Current Antithrombotic Therapy Strategies in Children with a Focus on Off-Label Direct Oral Anticoagulants—A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Summary—Findings from Clinical Trials
3.1. Thrombosis Pathways
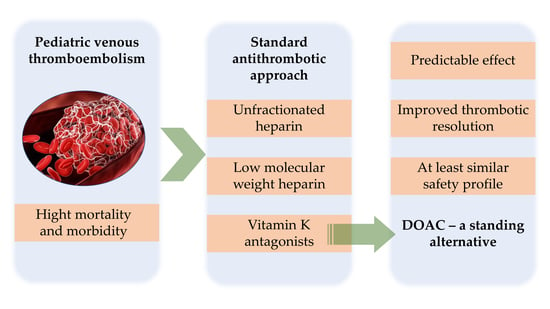
3.2. Thrombotic Events in Children: Numbers and Outcomes
3.3. Classical Antithrombotic Approach
3.4. DOACs in Children—The Future of OAT?
3.4.1. Dabigatran—The Flagship of DOAC in Children
3.4.2. Rivaroxaban—Evidence from Clinical Studies
3.4.3. Apixaban—Growing Evidence in Children
3.4.4. Edoxaban—A Valid Option in Children?
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celkan, T.; Dikme, G. Thrombosis in children: Which test to whom, when and how much necessary? Turk Pediatri Ars. 2018, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.L. Venous thromboembolism in children and adolescents. Blood Res. 2016, 51, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monagle, P.; Cuello, C.A.; Augustine, C.; Bonduel, M.; Brandão, L.R.; Capman, T.; Chan, A.K.C.; Hanson, S.; Male, C.; Meerpohl, J.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3292–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, A.; Albisetti, M. Management of Venous Thromboembolism in Children: Current Recommendations and Therapeutic Options. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, C.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Palumbo, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Nurmeev, I.; Hege, K.; Bonnet, D.; Connor, P.; Hooimeijer, H.L.; Torres, M.; et al. Rivaroxaban compared with standard anticoagulants for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism in children: A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e18–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Drug to Treat, Help Prevent Types of Blood Clots in Certain Pediatric Populations. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-drug-treat-help-prevent-types-blood-clots-certain-pediatric-populations#:~:text=FDA%20has%20approved%20Xarelto%20(rivaroxaban,days%20of%20injectable%20or%20intravenous (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- FDA Approves First Oral Blood Thinning Medication for Children. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-oral-blood-thinning-medication-children#:~:text=Today%2C%20the%20U.S.%20Food%20and,by%20injection%20for%20at%20least (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/pradaxa-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- van Ommen, C.H.; Middeldorp, S. Thrombophilia in childhood: To test or not to test. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 37, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odent, T.; de Courtivron, B.; Gruel, Y. Thrombotic risk in children undergoing orthopedic surgery. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, S109–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Venous thromboembolism in children. Circulation 2006, 113, e12–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monagle, P.; Adams, M.; Mahoney, M.; Ali, K.; Barnard, D.; Bernstein, M.; Brisson, L.; David, M.; Desai, S.; Scully, M.F.; et al. Outcome of pediatric thromboembolic disease: A report from the Canadian Childhood Thrombophilia Registry. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 47, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monagle, P.; Chan, A.K.C.; Goldenberg, N.A.; Ichord, R.N.; Journeycake, J.M.; Nowak-Göttl, U.; Vesely, S.K. Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e737S–e801S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.Y.; Ward, S.M. The Anti-Factor Xa Range for Low Molecular Weight Heparin Thromboprophylaxis. Hematol. Rep. 2015, 7, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Julia, S.; James, U. Direct Oral Anticoagulants: A Quick Guide. Eur. Cardiol. 2017, 12, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunois, C. Laboratory Monitoring of Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Biomedicines 2021, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrini, R. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Renal Failure. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarb, H.; Tsakiris, D.A. New Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOAC) and Their Use Today. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halton, J.M.L.; Albisetti, M.; Biss, B.; Bomgaars, L.; Brueckmann, M.; Gropper, S.; Harper, R.; Huang, F.; Luciani, M.; Maas, H.; et al. Phase IIa study of dabigatran etexilate in children with venous thrombosis: Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halton, J.M.L.; Picard, A.C.; Harper, R.; Huang, F.; Brueckmann, M.; Gropper, S.; Maas, H.; Tartakovsky, I.; Nurmeev, I.; Mitchell, L.G.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Safety and Tolerability of Dabigatran Etexilate Oral Liquid Formulation in Infants with Venous Thromboembolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halton, J.; Brandão, L.R.; Luciani, M.; Bomgaars, L.; Chalmers, E.; Mitchell, L.G.; Nurmeev, I.; Sharathkumar, A.; Svirin, P.; Gorbatikov, K.; et al. Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism in children (DIVERSITY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 2b/3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e22–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, L.R.; Albisetti, M.; Halton, J.; Bomgaars, L.; Chalmers, E.; Mitchell, L.G.; Nurmeev, I.; Svirin, P.; Kuhn, T.; Zapletal, O.; et al. Safety of dabigatran etexilate for the secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism in children. Blood 2020, 135, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willmann, S.; Thelen, K.; Kubitza, D.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Frede, M.; Coboeken, K.; Stampfuss, J.; Burghaus, R.; Mück, W.; Lippert, J. Pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in children using physiologically based and population pharmacokinetic modelling: An EINSTEIN-Jr phase I study. Thromb. J. 2018, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubitza, D.; Willmann, S.; Becka, M.; Thelen, K.; Young, G.; Brandão, L.R.; Monagle, P.; Male, C.; Chan, A.; Kennet, G.; et al. Exploratory evaluation of pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and safety of rivaroxaban in children and adolescents: An EINSTEIN-Jr phase I study. Thromb. J. 2018, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monagle, P.; Lensing, A.; Thelen, K.; Martinelli, I.; Male, C.; Santamaria, A.; Samochatova, E.; Kumar, R.; Holzhauer, S.; Saracco, P.; et al. Bodyweight-adjusted rivaroxaban for children with venous thromboembolism (EINSTEIN-Jr): Results from three multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 studies. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e500–e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Monagle, P.; Male, C.; Thelen, K.; Willmann, S.; Palumbo, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Nurmeev, I.; Hege, K.; et al. Rivaroxaban for treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. An Einstein-Jr phase 3 dose-exposure-response evaluation. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchinat, A.; Otero, N.; Mahanti, H.; Morris, E.; Brudnicki, A.; Friedman, D.; Li, S.; Levendoglu-Tugal, O.; Cairo, M.S. A Pilot Study of an Oral Anticoagulant, Apixaban, in Secondary Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Children and Adolescents. Blood 2019, 134, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. These Highlights Do Not Include All the Information Needed to Use PRADAXA Oral Pellets Safely and Effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for PRADAXA Oral Pellets. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/214358s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Albisetti, M.; Biss, B.; Bomgaars, L.; Brandão, L.R.; Brueckmann, M.; Chalmers, E.; Gropper, S.; Harper, R.; Huang, F.; Luciani, M.; et al. Design and rationale for the DIVERSITY study: An open-label, randomized study of dabigatran etexilate for pediatric venous thromboembolism. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. These Highlights Do Not Include All the Information Needed to Use XARELTO® Safely and Effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for XARELTO. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215859s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Radulescu, V.C. Anticoagulation Therapy in Children. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 43, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lensing, A.W.A.; Male, C.; Young, G.; Kubitza, D.; Kenet, G.; Patricia Massicotte, M.; Chan, A.; Molinari, A.C.; Nowak-Goettl, U.; Pap, Á.F.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus standard anticoagulation for acute venous thromboembolism in childhood. Design of the EINSTEIN-Jr phase III study. Thromb. J. 2018, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, R.M.; Burns, K.M.; Glatz, A.C.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Monagle, P.; Newburger, J.W.; Swan, E.A.; Wheaton, O.; Male, C. A multi-national trial of a direct oral anticoagulant in children with cardiac disease: Design and rationale of the Safety of ApiXaban on Pediatric Heart disease on the preventioN of Embolism (SAXOPHONE) study. Am. Heart J. 2019, 217, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Apixaban Versus Vitamin K Antagonist (VKA) or Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) in Pediatric Subjects with Congenital or Acquired Heart Disease Requiring Anticoagulation. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02981472 (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- A Study of the Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Preventing Blood Clots in Children with Leukemia Who Have a Central Venous Catheter and Are Treated with Asparaginase. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02369653?view=results (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Apixaban for the Acute Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism in Children. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02464969 (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Edoxaban for Prevention of Blood Vessels Being Blocked by Clots (Thrombotic Events) in Children at Risk Because of Cardiac Disease. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03395639 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- McCrindle, B.W.; Michelson, A.D.; Bergen, A.H.V.; Horowitz, E.S.; Sandoval, J.P.; Justino, H.; Harris, K.C.; Jefferies, J.L.; Pina, L.M.; Peluso, C.; et al. Thromboprophylaxis for Children Post-Fontan Procedure: Insights from the UNIVERSE Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study, Year | Design | Patients | Age | Intervention | Comparator | Outcomes | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halton et al., 2017 [19] | Multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase IIa study | 18 children who completed VTE treatment (UFH, LMWH, or OAT) | 1–12 years | Dabigatran in oral liquid formulation (the equivalent of 150 mg in adults) | NA | (a) Dabigatran had similar and predictable PK and PD profiles compared to adults (b) No reported severe bleeding events, recurrent VTE, or other adverse events | 30 days |
| Halton et al., 2017 [20] | Multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase IIa study | 8 children who completed VTE treatment (UFH, LMWH) | <12 months | Dabigatran in oral liquid formulation (the equivalent of 150 mg in adults) | NA | (a) Dabigatran had similar and predictable PK and PD profiles compared to adults (b) No reported bleeding events, death, or other adverse events | 37 days |
| Halton et al., 2021 [21] | Multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, phase 2b/3 study(DIVERSITY) | 328 children treated initially with UFH or LMWH | <18 years | Age- and weight-adjusted dose of Dabigatran | Standard anticoagulants (UFH, LMWH, VKAs, fondaparinux) | (a) Primary composite outcome (complete thrombus resolution, freedom from recurrent VTE, death) was similar in both groups (b) Risk of major bleeding events was similar (HR 0.94, 95% CI, 0.17–5.16, p = 0.95) | 4 months |
| Brandao et al., 2020 [22] | Open-label, single-arm, prospective cohort study | 203 children treated with standard therapy for ≥3 months or completed DIVERSITY study | 3 months–18 years | Age- and weight-adjusted dose of Dabigatran | NA | (a) No reported deaths (b) 1% of patients had VTE recurrence (c) Major bleedings were reported in 1.5% of patients (d) Minor bleedings were observed in 18.2% of patients | 12 months |
| Willman et al., 2018 [23] | Multicenter, phase I study (EINSTEIN-Jr) | 59 children who completed VTE treatment | 0.5–18 years | Bodyweight-adjusted single dose of rivaroxaban | NA | Plasma concentration-time profile was within 90% prediction interval, derived from PK modeling | NA |
| Kubitza et al., 2018 [24] | Multicenter, open-label, phase I study (EINSTEIN-Jr) | 59 children who completed VTE treatment | 0.5–18 years | Bodyweight-adjusted single dose of rivaroxaban | NA | (a) Rivaroxaban had predictable PK profile (b) Rivaroxaban was well tolerated, with no reported deaths, major or nonmajor bleeding events | 23 days |
| Monagle et al., 2019 [25] | Multicenter, single-arm, phase II studies | 93 children with VTE treated with LMWH or VKAs for at least 2 months (6 weeks for CR-VTE) | Birth to 17 years | Bodyweight-adjusted 20 mg-equivalent doses of rivaroxaban (once-daily, twice-daily, or three times daily) | NA | (a) No reported major bleeding events (b) 4% of patients had nonmajor bleeding events (c) No symptomatic recurrent VTE | 30 days |
| Young et al., 2019 [26] | Multicenter, open-label, phase III study | 335 children with VTE, treated initially with heparin or LMWH | Birth to 17 years | Bodyweight-adjusted dose of rivaroxaban (once-daily, twice-daily, or three times daily) | NA | (a) No reported major bleeding events (b) 3.2% of patients had nonmajor bleedings (c) Repeat imaging: 39.2% normalized, 39.6% improved, 0.3% deteriorated, no relevant changes in 5.1% | 3 months |
| Male et al., 2019 [5] | Multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase III study | 500 children with VTE were treated initially with heparin | Birth to 17 years | Bodyweight-adjusted 20 mg-equivalent doses of rivaroxaban | Standard anticoagulants (heparin or VKAs) | (a) Symptomatic recurrent VTE: HR 0.40, 95% CI, 0.11–1.41 (b) Major or nonmajor bleedings: HR 1.58, 95% CI, 0.51–6.27 (c) Only nonmajor bleedings in the rivaroxaban group (two major bleedings in heparin/VKAs group) | 91 days |
| Pinchinat et al., 2019 [27] | An observational, single-arm pilot study | 15 patients with bodyweight > 40 kg who experienced a primary VTE event | 12–21 years | Apixaban initiated within 72 h of VTE diagnosis | NA | (a) Thrombus resolution in 55% of cases and a reduction in thrombotic burden in the rest of the patients (b) No recurrent VTE was reported | 90 |
| Study | Design | Context | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02981472 | Multicenter, open-label, randomized study | Pediatric patients with congenital or acquired heart disease requiring chronic anticoagulation | Apixaban for thromboembolism prevention versus VKAs | (a) Major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events (b) Incidence of thrombotic events and death related to thromboembolic events (c) All-cause death |
| NCT02369653 | Multicenter, open-label, randomized study | Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoma treated with Asparaginase | Apixaban for thromboembolism prevention versus no anticoagulation | (a) Incidence of VTE, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and death related to VTE (b) Major bleeding (c) Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding |
| NCT02464969 | Open-label, randomized study | Children with VTE requiring anticoagulation | Apixaban versus standard of care (heparin, low molecular weight heparin, VKAs) | (a) Major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events (b) Symptomatic and asymptomatic recurrent VTE and mortality linked to VTE |
| NCT03395639 | Multicenter, open-label, randomized study | Children with cardiac disease with a high risk of thromboembolic events | Edoxaban versus standard of care (low molecular weight heparin, VKAs) | (a) Major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events (b) Symptomatic thromboembolic events (c) Death related to thromboembolic events |
| NCT02798471 | Multicenter, open-label, phase III, randomized study | Children with confirmed VTE | Edoxaban versus standard of care (low molecular weight heparin, heparin, VKAs, fondaparinux) | (a) Symptomatic recurrent VTE (b) Death linked to VTE (c) Thrombotic burden resolution/extension (d) Major bleeding (e) Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moisa, S.M.; Trandafir, L.M.; Brinza, C.; Miron, I.C.; Tarca, E.; Butnariu, L.I.; Burlacu, A. Current Antithrombotic Therapy Strategies in Children with a Focus on Off-Label Direct Oral Anticoagulants—A Narrative Review. Children 2022, 9, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071093
Moisa SM, Trandafir LM, Brinza C, Miron IC, Tarca E, Butnariu LI, Burlacu A. Current Antithrombotic Therapy Strategies in Children with a Focus on Off-Label Direct Oral Anticoagulants—A Narrative Review. Children. 2022; 9(7):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071093
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoisa, Stefana Maria, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Crischentian Brinza, Ingrith Crenguta Miron, Elena Tarca, Lacramioara Ionela Butnariu, and Alexandru Burlacu. 2022. "Current Antithrombotic Therapy Strategies in Children with a Focus on Off-Label Direct Oral Anticoagulants—A Narrative Review" Children 9, no. 7: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071093
APA StyleMoisa, S. M., Trandafir, L. M., Brinza, C., Miron, I. C., Tarca, E., Butnariu, L. I., & Burlacu, A. (2022). Current Antithrombotic Therapy Strategies in Children with a Focus on Off-Label Direct Oral Anticoagulants—A Narrative Review. Children, 9(7), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071093