A Pediatric Case of Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Presenting with Cyclic Vomiting-like Symptoms: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Report
2.1. Patient Information
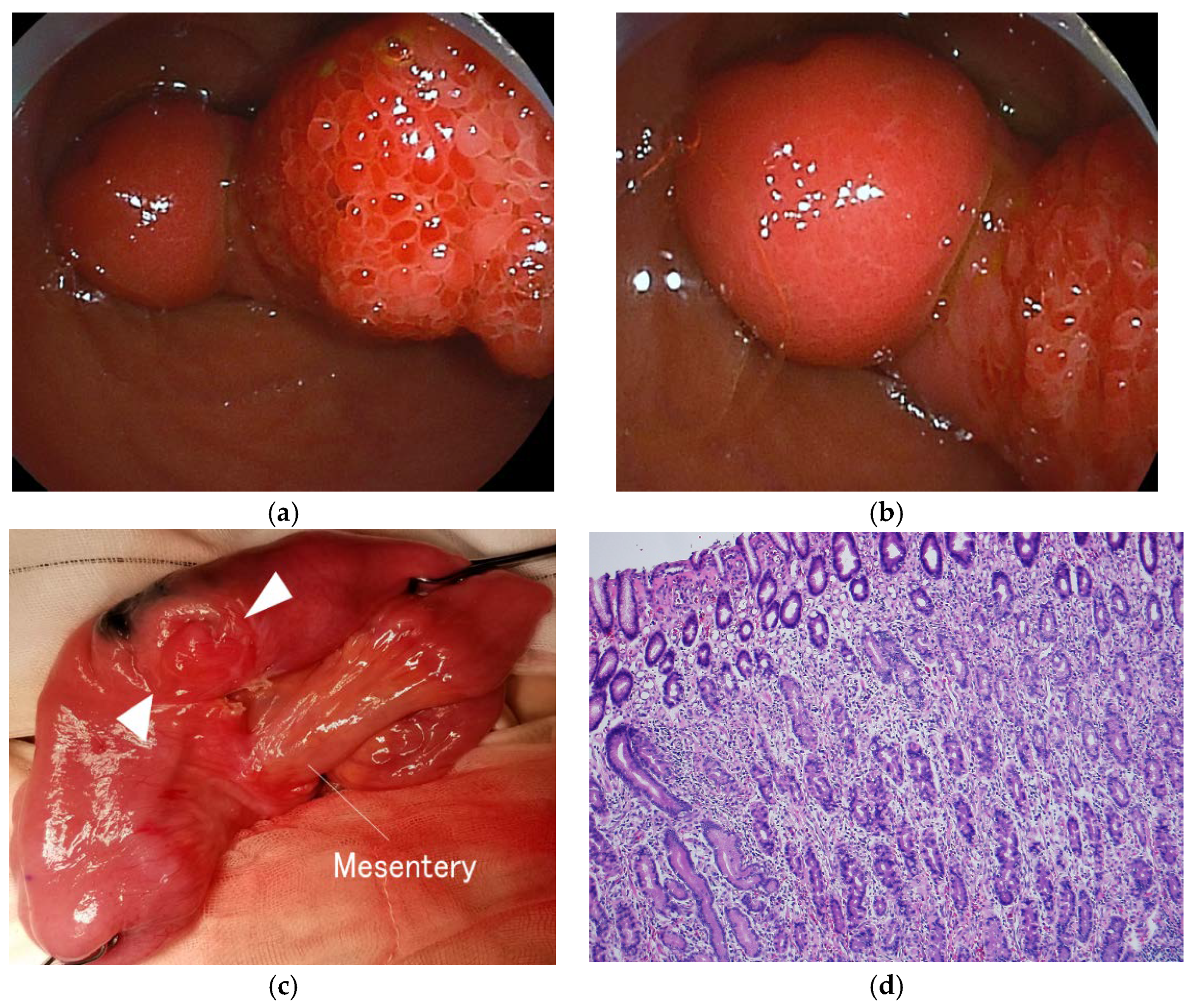
2.2. Symptoms and Clinical Findings
2.3. Therapeutic Intervention
2.4. Follow-up and Outcome
3. Discussion
3.1. Literature Review
3.2. Short Summary
3.3. Meckel’s Diverticulum
3.4. Clinical Course
3.5. Diagnosis and Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruscher, K.A.; Fisher, J.N.; Hughes, C.D.; Neff, S.; Lerer, T.J.; Hight, D.W.; Bourque, M.D.; Campbell, B.T. National trends in the surgical management of Meckel’s diverticulum. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.Y.; Su, Y.T.; Ko, P.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Shih, H.H.; Tsai, C.C. Chronic nocturnal abdominal pain as the presentation of inverted Meckel diverticulum: A case report. Children 2022, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, O.M.; Ku, J.K.; Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Takabe, K. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum as a cause of occult lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6155–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Huang, H.; Wei, D.; Lv, C.; Yang, Y. Diagnosis and minimally invasive surgical treatment of bleeding Meckel’s diverticulum in children using double-balloon enteroscopy. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 1610–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Cai, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z. The diagnostic and treatment values of double-balloon enteroscopy in children’s Meckel’s diverticular bleeding. Medicine 2021, 100, e24823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.M.; Sheu, J.N.; Wu, T.T.; Tsao, T.F.; Lin, C.P. Double-balloon enteroscopy for bleeding Meckel’s diverticulum in a child younger than 4 years of age. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, A.; Tsuchiya, K.; Oshima, S.; Okada, E.; Suzuki, S.; Akiyama, J.M.; Fujii, T.; Okamoto, R.; Watanabe, M. Endoscopic ultrasound with double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis of inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 6, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukushima, M.; Suga, Y.; Kawanami, C. Successful endoscopic resection of inverted Meckel’s diverticulum by double-balloon enteroscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, Y.O. Lipoma within inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: A case report. Korean J. Pathol 2013, 47, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.C.; Tyan, Y.S. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 46, e177–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, S.; Raman, S.P.; Blackford, A.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K. CT detection of symptomatic and asymptomatic Meckel diverticulum. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, G.; Kozman, D. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum causing intussusception in a Crohn’s patient. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 9, rjv112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Shankiti, S.; Halloran, B.; D’Urbano, D.; Zepeda-Gómez, S. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum with intussusception and ulceration diagnosed after rectal double-balloon enteroscopy. ACG Case Rep. J. 2016, 3, e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kang, K.A.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, K.G.; Kwon, T.J. Inverted Meckel diverticulum as a lead point of small bowel intussusception: Misinterpreting case as a lipoma. Clin. Imag. 2016, 40, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagaki, K.; Osawa, S.; Ito, T.; Iwaizumi, M.; Hamaya, Y.; Tsukui, H.; Furuta, T.; Wada, H.; Baba, S.; Sugimoto, K. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum preoperatively diagnosed using double-balloon enteroscopy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4416–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Shinozaki, S.; Yano, T.; Oshiro, K.; Morimoto, M.; Kawarai Lefor, A.; Yamamoto, H. Intussusception due to an inverted Meckel’s diverticulum diagnosed by double-balloon enteroscopy. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2017, 11, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konomatsu, K.; Kuwai, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Imagawa, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kouno, H.; Kohno, H. Endoscopic full-thickness resection for inverted Meckel’s diverticulum using double-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy 2017, 49, e66–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matek, J.; Ptacnik, J.; Krska, Z. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: A rare cause of ileo-ileal intussusceptions and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Rozhl. Chir. 2018, 97, 399–401. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, E.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Kim, W.R. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: Two case reports and a review of the literature. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2018, 10, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marascia, D.J. Small bowel obstruction secondary to intussuscepted Meckel’s diverticulum in an adult. Case Rep. Surg. 2019, 2019, 3241782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Saito, M.; Ikeda, T.; Fukuda, R.; Tanaka, A.; Rikiyama, T. Ileectomy performed on a case of adult intussusception due to inversion of Meckel’s diverticulum. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, rjz367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, N.; Ito, T.; Matsuoka, H.; Chohno, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kakeji, Y.; Ohnishi, T. Intussusception caused by a small intestinal lipoma with ectopic gastric mucosa containing gastric cystica profunda component cells within the inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, L.; Bhatia, R.; Kaushik, R.; Lal, P.; Rajpaul, G.; Veerpal. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, E.; Stone, T.; Spruill, L.; Hardie, A.D. A case report of inverted Meckel’s diverticulum. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 16, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajra Martínez, I.; Calvo, M.; Martínez-Porras, J.L.; Gomez-Pimpollo Garcia, L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Leon, C.; Calleja Panero, J.L. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum diagnosed using capsule endoscopy: A case report. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 6154–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, T.; Ishida, O.; Yasutomi, M. Inverted Meckel diverticulum with intussusception: Demonstration by CT. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1996, 20, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedero, M.D.; Ripollés, T.; Nicolau, M.J.; Martínez-Pérez, M.J. Pancreatic pseudotumor in Meckel diverticulum. Abdom. Imaging 2006, 31, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Papanikolaou, G.; Mitsis, M.; Nastos, D.; Kappas, A.M. Ileoileal intussusception due to an inverted Meckel’s diverticulum in a child. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2007, 70, 308. [Google Scholar]
- Yigiter, M.; Kiyici, H.; Yucesan, S.; Hicsonmez, A. An unusual cause of acute abdominal pain in a child: An inverted Meckel diverticulum: Report of a case. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2010, 38, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiough, G.E.; Bhatti, I.; Ratliff, D.A. Acute appendicitis with unusual dual pathology. Int J. Surg. Case Rep. 2012, 3, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza, B. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum simulating pedunculated polyp as a lead point for ileoileal intussusception in a child. APSP J. Case Rep. 2013, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Darlington, C.D.; Anitha, G.F.S. Meckel’s diverticulitis masquerading as acute pancreatitis: A diagnostic dilemma. Indian J. Crit Care Med. 2017, 21, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.C.; Søreide, K. Systematic review of epidemiology, presentation, and management of Meckel’s diverticulum in the 21st century. Medicine 2018, 97, e12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppal, K.; Tubbs, R.S.; Matusz, P.; Shaffer, K.; Loukas, M. Meckel’s diverticulum: A review. Clin. Anat. 2011, 24, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keese, D.; Rolle, U.; Gfroerer, S.; Fiegel, H. Symptomatic Meckel’s Diverticulum in pediatric patients-case reports and systematic review of the literature. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munden, M.M.; Bruzzi, J.F.; Coley, B.D.; Munden, R.F. Sonography of pediatric small-bowel intussusception: Differentiating surgical from nonsurgical cases. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Kusakawa, I.; Murata, Y.; Ukiyama, E.; Kawase, H.; Kamagata, S.; Ueno, S.; Osamura, T.; Kubo, M.; Yoshida, M. Japanese guidelines for the management of intussusception in children, 2011. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasaelap, A.; Lerner, D.; Southern, J.; Noe, J.; Chugh, A. Endoscopic Removal of a Single, Painless, Juvenile Polyp in the Small Intestine Causing Anemia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reviewed Items | Adult | Pediatric | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) (range) | 42 (18–78) | 8 (2–16) | <0.001 |
| Female (%) | 24/74 (32.4) | 4/9 (44.4) | 0.48 |
| Clinical signs and symptoms (%) | |||
| Abdominal pain/vomiting | 48/74 (64.9) | 9/9 (100) | 0.051 |
| Bloody stool | 55/74 (74.3) | 3/9 (33.3) | 0.019 |
| Anemia | 56/74 (75.7) | 0/9 (0) | <0.0001 |
| Intussusception | 31/74 (41.9) | 9/9 (100) | 0.001 |
| Time from onset to treatment (months) (range) | 3.5 (0.03–60) | 0.1 (0.02–6) | 0.019 |
| Positive diagnostic modality (%) | |||
| Abdominal CT scan | 42/42 (100) | 2/2 (100) | >0.99 |
| Meckel’s scan | 0/6 (0) | 0/0 (0) | >0.99 |
| Abdominal ultrasonography | 12/14 (85.7) | 8/8 (100) | 0.52 |
| Small intestinal capsule endoscopy | 3/4 (75.0) | 1/1 (100) | >0.99 |
| Double-balloon endoscopy | 6/6 (100) | 1/1 (100) | >0.99 |
| Treatments (%) | |||
| Diverticulectomy/partial ileal resection | 72/74 (97.3) | 9/9 (100) | >0.99 |
| Endoscopic resection with DBE | 2/74(2.7) | 0/9 (0) | >0.99 |
| Pathological finding (%) | |||
| Ulceration | 47/74 (63.5) | 3/9 (33.3) | 0.15 |
| Ectopic gastric mucosa | 30/74 (40.5) | 2/9 (22.2) | 0.47 |
| Ectopic pancreas | 18/74 (24.3) | 5/9 (55.6) | 0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Endo, Y.; Jimbo, K.; Arai, N.; Ochi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Yamataka, A.; Shimizu, T. A Pediatric Case of Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Presenting with Cyclic Vomiting-like Symptoms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children 2022, 9, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121817
Endo Y, Jimbo K, Arai N, Ochi T, Suzuki M, Yamataka A, Shimizu T. A Pediatric Case of Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Presenting with Cyclic Vomiting-like Symptoms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children. 2022; 9(12):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121817
Chicago/Turabian StyleEndo, Yoshiko, Keisuke Jimbo, Nobuyasu Arai, Takanori Ochi, Mitsuyoshi Suzuki, Atsuyuki Yamataka, and Toshiaki Shimizu. 2022. "A Pediatric Case of Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Presenting with Cyclic Vomiting-like Symptoms: A Case Report and Literature Review" Children 9, no. 12: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121817
APA StyleEndo, Y., Jimbo, K., Arai, N., Ochi, T., Suzuki, M., Yamataka, A., & Shimizu, T. (2022). A Pediatric Case of Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Presenting with Cyclic Vomiting-like Symptoms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children, 9(12), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121817





