Neonatal Seizures Revisited
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Pathophysiology
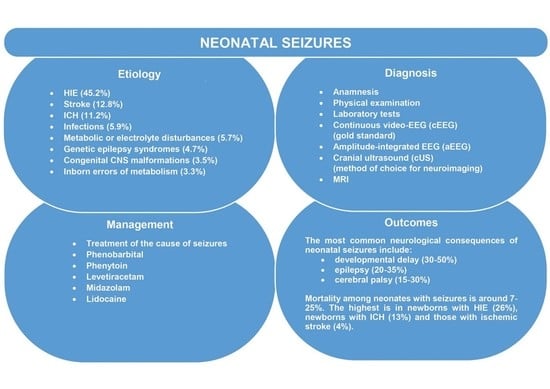
3.2. Etiology
3.3. Genetics of Neontal Seizures
3.3.1. Structural Brain Malformation
3.3.2. Inborn Errors of Metabolism
3.3.3. Syndromic Disorders
3.3.4. Nonsyndromic Disorders
3.4. Symptoms and Semiology Classification
3.5. Diagnosis
3.6. Management
3.6.1. Acute Intervention
3.6.2. Treatment of Neontal Epilepsy
3.7. Outcomes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramantani, G.; Schmitt, B.; Plecko, B.; Pressler, R.M.; Wohlrab, G.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Hagmann, C.; Pisani, F.; Boylan, G.B. Neonatal Seizures-Are We there Yet? Neuropediatrics 2019, 50, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, H.C.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Chang, T.; Abend, N.S.; Chu, C.J.; Cilio, M.R.; Glidden, D.V.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Massey, S.; et al. Contemporary Profile of Seizures in Neonates: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spagnoli, C.; Falsaperla, R.; Deolmi, M.; Corsello, G.; Pisani, F. Symptomatic seizures in preterm newborns: A review on clinical features and prognosis. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, H.C.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Tsuchida, T.N.; Chang, T.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Chu, C.J.; Cilio, M.R.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Massey, S.L.; Abend, N.S.; et al. Seizures in Preterm Neonates: A Multicenter Observational Cohort Study. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 72, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padiyar, S.; Nusairat, L.; Kadri, A.; Abu-Shaweesh, J.; Aly, H. Neonatal seizures in the U.S. National Inpatient Population: Prevalence and outcomes. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020, 61, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pellegrin, S.; Munoz, F.M.; Padula, M.; Heath, P.T.; Meller, L.; Top, K.; Wilmshurst, J.; Wiznitzer, M.; Das, M.K.; Hahn, C.D.; et al. Brighton Collaboration Neonatal Seizures Working Group. Neonatal seizures: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7596–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, F.; Piccolo, B.; Cantalupo, G.; Copioli, C.; Fusco, C.; Pelosi, A.; Tassinari, C.A.; Seri, S. Neonatal seizures and postneonatal epilepsy: A 7-y follow-up study. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 72, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yıldız, E.P.; Tatlı, B.; Ekici, B.; Eraslan, E.; Aydınlı, N.; Calışkan, M.; Ozmen, M. Evaluation of etiologic and prognostic factors in neonatal convulsions. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 47, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, V.; Nair, P.M. Neonatal seizures: Predictors of adverse outcome. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, N.S.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Goldberg, E.M.; Dlugos, D.J. Electrographic seizures and status epilepticus in critically ill children and neonates with encephalopathy. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressler, R.M.; Cilio, M.R.; Mizrahi, E.M.; Moshé, S.L.; Nunes, M.L.; Plouin, P.; Vanhatalo, S.; Yozawitz, E.; Zuberi, S.M. The ILAE classification of seizures & the epilepsies: Modification for seizures in the neonate. Proposal from the ILAE task force on neonatal seizures. Epilepsia 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellhaas, R.A. Continuous long-term electroencephalography: The gold standard for neonatal seizure diagnosis. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouin, P.; Kaminska, A. Neonatal seizures. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 111, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puskarjov, M.; Kahle, K.T.; Ruusuvuori, E.; Kaila, K. Pharmacotherapeutic targeting of cation-chloride cotransporters in neonatal seizures. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nardou, R.; Ferrari, D.C.; Ben-Ari, Y. Mechanisms and effects of seizures in the immature brain. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, M.; Stafstrom, C.E. How Early Can a Seizure Happen? Pathophysiological Considerations of Extremely Premature Infant Brain Development. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 40, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellhaas, R.A. Seizure classification, etiology, and management. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 162, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kadam, S. Pre-Clinical Models of Acquired Neonatal Seizures: Differential Effects of Injury on Function of Chloride Co-Transporters. Austin J. Cereb. Dis. Stroke 2014, 1, 1026. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.M.; Goasdoue, K.; Björkman, S.T. Neonatal seizures and disruption to neurotransmitter systems. Neural Regen Res. 2017, 12, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, C.; Levene, M. Epidemiology and aetiology of neonatal seizures. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, H.C. Neonatal seizures: Advances in mechanisms and management. Clin Perinatol. 2014, 41, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, D.K.; Zempel, J.; Barton, T.; Lukas, K.; Inder, T.E. Electrographic seizures in preterm infants during the first week of life are associated with cerebral injury. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisani, F.; Facini, C.; Pelosi, A.; Mazzotta, S.; Spagnoli, C.; Pavlidis, E. Neonatal seizures in preterm newborns: A predictive model for outcome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeke, L.C.; Groenendaal, F.; Toet, M.C.; Benders, M.J.; Nievelstein, R.A.; van Rooij, L.G.; de Vries, L.S. The aetiology of neonatal seizures and the diagnostic contribution of neonatal cerebral magnetic resonance imaging. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.E.; Berg, M.; Hunt, R.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.O.; Inder, T.E.; Davis, P.G. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, H.C.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Tsuchida, T.N.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Cordeiro, M.; Sullivan, J.; Abend, N.S.; Chang, T. Risk factors for EEG seizures in neonates treated with hypothermia: A multicenter cohort study. Neurology 2014, 82, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, G.B.; Kharoshankaya, L.; Wusthoff, C.J. Seizures and hypothermia: Importance of electroencephalographic monitoring and considerations for treatment. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirton, A.; Armstrong-Wells, J.; Chang, T.; Deveber, G.; Rivkin, M.J.; Hernandez, M.; Carpenter, J.; Yager, J.Y.; Lynch, J.K.; Ferriero, D.M. International Pediatric Stroke Study Investigators. Symptomatic neonatal arterial ischemic stroke: The International Pediatric Stroke Study. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Biarge, M.; Cheong, J.L.; Diez-Sebastian, J.; Mercuri, E.; Dubowitz, L.M.; Cowan, F.M. Risk Factors for Neonatal Arterial Ischemic Stroke: The Importance of the Intrapartum Period. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darmency-Stamboul, V.; Chantegret, C.; Ferdynus, C.; Mejean, N.; Durand, C.; Sagot, P.; Giroud, M.; Bejot, Y.; Gouyon, J.B. Antenatal factors associated with perinatal arterial ischemic stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziobro, J.; Shellhaas, R.A. Neonatal Seizures: Diagnosis, Etiologies, and Management. Semin Neurol. 2020, 40, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Okumura, A.; Fukuda, M. Epilepsies and epileptic syndromes starting in the neonatal period. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, A.; Thurman, D.J.; Kim, H. Independent role of neonatal seizures in subsequent neurological outcomes: A population-based study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, A.M.; ter Horst, H.J.; Lambrechtsen, F.A.; Lunsing, R.J. Neonatal seizures: Aetiology by means of a standardized work-up. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2014, 18, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axeen, E.J.T.; Olson, H.E. Neonatal epilepsy genetics. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Tsuchida, T.N.; Glass, H.C.; Chu, C.J.; Massey, S.L.; Soul, J.S.; Wiwattanadittakun, N.; Abend, N.S.; Cilio, M.R. Neonatal Seizure Registry. Profile of neonatal epilepsies: Characteristics of a prospective US cohort. Neurology 2017, 89, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Pappas, K. Genetic Etiologies of Neonatal Seizures. Neoreviews 2020, 21, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet, M.C.; Sands, T.T.; Cilio, M.R. Neonatal epilepsies: Clinical management. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficicioglu, C.; Bearden, D. Isolated neonatal seizures: When to suspect inborn errors of metabolism. Pediatr. Neurol. 2011, 45, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, O.; Plecko, B.; Gataullina, S.; Wolf, N.I. Occasional seizures, epilepsy, and inborn errors of metabolism. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E. Epilepsy genetics revolutionizes clinical practice. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mills, P.B.; Footitt, E.J.; Mills, K.A.; Tuschl, K.; Aylett, S.; Varadkar, S.; Hemingway, C.; Marlow, N.; Rennie, J.; Baxter, P.; et al. Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy (ALDH7A1 deficiency). Brain 2010, 133, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearl, P.L. Amenable Treatable Severe Pediatric Epilepsies. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 23, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campistol, J. Epilepsy in Inborn Errors of Metabolism with Therapeutic Options. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 23, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, M. Actual Insights into Treatable Inborn Errors of Metabolism Causing Epilepsy. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Prasad, A.N. Inborn Errors of Metabolism and Epilepsy: Current Understanding, Diagnosis, and Treatment Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stence, N.V.; Coughlin, C.R.; Fenton, L.Z.; Thomas, J.A. Distinctive pattern of restricted diffusion in a neonate with molybdenum cofactor deficiency. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah-Shmouni, F.; MacNeil, L.; Potter, M.; Jobling, R.; Yoon, G.; Laughlin, S.; Blaser, S.; Inbar-Feigenberg, M. Severe cystic degeneration and intractable seizures in a newborn with molybdenum cofactor deficiency type B. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2018, 20, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, T.T.; McDonough, T.L. Recent Advances in Neonatal Seizures. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tong, L.; Song, S.; Niu, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zai, C.C.; Luo, F.; Wu, J.; et al. Novel and de novo mutations in pediatric refractory epilepsy. Mol. Brain. 2018, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maljevic, S.; Vejzovic, S.; Bernhard, M.K.; Bertsche, A.; Weise, S.; Döcker, M.; Lerche, H.; Lemke, J.R.; Merkenschlager, A.; Syrbe, S. Novel KCNQ3 Mutation in a Large Family with Benign Familial Neonatal Epilepsy: A Rare Cause of Neonatal Seizures. Mol. Syndromol. 2016, 7, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saadeldin, I.Y.; Milhem, R.M.; Al-Gazali, L.; Ali, B.R. Novel KCNQ2 mutation in a large Emirati family with benign familial neonatal seizures. Pediatric Neurol. 2013, 48, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, P.L. Epilepsy Syndromes in Childhood. Continuum (Minneap Minn). Child Neurol. 2018, 24, 186–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.R.; Pilling, E.L.; Alix, J.J. Neonatal seizures-part 2: Aetiology of acute symptomatic seizures, treatments and the neonatal epilepsy syndromes. Arch. Dis. Child Educ. Pract. Ed. 2015, 100, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, J.C.; Cherian, K.; Moshe, S.L. Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies: Ohtahara syndrome and early myoclonic encephalopathy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 47, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McTague, A.; Appleton, R.; Avula, S.; Cross, J.H.; King, M.D.; Jacques, T.S.; Bhate, S.; Cronin, A.; Curran, A.; Desurkar, A.; et al. Migrating partial seizures of infancy: Expansion of the electroclinical, radiological and pathological disease spectrum. Brain 2013, 136, 1578–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, F.; Hua, Z. Genetic diagnosis of neonatal-onset seizures. Genes Dis. 2019, 8, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, B.; Blennow, M. Investigations for neonatal seizures. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, H.C.; Shellhaas, R.A. Acute Symptomatic Seizures in Neonates. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet Perez, E.; et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nash, K.B.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Glass, H.C.; Sullivan, J.E.; Barkovich, A.J.; Ferriero, D.M.; Cilio, M.R. Video-EEG monitoring in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. Neurology 2011, 76, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagarajan, L.; Ghosh, S.; Palumbo, L. Ictal electroencephalograms in neonatal seizures: Characteristics and associations. Pediatr. Neurol. 2011, 45, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Chang, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Scher, M.S.; Riviello, J.J.; Abend, N.S.; Nguyen, S.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Clancy, R.R. The American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Guideline on Continuous Electroencephalography Monitoring in Neonates. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 28, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benedetti, G.M.; Silverstein, F.S.; Rau, S.M.; Lester, S.G.; Benedetti, M.H.; Shellhaas, R.A. Sedation and Analgesia Influence Electroencephalography Monitoring in Pediatric Neurocritical Care. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 87, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, M.C.; Pasupuleti, A.; Fang, A.; Gonzalez, F.; Shimotake, T.; Ferriero, D.M.; Glass, H.C.; Cilio, M.R. Predictive value of early EEG for seizures in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathieson, S.R.; Livingstone, V.; Low, E.; Pressler, R.; Rennie, J.M.; Boylan, G.B. Phenobarbital reduces EEG amplitude and propagation of neonatal seizures but does not alter performance of automated seizure detection. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 3343–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakshasbhuvankar, A.; Paul, S.; Nagarajan, L.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, S. Amplitude-integrated EEG for detection of neonatal seizures: A systematic review. Seizure 2015, 33, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, H.C.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Shellhaas, R.A. Amplitude-integrated electro-encephalography: The child neurologist’s perspective. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Barks, A.K. Impact of amplitude-integrated electroencephalograms on clinical care for neonates with seizures. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 46, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathieson, S.; Rennie, J.; Livingstone, V.; Temko, A.; Low, E.; Pressler, R.M.; Boylan, G.B. In-depth performance analysis of an EEG based neonatal seizure detection algorithm. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2246–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weeke, L.C.; Van Rooij, L.G.; Toet, M.C.; Groenendaal, F.; de Vries, L.S. Neuroimaging in neonatal seizures. Epileptic Disord. 2015, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Neonatal Seizures; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, M.D.; Griffin, B.T.; Kharoshankaya, L.; Cryan, J.F.; Boylan, G.B. Pharmacotherapy for Neonatal Seizures: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Drugs 2016, 76, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, H.C.; Kan, J.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Ferriero, D.M. Neonatal seizures: Treatment practices among term and preterm infants. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 46, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bialer, M.; White, H.S. Key factors in the discovery and development of new antiepileptic drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, M.J.; Kwan, P. Current position of phenobarbital in epilepsy and its future. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.A.; Desai, S.J.; Bennett, M.M.; Ahmad, S.F.; Ng, Y.T.; Clark, R.H.; Tolia, V.N. Changing antiepileptic drug use for seizures in US neonatal intensive care units from 2005 to 2014. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramantani, G.; Ikonomidou, C.; Walter, B.; Rating, D.; Dinger, J. Levetiracetam: Safety and efficacy in neonatal seizures. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2011, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhar, S.L.; Schibler, K.R.; Sherwin, C.M.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Shi, J.; Balmakund, T.; Vinks, A.A. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in neonates with seizures. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, C.M.; Capparelli, E.V.; Mower, A.; Farrell, M.J.; Soldin, S.J.; Haas, R.H. A seven-day study of the pharmacokinetics of intravenous levetiracetam in neonates: Marked changes in pharmacokinetics occur during the first week of life. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 72, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weeke, L.C.; Toet, M.C.; van Rooij, L.G.; Groenendaal, F.; Boylan, G.B.; Pressler, R.M.; Hellström-Westas, L.; van den Broek, M.P.; de Vries, L.S. Lidocaine response rate in aEEG-confirmed neonatal seizures: Retrospective study of 413 full-term and preterm infants. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, M.P.; Kessler, S.K.; Abend, N.S. Early discontinuation of antiseizure medications in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Chang, T.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Soul, J.S.; Massey, S.L.; Chu, C.J.; Cilio, M.R.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Abend, N.S.; Tsuchida, T.N.; et al. Treatment Duration After Acute Symptomatic Seizures in Neonates: A Multicenter Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Rooij, L.G.; van den Broek, M.P.; Rademaker, C.M.; de Vries, L.S. Clinical management of seizures in newborns: Diagnosis and treatment. Paediatr. Drugs 2013, 15, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, T.T.; Balestri, M.; Bellini, G.; Mulkey, S.B.; Danhaive, O.; Bakken, E.H.; Taglialatela, M.; Oldham, M.S.; Vigevano, F.; Holmes, G.L.; et al. Rapid and safe response to low-dose carbamazepine in neonatal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Dib, M.; Soul, J.S. The use of phenobarbital and other anti-seizure drugs in newborns. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numis, A.L.; Angriman, M.; Sullivan, J.E.; Lewis, A.J.; Striano, P.; Nabbout, R.; Cilio, M.R. KCNQ2 encephalopathy: Delineation of the electroclinical phenotype and treatment response. Neurology 2014, 82, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Leary, H.; Bernard, P.B.; Castano, A.M.; Benke, T.A. Enhanced long term potentiation and decreased AMPA receptor desensitization in the acute period following a single kainate induced early life seizure. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 87, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, H.C.; Grinspan, Z.M.; Shellhaas, R.A. Outcomes after acute symptomatic seizures in neonates. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharoshankaya, L.; Stevenson, N.J.; Livingstone, V.; Murray, D.M.; Murphy, B.P.; Ahearne, C.E.; Boylan, G.B. Seizure burden and neurodevelopmental outcome in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinchefsky, E.F.; Hahn, C.D. Outcomes following electrographic seizures and electrographic status epilepticus in the pediatric and neonatal ICUs. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaniki, M.; Mathenge, A.; Gwer, S.; Mturi, N.; Bauni, E.; Newton, C.R.; Berkley, J.; Idro, R. Neonatal seizures in a rural Kenyan District Hospital: Aetiology, incidence and outcome of hospitalization. BMC Med. 2010, 17, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisani, F.; Copioli, C.; Turco, E.C.; Sisti, L.; Cossu, G.; Seri, S. Mortality risk after neonatal seizures in very preterm newborns. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heljic, S.; Uzicanin, S.; Catibusic, F.; Zubcevic, S. Predictors of Mortality in Neonates with Seizures; a Prospective Cohort Study. Med. Arch. 2016, 70, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Etiology | Studies Conducted between 2013 and 2015 % Sample = 426 Neonates [2] | Studies Conducted between 2009 and 2013 % Sample = 378 Neonates [24] | Studies Conducted between 2002 and 2009 % Sample = 221 Neonates [34] | Time of Seizure Onset [31] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIE | 38 | 46 | 57.5 | First 24 hours |
| Stroke | 18 | 10.6 | 7.7 | First week |
| ICH | 12 | 12.2 | 9.0 | First week |
| Metabolic or electrolyte disturbances | 4 | 4.7 | 10.9 | First few days |
| Infections | 4 | 7.1 | 6.3 | Days to weeks |
| Congenital CNS malformations | 4 | 2.9 | 3.2 | Variable |
| Inborn errors of metabolism | 3 | 4.2 | 2.3 | From day 2 |
| Genetic epilepsy syndromes | 9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | Perinatal period |
| Unknown | 9 | 6.3 | 0.5 | Variable |
| Disease | Urine | Plasma | CSF | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE | Increase in AASA and PA | Increase in PA | Increase in AASA, P6C and PADecrease in PLP Sec NT abnormalities | ALDH7A1 |
| PNPO | (Vanillactate) | Increase in pyridoxamine | Decrease in PLP sec NT abnormalities | PNPO |
| MOCOD, ISOD | Sulfocysteine Increase in AASA and P6C | Decrease in uric acid | Increase in AASA, P6C and PA Decrease in PLP | MOCS1, MOCS2, GPHN |
| NKH | Amino acids (glycine) | Amino acids (glycine) CSF/plasma > 0.004 | 4-enzyme cleavage system |
| Type of Condition | Syndrome | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosomal | Down syndrome | Trisomy 21 |
| Patau syndrome | Trisomy 13 | |
| Edwards syndrome | Trisomy 18 | |
| 22q11.2 deletion syndrome | Deletion of 22q11.2 | |
| Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome | Deletion of 4p16.3 | |
| Neurocutaneous | Tuberous sclerosis | TSC1, TSC2 |
| Sturge–Weber | GNAQ | |
| Incontinentia pigmenti | IBKKG | |
| Hypomelanosis of Ito | Mosaicism for aneuploidy or other chromosomal anomalies | |
| Other | COL4A1-related | COL4A1 |
| Pitt-Hopkins | TCF4 | |
| Coffin–Siris | ARID1A, ARID1B, SMARCA4, SMARCB1, SMARCE1, SOX11 | |
| Aicardi–Goutieres | ADAR, RNASEH2A, RNASEH2B, RNASEH2C, SAMHD1, TREX1, IFIH1 |
| Type | Time of Seizure Onset | Genetic Variants | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-limited neonatal seizures | Between 4th and 6th days of life | Most unknown, KCNQ2 | Good |
| Self-limited familial neonatal epilepsy | Days 2–3 | Autosomal dominant in KCNQ2, KCNQ3, SCN2A | Good |
| Early infantile epileptic encephalopathy | First two weeks | Structural brain malformations, gene variants in ARX, CDKL5, SLC25A22, STXBP1, KCNQ2, SPTAN1, SCN2A, metabolic disorders | Frequent early-life mortality, developmental disabilities |
| Early myoclonic encephalopathy | Hours to months | STXBP1, TBC1D24, GABRA1, metabolic disorders | Frequent early-life mortality, developmental disabilities |
| Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures | Days to months | KCNT1, SCN2A, SCN1A, SLC25A22, PLCB1, TBC1D24, QARS | Poor, developmental disabilities |
| Motor Seizures | Nonmotor Seizures | |
|---|---|---|
| Seizure Type | Modifiers | Seizure Type |
| Automatism | Unilateral Bilateral asymmetric Bilateral symmetric | Autonomic |
| Clonic seizures | Focal Multifocal Bilateral | Behavioral arrest |
| Tonic seizures | Focal Bilateral asymmetric Bilateral symmetric | |
| Myoclonic seizures | Focal Multifocal Bilateral asymmetric Bilateral symmetric | |
| Sequential seizure type | Depending on components | |
| Epileptic spasm | Unilateral Bilateral asymmetric Bilateral symmetric | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaminiów, K.; Kozak, S.; Paprocka, J. Neonatal Seizures Revisited. Children 2021, 8, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020155
Kaminiów K, Kozak S, Paprocka J. Neonatal Seizures Revisited. Children. 2021; 8(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaminiów, Konrad, Sylwia Kozak, and Justyna Paprocka. 2021. "Neonatal Seizures Revisited" Children 8, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020155
APA StyleKaminiów, K., Kozak, S., & Paprocka, J. (2021). Neonatal Seizures Revisited. Children, 8(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020155