Implementation of a Hybrid Educational Program between the Model of Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR) and the Teaching Games for Understanding (TGfU) in Physical Education and Its Effects on Health: An Approach Based on Mixed Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
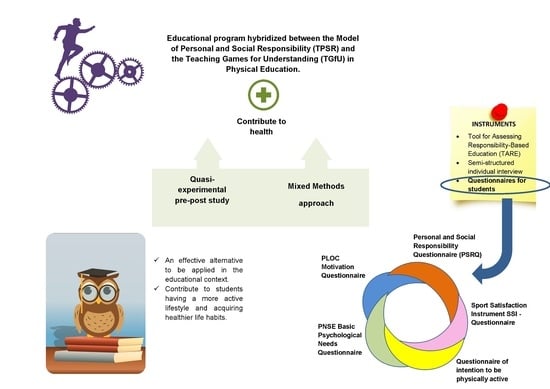
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Mesures and Instruments
2.3.1. Questionnaires for Students
2.3.2. Instruments for Teachers
2.4. Procedure
2.4.1. Hybrid Intervention Program TPSR + TGfU
2.4.2. Continuous Training of EG Teachers
2.4.3. Loyalty of the Hybrid Program Registry
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Strategies Used
3.2. Results of the Interviews
3.3. Results of the Inferential Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Constitution. 1946. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/about/who-we-are/constitution (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Gómez, S.F.; Homs, C.; Wärnberg, J.; Medrano, M.; González-Gross, M.; Gusi, N. Study protocol of a population-based cohort investigating physical activity, sedentarism, lifestyles and obesity in Spanish youth: The PASOS study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Physical Activity. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Celdrán-Rodríguez, A.; Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Sánchez-Alcaraz, B.J. The importance of physical education in the educational system. EmásF 2016, 43, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Río, J.; Calderón, A.; Hortigüela-Alcalá, D.H.; Pérez-Pueyo, Á.; Cebamanos, M.A. Pedagogical models in physical education: Theoretical-practical considerations for teachers. REEFD 2016, 413, 55–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mosston, M. Teaching Physical Education: From Command to Discovery; Charles, E., Ed.; Merrill Publishing Co: Columbus, OH, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, M.W. Instructional Models for Physical Education; Allyn & Bacon: Needham Heights, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, D. Physical Education Futures; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haerens, L.; Kirk, D.; Cardon, G.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I. Toward the development of a pedagogical model for health-based physical education. Quest 2011, 63, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Río, J.; Alcalá, D.H.; Pérez-Pueyo, A. Reviewing pedagogical models in physical education. Key ideas to incorporate into the classroom. REEFD 2018, 423, 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, A. Models-Based Practice. In Handbook of Physical Education Pedagogy; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cocca, A.; Carbajal Baca, J.E.; Hernández Cruz, G.; Cocca, M. Does A Multiple-Sport Intervention Based on the TGfU Pedagogical Model for Physical Education Increase Physical Fitness in Primary School Children? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 2020 17, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, R.; Bunker, D.; Almond, L. Rethinking Games Teaching; Department of Physical Education and Sports Science, Loughborough University of Technology: Loughborough, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- García-López, L.M.; Gutiérrez, D. Learning to Teach Sport: Comprehensive Teaching and Sports Education Models; Inde: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, O.R.; García, L.M.; Cervelló, E. Transfer of tactical knowledge from invasion games to floorball. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 2005, 49, 193–213. [Google Scholar]
- Hortigüela-Alcalá, D.H.; Hernando-Garijo, A. Teaching games for understanding: A comprehensive approach to promote student’s motivation in physical education. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 59, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L. Teaching games for understanding intervention to promote physical activity among secondary school students. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3737595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellison, D. Teaching Responsibility through Physical Activity, 3rd ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Conte-Marín, L.; Gómez-López, M.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Applying the Personal and Social Responsibility Model as a School-Wide Project in All Participants: Teachers’ Views. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alcaraz Martínez, B.J.; Courel Ibáñez, J.; Sánchez Ramírez, C.; Valero Valenzuela, A.; Gómez Mármol, A. Personal and social responsibility model through sports: A bibliographic review. Retos 2019, 37, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Implementation of a model-based programme to promote personal and social responsibility and its effects on motivation, prosocial behaviours, violence and classroom climate in primary and secondary education. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madrid, P.M.; Prieto-Ayuso, A.; Samalot-Riviera, A.; Gil, P. Evaluation of an extracurricular proposal of appropriate behaviors in physical and sports education. Retos 2016, 30, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mármol, A.; Sánchez-Alcaraz, B.J.; Valero, A.; González-Víllora, S. Personal and social responsibility development through sport participation in youth scholars. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Barrero, J.A.; Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Belando, N.; Fernández-Río, J. Impact of a sustained TPSR program on students’ responsibility, motivation, sportsmanship, and intention to be physically active. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2019, 39, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Martín, R.A.; Bores-García, D.; Hortigüela-Alcalá, D.; González-Calvo, G. The application of the teaching games for understanding in physical education. Systematic review of the last six years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, C.; Hastie, P.; Araújo, R.; Mesquita, I. What do we know about the development of personal and social skills within the sport education model: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 18, 812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bores-García, D.; Hortigüela-Alcalá, D.; Fernandez-Rio, F.J.; González-Calvo, G.; Barba-Martín, R. Research on cooperative learning in physical education: Systematic review of the last five years. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2021, 92, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Víllora, S.; Evangelio, C.; Sierra-Díaz, J.; Fernández-Río, J. Hybridizing pedagogical models: A systematic review. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2018, 25, 1056–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lave, J.; Wenger, E. Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, B.; Griffin, L.L.; Hastie, P. Sport education, tactical games, and cooperative learning: Theoretical and pedagogical considerations. Quest 2004, 56, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Arias, A.; Harvey, S.; Cárceles, A.; Práxedes, A.; Del Villar, F. Impact of a hybrid TGfU-Sport Education unit on student motivation in physical education. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubacs-Collins, K.; Olsen, E.B. Implementing a tactical games approach with sport education: A chronicle. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Dance 2010, 81, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.; MacPhail, A. Adopting a models-based approach to teaching physical education. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2018, 23, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirk, D. The normalization of innovation, models-based practice, and sustained curriculum renewal. In Proceedings of the Teaching Games for Understanding Symposium, AIESEP Conference, Limerick, Ireland, 22–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Río, J.; Menéndez-Santurio, J.I. Teachers and students’ perceptions of a hybrid sport education and teaching for personal and social responsibility learning unit. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2017, 36, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, P.A.; Buchanan, A.M. Teaching responsibility through sport education: Prospects of a coalition. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2000, 71, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez-Santurio, J.I.; Fernández-Río, J. Violence, responsibility, friendship and basic psychological needs: Effects of a Sports Education and Personal and Social Responsibility program. Rev. Psicodidáct. 2016, 21, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Río, J. Contributions of the model of personal and social responsibility to cooperative learning. In Proceedings of the IX Congreso Internacional de Actividades Físicas Cooperativas, Vélez-Málaga, Spain, 30 June–3 July 2014; pp. 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Gregorio García, D.; Camerino, O.; Manzano, D. Hybridisation of the Teaching Personal and Social Responsibility Model and Gamification in Physical Education. Apunt. Educ. Fis. Deportes 2020, 141, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Río, J.; de las Heras, E.; González, T.; Trillo, V.; Palomares, J. Gamification and physical education. Viability and preliminary views from students and teachers. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2020, 25, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, P.A.; O’Sullivan, M. Effective Professional Development—What We Now Know. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2006, 25, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodyear, V.A.; Casey, A. Innovation with change: Developing a community of practice to help teachers move beyond the ‘honeymoon’ of pedagogical renovation. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2015, 20, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stran, M.; Sinelnikov, O.; Woodruff, E. Pre-service teachers’ experiences implementing a hybrid curriculum: Sport education and teaching games for understanding. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2012, 18, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Hastie, P.A.; Pereira, C.H. The evolution of student-coach’s pedagogical content knowledge in a combined use of sport education and the step-game-approach model. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 22, 518–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. The ‘what’ and ‘why’ of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychol. Inq. 2000, 11, 227–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: Definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 61, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Overview of self-determination theory: An organismic dialectical perspective. In Handbook of Self-Determination Research, 2nd ed.; Deci, E.L., Ryan, R.M., Eds.; University of Rochester Press: Rochester, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Balaguer, I.; Castillo, I.; Duda, J.L. Autonomy support, needs satisfaction, motivation and well-being in competitive athletes: A test of the self-determination theory. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2008, 17, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez, J.L.; León, J. Autonomy support in the classroom: A review from self-determination theory. Eur. Psychol. 2015, 20, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Extremera, A.; Gómez-López, M.; Granero-Gallegos, A.; Martínez-Molina, M. Prediction model of satisfaction and fun in Physical Education based on autonomy and motivational climate. Univ. Psychol. 2016, 15, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Standage, M.; Duda, J.L.; Ntoumanis, N. A model of contextual motivation in physical education: Using constructs from selfdetermination and achievement goal theories to predict physical activity intentions. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 95, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, R.J. Toward a hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1997, 29, 271–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belando, N.; Férriz-Morel, R.; Rivas, S.; Almagro, B.; Sáenz-López, P.; Cervelló, E.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A. Sport commintment in adolescent soccer players. Motricidade 2015, 11, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Gómez-Mármol, A.; Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Jiménez-Parra, J.F. School Climate and Responsibility as Predictors of Antisocial and Prosocial Behaviors and Violence: A Study towards Self-Determination Theory. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Giménez, A.; Cecchini, J.A.; Fernández-Río, J.; González, C. Self-Determination and Social Goals: A Structural Model for Understanding Practice Intent, Effort, and Boredom in Physical Education. [Autodeterminación y metas sociales: Un modelo estructural para comprender la intención de práctica, el esfuerzo y el aburrimiento en educación física]. Aula Abierta 2012, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Garn, A.C.; Wallhead, T. Social goals and basic psychological needs in high school physical education. Sport Exerc. Perform. Psychol. 2014, 4, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, I.; León, O.G. Classification and description of research methodologies in Psychology. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2002, 2, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Anguera, M.T.; Camerino, O.; Castañer, M. Mixed methods research in sports and physical activity science. Apunt. Educ. Fis. Deportes 2013, 112, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuegbuzie, A.J.; Johnson, B. The Routledge Reviewer’s Guide to Mixed Methods Analysis, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tashakkori, A.; Teddlie, C. Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioural Research, 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escartí, A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Pascual, C. Psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Personal and Social Responsibility Questionnaire in physical education contexts. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2011, 20, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wright, P.M.; Rukavina, P.B.; Pickering, M. Measuring students’ perceptions of personal and social responsibility and the relationship to intrinsic motivation in urban physical education. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2008, 27, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Oliva, D.; Leo-Marcos, F.M.; Amado-Alonso, D.; Cuevas-Campos, R.; García-Calvo, T. Development and validation of the questionnaire to support basic psychological needs in physical education. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2013, 30, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand, R.J.; Rousseau, F.L. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in sport and exercise: A review using the hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. In Handbook of Sport Psychology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 389–416. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Murcia, J.A.; Gonzalez-Cutre Coll, D.; Chillon-Garzon, M.; Parra-Rojas, N. Adaptation of the basic psychological needs in exercise scale to physical education. Rev. Mex. Psicol. 2008, 25, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachopoulos, S.P.; Michailidou, S. Development and initial validation of a measure of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in exercise: The Basic Psychological Needs in Exercise Scale. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2006, 10, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Extremera, A.; Granero-Gallegos, A.; Bracho-Amador, C.; Pérez-Quero, F.J. Spanish version of the Sport Satisfaction Instrument (SSI) adapted to the learning of bilingual Physical Education in English. Porta Ling. 2015, 24, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, J.L.; Nicholls, J.G. Dimensions of achievement motivation in schoolwork and sport. J. Educ. Psychol. 1992, 84, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria 512 versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.H.; Charlotte, B.; Isabella, M.; Bob, C.S. SPSS Explained; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, J.A.; Moreno, R.; Cervelló, E. Physical self-concept as a predictor of the intention to be physically active. Psicol. Salud 2007, 17, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, V.; Müür, M.; Koka, A. Intention to be physically active after school graduation and its relationship to three types of intrinsic motivation. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2004, 10, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escartí, A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Pascual, C.; Wright, P. Observation of the strategies used by physical education teachers to teach personal and social responsibility. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2013, 22, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, P.M.; Craig, M.W. Tool for assessing responsibility-based education (TARE): Instrument development, content validity, and inter-rater reliability. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2011, 15, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.A.; Oslin, J.; Griffin, L.L. Teaching Sport Concepts and Skills: A Tactical Games Approach, 4th ed.; Human Kinetics Publishers: Windsor, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Arias, A.; Claver, F.; Práxedes, A.; Villar, F.D.; Harvey, S. Autonomy support, motivational climate, enjoyment and perceived competence in physical education: Impact of a hybrid teaching games for understanding/sport education unit. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2020, 26, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Allyn and Bacon: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Gómez-Mármol, A.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Student and teacher perceptions of teaching personal and social responsibility implementation, academic performance and gender differences in secondary education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organic Law 8/2013, of December 9, for the Improvement of Educational Quality; BOE Num 295, 10 of December; BOE: Madrid, Spain, 2013.
- Kirk, D.; MacPhail, A. Teaching games for understanding and situated learning: Rethinking the Bunker-Thorpe model. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2002, 21, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Choi, E. The influence of professional development on teachers’ implementation of the teaching personal and social responsibility model. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2015, 34, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerino, O.; Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Prat, Q.; Manzano Sánchez, D.; Castañer, M. Optimizing education: A mixed methods approach oriented to Teaching Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR). Front. Psychol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastie, P.A.; Casey, A. Fidelity in models-based practice research in sport pedagogy: A guide for future investigations. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2014, 33, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, M.A.; Templin, T.J.; Wright, P.M. Implementation and outcomes of a responsibility-based continuing professional development protocol in physical education. Sport Educ. Soc. 2015, 20, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sturmey, P.; Newton, J.T.; Cowley, A.; Bouras, N.; Holt, G. The PAS–ADD Checklist: Independent replication of its psychometric properties in a community sample. Br. J. Psychiatry 2005, 186, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melero-Cañas, D.; Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Navarro-Ardoy, D.; Morales-Baños, V.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. The Seneb’s Enigma: Impact of a Hybrid Personal and Social Responsibility and Gamification Model-Based Practice on Motivation and Healthy Habits in Physical Education. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Valero-Valenzuela, A.; Conde-Sánchez, A.; Chen, M.Y. Applying the personal and social responsibility model-based program: Differences according to gender between basic psychological needs, motivation, life satisfaction and intention to be physically active. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-García, J.; Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Belando-Pedreño, N.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Personal and Social Responsibility Programme Effects, Prosocial Behaviours, and Physical Activity Levels in Adolescents and Their Families. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez Santurio, J.; Fernández-Río, J. Social responsibility, basic psychological needs, intrinsic motivation, and friendship goals in physical education. Retos 2017, 32, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; García-López, L.M.; Chaparro-Jilete, R.; Fernández-Sánchez, A.J. Sport education model in second grade. Teachers and students’ perceptions. Cuad. Psicol. Deporte 2014, 14, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casey, A.; Dyson, B. The implementation of models-based practice in physical education through action research. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2009, 15, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracco, E.; Lodewyk, K.; Morrison, H. A case study of disengaged adolescent girls’ experiences with teaching games for understanding in physical education. Curric. Stud. Health Phys. Educ. 2019, 10, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Belando, M.T.; Calderón, A.; Arias-Estero, J.L. Improvement in game performance and adherence after an aligned TGfU floorball unit in physical education. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2018, 23, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, E.; Evangelio, C.; González Víllora, S.; Arias-Palencia, N.M. Hybridizing Teaching Games for Understanding and Cooperative Learning: An educational innovation. ESHPA 2020, 4, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Menéndez-Santurio, J.I.; Fernández-Río, J. Hybridization of Sports Education and Personal and Social Responsibility models: An experience through an educational kickboxing program. Retos 2016, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, P.; Grao-Cruces, A.; Pérez-Ordás, R. Teaching personal and social responsibility model-based programmes in physical education: A systematic review. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2018, 24, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero-Cañas, D.; Morales-Baños, V.; Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Navarro-Ardoy, D.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Effects of an Educational Hybrid Physical Education Program on Physical Fitness, Body Composition and Sedentary and Physical Activity Times in Adolescents: The Seneb’s Enigma. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 629335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Intervention Week | Objective | Content (CG) | Content (EG) | TGfU (Principle and Tactical Problem) | TGfU. Skill-Execution Task Example | TPSR (Level of Responsibility: Strategies) | TPSR. Example of Responsibility Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Initiate students in futsal. | Futsal: Ball control, passes, and shots. | Futsal: Decision making with the possession of the ball. | Keep possession of the ball Who to pass? | In groups of six students, they form a circle (rondo), and one student stands in the middle trying to take the ball while making passes. | Level 1: Class norms were established in consensus with the students. | The students made a mural showing the rules of class behavior that they made themselves place on the wall of the pavilion. |
| Week 2 | Understand the technical and tactical aspects of futsal. | Futsal: Shots on goal and opposition situations 1vs1. | Futsal: Decision making with the possession of the ball. | Advance with the mobile and invade the opponent’s field. Pass or advance? | Three students attack and two defend; the objective of the activity is to reach a goal line by passing the ball to the player who is free without resorting to dribbling. | Level 1: Teams were randomly configured to work on respect among students. | A discussion circle was held in the final part of the session where students had to adopt respectful attitudes, such as: Raising their hands before speaking or respecting their turn to speak. |
| Week 3 | Know aspects of futsal defensive and offensive tactics. | Futsal: Defensive and offensive situations with numerical superiority and inferiority. | Futsal: Defensive tactical situations | Avoid marking. Where should I stand? | Two students defend and two attack; the students who defend the goal, must prevent the attackers from having a shot because there is no goalkeeper. | Level 2: Success was redefined in the different activities to encourage participation and effort | Activities were proposed where the result of the competition was not taken into account, but also the effort made by the group or the student, valued by the teacher and the rest of the classmates. |
| Week 4 | Learn complex tactical aspects. | Futsal: Real game situations. | Futsal: Movements without the ball: lose the marks. | Attacking without the ball What is the best space to move to? | In groups of three, the students had to pass the ball to their teammates who came running to an area delimited with cones near the goal to get the point. | Level 2: We worked with an intensity scale, so that the students could measure their degree of effort from 0 to 10. | The students had a card during the activities they carried out this week to mark the perceived effort at the end of the activity from 1 to 10. |
| Week 5 | Start the students in volleyball. | Volleyball: Serve, forearm pass, and setting. | Volleyball: Making a decision between the different types of hitting | Control the ball What attack helps us the most to place the ball on a partner? | In pairs, the students decide what type of attack to use to achieve the greatest number of hits without the ball falling to the ground. | Level 2: A modification of the tasks was carried out depending on the group that was working on them to promote participation. | The students with greater motor competence had to achieve a greater number of attacks at a greater distance, while for the rest of the groups, the objective was to overcome themselves during the activity. |
| Week 6 | Know regulatory aspects of volleyball. | Volleyball: Collective games to develop technical-tactical aspects. | Volleyball: Regulation, rotations, and scoring. | Know the rules of the game What are the different field areas? | A reduced game situation was carried out (3 vs. 3) where a student assumed the role of referee to be able to explain the regulatory aspects of the game to his teammates. | Level 3: A distribution of tasks was carried out, the teacher explains the activity, but it must be the students who organize themselves independently to carry out the different roles and rotate. (coach, referee, player). | A game simulation was carried out, and the students themselves had to assume the roles of referee, player, coach, physical trainer, and scorer. |
| Week 7 | Learn to work as a team in volleyball. | Volleyball: Reduced game situations and team competition. | Volleyball: Team communication, modified game situations. | Communicate action How should we communicate during the play? | Groups of four. One player serves from the other side, the receiving player shouts “mine”, and the placing player says the name of the player to whom the ball is going so that he is ready and passes it to the opposite field. | Level 3: Independent work of the students was promoted, establishing a series of game problems to which they had to solve and offer activities to be able to develop them. | The teacher played a game where the students who had brilliant ideas to provide solutions to the problem raised had a reward. |
| Week 8 | Initiate students in basketball. | Basketball: Passes and shots. | Basketball: Decision-making between the different types of passes. | Keep possession of the ball. What type of pass to make? | In pairs, the students made passes between them, while moving laterally, choosing the type of pass depending on the distance that separates them. | Level 3: A personal work plan was provided, the students had a card that indicated the instructions for the task. | One student was in charge of reading the task to their group, and the rest were in charge of organizing the task independently, without resorting to the help of the teacher. |
| Week 9 | Know defensive tactical aspects of basketball. | Basketball: Layup, three point shots, and blocks. | Basketball: Defensive tactics and markings. | Regain possession of the ball. How should I defend? | 2 vs. 1, the objective of the activity is for the defending student to prevent the pass to the teammate who does not have the ball. | Level 3: During this week, the students continued to use the personal work plan strategy. | A student-teacher was chosen, who followed the instructions of the work plan, he was in charge of explaining the activities to the rest of the class. |
| Week 10 | Selecting the shots to the basket. | Basketball: Specific roles, functions, and movements. | Basketball: Cooperation-opposition played situations | Achieve to shoot and score. From where can I be more effective? | A game is played to a 3 vs. 3 basket, the attacking team must shoot from defined areas so that the basket scores double. | Level 4: Students set some group goals and helped each other to achieve them | The students proposed additional objectives to each activity, such as: Pass the ball to all the classmates. In addition to the objective of the activity, the students helped each other to achieve this group objective. |
| Week 11 | Solve situations of cooperation-opposition in basketball. | Basketball: Cooperation-opposition games and matches. | Basketball: Strategic principles of attack and defense, blockades. | Avoid marking. Where should I stand? | Basketball game 5 vs. 5 to a single basket, students who block an opponent’s shot achieve the same score as a basket. | Level 4: Reciprocal teaching was carried out, the students with the greatest experience in sport helped their classmates to improve in certain aspects. | Group captains were chosen to teach their teammates technical and tactical aspects of basketball during the activities, leaving a “time out”. |
| Teachers (EG) (N = 2) | Teachers (CG) (N = 2) | U of Mann Whitney | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | p-Value | |
| Example of respect | 98.33 | 4.08 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.280 |
| Sets expectations | 94.40 | 6.19 | 87.23 | 9.63 | 0.103 |
| Gives opportunities for success | 73.07 | 9.98 | 44.19 | 14.82 | 0.008 ** |
| Encourages social interaction | 76.63 | 7.41 | 50.43 | 16.44 | 0.006 * |
| Assigns tasks | 21.52 | 5.60 | 30.61 | 17.73 | 0.517 |
| Leadership | 16.75 | 11.81 | 17.06 | 10.23 | 0.942 |
| Granting of choice and voice | 62.32 | 8.98 | 15.39 | 8.17 | 0.003 ** |
| Role in Evaluation | 12.82 | 4.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.001 ** |
| Transfer | 11.15 | 7.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.004 ** |
| Modified sports game | 39.93 | 4.24 | 41.53 | 6.43 | 0.505 |
| Tactical awareness | 26.88 | 10.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.001 ** |
| Skill execution | 23.42 | 6.98 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.001 ** |
| Pretest | Posttest | Difference between Pre and Post | Intergroups Difference of Means | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p-Value | p-Value | |
| AutonomousM | Control | 5.636 | 0.762 | 5.711 | 0.804 | 0.504 | 0.001 ** |
| Experimental | 5.824 | 0.919 | 6.304 | 0.575 | 0.000 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.270 | 0.013 | 0.000 ** | 0.149 | |||
| ControlledM | Control | 3.991 | 1.297 | 4.064 | 1.335 | 0.672 | 0.211 |
| Experimental | 3.980 | 1.300 | 4.230 | 1.429 | 0.194 | ||
| p-valor + η2 | 0.967 | 0.000 | 0.551 | 0.004 | |||
| Demotivation | Control | 1.796 | 0.968 | 1.623 | 0.774 | 0.293 | 0.011 * |
| Experimental | 1.994 | 1.452 | 1.534 | 0.852 | 0.013 * | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.417 | 0.007 | 0.589 | 0.003 | |||
| SDI | Control | 9.350 | 3.545 | 9.709 | 3.526 | 0.535 | 0.012 * |
| Experimental | 9.639 | 4.945 | 11.486 | 3.179 | 0.005 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.736 | 0.001 | 0.011 * | 0.065 | |||
| Competences | Control | 4.532 | 1.079 | 4.323 | 1.271 | 0.210 | 0.887 |
| Experimental | 4.579 | 1.186 | 4.824 | 1.272 | 0.190 | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.835 | 0.000 | 0.054 | 0.038 | |||
| Relationship | Control | 5.296 | 1.055 | 5.646 | 1.028 | 0.035 * | 0.001 ** |
| Experimental | 5.159 | 0.937 | 5.693 | 1.226 | 0.004 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.504 | 0.005 | 0.834 | 0.000 | |||
| Autonomy | Control | 5.030 | 1.234 | 5.151 | 1.024 | 0.430 | 0.021* |
| Experimental | 5.144 | 1.058 | 5.561 | 1.068 | 0.017 * | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.629 | 0.002 | 0.056 | 0.037 | |||
| PMI | Control | 4.952 | 0.842 | 5.040 | 0.859 | 0.476 | 0.009** |
| Experimental | 4.961 | 0.792 | 5.359 | 0.921 | 0.004 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.980 | 0.000 | 0.078 | 0.032 | |||
| Enjoyment | Control | 4.367 | 0.578 | 4.494 | 0.506 | 0.162 | 0.001 ** |
| Experimental | 4.300 | 0.692 | 4.659 | 0.435 | 0.001 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.600 | 0.003 | 0.090 | 0.029 | |||
| Boredom | Control | 1.609 | 0.820 | 1.481 | 0.666 | 0.244 | 0.082 |
| Experimental | 1.420 | 0.828 | 1.261 | 0.523 | 0.193 | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.260 | 0.013 | 0.076 | 0.032 | |||
| Personal responsibility | Control | 5.161 | 0.741 | 5.200 | 0.786 | 0.724 | 0.040* |
| Experimental | 5.120 | 0.816 | 5.425 | 0.566 | 0.015 * | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.795 | 0.001 | 0.113 | 0.026 | |||
| Social responsibility | Control | 5.218 | 0.667 | 5.262 | 0.600 | 0.610 | 0.006** |
| Experimental | 5.081 | 0.569 | 5.403 | 0.598 | 0.001 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.273 | 0.012 | 0.249 | 0.014 | |||
| IPA | Control | 4.029 | 0.706 | 4.036 | 0.826 | 0.961 | 0.003 ** |
| Experimental | 4.000 | 0.646 | 4.341 | 0.506 | 0.000 ** | ||
| p-value + η2 | 0.833 | 0.000 | 0.029 * | 0.048 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Castejón, G.; Camerino, O.; Castañer, M.; Manzano-Sánchez, D.; Jiménez-Parra, J.F.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Implementation of a Hybrid Educational Program between the Model of Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR) and the Teaching Games for Understanding (TGfU) in Physical Education and Its Effects on Health: An Approach Based on Mixed Methods. Children 2021, 8, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070573
García-Castejón G, Camerino O, Castañer M, Manzano-Sánchez D, Jiménez-Parra JF, Valero-Valenzuela A. Implementation of a Hybrid Educational Program between the Model of Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR) and the Teaching Games for Understanding (TGfU) in Physical Education and Its Effects on Health: An Approach Based on Mixed Methods. Children. 2021; 8(7):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070573
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Castejón, Gregorio, Oleguer Camerino, Marta Castañer, David Manzano-Sánchez, José Francisco Jiménez-Parra, and Alfonso Valero-Valenzuela. 2021. "Implementation of a Hybrid Educational Program between the Model of Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR) and the Teaching Games for Understanding (TGfU) in Physical Education and Its Effects on Health: An Approach Based on Mixed Methods" Children 8, no. 7: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070573
APA StyleGarcía-Castejón, G., Camerino, O., Castañer, M., Manzano-Sánchez, D., Jiménez-Parra, J. F., & Valero-Valenzuela, A. (2021). Implementation of a Hybrid Educational Program between the Model of Personal and Social Responsibility (TPSR) and the Teaching Games for Understanding (TGfU) in Physical Education and Its Effects on Health: An Approach Based on Mixed Methods. Children, 8(7), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070573