Residence with a Person Who Used Substances and Childhood Anxiety and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2019 National Health Interview Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Variable Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipari, R.N.; VanHorn, S.L. Children Living with Parents Who Have a Substance Use Disorder. In The CBHSQ Report; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK464590/ (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Ali, M.M.; Dean, D.; Hedden, S.L. The relationship between parental mental illness and/or substance use disorder on adolescent substance use disorder: Results from a nationally representative survey. Addict. Behav. 2016, 59, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arria, A.M.; Mericle, A.A.; Meyers, K.; Inters, K.C. Parental substance use impairment, parenting and substance use disorder risk. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2012, 43, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, K.J. Psychological Characteristics of Children of Alcoholics. Alcohol Health Res. World 1997, 21, 247–254. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6826809/ (accessed on 20 January 2021). [PubMed]
- Lieb, R.; Merikangas, K.R.; Höfler, M.; Rfister, H.; Isensee, B.; Wittchen, H.U. Parental alcohol use disorders and alcohol use and disorders in offspring: A community study. Psychol. Med. 2002, 32, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straussner, S.L.A.; Fewell, C.H. A review of recent literature on the impact of parental substance use disorders on children and the provision of effective services. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2018, 31, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussong, A.M.; Zucker, R.A.; Wong, M.M.; Fitzgerald, H.E.; Puttler, L.I. Social Competence in Children of Alcoholic Parents Over Time. Dev. Psychol. 2005, 41, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, J.M.; Shadur, J.M.; Burns, A.R.; Hussong, A.M. Understanding the Diverse Needs of Children Whose Parents Abuse Substances. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2012, 5, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, L.; Howsare, J.; Byrne, M. The Impact of Substance Use Disorders on Families and Children: From Theory to Practice. Soc. Work Public Health 2013, 28, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, N.R.; Mechling, B.; Palumbo, R.; Woodard, E. Children of Parents with Opioid Use Disorder. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2020, 59, 1–7, Published online 9 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Venter, M.; Demyttenaere, K.; Bruffaerts, R. The Relationship between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Mental Health in Adulthood. A Systematic Literature Review. Tijdschr. Voor Psychiatr. 2013, 55, 259–268. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23595840/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Kroll, B. Living with an elephant: Growing up with parental substance misuse. Child Fam. Soc. Work 2004, 9, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussong, A.M.; Bauer, D.J.; Huang, W.; Hassin, L.; Her, K.J.; Zucker, R.A. Characterizing the life stressors of children of alcoholic parents. J. Fam. Psychol. JFPJD iv. Fam. Psychol. Am. Psychol. Assoc. Div. 2008, 22, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chae, W.; Min, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Jang, S.-I. Alcohol Consumption Frequency of Parents and Stress Status of Their Children: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007–2016). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bountress, K.; Hassin, L. Risk for behavior problems in children of parents with substance use disorders. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2015, 85, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Cornelius, J.; Wood, D.S.; Vanyukov, M. Psychopathology Risk Transmission in Children of Parents With Substance Use Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, R.; Gual, A.; Arcía, M.; García, M.; Arnau, J.; Pascual, F.; Cañuelo, B.; Rubio, G.; de Dios, Y.; Fernández-Eire, M.C.; et al. Children of alcoholics in Spain: From risk to pathology. Results from the ALFIL program. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2008, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.I.; Vandeleur, C.; Rothen, S.; Gholam-Rezaee, M.; Castelao, E.; Halfon, O.; Aubry, J.-M.; Ferrero, F.; Preisig, M. Risk of Mental Disorders in Children of Parents with Alcohol or Heroin Dependence: A Controlled High-Risk Study. Eur. Addict. Res. 2012, 18, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitasalo, K.; Holmila, M.; Jääskeläinen, M.; Santalahti, P. The effect of the severity of parental alcohol abuse on mental and behavioural disorders in children. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 28, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.Y.; Shen, S.; Lowers, L.; Locke-Wellman, J.; Matthews, A.G.; McDermott, M. Psychopathology in offspring from multiplex alcohol dependence families with and without parental alcohol dependence: A prospective study during childhood and adolescence. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 160, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikangas, K.R.; Dierker, L.C.; Szatmari, P. Psychopathology among Offspring of Parents with Substance Abuse and/or Anxiety Disorders: A High-Risk Study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1998, 39, 711–720. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9690934/ (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Chassin, L.; Pitts, S.C.; DeLucia, C.; Todd, M. A longitudinal study of children of alcoholics: Predicting young adult substance use disorders, anxiety, and depression. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1999, 108, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.D.; Patel, D.R. Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies for Anxiety Disorders in Childhood and Adolescence. In Anxiety Disorders Rethinking and Understanding Recent Discoveries; Kim, Y.-K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilens, T.E.; Biederman, J.; Bredin, E.; Hahesy, A.L.; Abrantes, A.; Neft, D.; Millstein, R.; Spencer, T.J. A Family Study of the High-Risk Children of Opioid- and Alcohol-Dependent Parents. Am. J. Addict. 2002, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, W.; Earls, F.; Frankel, O.; Shayka, J.J. Psychopathology in children of alcoholics. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1993, 32, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperman, S.; Schlosser, S.S.; Lidral, J.; Reich, W. Relationship of Child Psychopathology to Parental Alcoholism and Antisocial Personality Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1999, 38, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hill, S.Y.; Hruska, D.R. Childhood psychopathology in families with multigenerational alcoholism. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1992, 31, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, E.V.; Weissman, M.M.; Goldstein, R.B.; Mcavay, G.; Seracini, A.M.; Verdeli, H.; Wickramaratne, P.J. Psychopathology in children of parents with opiate dependence and/or major depression. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1998, 37, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsdóttir, J.; Orjasniemi, T.; Hrafnsdóttir, S. Psychosocial distress, physical illness, and social behaviour of close relatives to people with substance use disorders. J. Soc. Work Pract. Addict. 2020, 20, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Interview Survey; 2019. Public-Use Data File and Documentation. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/data-questionnaires-documentation.htm.2020 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Interview Survey. 2019; Public-Use Code Book for Sample Child. Available online: https://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS/Dataset_Documentation/NHIS/2019/child-codebook.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Cree, R.A.; Bitsko, R.H.; Robinson, L.R.; Holbrook, J.R.; Danielson, M.L.; Smith, C.; Kaminski, J.E.; Kenney, M.K.; Peacock, G. Health Care, Family, and Community Factors Associated with Mental, Behavioral, and Developmental Disordersand Poverty Among Children Aged 2–8 Years—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2018, 67, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golash-Boza, T. A Critical and Comprehensive Sociological Theory of Raceand Racism. Sociol Race Ethn. 2016, 2, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramlett, M.D.; Dahlhamer, J.M.; Bose, J.; Blumberg, S.J. New Procedures for Nonresponse Adjustments to the 2019 National Health Interview Survey Sampling Weights. Available online: https://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS/Dataset_Documentation/NHIS/2019/nonresponse-report-508.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Hardin, A.P.; Hackell, J.M. Age Limit of Pediatrics. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20172151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stata. Mlogit–Multinomial (Polytomous) Logistic Regression. Available online: https://www.stata.com/manuals/rmlogit.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Thapar, A.; Collishaw, S.; Pine, D.S.; Thapar, A.K. Depression in adolescence. Lancet 2012, 379, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, R.M.; Sherman, L.J.; Vladutiu, C.J.; Ali, M.M.; Lynch, S.E.; Bitsko, R.H.; Blumberg, S.J. Prevalence and Treatment of Depression, Anxiety, and Conduct Problems in US Children. J. Pediatr. 2019, 206, 256–267.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contractor, L.F.M.; Celedonia, K.L.; Cruz, M.; Douaihy, A.; Kogan, J.N.; Marin, R.; Stein, B.D. Mental Health Services for Children of Substance Abusing Parents: Voices from the Community. Community Ment. Health J. 2012, 48, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunins, H.V. Structural Racism and the Opioid Overdose Epidemic: The Need for Antiracist Public Health Practice. J. Public Health Manag. Pract. 2020, 26, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.P. An epigenetic, transgenerational model of increased mental health disorders in children, adolescents and young adults. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesdo, K.; Knappe, S.; Pine, D.S. Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Developmental Issues and Implications for DSM-V. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 32, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study | Parent(s) | Children | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authors | Diagnosis | n (% Male) | Age Range at Baseline (Years) | Outcome(s) * |
| Bountress and Chassin [15] | SUD | 567 (54.4) | 6–13 | internalizing behavior (including anxiety/depression) ** |
| Chassin et al. [22] | AD | 407 (53.1) | 10–15 | internalizing symptoms ∞ |
| Clark et al. [16] | SUD | 1167 (62.0) | 6–14 | Anxiety ** Depression ** |
| Díaz et al. [17] | AD | 518 (50.2) | 6–17 | Anxiety ** Depression ** |
| Hill et al. [20] | AD | 378 (not specified) | 8–18 | internalizing disorders (including anxiety/depression) ** ^ depression ** ^ |
| Hill and Hruska [27] | AD | 95 (52.6) | 8–18 | anxiety depression |
| Kuperman et al. [26] | AD | 463 (not specified) | (not specified) | anxiety (only separation anxiety) ** |
| Merikangas et al. [21] | SUD | 192 (51.0) | 7–18 | Anxiety ∞ depression |
| Nunes et al. [28] | SUD | 209 (50.7) | 6–17 | anxiety depression |
| Reich et al. [25] | AD | 158 (54.2) | 6–18 | Anxiety ** depression |
| Vidal et al. [18] | SUD | 276 (52.9) | 6–17 | anxiety depression ** |
| Wilens et al. [24] | SUD | 183 (58.5) | 6–18 | Anxiety ** Depression ** |
| Characteristic | Total n (%) | Has Lived with Someone Who Used Substances n (%) | Has Not Lived with Someone Who Used Substances n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 6642 (100.0) | 706 (9.7) | 5936 (90.3) |
| Anxiety frequency ** | |||
| never | 3718 (57.1) | 265 (38.2) | 3453 (59.1) |
| a few times a year | 1521 (22.7) | 181 (27.2) | 1340 (22.2) |
| monthly | 481 (6.7) | 80 (9.0) | 401 (6.5) |
| weekly | 560 (8.3) | 104 (15.5) | 456 (7.6) |
| daily | 362 (5.3) | 76 (10.2) | 286 (4.7) |
| Depression frequency ** | |||
| never | 4843 (74.7) | 353 (51.2) | 4490 (77.2) |
| a few times a year | 1126 (16.0) | 187 (27.2) | 939 (14.8) |
| monthly | 296 (4.2) | 70 (8.8) | 226 (3.7) |
| weekly | 263 (3.7) | 68 (8.8) | 195 (3.1) |
| daily | 114 (1.5) | 28 (4.0) | 86 (1.3) |
| Age ** (years) | |||
| Minimum–maximum | 5–17 | 5–17 | 5–17 |
| mean (95% CI) | 11.1 (10.9–11.2) | 11.9 (11.5–12.2) | 11.0 (10.8–11.1) |
| Sex | |||
| female | 3201 (48.9) | 342 (50.4) | 2859 (48.8) |
| male | 3441 (51.1) | 364 (49.6) | 3077 (51.2) |
| Race/ethnicity ** | |||
| Hispanic | 1567 (25.4) | 130 (19.5) | 1437 (26.1) |
| non-Hispanic Asian | 366 (4.3) | 3 (0.4) | 363 (4.8) |
| non-Hispanic Black | 766 (12.8) | 41 (6.0) | 725 (13.5) |
| non-Hispanic White | 3561 (52.1) | 479 (66.0) | 3082 (50.6) |
| 2+ races/non-Hispanic other | 382 (5.3) | 53 (8.1) | 329 (5.0) |
| Annual household income (USD) ** | |||
| $0–34,999 | 1381 (22.4) | 210 (30.9) | 1171 (21.5) |
| $35,000–49,999 | 770 (11.9) | 114 (16.2) | 656 (11.4) |
| $50,000–74,999 | 1127 (16.8) | 124 (18.2) | 1003 (16.6) |
| $75,000–99,999 | 871 (12.5) | 96 (11.6) | 775 (12.6) |
| $100,000 or greater | 2493 (36.4) | 162 (23.1) | 2331 (37.8) |
| Highest educational attainment by an adult in the household ** | |||
| less than high school diploma | 454 (8.7) | 62 (10.2) | 392 (8.6) |
| high school diploma | 1046 (16.0) | 128 (17.2) | 918 (15.9) |
| some college/associate degree | 1999 (29.1) | 290 (41.5) | 1709 (27.8) |
| college degree or greater | 3143 (46.2) | 226 (31.1) | 2917 (47.8) |
| Characteristic | Total n (%) | Included in Analysis n (%) | Excluded from Analysis n (%) *** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lived with someone who used substances ** | |||
| no | 8275 (92.0) | 5936 (90.3) | 2339 (96.5) |
| yes | 789 (8.0) | 706 (9.7) | 83 (3.5) |
| total | 9064 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2422 (100.0) |
| Anxiety frequency | |||
| never | 3785 (57.2) | 3718 (57.1) | 67 (62.8) |
| a few times a year | 1545 (22.6) | 1521 (22.7) | 24 (2.1) |
| monthly | 490 (6.7) | 481 (6.7) | 9 (7.4) |
| weekly | 566 (8.2) | 560 (8.3) | 6 (4.3) |
| daily | 369 (5.2) | 362 (5.3) | 7 (4.0) |
| total | 6755 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 113 (100.0) |
| Depression frequency | |||
| never | 4933 (74.8) | 4843 (74.7) | 90 (80.6) |
| a few times a year | 1144 (15.9) | 1126 (16.0) | 18 (13.8) |
| monthly | 297 (4.1) | 296 (4.2) | 1 (0.6) |
| weekly | 270 (3.7) | 263 (3.7) | 7 (5.0) |
| daily | 114 (1.5) | 114 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| total | 6758 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 116 (100.0) |
| Age **(years) | |||
| minimum–maximum | 0–17 | 5–17 | 0–17 |
| mean (95% CI) | 8.6 (8.5–8.7) | 11.1 (10.9–11.2) | 2.5 (2.4–2.6) |
| total | 9193 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2551 (100.0) |
| Sex | |||
| female | 4484 (49.0) | 3201 (48.9) | 1283 (49.0) |
| male | 4705 (51.1) | 3441 (51.1) | 1264 (51.0) |
| total | 9189 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2547 (100.0) |
| Race/ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic | 2173 (25.7) | 1567 (25.4) | 606 (26.4) |
| non-Hispanic Asian | 511 (4.4) | 366 (4.3) | 145 (4.5) |
| non-Hispanic Black | 1022 (12.7) | 766 (12.8) | 256 (12.6) |
| non-Hispanic White | 4921 (51.6) | 3561 (52.1) | 1360 (50.4) |
| 2+ races/non-Hispanic other | 566 (5.6) | 382 (5.3) | 184 (6.2) |
| total | 9193 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2551 (100.0) |
| Annual household income (USD) ** | |||
| $0–34,999 | 1921 (22.8) | 1381 (22.4) | 540 (23.9) |
| $35,000–49,999 | 1079 (12.1) | 770 (11.9) | 309 (12.5) |
| $50,000–74,999 | 1585 (17.4) | 1127 (16.8) | 458 (19.1) |
| $75,000–99,999 | 1257 (13.0) | 871 (12.5) | 386 (14.1) |
| $100,000 or greater | 3351 (34.7) | 2493 (36.4) | 858 (30.4) |
| total | 9193 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2551 (100.0) |
| Highest educational attainment by an adult in the household | |||
| less than high school diploma | 610 (8.5) | 454 (8.7) | 156 (8.1) |
| high school diploma | 1451 (16.4) | 1046 (16.0) | 405 (17.4) |
| some college/associate degree | 2693 (28.8) | 1999 (29.1) | 694 (27.9) |
| college degree or greater | 4426 (46.3) | 3143 (46.2) | 1283 (46.7) |
| total | 9180 (100.0) | 6642 (100.0) | 2538 (100.0) |
| Covariate | A Few Times a Year | Monthly | Weekly | Daily | F-Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) ** | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | ||
| Lived with someone who used substances | 17.24 * | ||||
| no (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
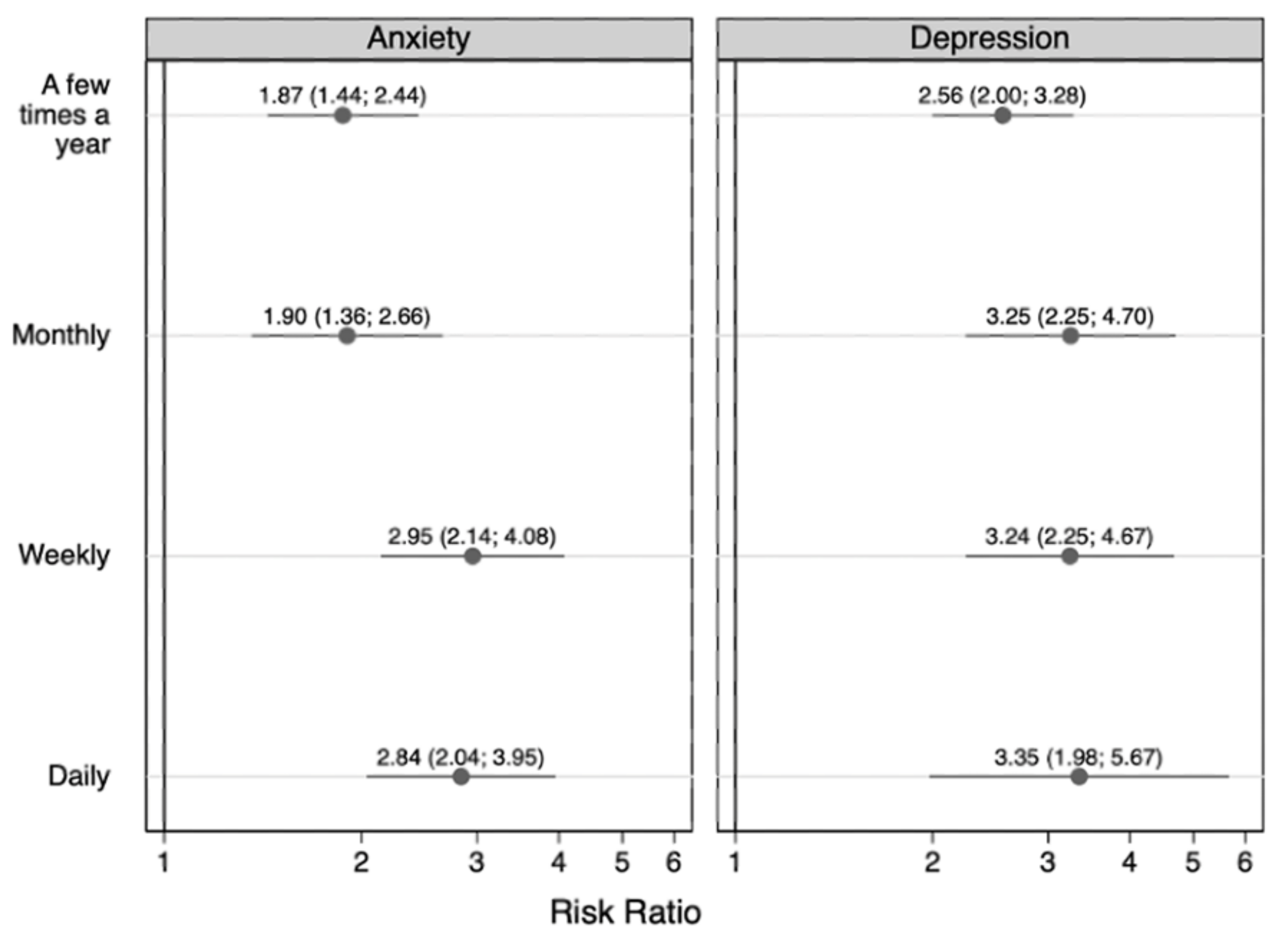
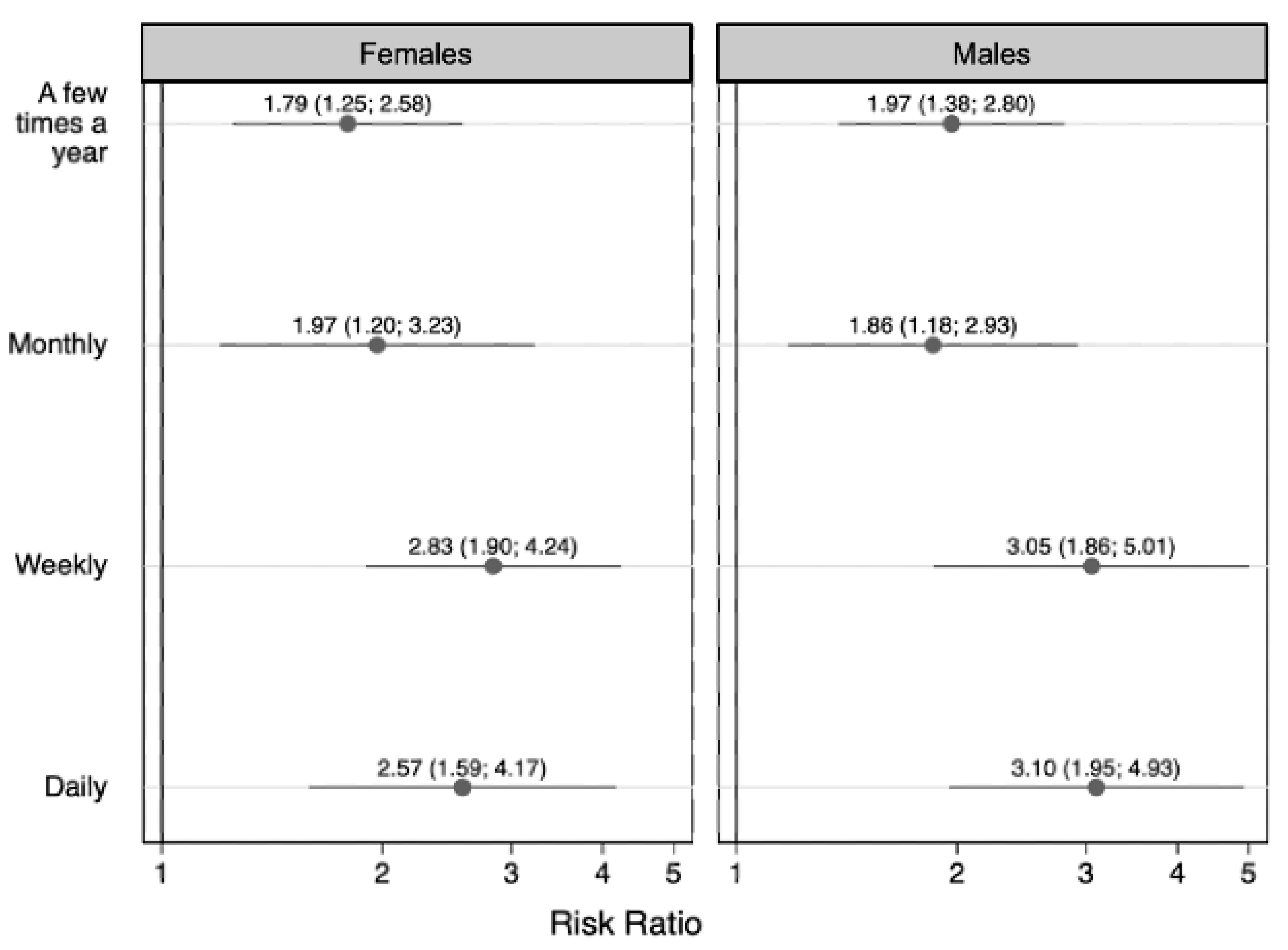
| yes | 1.87 (1.44, 2.44) | 1.90 (1.36, 2.66) | 2.95 (2.14, 4.08) | 2.84 (2.04, 3.95) | |
| Age | 9.24 * | ||||
| 1.05 (1.03, 1.06) | 1.07 (1.04, 1.11) | 1.04 (1.01, 1.07) | 1.05 (1.01, 1.09) | ||
| Sex | 4.09 * | ||||
| female (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| male | 0.85 (0.74, 0.97) | 0.80 (0.64, 0.99) | 0.70 (0.56, 0.87) | 1.00 (0.77, 1.29) | |
| Race/ethnicity | 6.16 * | ||||
| non-Hispanic White (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| Hispanic | 0.70 (0.58, 0.84) | 0.54 (0.38, 0.76) | 0.52 (0.37, 0.73) | 0.67 (0.49, 0.94) | |
| non-Hispanic Asian | 0.77 (0.57, 1.04) | 0.24 (0.10, 0.54) | 0.26 (0.14, 0.49) | 0.31 (0.13, 0.75) | |
| non-Hispanic Black | 0.60 (0.46, 0.78) | 0.26 (0.15, 0.44) | 0.32 (0.21, 0.49) | 0.62 (0.39, 0.96) | |
| 2+ races/non-Hispanic other | 0.66 (0.46, 0.94) | 0.65 (0.40, 1.05) | 0.68 (0.42, 1.10) | 0.82 (0.50, 1.35) | |
| Annual household income (USD) | 2.57 * | ||||
| $0–34,999 (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| $35,000–49,999 | 1.28 (0.97, 1.69) | 0.84 (0.56, 1.25) | 1.15 (0.74, 1.80) | 0.94 (0.60, 1.49) | |
| $50,000–74,999 | 1.14 (0.90, 1.45) | 0.55 (0.37, 0.81) | 1.13 (0.73, 1.73) | 0.52 (0.33, 0.84) | |
| $75,000–99,999 | 1.66 (1.27, 2.18) | 0.89 (0.56, 1.42) | 1.40 (0.85, 2.30) | 0.97 (0.62, 1.52) | |
| $100,000 or greater | 1.52 (1.20, 1.91) | 0.97 (0.68, 1.39) | 1.39 (0.93, 2.08) | 0.65 (0.43, 0.99) | |
| Highest educational attainment by an adult in the household | 2.41 * | ||||
| less than high school diploma (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| high school diploma | 1.32 (0.90, 1.94) | 2.21 (1.05, 4.64) | 1.63 (0.85, 3.10) | 0.59 (0.35, 1.00) | |
| some college/associate degree | 1.62 (1.11, 2.37) | 2.77 (1.42, 5.42) | 1.76 (0.92, 3.37) | 0.71 (0.43, 1.18) | |
| college degree or greater | 1.63 (1.13, 2.35) | 3.26 (1.62, 6.58) | 2.02 (1.03, 3.94) | 0.85 (0.49, 1.46) |
| Covariate | A Few Times a Year | Monthly | Weekly | Daily | F-Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) ** | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | ||
| Lived with someone who used substances | 24.59 * | ||||
| no (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| yes | 2.56 (2.00, 3.28) | 3.25 (2.25, 4.70) | 3.24 (2.25, 4.67) | 3.35 (1.98, 5.67) | |
| Age | 32.38 * | ||||
| 1.11 (1.09, 1.13) | 1.13 (1.09, 1.17) | 1.11 (1.06, 1.15) | 1.16 (1.08, 1.24) | ||
| Sex | 5.12 * | ||||
| female (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| male | 0.81 (0.69, 0.95) | 0.70 (0.53, 0.91) | 0.59 (0.43, 0.82) | 0.97 (0.61, 1.52) | |
| Race/ethnicity | 3.83 * | ||||
| non-Hispanic White (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| Hispanic | 0.69 (0.55, 0.86) | 0.46 (0.31, 0.69) | 0.52 (0.34, 0.77) | 0.55 (0.31, 0.97) | |
| non-Hispanic Asian | 0.68 (0.45, 1.00) | 0.27 (0.12, 0.62) | 0.19 (0.07, 0.49) | 0.23 (0.05, 0.97) | |
| non-Hispanic Black | 0.75 (0.56, 0.99) | 0.53 (0.33, 0.86) | 0.48 (0.27, 0.84) | 0.58 (0.27, 1.23) | |
| 2+ races/non-Hispanic other | 1.09 (0.78, 1.53) | 0.80 (0.39, 1.64) | 0.95 (0.55, 1.63) | 1.18 (0.57, 2.44) | |
| Annual household income (USD) | 2.18 * | ||||
| $0–$34,999 (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| $35,000–$49,999 | 1.06 (0.79, 1.43) | 1.30 (0.76, 2.25) | 0.79 (0.45, 1.39) | 0.54 (0.26, 1.11) | |
| $50,000–$74,999 | 0.95 (0.72, 1.26) | 1.06 (0.63, 1.78) | 0.42 (0.25, 0.71) | 0.32 (0.15, 0.69) | |
| $75,000–$99,999 | 1.14 (0.82, 1.57) | 1.09 (0.63, 1.90) | 0.44 (0.25, 0.77) | 0.71 (0.38, 1.34) | |
| $100,000 or greater | 1.03 (0.79, 1.34) | 1.45 (0.92, 2.29) | 0.44 (0.27, 0.73) | 0.34 (0.16, 0.75) | |
| Highest educational attainment by an adult in the household | 1.55 | ||||
| less than high school diploma (reference) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | 1.0 (referent) | |
| high school diploma | 1.01 (0.68, 1.51) | 1.84 (0.91, 3.71) | 0.88 (0.46, 1.71) | 0.61 (0.28, 1.30) | |
| some college/associate degree | 0.93 (0.64, 1.35) | 1.32 (0.67, 2.59) | 1.29 (0.70, 2.39) | 0.41 (0.20, 0.83) | |
| college degree or greater | 1.08 (0.74, 1.57) | 1.45 (0.72, 2.91) | 1.46 (0.77, 2.78) | 0.35 (0.15, 0.81) |
| Characteristic | Children’s Age | Children’s Sex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–11 Years n (%) | 12–17 Years n (%) | Females n (%) | Males n (%) | |
| Total | 3135 (100.0) | 3507 (100.0) | 3201 (100.0) | 3441 (100.0) |
| Anxiety | ||||
| never | 1904 (60.6) | 1814 (53.2) | 1701 (54.7) | 2017 (59.3) |
| a few times a year | 648 (20.9) | 873 (24.6) | 751 (23.6) | 770 (21.8) |
| monthly | 206 (5.9) | 275 (7.6) | 249 (7.2) | 232 (6.2) |
| weekly | 233 (7.8) | 327 (8.8) | 313 (9.5) | 247 (7.2) |
| daily | 144 (4.8) | 218 (5.8) | 187 (5.0) | 175 (5.5) |
| Depression | ||||
| never | 2504 (80.6) | 2339 (68.1) | 2252 (72.2) | 2591 (77.1) |
| a few times a year | 414 (12.6) | 712 (19.8) | 573 (17.1) | 553 (14.9) |
| monthly | 99 (3.0) | 197 (5.4) | 159 (4.8) | 137 (3.6) |
| weekly | 85 (2.9) | 178 (4.5) | 160 (4.5) | 103 (2.9) |
| daily | 33 (0.9) | 81 (2.2) | 57 (1.5) | 57 (1.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafry, Z.; Chui, K.; Stopka, T.J.; Corlin, L. Residence with a Person Who Used Substances and Childhood Anxiety and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2019 National Health Interview Survey. Children 2022, 9, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091296
Jafry Z, Chui K, Stopka TJ, Corlin L. Residence with a Person Who Used Substances and Childhood Anxiety and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2019 National Health Interview Survey. Children. 2022; 9(9):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091296
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafry, Zarena, Kenneth Chui, Thomas J. Stopka, and Laura Corlin. 2022. "Residence with a Person Who Used Substances and Childhood Anxiety and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2019 National Health Interview Survey" Children 9, no. 9: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091296
APA StyleJafry, Z., Chui, K., Stopka, T. J., & Corlin, L. (2022). Residence with a Person Who Used Substances and Childhood Anxiety and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2019 National Health Interview Survey. Children, 9(9), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091296







