Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
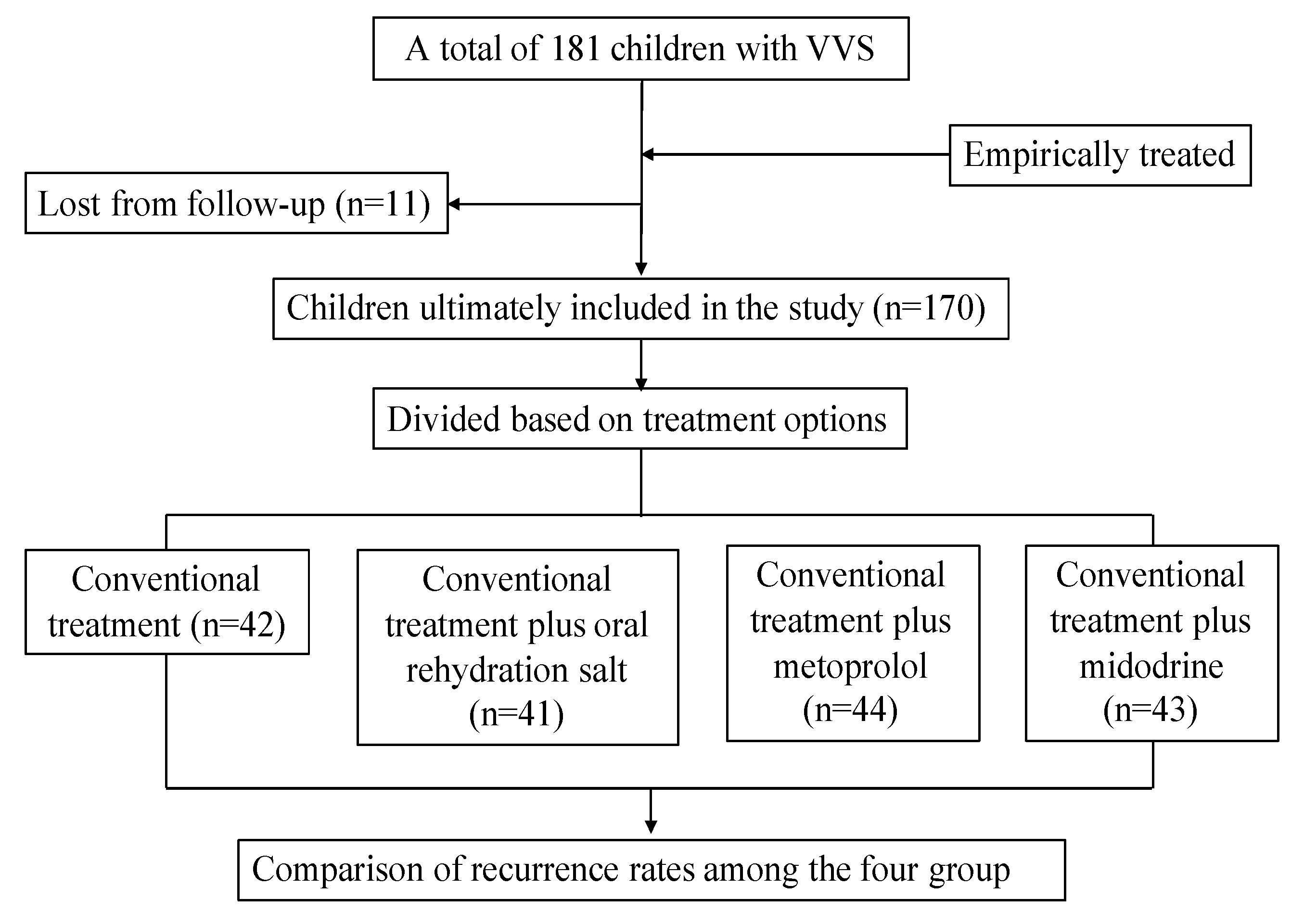
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Head-Up Tilt Test
2.3. Treatment and Follow-Up Protocol
2.4. Statistical Process and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Comparison of Baseline Characteristics among Study Participants Receiving Different Treatment Options
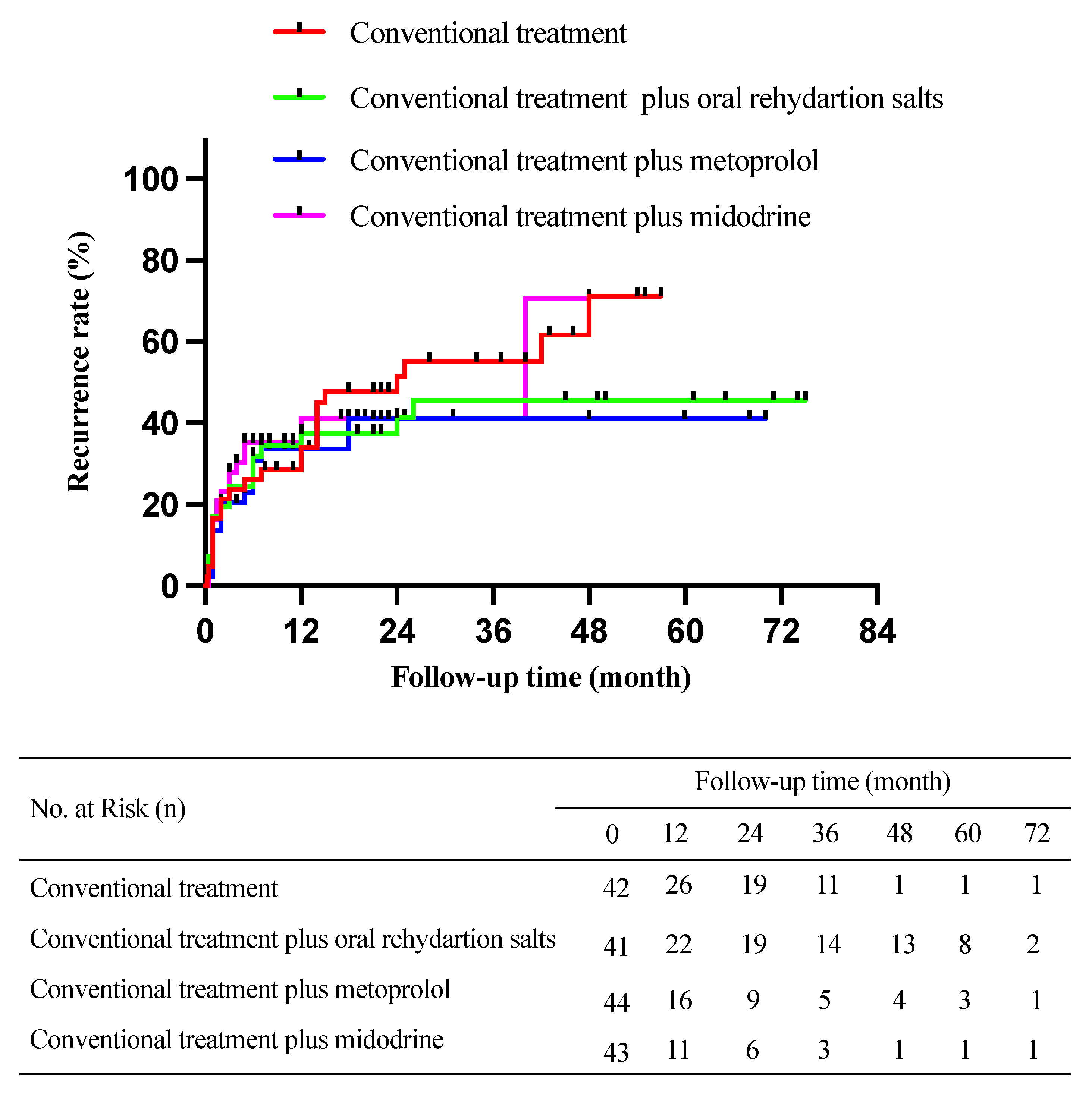
3.3. Comparison of Syncopal or Presyncopal Recurrence among Participants Receiving Different Treatment Options
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilz, M.J.; Marthol, H.; Neundörfer, B. Syncope—A systematic overview of classification, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2002, 70, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.W.J.; Cho, C.S. Pediatric syncope: Cases from the emergency department. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 2010, 28, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala, R.; Metais, B.; Tuckfield, L.; DelVecchio, M.; Aronoff, S. Pediatric Syncope: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2020, 36, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massin, M.M.; Bourguignont, A.; Coremans, C.; Comté, L.; Lepage, P.; Gérard, P. Syncope in pediatric patients presenting to an emergency department. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ingrid, S.; Chen, J.; Qin, J.; Du, J. Aetiologic and clinical characteristics of syncope in Chinese children. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Du, J. Interpretation of diagnostic guidelines for syncope in children. Zhong Hua Er. Ke Za Zhi 2010, 48, 262–265. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouakam, C.; Vaksmann, G.; Pachy, E.; Lacroix, D.; Rey, C.; Kacet, S. Long-term follow-up of children and adolescents with syncope; predictor of syncope recurrence. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrıverdi Yılmaz, S.; Binnetoğlu, K.; Babaoğlu, K.; Altun, G. Predictoral rehydration salts of vasovagal syncope recurrence in children and adolescents and value of head-up tilt table test. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2013, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.B.; Czosek, R.J.; Knilans, T.K.; Marino, B.S. The effect of paediatric syncope on health-related quality of life. Cardiol. Young 2012, 22, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.B.; Willis, M.; Lancaster, H.; Leonard, K.; Thomas, C. The evaluation and management of pediatric syncope. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 55, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, A.; Lerma, C.; Márquez, M.F.; Cárdenas, M.; Hermosillo, A.G. Correlation of syncopal burden with anxiety symptoms score in recurrent vasovagal syncope. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.Q.; Liao, Y.; Tian, H.; Huang, M.; Dong, X.Y.; Shi, L.; Sung, J.H.; Jin, H.F.; Du, J.B.; et al. 2018 Chinese Pediatric Cardiology Society (CPCS) guideline for diagnosis and treatment of syncope in children and adolescents. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyas, A.; Swaminathan, P.D.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Olshansky, B. Are treatments for vasovagal syncope effective? A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1906–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, S.T.; Raj, S.R. Non-invasive management of vasovagal syncope. Auton. Neurosci. 2014, 184, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.-K.; Sheldon, R.S.; Benditt, D.G.; Cohen, M.I.; Forman, D.E.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Grubb, B.P.; Hamdan, M.H.; Krahn, A.D.; Link, M.S.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, e39–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignole, M.; Moya, A.; de Lange, F.J.; Deharo, J.-C.; Elliott, P.M.; Fanciulli, A.; Fedorowski, A.; Furlan, R.; Kenny, R.A.; Martín, A.; et al. Practical Instructions for the 2018 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, e43–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Li, X.; Tang, C.; Jin, H.; Du, J. Baroreflex sensitivity predicts response to metoprolol in children with vasovagal syncope: A pilot study. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Liu, A.D.; Holmberg, L.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Xiong, Z.; Gai, Y.; et al. A cross-sectional study on upright heart rate and BP changing characteristics: Basic data for establishing diagnosis of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and orthostatic hypertension. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liao, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Tang, C.; Du, J.; Jin, H. Head-up tilt test provokes dynamic alterations in total peripheral resistance and cardiac output in children with vasovagal syncope. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, A.; Rivas, N.; Perez-Rodon, J. Overview of the contribution of recent clinical trials to advancement of syncope management. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 55, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajek, J.; Zyśko, D.; Mazurek, W. Efficacy of tilt training in patients with vasovagal syncope. Kardiol. Pol. 2006, 64, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zou, R.; Tan, C.; Wang, C. Assessment of efficacy of oral rehydration salts in children with neurally mediated syncope of different hemodynamic patterns. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, H.; Liao, Y. Efficacy of increased salt and water intake on pediatric vasovagal syncope: A meta-analysis based on global published data. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 663016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.S.; Morillo, C.A.; Klingenheben, T.; Krahn, A.D.; Sheldon, A.; Rose, M.S. Age-dependent effect of β-blockers in preventing vasovagal syncope. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.Y.; Raj, S.R.; Sheldon, R.S. Midodrine for the prevention of vasovagal syncope: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace, 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, Y.K.; Park, J.; Huh, J.; Kim, J.S. Is home orthostatic self-training effective in preventing neurally mediated syncope? Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellard, E.; Fortrat, J.-O.; Custaud, M.-A.; Victor, J.; Greenleaf, J.; Lefthériotis, G. Increased hydration alone does not improve orthostatic tolerance in patients with neurocardiogenic syncope. Clin. Auton. Res. 2007, 17, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jin, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Du, J. Randomized comparison of metoprolol versus conventional treatment in preventing recurrence of vasovagal syncope in children and adolescents. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, CR199–CR203. [Google Scholar]
- Romme, J.J.C.M.; van Dijk, N.; Go-Schön, I.K.; Reitsma, J.B.; Wieling, W. Effectiveness of midodrine treatment in patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope not responding to non-pharmacological treatment (STAND-trial). Europace 2011, 13, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Jin, H.; Du, J. Assessment of therapeutic biomarkers in the treatment of children with postural tachycardia syndrome and vasovagal syncope. Cardiol. Young 2014, 24, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, D.L.; Wieling, W.; Brignole, M.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Sutton, R.; Stewart, J. The pathophysiology of the vasovagal response. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajek, J.; Zyśko, D.; Halawa, B.; Mazurek, W. Influence of tilt training on activation of the autonomic nervous system in patients with vasovagal syncope. Acta Cardiol. 2006, 61, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, H.; Hainsworth, R. Salt supplement increases plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope. Heart 1996, 75, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dendi, R.; Goldstein, D.S. Meta-analysis of nonselective versus beta-1 adrenoceptor-selective blockade in prevention of tilt-induced neurocardiogenic syncope. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 1319–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Yang, X.; Cai, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C. Twenty-four-hour urine NE level as a predictor of the therapeutic response to metoprolol in children with recurrent vasovagal syncope. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Garg, A.X.; Heidenheim, A.P.; House, A.A. Midodrine appears to be safe and effective for dialysis-induced hypotension: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Du, J. Pathophysiology and individualized management of vasovagal syncope and postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents: An update. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Follow-Up | n | Sex (Female %) | Visiting Age (Year) | Age at Onset (Year) | Course of Illness (Month) a | Episodes of Syncope and Presyncope a |
| Completed | 170 | 102 (60) | 10.9 ± 2.7 | 8.8 ± 3.3 | 12.0 (3.0, 36.0) | 4.0 (2.0, 6.0) |
| Lost | 11 | 6 (55) | 11.9 ± 3.9 | 10.1 ± 4.6 | 14.0 (4.0, 36.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 12.0) |
| Z/χ2 | - | 0.002 | −1.328 | −1.225 | −0.518 | −0.749 |
| p value | - | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
| Follow-Up | n | Time of TLOC ≥ 1 min (%) | Syncope-Related Injury (%) | Allergic History (%) | Positive Family History (%) | Type of Syncope (Vasodepressor Type %) |
| Completed | 170 | 112 (66) | 19 (11) | 45 (26) | 41 (24) | 122 (72) |
| Lost | 11 | 7 (64) | 0 (0) | 4 (36) | 2 (18) | 7 (64) |
| Z/χ2 | - | 0.023 | 1.374 | 0.512 | 0.201 | 0.055 |
| p value | - | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
| Group | n | Sex (Female %) | Visiting Age (Year) | Age at Onset (Year) | Course of Illness (Month) b | Episodes of Syncope and Presyncope b |
| Conventional treatment | 42 | 26 (62) | 10.3 ± 2.5 | 8.6 ± 3.1 | 12.0 (1.8, 30.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 6.0) |
| Conventional treatment plus oral rehydration salts | 41 | 21 (51) | 10.5 ± 2.7 a | 8.7 ± 2.9 | 12.0 (2.5, 35.0) | 4.0 (2.5, 6.0) |
| Conventional treatment plus metoprolol | 44 | 30 (68) | 11.6 ± 2.5 | 9.4 ± 3.7 a | 11.5 (3.6, 45.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 7.0) |
| Conventional treatment plus midodrine hydrochloride | 43 | 25 (58) | 11.0 ± 2.8 a | 8.6 ± 3.2 a | 13.0 (4.0, 48.0) | 5.0 (3.0, 7.0) |
| H/χ2 | - | 2.670 | 2.380 | 0.527 | 0.893 | 5.307 |
| p value | - | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
| Group | n | Time of TLOC ≥ 1 min (%) | Syncope-Related Injury (%) | Allergic History (%) | Positive Family History (%) | Type of Syncope (Vasodepressor Type %) |
| Conventional treatment | 42 | 25 (60) | 4 (10) | 11 (26) | 11 (26) | 28 (67) |
| Conventional treatment plus oral rehydration salts | 41 | 28 (68) | 3 (7) | 11 (27) | 15 (37) | 28 (68) |
| Conventional treatment plus metoprolol | 44 | 30 (68) | 6 (14) | 14 (32) | 8 (18) | 34 (77) |
| Conventional treatment plus midodrine hydrochloride | 43 | 29 (67) | 6 (14) | 9 (21) | 7 (16) | 32 (74) |
| χ2 | - | 1.011 | 1.333 | 1.329 | 5.872 | 1.591 |
| p value | - | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Jin, H. Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope. Children 2022, 9, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071065
Tao C, Cui Y, Zhang C, Liu X, Zhang Q, Liu P, Wang Y, Du J, Jin H. Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope. Children. 2022; 9(7):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071065
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Chunyan, Yaxi Cui, Chunyu Zhang, Xueqin Liu, Qingyou Zhang, Ping Liu, Yuli Wang, Junbao Du, and Hongfang Jin. 2022. "Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope" Children 9, no. 7: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071065
APA StyleTao, C., Cui, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, X., Zhang, Q., Liu, P., Wang, Y., Du, J., & Jin, H. (2022). Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope. Children, 9(7), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071065








