To Mask or Not to Mask—Evaluation of Cognitive Performance in Children Wearing Face Masks during School Lessons (MasKids)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
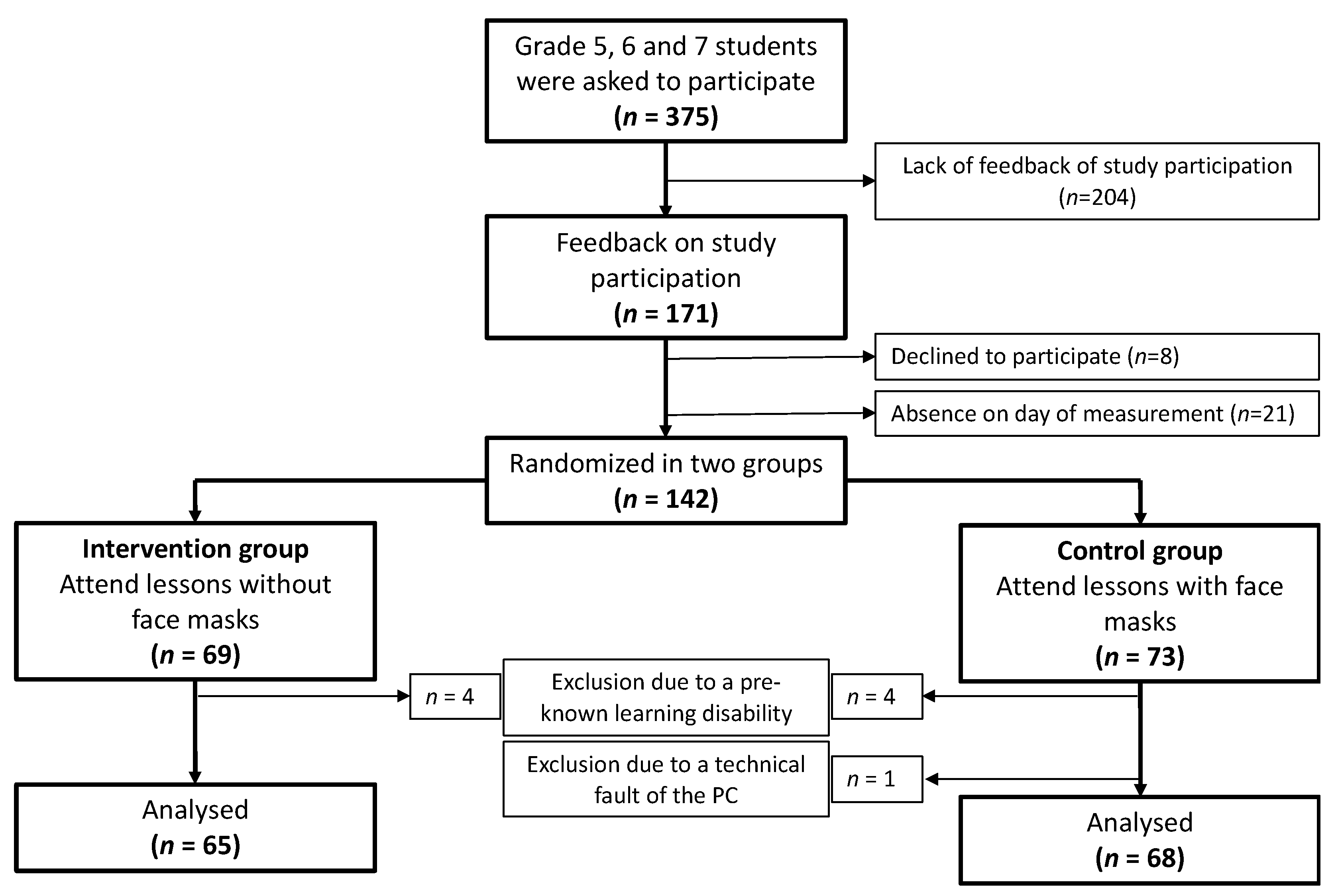
2.2. Participants and Randomization
2.3. Study Schedule
2.4. Cognitive Assessment
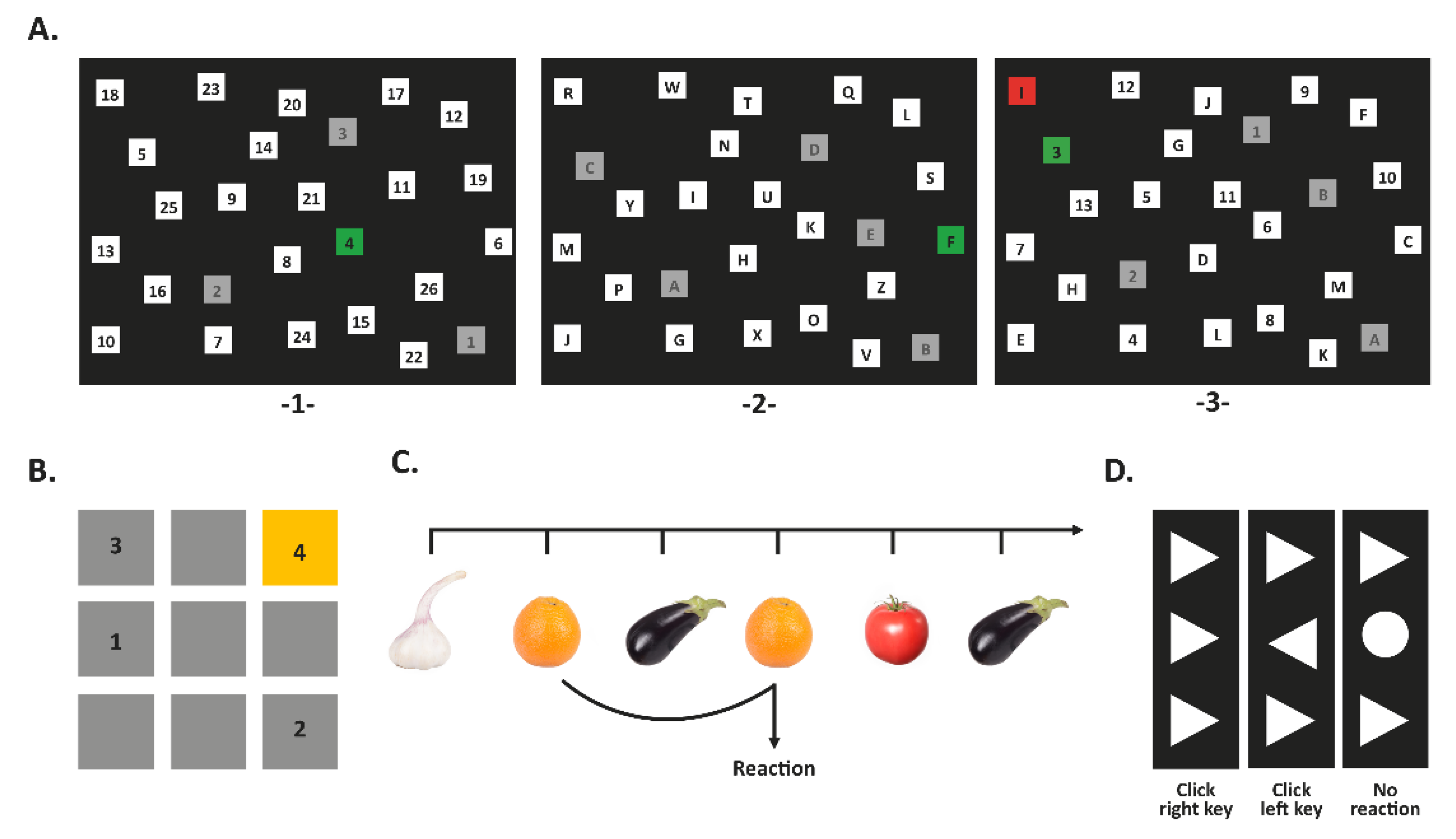
2.4.1. Switch Task
2.4.2. Corsi Block-Tapping Task (CORSI)
2.4.3. 2-Back Task
2.4.4. Flanker Task
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Cognition
3.3. Wearing Masks and Cognition
3.4. Wearing Masks and Cognition: Non-Sport-Focused Classes (N-SC) vs. Sport-Focused Classes (SC)
3.5. Wearing Masks and Cognition: Age-Specific Differences
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, D.K.; Akl, E.A.; Duda, S.; Solo, K.; Yaacoub, S.; Schünemann, H.J.; COVID-19 Systematic Urgent Review Group Effort (SURGE) Study Authors. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2020, 395, s1973–s1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, R.; Bloise, S.; Testa, A.; Marcellino, A.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; Sanseviero, M.; Del Giudice, E.; et al. Assessment of Respiratory Function in Infants and Young Children Wearing Face Masks During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, D.Y.T.; Mun, M.W.; Lee, W.L.J.; Teoh, O.H.; Rajgor, D.D. A randomised clinical trial to evaluate the safety, fit, comfort of a novel N95 mask in children. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mapelli, M.; Salvioni, E.; De Martino, F.; Mattavelli, I.; Gugliandolo, P.; Vignati, C.; Farina, S.; Palermo, P.; Campodonico, J.; Maragna, R.; et al. “You can leave your mask on”: Effects on cardiopulmonary parameters of different airway protection masks at rest and during maximal exercise. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, S.R.; Dominelli, P.B.; Davis, C.K.; Guenette, J.A.; Luks, A.M.; Molgat-Seon, Y.; Sá, R.C.; Sheel, A.W.; Swenson, E.R.; Stickland, M.K. Face Masks and the Cardiorespiratory Response to Physical Activity in Health and Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, K.A.; Zello, G.A.; Butcher, S.J.; Ko, J.B.; Bertrand, L.; Chilibeck, P.D. The impact of face masks on performance and physiological outcomes during exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Zheng, M.; Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yilifate, A.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liang, J.; et al. Effect of Surgical Masks on Cardiopulmonary Function in Healthy Young Subjects: A Crossover Study. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 710573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubrano, R.; Bloise, S.; Marcellino, A.; Ciolli, C.P.; Testa, A.; De Luca, E.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; et al. Effects of N95 Mask Use on Pulmonary Function in Children. J. Pediatr. 2021, 237, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, K.; Tempes, J.; Drozdowska, A.; Gutmann, M.; Falkenstein, M.; Buyken, A.E.; Libuda, L.; Rudolf, H.; Lücke, T.; Kersting, M. Short-term effects of carbohydrates differing in glycemic index (GI) consumed at lunch on children’s cognitive function in a randomized crossover study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdowska, A.; Falkenstein, M.; Jendrusch, G.; Platen, P.; Lücke, T.; Kersting, M.; Jansen, K. Water consumption during a school day and children’s short-term cognitive performance: The CogniDROP randomized intervention trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdowska, A.; Falkenstein, M.; Jendrusch, G.; Platen, P.; Lücke, T.; Kersting, M.; Sinningen, K. Interrelations of physical fitness and cognitive functions in german schoolchildren. Children 2021, 8, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdowska, A.; Sinningen, K.; Falkenstein, M.; Rudolf, H.; Libuda, L.; Buyken, A.E.; Lücke, T.; Kersting, M. Impact of lunch with carbohydrates differing in glycemic index on children’s cognitive functioning in the late postprandial phase: A randomized crossover study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bös, K.; Schlenker, L.; Seidel, I. Motorischer Test für Nordrhein-Westfalen, Testanleitung Mit DVD; Dieser Test ist Identisch Mit Dem Deutschen Motorik-Test (DMT 6-18). Düsseldorf. 2009. Available online: http://www.fbg.schwerte.de/fbg/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/Sportklasseneingangstest.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Cheng, Y.; Ma, N.; Witt, C.; Rapp, S.; Wild, P.S.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; Su, H. Face masks effectively limit the probability of SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Science 2021, 20, eabg6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Helleis, F.; Borrmann, S.; Cheng, Y.; Drewnick, F.; Haug, G.; Klimach, T.; Sciare, J.; Su, H.; Pöschl, U. Model Calculations of Aerosol Transmission and Infection Risk of COVID-19 in Indoor Environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisielinski, K.; Giboni, P.; Prescher, A.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Graessel, D.; Funken, S.; Kempski, O.; Hirsch, O. Is a Mask That Covers the Mouth and Nose Free from Undesirable Side Effects in Everyday Use and Free of Potential Hazards? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Jenetzky, E.; Krafft, H.; Maurer, T.; Martin, D. Coronakinderstudien „Co-Ki“: Erste Ergebnisse eines deutschlandweiten Registers zur Mund-Nasen-Bedeckung (Maske) bei Kindern [Corona child studies “Co-Ki”: First results of a Germany-wide register on mouth and nose covering (mask) in children]. Mon. Kinderheilkd 2021, 169, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walach, H.; Weikl, R.; Prentice, J.; Diemer, A.; Traindl, H.; Kappes, A.; Hockertz, S. Experimental Assessment of Carbon Dioxide Content in Inhaled Air with or without Face Masks in Healthy Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, e213252, (Paper retracted). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charney, S.A.; Camarata, S.M.; Chern, A. Potential Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Communication and Language Skills in Children. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 165, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| −Mask | +Mask | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total, n (%) | 68 | 65 | |
| Girls, n (%) | 42 (61.8) | 30 (46.2) | 0.07 |
| Grade 5, n (%) | 23 (33.8) | 37 (56.9) | 0.07 |
| Grade 6, n (%) | 28 (41.2) | 15 (23.1) | 0.05 |
| Grade 7, n (%) | 17 (25.0) | 13 (20.0) | 0.53 |
| Children from sport-focused class n (%) | 33 (48.5) | 34 (52.3) | 0.66 |
| −Mask | +Mask | p | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switch Task | n = 62 | n = 62 | ||
| Switch costs (s) | 27.2 ± 18.1 | 28.6 ± 18.2 | 0.68 | 1.00 |
| Visual search letters (s) # | 34.8 (30.0–42.3) | 36.7 (31.6–43.5) | 0.25 | 1.00 |
| Visual search numbers (s) | 50.1 (43.6–58.9) | 49.5 (43.7–58.4) | 0.68 | 1.00 |
| 2-Back Task | n = 68 | n = 65 | ||
| RT (ms) | 512 ± 108 | 534 ± 88.7 | 0.18 | 1.00 |
| Ratio of missings (%) | 31.0 (20.2–42.9) | 38.1 (26.2–52.4) | 0.03 | 0.36 |
| Ratio of false alarms (%) | 8.24 (4.71–12.9) | 9.41 (5.88–21.2) | 0.29 | 1.00 |
| Corsi Block-Tapping Task | n = 68 | n = 64 | ||
| Immediate block span (n) | 5.00 (5.00–6.00) | 5.00 (5.00–6.00) | 0.87 | 1.00 |
| Correct sequences (n) | 7.00 (5.00–8.00) | 7.00 (5.00–8.00) | 0.73 | 1.00 |
| Score | 12.0 (9.00–17.0) | 12.5 (9.00–17.8) | 0.84 | 1.00 |
| Flanker Task | n = 60 | n = 49 | ||
| RT slowing (ms) | 75.2 ± 33.9 | 74.6 ± 43.8 | 0.93 | 1.00 |
| Difference error rate (%) | 19.4 (10.1–50.1) | 35.5 (14.2–73.4) | 0.12 | 1.00 |
| Count of false alarms (n) | 3.00 (1.00–8.75) | 7.00 (3.50–18.0) | 0.006 | 0.07 |
| 5th Grade | 6th Grade | 7th Grade | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −Mask | +Mask | p | p * | −Mask | +Mask | p | p * | −Mask | +Mask | p | p * | |
| Switch Task | n = 20 | n = 35 | n = 26 | n = 14 | n = 16 | n = 13 | ||||||
| Switch costs (s) | 30.9 (19.8–46.4) | 23.6 (17.0–40.4) | 0.38 | >0.99 | 22.9 ± 12.5 | 27.3 ± 15.7 | 0.33 | >0.99 | 24.3 ± 16.5 | 25.0 ± 19.2 | 0.92 | >0.99 |
| Visual search letters (s) # | 36.0 (30.5–43.4) | 38.5 (31.6–46.3) | 0.50 | >0.99 | 36.5 (31.4–44.0) | 34.2 (31.4–43.0) | 0.75 | >0.99 | 31.1 (27.5–38.8) | 36.5 (30.1–41.1) | 0.22 | >0.99 |
| Visual search numbers (s) | 54.1 ± 15.7 | 54.7 ± 14.7 | 0.90 | >0.99 | 53.6 ± 12.2 | 48.1 ± 8.92 | 0.15 | >0.99 | 48.7 7.75 | 48.7 ± 13.1 | > 0.99 | >0.99 |
| 2-back task | n = 23 | n = 37 | n = 28 | n = 15 | n = 17 | n = 13 | ||||||
| RT (ms) | 510 ± 84.2 | 554 ± 88.6 | 0.06 | 0.72 | 500 ± 135 | 511 ± 85.3 | 0.76 | >0.99 | 550 (457–593) | 540 (430–562) | 0.34 | >0.99 |
| Ratio of missings (%) | 36.2 ± 20.9 | 43.5 ± 20.8 | 0.19 | >0.99 | 33.3 (23.8–42.9) | 38.1 (14.3–47.6) | 0.65 | >0.99 | 25.8 ± 12.5 | 37.0 ± 18.8 | 0.06 | 0.72 |
| Ratio of false alarms (%) | 10.6 (4.71–22.6) | 9.41 (5.88–21.2) | 0.93 | >0.99 | 7.65 (5.88–11.5) | 9.41 (1.18–20.0) | 0.90 | >0.99 | 9.41 (4.71–12.4) | 10.6 (5.29–27.7) | 0.30 | >0.99 |
| Corsi block tapping task | n = 23 | n = 37 | n = 28 | n = 14 | n = 17 | n = 13 | ||||||
| Correct immediate block span (n) | 5.00 (4.00–6.00) | 5.00 (4.00–6.00) | 0.45 | >0.99 | 5.00 (5.00–6.00) | 5.50 (5.00–6.00) | 0.74 | >0.99 | 6.00 (5.00–6.00) | 5.00 (5.00–6.00) | 0.87 | >0.99 |
| Correct sequences (n) | 5.70 ± 2.08 | 6.05 ± 2.09 | 0.52 | >0.99 | 7.00 (6.00–8.00) | 7.50 (6.00–9.00) | 0.89 | >0.99 | 8.00 (5.50–9.00) | 8.00 (6.50–9.00) | 0.77 | >0.99 |
| Score | 9.00 (6.00–13.0) | 11.0 (7.00–16.0) | 0.37 | >0.99 | 14.6 ± 5.54 | 14.4 ± 5.12 | 0.52 | >0.99 | 15.5 ± 5.94 | 16.6 ± 5.70 | 0.60 | >0.99 |
| Flanker task | n = 20 | n = 27 | n = 24 | n = 12 | n = 16 | n = 10 | ||||||
| RT slowing (ms) | 58.2 ± 28.1 | 71.3 ± 48.2 | 0.25 | >0.99 | 91.4 ± 38.4 | 71.4 ± 35.2 | 0.14 | >0.99 | 72.2 21.1 | 87.1 42.2 | 0.32 | >0.99 |
| Difference error rate (%) | 34.6 (14.2–71.6) | 35.5 (15.6–89.2) | 0.61 | >0.99 | 22.9 (10.3–58.4) | 45.8 (13.9–75.6) | 0.28 | >0.99 | 13.3 (6.64–36.7) | 21.0 (5.74–81.6) | 0.59 | >0.99 |
| Count of false alarms (n) | 5.50 (2.25–18.0) | 11.0 (3.00–19.0) | 0.28 | >0.99 | 3.50 (1.00–11.3) | 7.50 (4.25–16.8) | 0.04 | 0.48 | 2.00 (1.00–5.75) | 4.50 (1.75–7.25) | 0.22 | >0.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlegtendal, A.; Eitner, L.; Falkenstein, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Lücke, T.; Sinningen, K.; Brinkmann, F. To Mask or Not to Mask—Evaluation of Cognitive Performance in Children Wearing Face Masks during School Lessons (MasKids). Children 2022, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010095
Schlegtendal A, Eitner L, Falkenstein M, Hoffmann A, Lücke T, Sinningen K, Brinkmann F. To Mask or Not to Mask—Evaluation of Cognitive Performance in Children Wearing Face Masks during School Lessons (MasKids). Children. 2022; 9(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlegtendal, Anne, Lynn Eitner, Michael Falkenstein, Anna Hoffmann, Thomas Lücke, Kathrin Sinningen, and Folke Brinkmann. 2022. "To Mask or Not to Mask—Evaluation of Cognitive Performance in Children Wearing Face Masks during School Lessons (MasKids)" Children 9, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010095
APA StyleSchlegtendal, A., Eitner, L., Falkenstein, M., Hoffmann, A., Lücke, T., Sinningen, K., & Brinkmann, F. (2022). To Mask or Not to Mask—Evaluation of Cognitive Performance in Children Wearing Face Masks during School Lessons (MasKids). Children, 9(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010095







