Adipokines Profile and Inflammation Biomarkers in Prepubertal Population with Obesity and Healthy Metabolic State
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
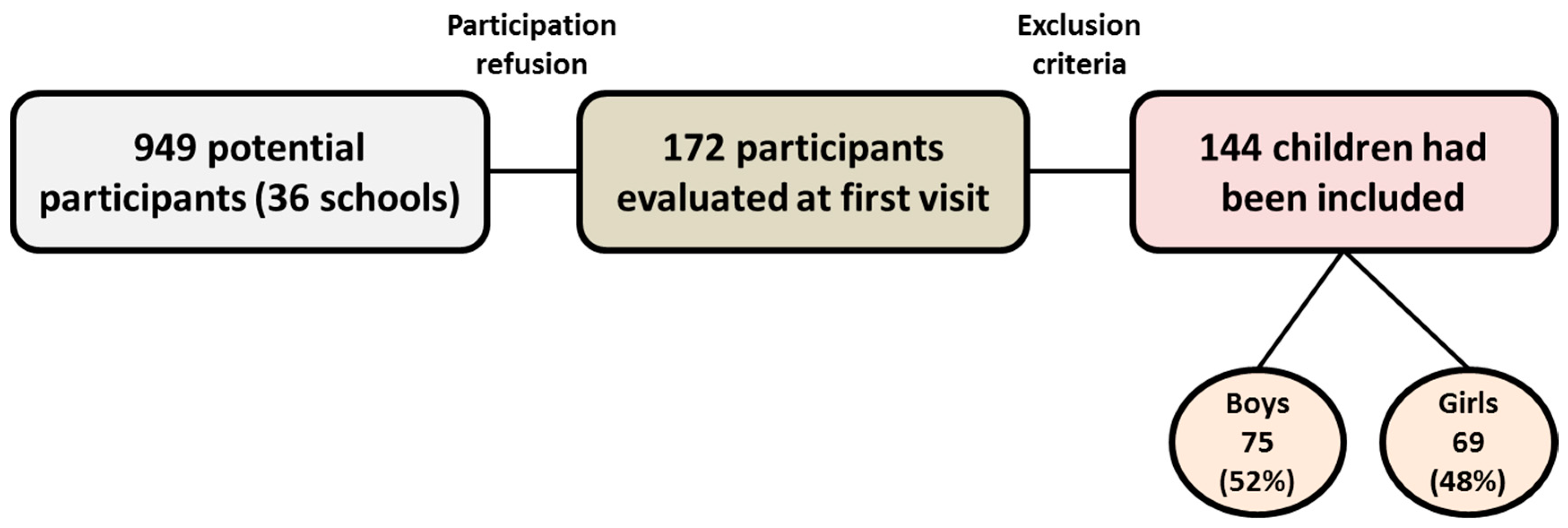
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Visits
2.4. Assays
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| hsCRP | high-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| TNF-alpha | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| MedDiet | Mediterranean Diet |
| PA | physical activity |
| MHOPp | metabolically healthy prepubertal population with obesity |
| MetS | metabolic syndrome |
| SD | standard deviation |
| NV | normal values |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| SDS | standard deviation score |
| IR | insulin resistance |
| HDL-col | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-c | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | homeostatic model assessment |
| JNK | c-Jun-NH(2)-terminal kinase |
References
- Organización Mundial de la Salud (Sede Web). Centro de Prensa. Obesidad y Sobrepeso. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Marrodán, M.D.; Martínez-Álvarez, J.R.; González-Montero De Espinosa, M.; López-Ejeda, N.; Cabañas, M.D.; Prado, C. Diagnostic accuracy of waist to height ratio in screening of overweight and infant obesity. Med. Clin. 2013, 140, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Konstabel, K.; Bergman, P.; Ahrens, W.; Pohlabeln, H.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; Siani, A.; Iacoviello, L.; Molnár, D.; De Henauw, S.; et al. Physical activity and clustered cardiovascular disease risk factors in young children: A cross-sectional study (the IDEFICS study). BMC Med. 2013, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, K.; Sahoo, B.; Choudhury, A.K.; Sofi, N.Y.; Kumar, R.; Bhadoria, A.S. Childhood obesity: Causes and consequences. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B. Global pandemics interconnected—Obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira-De-Almeida, C.A.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, I.R.L.; Contini, A.A.; Ued, F.D.V. COVID-19 and obesity in childhood and adolescence: A clinical review. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehus, E.; Mitsnefes, M. Childhood obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-López, L.; Santiago-Díaz, G.; Nava-Hernández, J.; Muñoz-Torres, A.V.; Medina-Bravo, P.; Torres-Tamayo, M. Mediterranean-style diet reduces metabolic syndrome components in obese children and adolescents with obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegiopoulos, A.; Rohm, M.; Herzig, S. Adipose tissue: Between the extremes. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, B.K.; Flatt, S.W.; Health, D.D.; Pakiz, B.; Quintana, E.L.; Natarajan, L.; Rock, C.L.; Dennis, D. Health the IL6 gene promoter SNP and plasma IL-6 in response to diet intervention. Nutrients 2017, 9, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, A.-L.; Nazare, J.-A.; Baillot, A.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Poirier, P.; Després, J.-P. Cardiometabolic risk improvement in response to a 3-yr lifestyle modification program in men: Contribution of improved cardiorespiratory fitness vs. weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2017, 312, E273–E281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.V.; Du, M.; Wang, S.; Bergen, W.G.; Fernyhough-Culver, M.; Basu, U.; Poulos, S.; Hausman, G.J. Adipose depots differ in cellularity, adipokines produced, gene expression, and cell systems. Adipocyte 2014, 3, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Yin, X.; Larson, M.; Yamamoto, J.F.; Fontes, J.D.; Kathiresan, S.; Rong, J.; Levy, D.; Keaney, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Multiple inflammatory biomarkers in relation to cardiovascular events and mortality in the community. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Pennells, L.; Wood, A.M.; White, I.R.; Gao, P.; Walker, M.; Thompson, A.; Sarwar, N.; et al. C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, and cardiovascular disease prediction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spranger, J.; Kroke, A.; Möhlig, M.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.M.; Ristow, M.; Boeing, H.; Pfeiffer, A.F. Inflammatory cytokines and the risk to develop type 2 diabetes: Results of the prospective population-based european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC)-potsdam study. Diabetes 2003, 52, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, A.G.; Burke, G.L.; Owusu, J.A.; Carnethon, M.R.; Vaidya, D.; Barr, R.G.; Jenny, N.S.; Ouyang, P.; Rotter, J.I. Inflammation and the incidence of type 2 diabetes: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Lee, D.-C.; Katzmarzyk, P.; Ruiz, J.; Sui, X.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N. The intriguing metabolically healthy but obese phenotype: Cardiovascular prognosis and role of fitness. Eur. Hear. J. 2013, 34, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InterAct Consortium; Romaguera, D.; Guevara, M.; Norat, T.; Langenberg, C.; Forouhi, N.G.; Sharp, S.; Slimani, N.; Schulze, M.B.; Buijsse, B.; et al. Mediterranean diet and type 2 diabetes risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study: The InterAct project. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. Chapter 3. Available online: https://health.gov/our-work/physical-activity/current-guidelines (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Kavey, R.E.W. Dyslipidemia and Pediatric Obesity. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 58, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, A.; Johnson, L.; Toumpakari, Z.; England, C.; Rai, M.; Toms, S.; Penfold, C.; Zazpe, I.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Feder, G. Validation of the English version of the 14-item mediterranean diet adherence screener of the PREDIMED study, in people at high cardiovascular risk in the UK. Nutrients 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.T.; Ballart, J.F.; Pastor, G.C.; Jordà, E.B.; Val, V.A. Validation of a short questionnaire on frequency of dietary intake: Reproducibility and validity. Nutr. Hosp. 2008, 23, 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Calorie (Energy) Intake: Recommended Amounts of Food and Drink for Children. Available online: https://www.healthychildren.org/Spanish/healthy-living/nutrition/Paginas/Energy-In-Recommended-Food-Drink-Amounts-for-children.aspx (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Martín-Moreno, J.M.; Gorgojo, L. Assessment of dietary intake at the population level through individual questionnaires: Methodological shadows and lights. Rev. Esp. Salud. Publica. 2007, 81, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T.; Elfers, C.; Lass, N.; Roth, C.L. Irisin and its relation to insulin resistance and pube rty in obese children: A longitudinal analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.webpediatrica.com/endocrinoped/antropometria.php (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Lycett, K.; Juonala, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Norrish, D.; Mensah, F.K.; Liu, R.; Clifford, S.A.; Carlin, J.B.; Olds, T.; Saffery, R.; et al. Body mass index from early to late childhood and cardiometabolic measurements at 11 to 12 years. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20193666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Fytanidis, G.; Papadimitriou, D.T.; Priftis, K.N.; Nicolaidou, P.; Fretzayas, A. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in young Greek men. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleanthous, K.; Dermitzaki, E.; Papadimitriou, D.T.; Papaevangelou, V.; Papadimitriou, A. Overweight and obesity decreased in Greek schoolchildren from 2009 to 2012 during the early phase of the economic crisis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 105, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Gil-Campos, M.; Bueno, G.; Bahillo, P.; Bernal, S.; Feliu, A.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M.; Palomo, E.; Ruiz, R.; Grupo de Trabajo de Obesidad de la Sociedad Española de Endocrinología Pediátrica (SEEP); et al. Obesity associated metabolic impairment is evident at early ages: Spanish collaborative study. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 787–793. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussler, S.; Penke, M.; Flemming, G.; Elhassan, Y.; Kratzsch, J.; Sergeyev, E.; Lipek, T.; Vogel, M.; Spielau, U.; Körner, A.; et al. Novel insights in the metabolic syndrome in childhood and adolescence. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D. Assessing and managing the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gepstein, V.; Weiss, R. Obesity as the main risk factor for metabolic syndrome in children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihe, P.; Weihrauch-Blüher, S. Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: Diagnostic criteria, therapeutic options and perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, A.; Visiedo-García, F.M.; Domínguez-Riscart, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Mateos, R.M.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M. Iron metabolism in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.; Dziura, J.; Burgert, T.S.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Taksali, S.E.; Yeckel, C.W.; Allen, K.; Lopes, M.; Savoye, M.; Morrison, J.; et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N. Causes, consequences, and treatment of metabolically unhealthy fat distribution. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, I.; Martakis, K.; Rehberg, M.; Stark, C.; Schafmeyer, L.; Schönau, E. Reference centiles for the evaluation of nutritional status in children using body fat percentage, fat mass and lean body mass index. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ali, V.; Goodrick, S.; Rawesh, A.; Katz, D.R.; Miles, J.M.; Yudkin, J.S.; Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Releases Interleukin-6, But Not Tumor Necrosis Factor-α,in Vivo1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4196–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyenechea, E.; Parra, M.D.; Hernández, J.A.M. Implicación de la IL-6 y su polimorfismo -174G>C en el control del peso corporal y en las complicaciones metabólicas asociadas a la obesidad. An. Sist. Sanit. Navar. 2005, 28, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Caro, J.F.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.M.W.; Pedersen, B.K. The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L. Obesity and C-reactive protein in various populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 14, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Cushman, M.; Stampfer, M.J.; Tracy, R.P.; Hennekens, C.H. Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and risk of developing peripheral vascular disease. Circulation 1998, 97, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Bouter, L.M.; McQuillan, G.M.; Wener, M.H.; Harris, T.B. Low-grade systemic inflammation in overweight children. Pediatrics 2001, 107, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahceci, M.; Gokalp, D.; Tuzcu, A.; Atmaca, S.; Arikan, S. The correlation between adiposity and adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin-6 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein levels. Is adipocyte size associated with inflammation in adults? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a therapeutic target for obesity, diabetes, and endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Pessin, J.E. Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppen, S.; Riestra, P.; García-Anguita, A.; López-Simón, L.; Cano, B.; De Oya, I.; De Oya, M.; Garcés, C. Leptin and adiponectin levels in pubertal children: Relationship with anthropometric variables and body composition. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Klersy, C.; Perna, S.; Faliva, M.A.; Montorfano, G.; Roderi, P.; Colombo, I.; Corsetto, P.A.; Fioravanti, M.; Solerte, S.B.; et al. Effects of two-months balanced diet in metabolically healthy obesity: Lipid correlations with gender and BMI-related differences. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of physical exercise on adiponectin, leptin, and inflammatory markers in childhood obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, R.; Sano, H.; Matsudaira, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Morimoto, A.; Shirasawa, T.; Takahashi, E.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tajima, N. Childhood obesity and its relation to serum adiponectin and leptin: A report from a population-based study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2007, 76, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalding, K.L.; Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Bernard, S.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bergmann, O.; Blomqvist, L.; Hoffstedt, J.; Näslund, E.; Britton, T.; et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008, 453, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, A.N.; Murphy, M.J.; Metcalf, B.S.; Hosking, J.; Voss, L.D.; English, P.; Sattar, N.; Wilkin, T.J. Adiponectin in childhood. Pediatr. Obes. 2008, 3, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquarone, E.; Monacelli, F.; Borghi, R.; Nencioni, A.; Odetti, P. Resistin: A reappraisal. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 178, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costandi, J.; Melone, M.; Zhao, A.; Rashid, S. Human resistin stimulates hepatic overproduction of atherogenic ApoB-containing lipoprotein particles by enhancing ApoB stability and impairing intracellular insulin signaling. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, J.-P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Feve, B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ahima, R.S. Linking resistin, inflammation, and cardiometabolic diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Huelgas, R.; Ruiz-Nava, J.; Santamaria-Fernandez, S.; Vargas-Candela, A.; Alarcon-Martin, A.V.; Tinahones, F.J.; Bernal-Lopez, M.R. Impact of intensive lifestyle modification on levels of adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in metabolically healthy obese women. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 4165260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Roth, C.L.; Andler, W. High-sensitive C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and cardiovascular risk factors before and after weight loss in obese children. Metabolism 2005, 54, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, A.; Morell-Azanza, L.; Rendo-Urteaga, T.; García-Calzón, S.; Ojeda-Rodríguez, A.; Martín-Calvo, N.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Martínez, J.A.; Julián, M.C.A.-S. Serum and gene expression levels of CT-1, IL-6, and TNF-α after a lifestyle intervention in obese children. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 19, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline (B) | 12 Months (12 m) | 24 Months (24 m) | p-Value (B vs. 12 m) | p-Value (B vs. 24 m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (Kg) NV: 20.1–39.6 | Boys | 47.6 ± 10.0 | 50.7 ± 11.2 | 58.1 ± 12.7 | <0.0001 | 0.002 |
| Girls | 44.0 ± 10.3 | 49.9 ± 10.9 | 55.9 ± 11.4 | <0.0001 | 0.16 | |
| All | 45.9 ± 10.3 | 50.3 ± 11.0 | 57.1 ± 12.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Height (cm) NV: 114.4–144.2 | Boys | 137.8 ± 8.2 | 143.8 ± 8.5 | 150.4 ± 8.8 | 0.93 | 0.32 |
| Girls | 133.3 ± 10.3 | 140.7 ± 8.9 | 148.7 ± 9.6 | 0.13 | 0.17 | |
| All | 135.7 ± 9.5 | 142.2 ± 8.9 | 149.7 ± 9.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) NV:17.3–20.7 | Boys | 24.9 ± 3.6 | 24.3 ± 3.5 | 25.5 ± 3.9 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 24.4 ± 3.1 | 24.9 ± 3.5 | 25.1 ± 2.9 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | |
| All | 24.6 ± 3.3 | 24.6 ± 3.5 | 25. 3 ± 3.5 | 0.27 | <0.0001 | |
| Waist circumference (cm) NV: 53.0–64.7 | Boys | 80.8 ± 9.6 | 82.4 ± 10.5 | 85.3 ± 11.5 | 0.003 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 77.7 ± 7.4 | 80.0 ± 8.6 | 81.10 ± 8.6 | 0.06 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 80.8 ± 9.6 | 82.4 ± 10.5 | 85.3 ± 11.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| SBP (mmHg) NV < p90 | Boys | 107.2 ± 10.9 | 109.4 ± 9.8 | 105.8 ± 14.5 | 0.86 | 0.03 |
| Girls | 106.3 ± 13.7 | 110.3 ± 13.2 | 107.4 ± 11.9 | 0.08 | 0.72 | |
| All | 106.8 ± 12.3 | 109.9 ± 11.6 | 106.5 ± 13.4 | 0.01 | 0.91 | |
| DBP (mmHg) NV < p90 | Boys | 71.1 ± 11.0 | 69.6 ± 20.0 | 65.4 ± 26.9 | 0.28 | 0.32 |
| Girls | 67.5 ± 9.5 | 72.3 ± 25.0 | 64.8 ± 26.3 | 0.38 | 0.68 | |
| All | 69.4 ± 10.4 | 71.0 ± 22.6 | 65.2 ± 26.5 | 0.27 | 0.60 |
| Baseline (B) | 12 Months (12 m) | 24 Months (24 m) | p-Value (B vs. 12 m) | p-Value (B vs. 24 m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (Kg) | Boys | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 2.0 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 | 0.002 |
| Girls | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 2.1 ± 1.6 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 | 0.16 | |
| All | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 2.0 ± 1.4 | 2.0 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| Height (cm) | Boys | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 0.9 ± 0.8 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | 0.93 | 0.32 |
| Girls | 0.8 ± 1.3 | 0.6 ± 1.3 | 0.7 ± 1.3 | 0.13 | 0.17 | |
| All | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 0.8 ± 1.1 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 0.32 | 0.30 | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | Boys | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | |
| All | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| SBP (mmHg) | Boys | 0.5 ± 1.0 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | −0.02 ± 1.3 | 0.86 | 0.03 |
| Girls | 0.6 ± 1.2 | 0.7 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 1.1 | 0.08 | 0.72 | |
| All | 0.5 ± 1.1 | 0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.1 ± 1.2 | 0.27 | 0.06 | |
| DBP (mmHg) | Boys | 0.9 ± 0.9 | 0.7 ± 0.8 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 0.28 | 0.32 |
| Girls | 0.8 ± 1.0 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 1.2 | 0.38 | 0.68 | |
| All | 0.8 ± 1.0 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.99 | 0.33 |
| Baseline (B) | 12 Months (12 m) | 24 Months (24 m) | p-Value (B vs. 12 m) | p-Value (B vs. 24 m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | Boys | 2.9 ± 2.4 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | 2.3 ± 2.2 | 0.74 | 0.33 |
| Girls | 3.5 ± 3.1 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | 2.1 ± 2.1 | 0.09 | 0.05 | |
| All | 3.2 ± 2.8 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | 2.2 ± 2.1 | 0.14 | 0.05 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | Boys | 1.8 ± 1.6 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 2.0 ± 1.6 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 1.9 ± 1.6 | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| TNF-alpha (pg/mL) | Boys | 2.1 ± 1.5 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 | 0.004 |
| Girls | 2.2 ± 1.8 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | |
| All | 2.1 ± 1.6 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | Boys | 9.8 ± 1.8 | 6.5 ± 1.7 | 7.6 ± 4.7 | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| Girls | 9.9 ± 1.9 | 6.7 ± 1.1 | 7.8 ± 3.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 9.8 ± 1.8 | 6.6 ± 1.4 | 7.7 ± 4.0 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | Boys | 3.7 ± 2.4 | 5.0 ± 2.6 | 5.5 ± 2.6 | 0.04 | 0.005 |
| Girls | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 5.5 ± 2.7 | 5.8 ± 2.1 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |
| All | 3.7 ± 2.2 | 5.2 ± 2.6 | 5.6 ± 2.4 | <0.0010 | <0.0001 |
| Baseline (B) | 12 Months (12 m) | 24 Months (24 m) | p-Value (B vs. 12 m) | p-Value (B vs. 24 m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedentarism (min/d) | Boys | 397.0 ± 68.3 | 243.0 ± 78.4 | 338.1 ± 123.9 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 397.1 ± 85.6 | 268.9 ± 92.1 | 399.8 ± 164.4 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 397.0 ± 77.0 | 255.5 ± 85.2 | 367.6 ± 146.4 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Physical activity | ||||||
| Light (min/d) | Boys | 663.6 ± 63.2 | 797.5 ± 91.9 | 363.9 ± 106.8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 671.4 ± 80.9 | 780.4 ± 92.1 | 308.6 ± 123.8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 667.4 ± 72.3 | 789.2 ± 92.0 | 337.7 ± 117.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Moderate (min/d) | Boys | 18.9 ± 18.0 | 31.7 ± 19.9 | 33.3 ± 16.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Girls | 11.6 ± 11.5 | 24.0 ± 13.4 | 20.3 ± 12.7 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| All | 15.3 ± 15.5 | 28.0 ± 17.4 | 27.1 ± 16.1 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| Vigorous (min/d) | Boys | 1.5 ± 3.9 | 7.8 ± 6.9 | 9.2 ± 8.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Girls | 1.0 ± 1.8 | 6.7 ± 5.8 | 6.6 ± 5.6 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| All | 1.2 ± 3.1 | 7.3 ± 6.4 | 8.0 ± 7.0 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Baseline (B) | 12 Months (12 m) | 24 Months (24 m) | p-Value (B vs. 12 m) | p-Value (B vs. 24 m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat Mass (Kg) | Boys | 18.6 ± 5.4 | 19.0 ± 6.8 | 23.2 ± 8.4 | 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Girls | 18.5 ± 5.2 | 19.4 ± 6.0 | 21.4 ± 5.4 | 0.01 | <0.001 | |
| All | 18.5 ± 5.3 | 19.2 ± 6.4 | 22.4 ± 7.2 | 0.01 | <0.001 | |
| Lean Mass (kg) | Boys | 28.1 ± 4.7 | 31.7 ± 4.9 | 34.8 ± 5.7 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Girls | 25.8 ± 5.2 | 29.8 ± 5.9 | 33.3 ± 6.8 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| All | 27.0 ± 5.1 | 30.8 ± 5.5 | 34.1 ± 5.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Total Mass (kg) | Boys | 46.8 ± 9.7 | 50.6 ± 10.8 | 58.0 ± 7.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Girls | 44.3 ± 9.8 | 49.2 ± 11.4 | 54.7 ± 6.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| All | 45.5 ± 9.8 | 49.9 ± 11.1 | 56.5 ± 6.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Total Fat (%) | Boys | 39.3 ± 4.1 | 36.8 ± 5.0 | 39.3 ± 5.7 | <0.001 | 0.8 |
| Girls | 41.4 ± 3.7 | 38.9 ± 4.0 | 39.0 ± 3.9 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| All | 40.3 ± 4.0 | 37.8 ± 4.6 | 39.1 ± 4.9 | <0.001 | 0.01 |
| Baseline | Glucose | Insulin | HOMA-IR | Total Cholesterol | HDL-c | LDL-c | Triglycerides | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Abdominal Fat Mass | 0.08 | 0.35 | 0.55 | <0.0001 | 0.53 | <0.0001 | −0.05 | 0.57 | −0.09 | 0.29 | −0.10 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| Abdominal Lean Mass | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.50 | <0.0001 | 0.49 | <0.0001 | −0.19 | 0.03 | −0.15 | 0.10 | −0.23 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Total Abdominal Mass | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.57 | <0.0001 | 0.55 | <0.0001 | −0.11 | 0.20 | −0.12 | 0.16 | −0.17 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.01 |
| Total Fat | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.39 | <0.0001 | 0.37 | <0.0001 | 0.06 | 0.54 | −0.10 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| 12 Months | ||||||||||||||
| Abdominal Fat Mass | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.51 | <0.0001 | 0.53 | <0.0001 | −0.01 | 0.93 | −0.18 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
| Abdominal Lean Mass | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.48 | <0.0001 | 0.50 | <0.0001 | −0.08 | 0.48 | −0.07 | 0.51 | −0.12 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.02 |
| Total Abdominal Mass | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.52 | <0.0001 | 0.55 | <0.0001 | −0.04 | 0.74 | −0.15 | 0.19 | −0.02 | 0.89 | 0.22 | 0.04 |
| Total Fat | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.001 | 0.39 | <0.0001 | 0.07 | 0.56 | −0.16 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.19 |
| 24 Months | ||||||||||||||
| Abdominal Fat Mass | −0.08 | 0.59 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.31 | −0.04 | 0.80 | −0.20 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.79 |
| Abdominal Lean Mass | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.22 | −0.16 | 0.26 | −0.03 | 0.85 | −0.16 | 0.28 | −0.10 | 0.51 |
| Total Abdominal Mass | −0.05 | 0.74 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.24 | −0.09 | 0.52 | −0.14 | 0.31 | −0.03 | 0.82 | −0.02 | 0.92 |
| Total Fat | −0.03 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 0.10 | 0.47 | −0.29 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| Baseline | Weight | SDS Weight | BMI | SDS BMI | WC | WHI | Abdominal Fat Mass | Abdominal Lean Mass | Total Abdominal Mass | MedDiet Adherence | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| CRP | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.35 | <0.0001 | 0.27 | 0.002 | 0.39 | <0.0001 | 0.26 | 0.01 | −0.01 | 0.91 | 0.30 | 0.001 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.01 | −0.09 | 0.32 |
| IL-6 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.07 | 0.41 | −0.02 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.95 |
| TNF-alpha | 0.01 | 0.11 | −0.34 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 0.53 | −0.05 | 0.54 | −0.01 | 0.91 | −0.19 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.34 | −0.27 | 0.75 |
| Adiponectin | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.24 | −0.03 | 0.71 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0. 03 | 0.75 |
| Resistin | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.13 | −0.08 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.51 |
| 12 Months | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CRP | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.08 | −0.14 | 0.22 |
| IL-6 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.81 | 0.05 | 0.66 | −0.13 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.59 | −0.28 | 0.01 |
| TNF-alpha | 0.06 | 0.56 | −0.11 | 0.30 | −0.04 | 0.71 | −0.13 | 0.22 | −0.03 | 0.75 | −0.24 | 0.03 | −0.06 | 0.59 | 0.03 | 0.76 | −0.03 | 0.81 | −0.18 | 0.09 |
| Adiponectin | −0.20 | 0.07 | −0.22 | 0.04 | −0.21 | 0.05 | −0.21 | 0.05 | −0.28 | 0.01 | −0.31 | 0.003 | −0.23 | 0.03 | −0.17 | 0.12 | −0.22 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.54 |
| Resistin | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.52 |
| 24 Months | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CRP | 0.06 | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 0.002 | −0.02 | 0.89 | -0.12 | 0.40 | −0.06 | 0.65 | −0.15 | 0.20 |
| IL-6 | 0.05 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.42 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.01 | −0.004 | 0.98 | −0.09 | 0.54 | -0.04 | 0.78 | −0.02 | 0.88 |
| TNF-alpha | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.70 | −0.01 | 0.92 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 0.83 | −0.04 | 0.75 |
| Adiponectin | −0.28 | 0.02 | −0.20 | 0.09 | −0.23 | 0.06 | −0.17 | 0.16 | −0.28 | 0.02 | −0.23 | 0.05 | −0.13 | 0.38 | −0.12 | 0.40 | −0.13 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.60 |
| Resistin | 0.46 | <0.0001 | 0.45 | <0.0001 | 0.49 | <0.0001 | 0.46 | <0.0001 | 0.37 | 0.001 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.002 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.004 | −0.09 | 0.46 |
| Physical Activity | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | Light | Moderate | Vigorous | Moderate to Vigorous | CRP | IL6 | TNF-alpha | Adiponectin | Resistin | |||||||||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |||
| CRP | 0.08 | 0.40 | −0.06 | 0.54 | −0.05 | 0.60 | −0.06 | 0.54 | - | - | −0.04 | 0.66 | −0.09 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.001 | ||
| IL-6 | 0.12 | 0.20 | −0.06 | 0.51 | −0.12 | 0.19 | −0.07 | 0.43 | −0.38 | 0.66 | - | - | 0.35 | <0.0001 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.17 | 0.05 | ||
| TNF-alpha | 0.06 | 0.55 | −0.04 | 0.68 | −0.07 | 0.44 | −0.04 | 0.63 | −0.09 | 0.32 | 0.35 | <0.0001 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.37 | <0.0001 | ||
| Adiponectin | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.49 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.01 | 0.88 | - | - | −0.08 | 0.38 | ||
| Resistin | 0.12 | 0.21 | −0.05 | 0.58 | −0.08 | 0.37 | −0.06 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.001 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.37 | <0.0001 | −0.08 | 0.38 | - | - | ||
| 12 Months | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CRP | 0.002 | 0.99 | −0.19 | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.99 | −0.15 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.89 | −0.14 | 0.22 | −0.11 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.13 | ||
| IL-6 | −0.26 | 0.02 | −0.24 | 0.03 | −0.16 | 0.16 | −0.24 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | - | 0.54 | <0.0001 | −0.04 | 0.70 | −0.17 | 0.88 | ||
| TNF-alpha | −0.16 | 0.15 | −0.07 | 0.54 | −0.04 | 0.73 | −0.07 | 0.56 | −0.14 | 0.22 | 0.55 | <0.0001 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.07 | 0.50 | ||
| Adiponectin | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.01 | −0.11 | 0.31 | −0.04 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.90 | - | - | 0.10 | 0.38 | ||
| Resistin | 0.03 | 0.79 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.57 | 0.17 | 0.13 | −0.17 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.38 | - | - | ||
| 24 Months | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CRP | 0.04 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 0.90 | −0.09 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 0.52 | - | - | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.84 | −0.29 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.04 | ||
| IL-6 | −0.08 | 0.53 | −0.01 | 0.93 | −0.10 | 0.45 | −0.10 | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.15 | - | 0.13 | 0.28 | −0.02 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 0.35 | |||
| TNF-alpha | −0.02 | 0.88 | −0.02 | 0.88 | −0.06 | 0.67 | −0.08 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.13 | 0.27 | - | 0.05 | 0.71 | −0.20 | 0.87 | |||
| Adiponectin | 0.10 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.49 | −0.29 | 0.01 | −0.02 | 0.86 | 0.05 | 0.71 | - | - | −0.10 | 0.42 | ||
| Resistin | 0.06 | 0.61 | −0.10 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.82 | −0.06 | 0.52 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.35 | −0.20 | 0.87 | −0.10 | 0.42 | - | - | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cobos-Palacios, L.; Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Gallardo-Escribano, C.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.I.; Vilches-Pérez, A.; Vargas-Candela, A.; Leiva-Gea, I.; Tinahones, F.J.; Gómez-Huelgas, R.; Bernal-López, M.R. Adipokines Profile and Inflammation Biomarkers in Prepubertal Population with Obesity and Healthy Metabolic State. Children 2022, 9, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010042
Cobos-Palacios L, Muñoz-Úbeda M, Gallardo-Escribano C, Ruiz-Moreno MI, Vilches-Pérez A, Vargas-Candela A, Leiva-Gea I, Tinahones FJ, Gómez-Huelgas R, Bernal-López MR. Adipokines Profile and Inflammation Biomarkers in Prepubertal Population with Obesity and Healthy Metabolic State. Children. 2022; 9(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleCobos-Palacios, Lidia, Mónica Muñoz-Úbeda, Cristina Gallardo-Escribano, María Isabel Ruiz-Moreno, Alberto Vilches-Pérez, Antonio Vargas-Candela, Isabel Leiva-Gea, Francisco J. Tinahones, Ricardo Gómez-Huelgas, and María Rosa Bernal-López. 2022. "Adipokines Profile and Inflammation Biomarkers in Prepubertal Population with Obesity and Healthy Metabolic State" Children 9, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010042
APA StyleCobos-Palacios, L., Muñoz-Úbeda, M., Gallardo-Escribano, C., Ruiz-Moreno, M. I., Vilches-Pérez, A., Vargas-Candela, A., Leiva-Gea, I., Tinahones, F. J., Gómez-Huelgas, R., & Bernal-López, M. R. (2022). Adipokines Profile and Inflammation Biomarkers in Prepubertal Population with Obesity and Healthy Metabolic State. Children, 9(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010042







