. Acute Infectious Gastroenteritis: The Causative Agents, Omics-Based Detection of Antigens and Novel Biomarkers. Children. 2021; 8(12):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121112
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Haziqah, Nor Ashika Nasirudeen, Muhammad Alif Farhan Ruzlan, Muhammad Aiman Mohd Jamil, Noor Akmal Shareela Ismail, Asrul Abdul Wahab, and Adli Ali. 2021. "Acute Infectious Gastroenteritis: The Causative Agents, Omics-Based Detection of Antigens and Novel Biomarkers" Children 8, no. 12: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121112
APA StyleHasan, H., Nasirudeen, N. A., Ruzlan, M. A. F., Mohd Jamil, M. A., Ismail, N. A. S., Wahab, A. A., & Ali, A. (2021). Acute Infectious Gastroenteritis: The Causative Agents, Omics-Based Detection of Antigens and Novel Biomarkers. Children, 8(12), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121112