Effectiveness of Indirect and Direct Laryngoscopes in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection and Data Collection
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
2.5. Risk of Bias within Individual Studies
2.6. Certainty of Evidence
2.7. Publication Bias
2.8. Sensitivity Analysis
2.9. Subgroup Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Studies in the Meta-Analysis
3.2. Risk of Bias
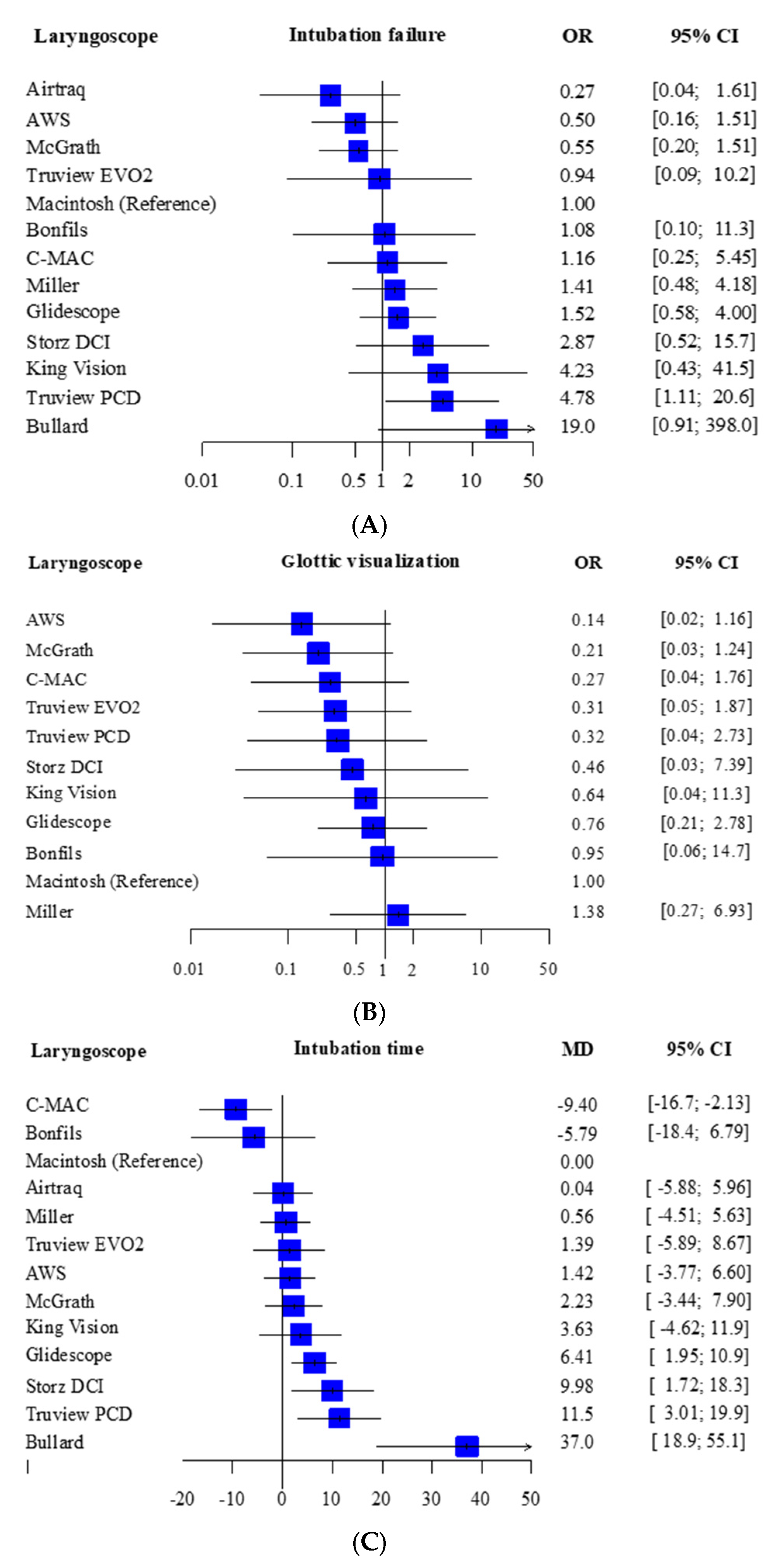
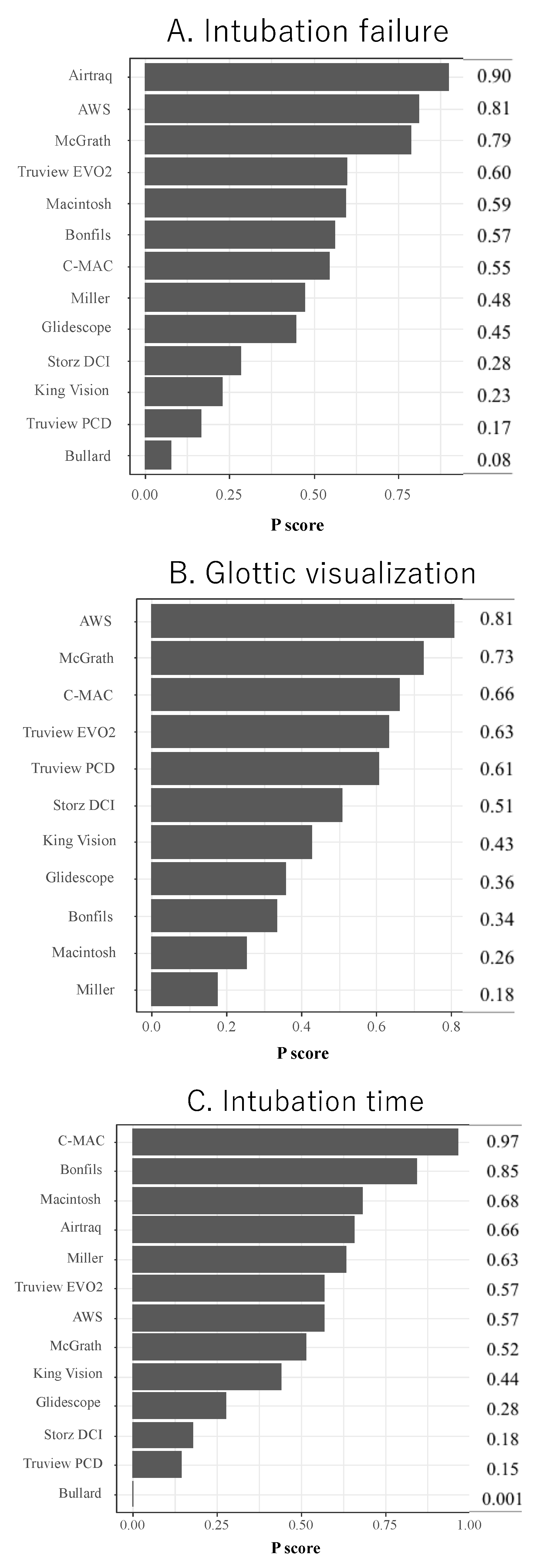
3.3. Primary Outcome
Intubation Failure at First Attempt
3.4. Secondary Outcome
Glottic Visualization and Intubation Time
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3.6. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinrich, S.; Birkholz, T.; Ihmsen, H.; Irouschek, A.; Ackermann, A.; Cesnjevar, R.; Schmidt, J. Incidence and predictors of poor laryngoscopic view in children undergoing pediatric cardiac surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.; von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S. The normal and the challenging pediatric airway. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2012, 22, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, R.A.; Posner, K.L.; Ward, R.J.; Cheney, F.W. Adverse respiratory events in anesthesia: A closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology 1990, 72, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.K.; Cohen, M.M. The airway: Problems and predictions in 18,500 patients. Can. J. Anaesth. 1994, 41, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mort, T.C. Emergency tracheal intubation: Complications associated with repeated laryngoscopic attempts. Anesth. Analg. 2004, 99, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatten, A.; Litz, S.; MacManus, B.; Launcelott, S.; Soder, C. A comparison of the GlideScope video laryngoscope and standard direct laryngoscopy in children with immobilized cervical spine. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Xin, J.; Yang, Z. Efficacy and safety of videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy in paediatric intubation: A meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020, 66, 109968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, H. Pediatric video laryngoscope versus direct laryngoscope: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2014, 24, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Moher, D.; Cameron, C. The PRISMA Extension Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available online: www.cochrane.org/training/cochranehandbook (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J.; Group, G.W. GRADE- an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valkenhoef, G.; Dias, S.; Ades, A.E.; Welton, N.J. Automated generation of node-splitting models for assessment of inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2016, 7, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakopoulou, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Papakonstantinou, T.; Chaimani, A.; Del Giovane, C.; Egger, M.; Salanti, G. CINeMA: An approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis. PLoS Med 2020, 17, e1003082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucker, G.; Schwarzer, G. Ranking treatments in frequentist network meta-analysis works without resampling methods. BMC Med Res Methodol 2015, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, I.K.; Kwak, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Comparison of Pentax Airway Scope and Macintosh laryngoscope for orotracheal intubation in children: A randomised non-inferiority trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2019, 63, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnair, D.; Baraclough, D.; Wilson, G.; Bloch, M.; Engelhardt, T. Pediatric airway management: Comparing the Berci-Kaplan Video Laryngoscope with direct laryngoscopy. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2009, 19, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redel, A.; Karademir, F.; Schlitterlau, A.; Frommer, M.; Scholtz, L.U.; Kranke, P.; Kehl, F.; Roewer, N.; Lange, M. Validation of the GlideScope video laryngoscope in pediatric patients. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2009, 19, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Na, H.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.D. GlideScope video laryngoscope: A randomized clinical trial in 203 paediatric patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, P.; Vajifdar, H. A comparison of Truview infant EVO2 laryngoscope with the Miller blade in neonates and infants. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2009, 19, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nileshwar, A.; Garg, V. Comparison of Bullard laryngoscope and short-handled Macintosh laryngoscope for orotracheal intubation in pediatric patients with simulated restriction of cervical spine movements. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2010, 20, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, M.T.; Memis, D.; Kargi, M.; Oktay, Z.; Sut, N. Comparison of TruView EVO2 with Miller laryngoscope in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 27, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.S. A comparison of GlideScope videolaryngoscopy with direct laryngoscopy for nasotracheal intubation in children. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2011, 21, 1165–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiadjoe, J.E.; Gurnaney, H.; Dalesio, N.; Sussman, E.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Stricker, P.A. A prospective randomized equivalence trial of the GlideScope Cobalt(R) video laryngoscope to traditional direct laryngoscopy in neonates and infants. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riad, W.; Moussa, A.; Wong, D.T. Airtraq versus Macintoch laryngoscope in intubation performance in the pediatric population. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2012, 6, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlatten, A.; Fielding, A.; Bernard, A.; Litz, S.; MacManus, B.; Soder, C. Comparison of the airtraq laryngoscope to the direct laryngoscopy in the pediatric airway. J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2012, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.C.; Marsh, C.J.; Beringer, R.M.; Nolan, J.A.; Choi, A.Y.; Medlock, K.E.; Mason, D.G. A randomised, controlled trial comparing the Airtraq optical laryngoscope with conventional laryngoscopy in infants and children. Anaesthesia 2012, 67, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Q.E.; Amir, S.H.; Firdaus, U.; Siddiqui, O.A.; Azhar, A.Z. A comparative study of the efficacy of Pediatric Airtraq(R) with conventional laryngoscope in children. Minerva Anestesiol. 2013, 79, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, J.; Laschat, M.; Hellmich, M.; Wappler, F. A randomized controlled comparison of the Bonfils fiberscope and the GlideScope Cobalt AVL video laryngoscope for visualization of the larynx and intubation of the trachea in infants and small children with normal airways. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2013, 23, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, R.; Sung, W.; Sessler, D.I.; Sanchez, I.P.; Mendoza, M.L.; Mascha, E.J.; Niezgoda, J. Comparison of the Truview PCD and the GlideScope((R)) video laryngoscopes with direct laryngoscopy in pediatric patients: A randomized trial. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Samanta, A.; Mitra, S.; Jamil, S.N. Comparative evaluation of Airtraq optical Laryngoscope and Miller’s blade in paediatric patients undergoing elective surgery requiring tracheal intubation: A randomized, controlled trial. Indian J. Anaesth. 2017, 61, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudon, A.; Bordes-Demolis, M.; Blondeau, B.; Sibai de Panthou, N.; Ferrand, N.; Bello, M.; Dahlet, V.; Semjen, F.; Biais, M.; Nouette-Gaulain, K. Comparison of the McGrath((R)) MAC video laryngoscope with direct Macintosh laryngoscopy for novice laryngoscopists in children without difficult intubation: A randomised controlled trial. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2017, 36, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, N.; Hajduk, J.; Sohn, L.; Huang, A.; Sawardekar, A.; Albers, B.; Bienia, S.; De Oliveira, G.S. Randomized equivalence trial of the King Vision aBlade videolaryngoscope with the Miller direct laryngoscope for routine tracheal intubation in children <2 yr of age. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Konoike, Y.; Tsujimoto, T.; Syoji, Y.; Hananoka, T.; Abe, S.; Ohata, J. Comparison of McGRATH MAC, Airway scope, and Miller laryngoscope for pediatric tracheal intubation by novice anesthesiologists: A randomized clinical trial. Jpn. Clin. Pediatric Anesth. 2017, 23, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, N.; Jain, A. A randomised trial to compare Truview PCD((R)), C-MAC((R)) and Macintosh laryngoscopes in paediatric airway management. Asian J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 55, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadi, M.G.; Roddy, K.J.; Ghazal, E.A.; Um, M.; Neiheisel, A.J.; Applegate, R.L., 2nd. Comparison of the GlideScope Cobalt(R) and Storz DCI(R) Video Laryngoscopes in Children Younger Than 2 Years of Age During Manual In-Line Stabilization: A Randomized Trainee Evaluation Study. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2017, 33, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Mehta, S.; Gandhi, K.; Arora, S.; Parikh, B.; Abas, M. Comparison of intubation conditions with CMAC Miller videolaryngoscope and conventional Miller laryngoscope in lateral position in infants: A prospective randomized trial. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2018, 28, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kwak, H.J.; Jung, W.S.; Chang, M.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y. A comparison between McGrath MAC videolaryngoscopy and Macintosh laryngoscopy in children. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2018, 62, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.A.; Rojas, J.L.; Medina-Vera, A.J. Haemodynamic response and effectiveness of tracheal intubation with Airtraq(R) versus Macintosh laryngoscope in paediatric patient undergoing elective surgery: Prospective, randomised and blind clinical trial. Rev. Española Anestesiol. Reanim. 2018, 65, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Chae, Y.J.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H. A comparison of the Macintosh laryngoscope, McGrath video laryngoscope, and Pentax Airway Scope in paediatric nasotracheal intubation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, L.; Cinar, A.S. Comparison of Macintosh Laryngoscope and GlideScope(R) for Orotracheal Intubation in Children Older Than One Year. Şişli Etfal Hastanesi Tıp Bülteni 2019, 53, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Okuda, M.; Sato Boku, A.; Tachi, N.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamada, T.; Yamada, M. Usefulness of Airway Scope for intubation of infants with cleft lip and palate-comparison with Macintosh laryngoscope: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.R.; El Amrousy, D. GlideScope((R)) cobalt video laryngoscope versus direct Miller laryngoscope for lateral position-tracheal intubation in neonates with myelodysplasia: A prospective randomized study. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangasa, N.; Dali, J.S.; Sharma, K.R.; Arya, M.; Pachisia, A.V. Comparative evaluation of Truview evo2 and Macintosh laryngoscope for ease of orotracheal intubation in children—A prospective randomized controlled trial. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 35, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, B.; Liu, K.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yin, H. Comparison of GlideScope Video Laryngoscopy and Direct Laryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Neonates. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, T.B.; Reis, A.G.; Farhat, S.C.L.; Carvalho, V.E.L.; Schvartsman, C. Changing the view: Video versus direct laryngoscopy for intubation in the pediatric emergency department. Medicine 2020, 99, e22289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manirajan, M.; Bidkar, P.U.; Sivakumar, R.K.; Lata, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Jha, A.K. Comparison of paediatric King Vision videolaryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope for elective tracheal intubation in children of age less than 1 year: A randomised clinical trial. Indian J. Anaesth. 2020, 64, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiyeva, K.; Can, O.S.; Baytas, V.; Yildirim Guclu, C. Comparison of the C-MAC D-Blade videolaryngoscope and direct laryngoscope in pediatric patients: Randomized controlled trial. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2021, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, R.S.; Lehane, J. Difficult tracheal intubation in obstetrics. Anaesthesia 1984, 39, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshijima, H.; Kuratani, N.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Takeuchi, R.; Shiga, T.; Masaki, E. Pentax Airway Scope(R) vs Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia 2014, 69, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshijima, H.; Mihara, T.; Maruyama, K.; Denawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Shiga, T.; Nagasaka, H. McGrath videolaryngoscope versus Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 46, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesdale, D.E.; Chau, A.; Isac, G.; Ayas, N.; Foster, D.; Irwin, C.; Choi, P.; Canadian Critical Care Trials, G. Video-laryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy in critically ill patients: A pilot randomized trial. Can. J. Anaesth. 2012, 59, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, D.R.; Semler, M.W.; Lentz, R.J.; Matthews, D.T.; Assad, T.R.; Norman, B.C.; Keriwala, R.D.; Ferrell, B.A.; Noto, M.J.; Shaver, C.M.; et al. Randomized Trial of Video Laryngoscopy for Endotracheal Intubation of Critically Ill Adults. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
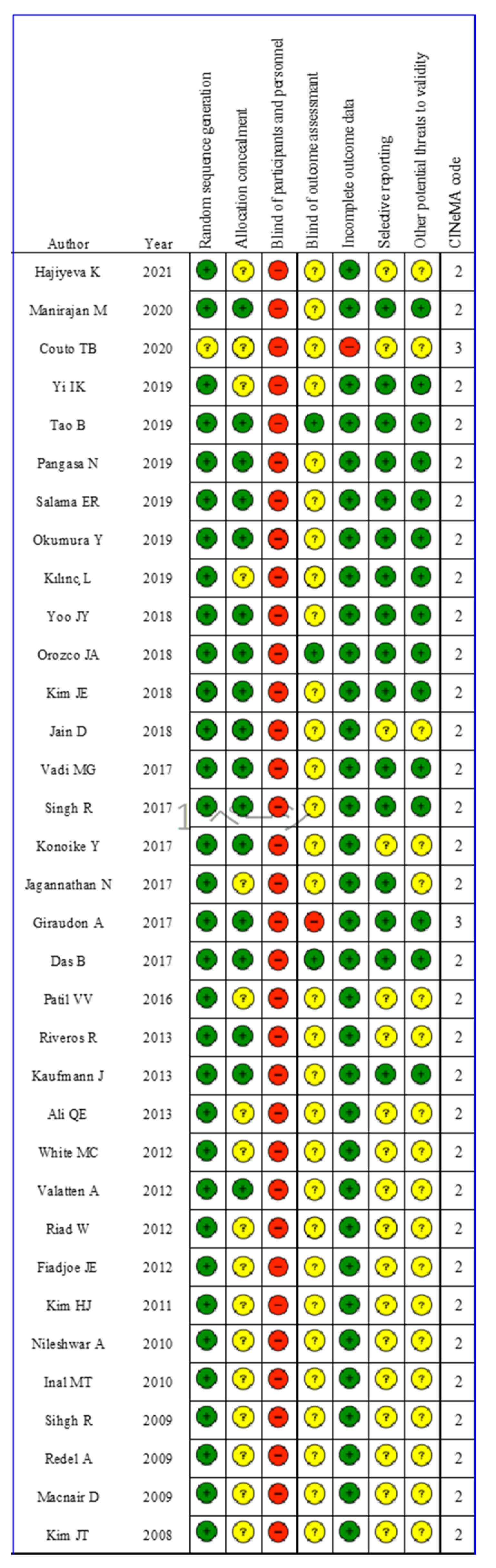
| Author | Year | Type of Laryngoscopes | Number of Participants | Patients Age or Weight | ASA-PS | Airway Condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hajiyeva K | 2021 | Macintosh | 28 | 10–40 kg | Ⅰ–Ⅲ | Normal |
| C-MAC | 28 | ||||||
| 2 | Manirajan M | 2020 | Macintosh | 39 | 0–1 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| King Vision | 39 | ||||||
| 3 | Couto TB | 2020 | Macintosh | 141 | 1–19 y | N/A | Difficult (Emergency department) |
| McGrath | 50 | ||||||
| 4 | Yi IK | 2019 | Macintosh | 68 | 1–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| AWS | 68 | ||||||
| 5 | Tao B | 2019 | Macintosh | 35 | ≦28 d | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | No limitation |
| Glidescope | 35 | ||||||
| 6 | Pangasa N | 2019 | Macintosh | 25 | 2–8 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Truview EVO2 | 25 | ||||||
| 7 | Salama ER | 2019 | Miller | 30 | ≦28 d | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 30 | ||||||
| 8 | Okumura Y | 2019 | Macintosh | 20 | 3–11 m | Ⅰ | Normal |
| AWS | 20 | ||||||
| 9 | Kılınç L | 2019 | Macintosh | 40 | 1–12 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 40 | ||||||
| 10 | Yoo JY | 2018 | Macintosh | 36 | 1–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| AWS | 35 | ||||||
| McGrath | 35 | ||||||
| 11 | Orozco JA | 2018 | Macintosh | 40 | 2–8 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| AWS | 40 | ||||||
| 12 | Kim JE | 2018 | Macintosh | 42 | 1–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| McGrath | 42 | ||||||
| 13 | Jain D | 2018 | Miller | 32 | <1 y | Ⅰ–Ⅲ | Difficult (lateral position) |
| C-MAC | 31 | ||||||
| 14 | Vadi MG | 2017 | Miller | 31 | 2–24 m | Ⅰ–Ⅲ | Difficult (MILS) |
| Glidescope | 31 | ||||||
| Storz DCI | 31 | ||||||
| 15 | Singh R | 2017 | Macintosh | 50 | 1–6 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | No limitation |
| C-MAC | 50 | ||||||
| Truview PCD | 50 | ||||||
| 16 | Konoike Y | 2017 | Miller | 29 | 1.7–6 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| AWS | 30 | ||||||
| McGrath | 31 | ||||||
| 17 | Jagannathan N | 2017 | Miller | 100 | <2 y | N/A | Normal |
| King Vision | 100 | ||||||
| 18 | Giraudon A | 2017 | Macintosh | 67 | 10–20 kg | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| McGrath | 65 | ||||||
| 19 | Das B | 2017 | Miller | 30 | 2–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Airtraq | 30 | ||||||
| 20 | Patil VV | 2016 | Macintosh | 30 | 8–18 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| C-MAC | 30 | ||||||
| 21 | Riveros R | 2013 | Macintosh | 45 | 0–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅲ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 44 | ||||||
| Truview PCD | 45 | ||||||
| 22 | Kaufmann J | 2013 | Glidescope | 47 | <7 y | Ⅱ | Normal |
| Bonfils | 44 | ||||||
| 23 | Ali QE | 2013 | Macintosh | 17 | 1–5 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Airtraq | 17 | ||||||
| 24 | White MC | 2012 | Macintosh | 30 | 0–6 m, 6 m–6 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Airtraq | 30 | ||||||
| 25 | Valatten A | 2012 | Macintosh | 25 | ≦5 y | N/A | Normal |
| Airtraq | 24 | ||||||
| 26 | Riad W | 2012 | Macintosh | 25 | 2–10 y | Ⅰ | Normal |
| Airtraq | 25 | ||||||
| 27 | Fiadjoe JE | 2012 | Macintosh | 30 | ≦12 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 30 | ||||||
| 28 | Kim HJ | 2011 | Macintosh | 40 | <10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 40 | ||||||
| 29 | Nileshwar A | 2010 | Macintosh | 20 | 2–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Bullard | 20 | ||||||
| 30 | Inal MT | 2010 | Miller | 25 | 2–8 y | N/A | N/A |
| Truview EVO2 | 25 | ||||||
| 31 | Sihgh R | 2009 | Miller | 30 | 1–10 kg | N/A | N/A |
| Truview EVO2 | 30 | ||||||
| 32 | Redel A | 2009 | Macintosh | 30 | 7 m–10 y | Ⅰ–Ⅲ | Normal |
| Glidescope | 30 | ||||||
| 33 | Macnair D | 2009 | Macintosh | 30 | 2–16 y | Ⅰ–Ⅱ | Normal |
| Storz DCI | 30 | ||||||
| 34 | Kim JT | 2008 | Macintosh | 100 | 3 m–17 y | N/A | No limitation |
| Glidescope | 103 |
| Patients: pediatric patients who received tracheal intubation | 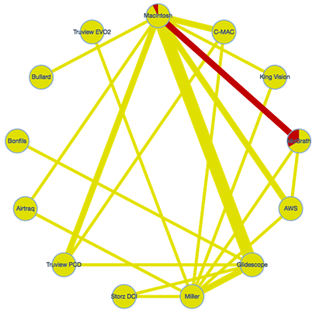 | |||
| Interventions: indirect laryngoscope, miller laryngoscope | ||||
| Comparator (reference): macintosh laryngoscope | ||||
| Outcome: failure of tracheal intubation at first attempt | ||||
| Setting: elective surgery | ||||
| Total studies: 31 RCT Total Participants: 1930 | Relative effect (95% CI) | Certainty of evidence | Reasons for downgrading | P score |
| Airtraq (1 RCT; 34 participants) | 0.27 (0.04–1.61) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.90 |
| Airway scope (2 RCT; 137 participants) | 0.50 (0.16–1.51) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.81 |
| Bonfils (1 RCT; 84 participants) | 1.08 (0.10–11.3) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.57 |
| Bullard (1 RCT; 40 participants) | 19.0 (0.91–398.0) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and heterogeneity | 0.08 |
| C-MAC (3 RCT; 256 participants) | 1.16 (0.25–5.45) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.55 |
| Glidescope (5 RCT; 408 participants) | 1.52 (0.58–4.00) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.45 |
| King Vision (1 RCT; 78 participants) | 4.23 (0.43–41.5) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.23 |
| Macintosh (13 RCT; 659 participants) | No estimable | Reference comparator | No estimable | 0.60 |
| McGrath (3 RCT; 347 participants) | 0.55 (0.20–1.51) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.79 |
| Miller (8 RCT; 594 participants) | 1.41 (0.48–4.18) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.48 |
| Storz DCI (1 RCT; 62 participants) | 2.87 (0.52–15.7) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.28 |
| Truview EVO2 (1 RCT; 60 participants) | 0.94 (0.09–10.2) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.60 |
| Truview PCD (2 RCT; 142 participants) | 4.78 (1.11–20.6) | ⨁◯◯◯ Low | Risk of bias and imprecision | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoshijima, H.; Mihara, T.; Kokubu, S.; Takeda, S.; Shiga, T.; Mizuta, K. Effectiveness of Indirect and Direct Laryngoscopes in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Children 2022, 9, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091280
Hoshijima H, Mihara T, Kokubu S, Takeda S, Shiga T, Mizuta K. Effectiveness of Indirect and Direct Laryngoscopes in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Children. 2022; 9(9):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091280
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoshijima, Hiroshi, Takahiro Mihara, Shinichi Kokubu, Sakura Takeda, Toshiya Shiga, and Kentaro Mizuta. 2022. "Effectiveness of Indirect and Direct Laryngoscopes in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Children 9, no. 9: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091280
APA StyleHoshijima, H., Mihara, T., Kokubu, S., Takeda, S., Shiga, T., & Mizuta, K. (2022). Effectiveness of Indirect and Direct Laryngoscopes in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Children, 9(9), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091280






