Association of Image-Defined Risk Factors with Clinical, Biological Features and Outcome in Neuroblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
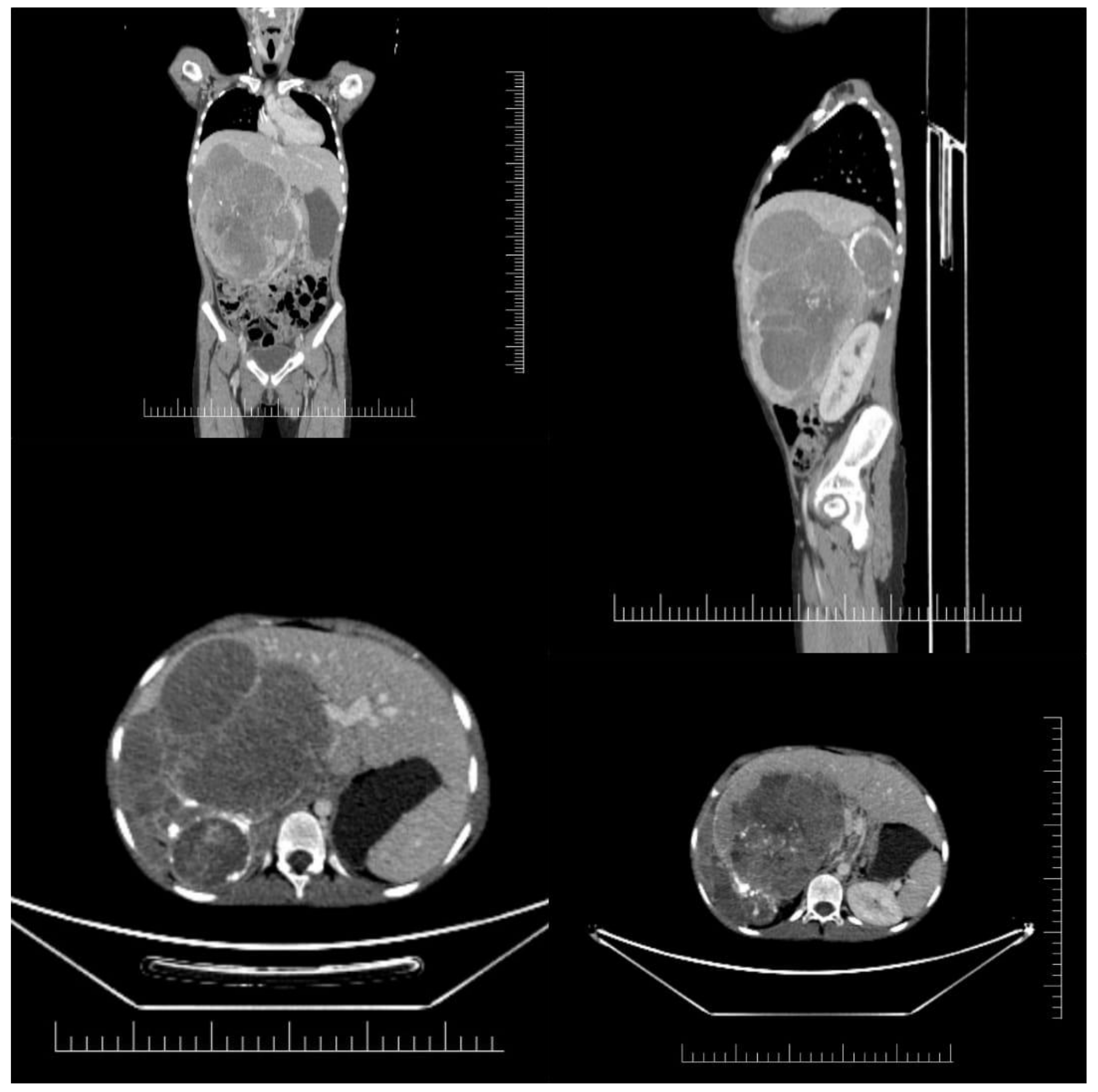
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swift, C.C.; Eklund, M.J.; Kraveka, J.M.; Alazraki, A.L. Updates in diagnosis, management, and treatment of neuroblastoma. Radiographics 2018, 38, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, A.; Erichsen, M.; Stehr, M.; Hubertus, J.; Bergmann, F.; Kammer, B.; Von Schweinitz, D. Image-defined Risk Factors Correlate with Surgical Radicality and Local Recurrence in Patients with Neuroblastoma. Klin. Padiatr. 2016, 228, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, B.H. Neuroblastoma: A Disease Requiring a Multitude of Imaging Studies Continuing Education. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1172–1188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.M.; Trout, A.T.; Towbin, A.J. A review of neuroblastoma image-defined risk factors on magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braoudaki, M.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Zaravinos, A.; Lambrou, G.I. MYCN in Neuroblastoma: “Old Wine into New Wineskins”. Diseases 2021, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.L.; Akinkuotu, A.; Pierro, A.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Irwin, M.S. The Role of Surgery in High-risk Neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; McHugh, K. Neuroblastoma in childhood: Review and radiological findings. Cancer Imaging 2005, 5, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, W.C.; Vo, K.T.; Matthay, K.K.; Balliu, B.; Coleman, C.; Michlitsch, J.; Phelps, A.; Behr, S.; Zapala, M.A. Association of image-defined risk factors with clinical features, histopathology, and outcomes in neuroblastoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarville, M.B. Imaging neuroblastoma: What the radiologist needs to know. Cancer Imaging 2011, 11, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lonergan, G.J.; Schwab, C.M.; Suarez, E.S.; Carlson, C.L. From the archives of the AFIP—Neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2002, 22, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monclair, T.; Brodeur, G.M.; Ambros, P.F.; Brisse, H.J.; Cecchetto, G.; Holmes, K.; Kaneko, M.; London, W.B.; Matthay, K.K.; Nuchtern, J.G.; et al. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) staging system: An INRG Task Force report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolbert, V.P.; Matthay, K.K. Neuroblastoma: Clinical and biological approach to risk stratification and treatment. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Arendonk, K.J.; Chung, D.H. Neuroblastoma: Tumor biology and its implications for staging and treatment. Children 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, F.C.; Salman, M.; Guleryuz, H.; Ozer, E.; Cecen, E.; Ince, D.; Olgun, N. Radiological staging in neuroblastoma: Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging? Pol. J. Radiol. 2019, 84, e46–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, M.; Sakai, K.; Fumino, S.; Aoi, S.; Furukawa, T.; Tajiri, T. The roles played by the MYCN, Trk, and ALK genes in neuroblastoma and neural development. Surg. Today 2019, 49, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Zhang, L.; Reddivalla, N.; Hetherington, M. Neuroblastoma in children: Update on clinicopathologic and genetic prognostic factors. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 34, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Qian, L.; Yang, S.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, S.; Qin, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Prediction for Mitosis-Karyorrhexis Index Status of Pediatric Neuroblastoma via Machine Learning Based18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, E.; Desai, A.V.; Applebaum, M.A.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Park, J.R.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Schleiermacher, G.; Irwin, M.S.; Hogarty, M.; Naranjo, A.; et al. Age, Diagnostic Category, Tumor Grade, and Mitosis-Karyorrhexis Index Are Independently Prognostic in Neuroblastoma: An INRG Project. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1906–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchionda, F.; Oncology, P.; Spreafico, F.; Unit, P.O.; Hemato-oncology, P.; Ciceri, S.; Unit, G.T.; Medicine, P.; Lima, M.; Unit, P.S.; et al. A Novel WT1 Mutation in Familial Wilms Tumor. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1388–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumino, S.; Kimura, K.; Iehara, T.; Nishimura, M.; Nakamura, S.; Souzaki, R.; Nishie, A.; Taguchi, T.; Hosoi, H.; Tajiri, T. Validity of image-defined risk factors in localized neuroblastoma: A report from two centers in Western Japan. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.A.; Pan, C.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.X.; Ye, Q.D.; Gao, Y.J.; Tang, J.Y. Association of image-defined risk factors, tumor resectability, and prognosis in children with localized neuroblastoma. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penazzi, A.C.S.; Tostes, V.S.; Duarte, A.A.B.; Lederman, H.M.; Caran, E.M.M.; Abib, S.D.C.V. Do the Radiological Criteria with the Use of Risk Factors Impact the Forecasting of Abdominal Neuroblastic Tumor Resection in Children? Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2017, 30, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Park, J.R.; Eggert, A.; Caron, H. Neuroblastoma: Biology, Prognosis, and Treatment. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2010, 24, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rha, S.E.; Byun, J.Y.; Jung, S.E.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, H.G.; Lee, J.M. Neurogenic Tumors in the Abdomen: Tumor Types and Imaging Characteristics. Radiographics 2003, 23, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubota, S.; Kadomatsu, K. Origin and initiation mechanisms of neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulack, B.C.; Yang, C.F.J.; Speicher, P.J.; Meza, J.M.; Gu, L.; Wang, X.; D’Amico, T.A.; Hartwig, M.G.; Berry, M.F. The impact of tumor size on the association of the extent of lymph node resection and survival in clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Cai, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z. Large tumor size is a poor prognostic factor of gastric cancer with signet ring cell. Medicine 2019, 98, e17367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Cao, Z.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Fan, F.L.; Zhang, J.; He, X.Y.; Liu, N.J.; Liu, J.B.; Zou, L. Prognostic impact of tumor size on patients with neuroblastoma in a SEER-based study. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaste, S.C.; McCarville, M.B. Imaging Pediatric Abdominal Tumors. Semin. Roentgenol. 2008, 43, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Braga, F.; Luksch, R.; Terenziani, M.; Caruso, S.; Panteghini, M. Measurement of Serum Neuron-Specific Enolase in Neuroblastoma: Is There a Clinical Role? Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhaya, S.R.; Joshi, U.; Gyawali, S.; Thapa, B.; Thapa, A. A late presenting left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia repair complicated by postoperative chylothorax: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Duan, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Q. A single center clinical analysis of children with high-risk neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30357–30368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, D.; Gianferante, M.; Lynch, C.F.; Stevens, J.L.; Harlan, L.C. Treatment and survival of childhood neuroblastoma: Evidence from a population-based study in the United States. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 34, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Son, M.H.; Cho, H.W.; Ma, Y.E.; Yoo, K.H.; Sung, K.W.; Koo, H.H. Clinical significance of MYCN amplification in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, V.V.; Larkin, E.W.; Holbrook, C.T.; Silverman, J.F.; Norris, H.T.; Cantor, A.B.; Shuster, J.J.; Brodeur, G.M.; Look, A.T.; Hayes, F.A.; et al. Correlation between morphologic and other prognostic markers of neuroblastoma a study of histologic grade, DNA index, N-myc gene copy number, and lactic dehydrogenase in patients in the pediatric oncology group. Cancer 1993, 71, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Quaglia, M.P.; Kushner, B.H.; Heller, G.; Bonilla, M.A.; Lindsley, K.L.; Cheung, N.K.V. Stage 4 neuroblastoma diagnosed at more than 1 year of age: Gross total resection and clinical outcome. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1994, 29, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangjitgamol, S.; Manusirivithaya, S.; Laopaiboon, M.; Lumbiganon, P.; Bryant, A. Interval debulking surgery for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, D.A.; Bagatell, R.; Cohn, S.L.; Hogarty, M.D.; Maris, J.M.; Moreno, L.; Park, J.R.; Pearson, A.D.; Schleiermacher, G.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; et al. The challenge of defining “ultra-high-risk” neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Pohl, A.; Volland, R.; Hero, B.; Dübbers, M.; Cernaianu, G.; Berthold, F.; von Schweinitz, D.; Simon, T. Complete surgical resection improves outcome in INRG high-risk patients with localized neuroblastoma older than 18 months. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, Ş.; Özcan, R.; Bakır, A.C.; Kuruğoğlu, S.; Çomunoğlu, N.; Şen, H.S.; Celkan, T.; Tekant, G.T. Adrenal masses in children: Imaging, surgical treatment and outcome. Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeba-Pohl, A.; Von Schweinitz, D.; Muehling, J.; Paolini, M.; Hubertus, J. Implication of Image-Defined Risk Factors for the Extent of Surgical Resection and Clinical Outcome in Patients with Pelvic Neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 31, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iehara, T.; Yoneda, A.; Kikuta, A.; Muraji, T.; Tokiwa, K.; Takahashi, H.; Teramukai, S.; Takimoto, T.; Yagyu, S.; Hosoi, H.; et al. A phase II JN-I-10 efficacy study of IDRF-based surgical decisions and stepwise treatment intensification for patients with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma: A study protocol. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, A.; Nishikawa, M.; Uehara, S.; Oue, T.; Usui, N.; Inoue, M.; Fukuzawa, M.; Okuyama, H. Can Image-Defined Risk Factors Predict Surgical Complications in Localized Neuroblastoma? Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 26, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhar, D.; Joharifard, S.; Lo, A.C.; Schlosser, M.P.; Daodu, O.O. How well do image-defined risk factors (IDRFs) predict surgical outcomes and survival in patients with neuroblastoma? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2020, 36, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenstein, H.M.; Kent, P.M.; London, W.B.; Cohn, S.L. Treatment and outcome of 83 children with intraspinal neuroblastoma: The pediatric oncology group experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, I.I.P.; Goldman, D.A.; Farber, B.A.; Murphy, J.M.; Abramson, S.J.; Basu, E.; Roberts, S.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Price, A.P. Image-defined risk factors for nephrectomy in patients undergoing neuroblastoma resection. J. Pediatric Surg. 2016, 51, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, V.; Tovar, J.A.; Costa, E.; Cuadros, J.; Ruiz, A.; Rollan, V.; Ruiz-Jimenez, J.I.; Perez-Hernández, R.; Cañete, A. The role of surgery in stage IV neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002, 37, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, N.C.; Chung, D.H. Neuroblastina. NIH Public Access. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lv, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Sheng, Q. Role of image-defined risk factors in predicting surgical complications of localized neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2020, 36, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabra, H.O.; Irtan, S.; Cross, K.; Lobos, P.; Froeba-Pohl, A.; Pio, L.; Virgone, C.; Guillén Burrieza, G.; Gómez Chacón Villalba, J.; Riccipetitoni, G.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery for neuroblastic tumours: A SIOPEN multicentre study: Proposal for guidelines. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthyssens, L.E.; Nuchtern, J.G.; Van De Ven, C.P.; Gabra, H.O.S.; Bjornland, K.; Irtan, S.; Stenman, J.; Pio, L.; Cross, K.M.; Avanzini, S.; et al. A Novel Standard for Systematic Reporting of Neuroblastoma Surgery: The International Neuroblastoma Surgical Report Form (INSRF): A Joint Initiative by the Pediatric Oncological Cooperative Groups SIOPEN∗, COG∗∗, and GPOH∗∗∗. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, e575–e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurria, J.P.; Malek, M.M.; Heaton, T.E.; Gehred, A.; Lautz, T.B.; Rhee, D.S.; Tracy, E.T.; Grant, C.N.; Baertshiger, R.M.; Bruny, J.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery for abdominal and thoracic neuroblastic tumors: A systematic review by the APSA Cancer committee. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 2260–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirota, C.; Tainaka, T.; Uchida, H.; Hinoki, A.; Chiba, K.; Tanaka, Y. Laparoscopic resection of neuroblastomas in low- to high-risk patients without image-defined risk factors is safe and feasible. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, N. Biological and Genetic Features of Neuroblastoma and Their Clinical Importance. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 14, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, S.; Cartolano, M.; Hero, B.; Welte, A.; Kahlert, Y.; Roderwieser, A.; Bartenhagen, C.; Walter, E.; Gecht, J.; Kerschke, L.; et al. A mechanistic classification of clinical phenotypes in neuroblastoma. Science 2018, 362, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, S.B.; Smith, V.; Doherty, E.; Zhao, S.; McCarty, S.; Zage, P.E. Overview and recent advances in the treatment of neuroblastoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Mer, J.; Lion, A.; Vik, T.A. Clinical presentation, evaluation, and management of neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anatomic Region | Description |
|---|---|
| Different body compartments | Ipsilateral tumor extension within two body compartments (neck and chest or pelvis and abdomen |
| Cervical region | Tumor encasing internal jugular vein, the carotid artery, or the vertebral artery Extension of tumor to skull base Compression of the trachea |
| Thoracocervical Junction | Tumor encasing the brachial plexus roots Tumor encasing carotid artery, subclavian vessels, vertebral artery Compression of the trachea |
| Thorax | Tumor encasing the aorta or important branches Tumor compressing the trachea/bronchi Lower mediastinal tumor with costovertebral junction infiltration (T9 and T12) |
| Thoracoabdominal junction | Tumor encasing the vena cava or the aorta |
| Pelvis or Abdomen | Tumor infiltrating the hepatoduodenal ligament or the porta hepatis Tumor encasing branches of the superior mesenteric artery Tumor encasing the origin of celiac axis or of the superior mesenteric artery Invasion of one or both renal pedicles Tumor encasing the vena cava or the aorta Tumor encasing the iliac vessels Pelvic tumor crossing the sciatic notch |
| Infiltration of adjacent structures | Diaphragm, pericardium, liver, kidney, mesentery, and the duodenopancreatic block |
| Intraspinal tumor extension | Invasion of more than 1/3 of the spinal canal, non-visible perimedullary leptomeningeal spaces or abnormal signal intensity of the spinal cord |
| Characteristic | No. |
|---|---|
| Sex | N = 31 |
| Male | 20 |
| Female | 11 |
| Primary tumor site | |
| Neck | 0 |
| Chest | 1 |
| Abdomen | 7 |
| Adrenal | 23 |
| Abnormal NSE at diagnosis | 31 |
| MYCN status | |
| Non-amplified | 14 |
| Amplified | 11 |
| Not specified | 6 |
| INSS stage | |
| ½ | 7 |
| ¾ | 24 |
| INRGSS stage | |
| L1 | 6 |
| L2 | 6 |
| M | 9 |
| MS | 10 |
| IDRF | |
| Positive | 16 |
| Negative | 13 |
| Characteristic | No. (n = 31) |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary metastasis | 1 |
| Hepatic metastasis | 12 |
| Bone metastasis | 7 |
| Bone marrow | 5 |
| Skin/soft tissue metastasis | 4 |
| Ganglia metastasis | 15 |
| Renal metastasis | 2 |
| Surgical Treatment | N = 31 |
|---|---|
| Upfront resection | 9 |
| After neoadjuvant treatment | 14 |
| No excision | 11 |
| Biopsy | 10 |
| Complete excision | 12 |
| Incomplete excision | 8 |
| Upfront chemotherapy | 17 |
| Type of intervention | |
| MIS | 5 |
| Open | 17 |
| Adjacent organ resection | 7 |
| Reintervention | 8 |
| Autologous stem cell transplantation | 7 |
| Retinoid therapy | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laura, B.; Radu, B.; Patricia, C.; Andreea, M. Association of Image-Defined Risk Factors with Clinical, Biological Features and Outcome in Neuroblastoma. Children 2022, 9, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111707
Laura B, Radu B, Patricia C, Andreea M. Association of Image-Defined Risk Factors with Clinical, Biological Features and Outcome in Neuroblastoma. Children. 2022; 9(11):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111707
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaura, Balanescu, Balanescu Radu, Cimpeanu Patricia, and Moga Andreea. 2022. "Association of Image-Defined Risk Factors with Clinical, Biological Features and Outcome in Neuroblastoma" Children 9, no. 11: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111707
APA StyleLaura, B., Radu, B., Patricia, C., & Andreea, M. (2022). Association of Image-Defined Risk Factors with Clinical, Biological Features and Outcome in Neuroblastoma. Children, 9(11), 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111707





