Reading Skills of Children with Dyslexia Improved Less Than Expected during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Measures
2.4. Plan of Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
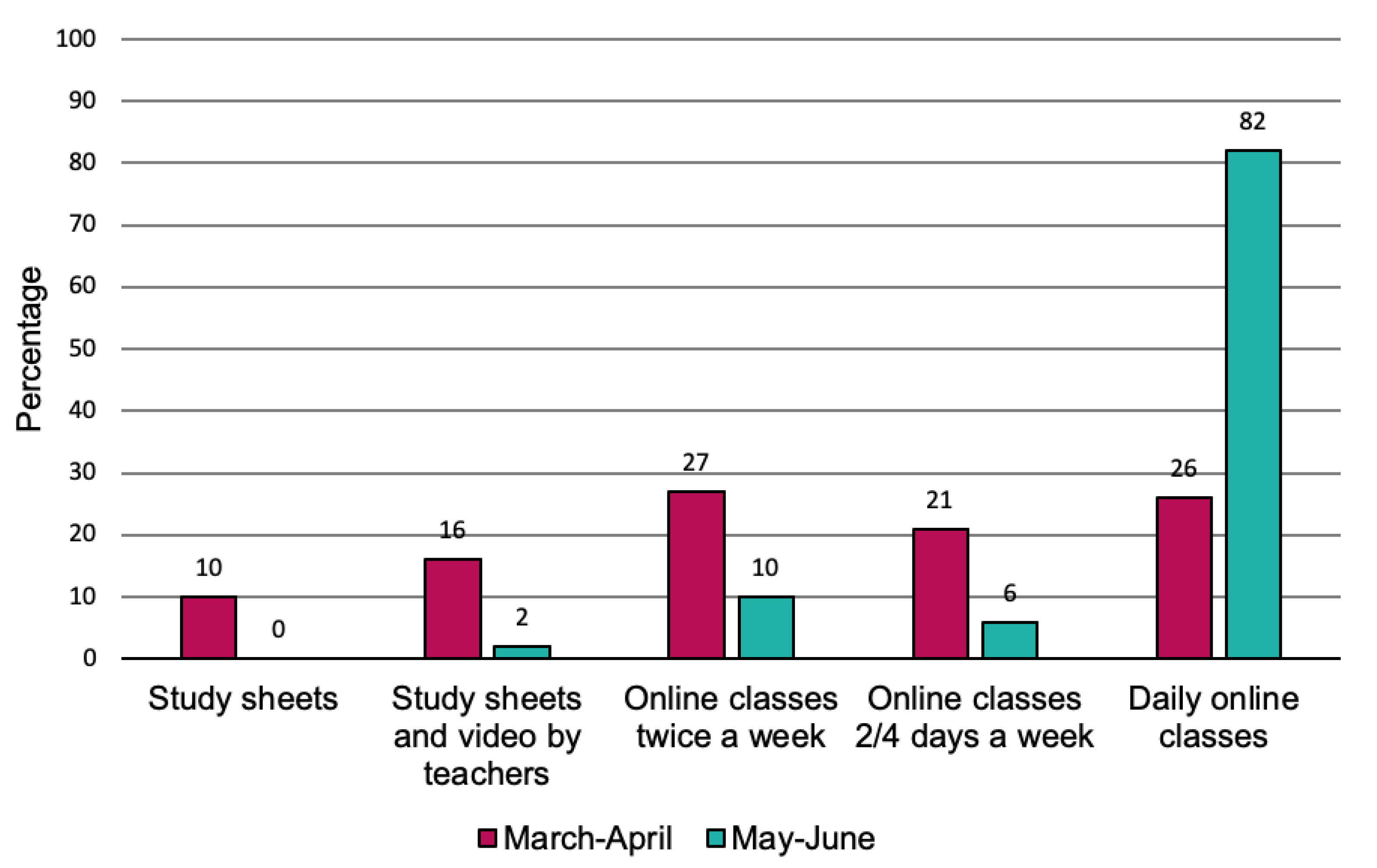
3.1. Survey
3.2. Reading Skills Group Analysis
3.3. Expected Improvement in Reading Speed
4. Discussion
5. Practical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Remuzzi, A.; Remuzzi, G. COVID-19 and Italy: What next? Lancet 2020, 395, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, S.M.; Liu, V.X. From Containment to Mitigation of COVID-19 in the US. JAMA 2020, 323, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petretto, D.R.; Masala, I.; Masala, C. School Closure and Children in the Outbreak of COVID-19. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2020, 16, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonal, X.; González, S. The impact of lockdown on the learning gap: Family and school divisions in times of crisis. Int. Rev. Educ. 2020. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; APA Publisher: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Smirni, P.; Vetri, L.; Misuraca, E.; Cappadonna, M.; Operto, F.F.; Pastorino, G.M.G.; Marotta, R. Misunderstandings about developmental dyslexia: A historical overview. Pediatr. Rep. 2020, 12, 8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeau, M.F.; Massé, L.; Argumedes, M.; Verret, C. Education for students with neurodevelopmental disabilities-Resources and educational adjustments. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 174, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Provenzi, L.; Grumi, S.; Borgatti, R. Alone with the Kids: Tele-Medicine for Children with Special Healthcare Needs during COVID-19 Emergency. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbury, K.; Fox, L.; Deniz, E.; Code, A.; Toseeb, U. How is COVID-19 Affecting the Mental Health of Children with Special Educational Needs and Disabilities and Their Families? J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumi, S.; Provenzi, L.; Gardani, A.; Aramini, V.; Dargenio, E.; Naboni, C.; Vacchini, V.; Borgatti, R. Engaging with Families through On-line Rehabilitation for Children during the Emergency (EnFORCE) Group. Rehabilitation services lockdown during the COVID-19 emergency: The mental health response of caregivers of children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sartori, G.; Job, R.; Tressoldi, P.E. DDE-2. Batteria per la Valutazione della Dislessia e della Disortografia Evolutiva (Battery for the Assessment of Developmental Dyslexia and Dysorthographia); Giunti OS: Firenze, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cornoldi, C.; Carretti, B. Prove MT-3-Clinica—La Valutazione delle Abilità di Lettura e Comprensione per la Scuola Primaria e Secondaria di I Grado (MT-3—Clinic Tasks. The Assessment of Reading and Comprehension Skills for Elementary and Middle School); Giunti EDU: Firenze, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tressoldi, P.E.; Stella, G.; Faggella, M. The development of reading speed in Italians with dyslexia: A longitudinal study. J. Learn. Disabil. 2001, 34, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappedi, M.; Baschenis, I.M. Specific learning disorders and anxiety: A matter of school experience? Min. Pediatr. 2016, 68, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Shinwell, J.; Defeyter, M.A. Investigation of Summer Learning Loss in the UK-Implications for Holiday Club Provision. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, K.L.; Entwisle, D.R.; Olson, L.S. Summer learning and its implications: Insights from the Beginning School Study. New Dir. Youth Dev. 2007, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, H.; Nye, B.; Charlton, K.; Lindsay, J.; Greathouse, S. The effects of summer vacation on achievement test scores: A narrative and meta-analytic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 1996, 66, 227–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Development of Dyslexia: The Delayed Neural Commitment Framework. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaabane, S.; Doraiswamy, S.; Chaabna, K.; Mamtani, R.; Cheema, S. The Impact of COVID-19 School Closure on Child and Adolescent Health: A Rapid Systematic Review. Children 2021, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, F.; Segre, G.; Cartabia, M.; Zanetti, M.; Campi, R.; Clavenna, A.; Bonati, M. Distance learning in Italian primary and middle school children during the COVID-19 pandemic: A national survey. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovagnoli, S.; Mandolesi, L.; Magri, S.; Gualtieri, L.; Fabbri, D.; Tossani, E.; Benassi, M. Internalizing Symptoms in Developmental Dyslexia: A Comparison Between Primary and Secondary School. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappedi, M.; Baschenis, I.M.; Dolci, R.; Bejor, M. Importance of a critical reading of neuropsychological testing. Min. Pediatr. 2011, 63, 239–245. [Google Scholar]


| Survey Items (Children) | DG, n = 65 | CG, n = 52 | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difficulties following online classes | 48% | 23% | 6.56 | <0.05 |
| Difficulties in doing homework | 62% | 13% | 24.4 | <0.001 |
| Perceiving that learning abilities worsened during quarantine | 19% | 3% | 14.86 | <0.01 |
| Perceiving that reading abilities remained the same during quarantine | 64% | 93% | 11.35 | <0.05 |
| More difficulties in text comprehension without teacher’s oral explanation | 60% | 33% | 8.77 | <0.05 |
| Difficulties in mathematics | 35% | 10% | 8.05 | <0.01 |
| More errors in mathematics | 49% | 18% | 10.62 | <0.01 |
| Worsening in text comprehension | 49% | 18% | 10.62 | <0.01 |
| More difficulties in studying | 51% | 13% | 15.68 | <0.01 |
| Worsening in vocabulary | 38% | 8% | 12.43 | <0.01 |
| More family conflicts | 46% | 20% | 7.30 | <0.05 |
| Asking often when the school will reopen | 19% | 65% | 22.36 | <0.001 |
| Missing friends | 67% | 93% | 9.92 | <0.01 |
| Concerns about COVID-19 | 3% | 25% | 11.54 | <0.01 |
| Asking for information about COVID-19 | 30% | 73% | 32.66 | <0.001 |
| Survey Items (Parents) | DG, n = 63 | CG, n = 38 | χ2 | p |
| Difficulties following online classes | 52% | 0% | 30.91 | <0.001 |
| Difficulties in doing homework | 67% | 11% | 33.50 | <0.001 |
| Perceiving that reading worsened during quarantine | 41% | 16% | 12.33 | <0.05 |
| Using more the keyboard | 46% | 76% | 8.89 | <0.01 |
| More errors in mathematics | 46% | 13% | 13.12 | <0.05 |
| Worsening in text comprehension | 38% | 5% | 18.71 | <0.001 |
| Worsening in oral presentation | 35% | 3% | 18.71 | <0.001 |
| Contac classmates for homework | 11% | 40% | 14.81 | <0.01 |
| Teachers as emotional support | 44% | 82% | 14.47 | <0.01 |
| Less contacts with friends | 32% | 11% | 9.45 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baschenis, I.M.C.; Farinotti, L.; Zavani, E.; Grumi, S.; Bernasconi, P.; Rosso, E.; Provenzi, L.; Borgatti, R.; Termine, C.; Chiappedi, M. Reading Skills of Children with Dyslexia Improved Less Than Expected during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy. Children 2021, 8, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070560
Baschenis IMC, Farinotti L, Zavani E, Grumi S, Bernasconi P, Rosso E, Provenzi L, Borgatti R, Termine C, Chiappedi M. Reading Skills of Children with Dyslexia Improved Less Than Expected during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy. Children. 2021; 8(7):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070560
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaschenis, Ilaria Maria Carlotta, Laura Farinotti, Elena Zavani, Serena Grumi, Patrizia Bernasconi, Enrica Rosso, Livio Provenzi, Renato Borgatti, Cristiano Termine, and Matteo Chiappedi. 2021. "Reading Skills of Children with Dyslexia Improved Less Than Expected during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy" Children 8, no. 7: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070560
APA StyleBaschenis, I. M. C., Farinotti, L., Zavani, E., Grumi, S., Bernasconi, P., Rosso, E., Provenzi, L., Borgatti, R., Termine, C., & Chiappedi, M. (2021). Reading Skills of Children with Dyslexia Improved Less Than Expected during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy. Children, 8(7), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070560









