Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Neonates during Intermittent and Continuous Feeding-GRV and Feeding Mode in Preterm Neonates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
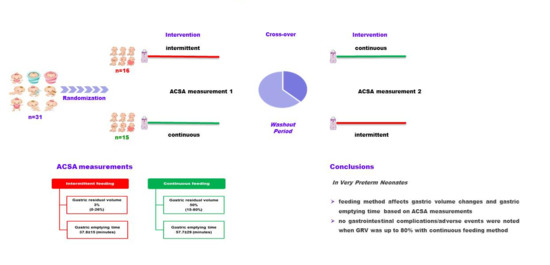
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Ultrasound Examination
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herbst, J.J. Development of suck and swallow. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1983, 2 (Suppl. 1), S131–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G. The Role of Lower Esophageal Sphincter Function and Dysmotility in Gastroesophageal Reflux in Premature Infants and in the First Year of Life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 37, S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berseth, C.L. Gastrointestinal motility in the neonate. Clin. Perinatol. 1996, 23, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.H.F.; Martinez, F.E.; Crott, G.C.; Belik, J. Gavage Feed Volume Determines the Gastric Emptying Rate in Preterm In-fants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, e43–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, S.L.; Hepworth, A.R.; Simmer, K.N.; Geddes, D.T. Influences of Breast Milk Composition on Gastric Emptying in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Mandel, D.; Mimouni, F.B.; Solovkin, L.; Dollberg, S. Gastric residual in growing preterm infants: Effect of body posi-tion. Am. J. Perinatol. 2004, 21, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premji, S.S.; Chessell, L. Continuous nasogastric milk feeding versus intermittent bolus milk feeding for premature infants less than 1500 grams. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, CD001819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, B.A.; Carlo, W.A.; Ambalavanan, N. Gastric residuals and their relationship to necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2003, 113 Pt 1, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.; Giuliani, F.; Prandi, G.; Coscia, A.; Martano, C.; Fabris, C. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Risk Factor Analysis and Role of Gastric Residuals in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiramalatha, T.; Thanigainathan, S.; Ninan, B. Routine monitoring of gastric residual for prevention of necrotising entero-colitis in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD012937. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, J.; Courtney, C.M.; Steinberger, A.E.; Tecos, M.E.; Warner, B.W. Nutrition in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Following Intesti-nal Resection. Nutrients 2020, 12, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, L.; Torrazza, R.M.; Li, Y.; Talaga, E.; Shuster, J.; Neu, J. Aspiration and evaluation of gastric residuals in the neonatal in-tensive care unit: State of the science. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 2015, 29, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounaris, A.K.; Grivea, I.N.; Baltogianni, M.; Gounari, E.; Antonogeorgos, G.; Kokori, F.; Panagiotounakou, P.; Theodoraki, M.; Konstantinidi, A.; Sokou, R. Caffeine and Gastric Emptying Time in Very Preterm Neonates. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, S.L.; Hepworth, A.R.; Simmer, K.N.; Geddes, D.T. Validation of Ultrasound Methods to Monitor Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrella, S.L.; Hepworth, A.R.; Simmer, K.N.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T. Repeatability of Gastric Volume Measurements and Intragastric Content Using Ultrasound in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Luo, B.-R. Continuous feeding versus intermittent bolus feeding for premature infants with low birth weight: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 74, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollberg, S.; Kuint, J.; Mazkereth, R.; Mimouni, F.B. Feeding tolerance in preterm infants: Randomized trial of bolus and con-tinuous feeding. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsilna, A.; Christensson, K.; Alfredsson, L.; Lagercrantz, H.; Blennow, M. Continuous feeding promotes gastrointestinal toler-ance and growth in very low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Kliegman, R.M. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Treatment Based on Staging Criteria. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 33, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.J.; Chapman, S.; Booth, I.W. Ultrasonic assessment of gastric emptying in the preterm infant. Arch. Dis. Child. 1993, 69, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walti, H.; Couchard, M.; Relier, J.P. Neonatal diagnosis of respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 1989, 3, 22s–26s. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaudecker, E.P.; Munoz, F.M.; Bardají, A.; Boghossian, N.S.; Khalil, A.; Mousa, H.; Nesin, M.; Nisar, M.I.; Pool, V.; Spiegel, H.M.; et al. Small for gestational age: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of maternal immunisation safety data. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6518–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Corsini, I.; Generoso, M.; Gozzini, E.; Bianconi, T.; Pratesi, S. Splanchnic Tissue Oxygenation for Predicting Feeding Tolerance in Preterm Infants. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 39, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berseth, C.L. Effect of early feeding on maturation of the preterm infant’s small intestine. J. Pediatr. 1992, 120, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, C.; Pratesi, S.; Barp, J.; Bertini, G.; Gozzini, E.; Mele, L.; Parrini, L. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements of Splanchnic Tissue Oxygenation During Continuous Versus Intermittent Feeding Method in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodé, S.; Dreyer, M.; Greisen, G. Gastric Emptying and Small Intestinal Transit Time in Preterm Infants: A Scintigraphic Method. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 39, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, A.; Bolisetty, S.; Patole, S.; A Garvey, P.; Campbell, P.J. Randomised controlled trial of cisapride in feed intolerance in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1998, 79, F110–F113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihatsch, W.A.; Von Schoenaich, P.; Fahnenstich, H.; Dehne, N.; Ebbecke, H.; Plath, C.; Von Stockhausen, H.-B.; Muche, R.; Franz, A.; Pohlandt, F. The Significance of Gastric Residuals in the Early Enteral Feeding Advancement of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rövekamp-Abels, L.W.W.; Hogewind-Schoonenboom, J.E.; de Wijs-Meijler, D.P.; Maduro, M.D.; Jansen-van der Weide, M.C.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Hulst, J.M. Intermittent Bolus or Semicontinuous Feeding for Preterm Infants? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Lin, H.C.; Torrazza, R.M.; Parker, L.; Talaga, E.; Neu, J. Gastric residual evaluation in preterm neonates: A useful monitoring technique or a hindrance? Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, L.A.; Weaver, M.; Murgas Torrazza, R.J.; Shuster, J.; Li, N.; Krueger, C.; Neu, J. Effect of Gastric Residual Evaluation on Enter-al Intake in Extremely Preterm Infants: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounaris, A.; Costalos, C.; Varchalama, L.; Kokori, P.; Kolovou, E.; Alexiou, N. Gastric emptying in very-low-birth-weight in-fants treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaile, J.C.; Levin, T.; Wung, J.T.; Abramson, S.J.; Ruzal-Shapiro, C.; Berdon, W.E. Benign gaseous distension of the bowel in prema-ture infants treated with nasal continuous airway pressure: A study of contributing factors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 158, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, C.E.; Witt, L.; Albrecht, L.; Winstroth, A.M.; Lange, M.; Dennhardt, N.; Boethig, D.; Sumpelmann, R. Ultrasound assessment of gastric emptying time in preterm infants: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 36, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of neonates included | 31 |
| Males/Females | 14/17 |
| BW g (mean, SD) | 982 (28) |
| GA weeks (mean, SD) | 28 (1.5) |
| SGA (n) | 7/31 |
| Antepartum corticosteroids | 19/31 |
| 1 min Apgar Score (median, range) | 6 (1–9) |
| 5 min Apgar Score (median, range) | 8 (2–9) |
| Inborns/outborns (n) | 15/16 |
| RDS (n) | 29 |
| BPD (n) | 19 |
| Respiratory support during measurements (n, %) | |
| nCPAP | 18 (58.06) |
| O2 < 30% | 7 (22.58) |
| room air | 6 (19.35) |
| Full enteral feeding days (median, range) | 12 (10–21) |
| First measurement (days/median, range) | 15.5 (11–32) |
| Second measurement (days/median, range) | 19 (14–35) |
| Milk volume (mL/2 h) during the assessments (median, range) | 17 (9–22) |
| Breast milk + suppl/formula (n) | 21/10 |
| ACSA (cm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment Time after the End of Milk Administration | Bolus Feeding | Continuous Feeding | p-Value |
| 0′ | 1.9 (1.4–3.6) | 1.0 (0.6–1.7) | <0.001 |
| 10′ | 1.8 (1.5–3.0) | 1.0 (0.7–1.7) | <0.001 |
| 20′ | 1.5 (1.2–2.5) | 0.9 (0.6–1.7) | <0.001 |
| 30′ | 1.3 (1.0–2.0) | 0.8 (0.5–1.8) | <0.001 |
| 60′ | 1.0 (0.5–1.0) | 0.8 (0.5–1.8) | 0.328 |
| 90′ | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 0.7 (0.4–1.4) | <0.001 |
| 120′ | 0.1 (0.0–0.2) | 0.8 (0.5–1.95) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokou, R.; Grivea, I.N.; Gounari, E.; Panagiotounakou, P.; Baltogianni, M.; Antonogeorgos, G.; Kokori, F.; Konstantinidi, A.; Gounaris, A.K. Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Neonates during Intermittent and Continuous Feeding-GRV and Feeding Mode in Preterm Neonates. Children 2021, 8, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8040300
Sokou R, Grivea IN, Gounari E, Panagiotounakou P, Baltogianni M, Antonogeorgos G, Kokori F, Konstantinidi A, Gounaris AK. Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Neonates during Intermittent and Continuous Feeding-GRV and Feeding Mode in Preterm Neonates. Children. 2021; 8(4):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8040300
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokou, Rozeta, Ioanna N. Grivea, Eleni Gounari, Polytimi Panagiotounakou, Maria Baltogianni, George Antonogeorgos, Fedra Kokori, Aikaterini Konstantinidi, and Antonios K. Gounaris. 2021. "Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Neonates during Intermittent and Continuous Feeding-GRV and Feeding Mode in Preterm Neonates" Children 8, no. 4: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8040300
APA StyleSokou, R., Grivea, I. N., Gounari, E., Panagiotounakou, P., Baltogianni, M., Antonogeorgos, G., Kokori, F., Konstantinidi, A., & Gounaris, A. K. (2021). Gastric Volume Changes in Preterm Neonates during Intermittent and Continuous Feeding-GRV and Feeding Mode in Preterm Neonates. Children, 8(4), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8040300