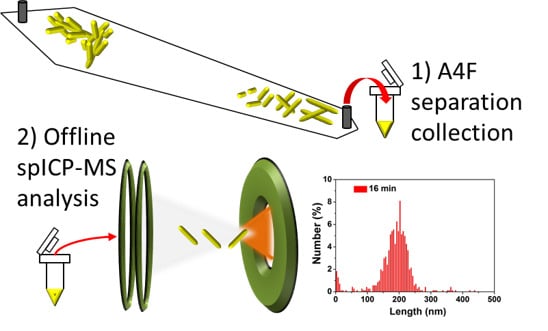
Fractionation and Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Gold Nanorods Using Asymmetric-Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Methods
| Channel parameters | Membrane | polyethersulfone (PES) |
| Membrane cut-off | 10 kDa | |
| Spacer | 250 µm or 350 µm | |
| Fractionation time | Elution time | 1 min |
| Focus + Injection time | 3 min | |
| Focusing time | 2 min | |
| Elution time | (45–65) min | |
| Injection volume | 100 µL | |
| Fractionation step, flow and volume | Injection flow | 0.2 mL min−1 |
| Elution flow (Vp) | 0.3 mL min−1 | |
| Cross flow (Vx) | 0.3–0.75 mL min−1 |
| ICP-MS | Thermo X series II |
| Sample introduction | PFA-ST MicroFlow nebulizer |
| cooled impact bead spray chamber | |
| Sample flow rate (mL min−1) | 0.18 |
| RF power (W) | 1400 |
| Plasma gas flow (L min−1) | 14.0 |
| Sample gas flow (L min−1) | 0.90 |
| Nebulizer gas flow (L min−1) | 0.90 |
| Extraction (V) | −149.0 |
| Hexapole bias (V) | −1.0 |
| Quadrupole bias (V) | −5.0 |
| Data acquisition mode | Time-resolved analysis (TRA) |
| Dwell time (ms) | 10 |
| Acquisition time (s) | 600 |
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion



| Collection time (min) | Mean * (nm) | Standard deviation * |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 125.5 | 5.7 |
| 14 | 155.4 | 4.6 |
| 16 | 184.1 | 1.9 |
| 19 | 197.2 | 2.1 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.H.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charan, S.; Sanjiv, K.; Singh, N.; Chien, F.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Nergui, N.N.; Huang, S.H.; Kuo, C.W.; Lee, T.C.; Chen, P.L. Development of Chitosan Oligosaccharide-Modified Gold Nanorods for in Vivo Targeted Delivery and Noninvasive Imaging by NIR Irradiation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, P.X.; Astruc, D. Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Applications, and Toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1756–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Xia, H.X.; Liu, Y.P.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.D. Applications of gold nanorods in biomedical imaging and related fields. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigderman, L.; Khanal, B.P.; Zubarev, E.R. Functional Gold Nanorods: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Sensing Applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4811–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Park, K.; Srinivasarao, M. Colloidal dispersion of gold nanorods: Historical background, optical properties, seed-mediated synthesis, shape separation and self-assembly. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 65, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzan, L.M.; Mulvaney, P. Gold nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1870–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Neretina, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanorods: From Synthesis and Properties to Biological and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4880–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz, M.; Martin, C.R. Template-fabricated gold nanowires and nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.J.; Hackley, V.A. Fractionation and characterization of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with MALS, DLS, and UV-Vis detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippel, R.A.; Seifalian, A.M. Gold Revolution-Gold Nanoparticles for Modern Medicine and Surgery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, B.P.; Zubarev, E.R. Purification of high aspect ratio gold nanorods: Complete removal of platelets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12634–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, G.; Mougin, K.; Haidara, H.; Vidal, L.; Gnecco, E. Shape and size transformation of gold nanorods (GNRs) via oxidation process: A reverse growth mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4175–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespes, G.; Gigault, J. Hyphenated analytical techniques for multidimensional characterisation of submicron particles: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 692, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Zandvliet, H.J.W.; Kooij, E.S. Shape-Induced Separation of Nanospheres and Aligned Nanorods. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7953–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordel, M.; Olesiak-Banska, J.; Matczyszyn, K.; Nogues, C.; Pawlik, K.; Buckle, M.; Samoc, M. Shape and size separation of gold nanoparticles using glucose gradient density. In Nanophotonics Iv; Andrews, D.L., Nunzi, J.M., Ostendorf, A., Eds.; Proceedings of the SPIE: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; Volume 8424, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Fan, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, X.; Gu, C.; Bian, Z.; Gu, N.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D. Shape separation of colloidal gold nanoparticles through salt-triggered selective precipitation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4180–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Y.X.; Zhou, R.; He, Y.; Yeung, E.S. Separation of nanorods by density gradient centrifugation. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; Cho, T.J.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Hackley, V.A. Gold nanorod separation and characterization by asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with UV-Vis detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Gigault, J.; Hackley, V. PEGylated gold nanorod separation based on aspect ratio: characterization by asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with UV-Vis detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; Pettibone, J.M.; Schmitt, C.; Hackley, V.A. Rational strategy for characterization of nanoscale particles by asymmetric- flow field flow fractionation: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimpf, M.; Caldwell, K.; Giddings, J.C. (Eds.) Field Flow Fractionation Handbook; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 592.
- Beckett, R.; Giddings, J.C. Entropic contribution to the retention of nonspherical particles in field-flow fractionation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1997, 186, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; Le Hecho, I.; Dubascoux, S.; Potin-Gautier, M.; Lespes, G. Single walled carbon nanotube length determination by asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation hyphenated to multi-angle laser-light scattering. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7891–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; Grassl, B.; Lespes, G. Multi-wall carbon nanotube aqueous dispersion monitoring by using A4F-UV-MALS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3345–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8410–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; Mohamed, M.B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Simulation of the optical absorption spectra of gold nanorods as a function of their aspect ratio and the effect of the medium dielectric constant. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 3073–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Jimenez-Lamana, J. Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: A Powerful Tool for Nanoanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Murphy, K.E.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Winchester, M.R. Capabilities of Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry for the Size Measurement of Nanoparticles: A Case Study on Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuoriniemi, J.; Cornelis, G.; Hassellöv, M. Size discrimination and detection capabilities of single-particle ICPMS for environmental analysis of silver nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3965–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Barber, A.; Bednar, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Silver nanoparticle characterization using single particle ICP-MS (SP-ICP-MS) and asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation ICP-MS (AF4-ICP-MS). J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouby, M.; Geckeis, H.; Geyer, F.W. Application of asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AsFlFFF) coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS) to the quantitative characterization of natural colloids and synthetic nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Kim, H.K.; Han, S.H.; Jung, E.C.; Lee, S. Determination of size distribution of colloidal TiO2 nanoparticles using sedimentation field-flow fractionation combined with single particle mode of inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.B.; Higgins, C.P.; Westerhoff, P.; Tadjiki, S.; Ranville, J.F. Overcoming challenges in analysis of polydisperse metal-containing nanoparticles by single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J. Seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanorods: Role of the size and nature of the seed. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3633–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelczak, M.; Perez-Juste, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Shape control in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4065–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Dujardin, E.; Davis, S.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Mann, S. Growth and form of gold nanorods prepared by seed-mediated, surfactant-directed synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Thompson, L.B.; Chernak, D.J.; Yang, J.A.; Sivapalan, S.T.; Boulos, S.P.; Huang, J.Y.; Alkilany, A.M.; Sisco, P.N. Gold nanorod crystal growth: From seed-mediated synthesis to nanoscale sculpting. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 16, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sau, T.K.; Murphy, C.J. Self-assembly patterns formed upon solvent evaporation of aqueous cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated gold nanoparticles of various shapes. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Evidence for bilayer assembly of cationic surfactants on the surface of gold nanorods. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6368–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Jimenez-Lamana, J.; Bolea, E.; Castillo, J.R. Critical considerations for the determination of nanoparticle number concentrations, size and number size distributions by single particle ICP-MS. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigderman, L.; Zubarev, E.R. High-Yield Synthesis of Gold Nanorods with Longitudinal SPR Peak Greater than 1200 nm Using Hydroquinone as a Reducing Agent. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Selegue, J.P. Separation and characterization of single-walled and multiwalled carbon nanotubes by using flow field-flow fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4774–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toy, R.; Hayden, E.; Shoup, C.; Baskaran, H.; Karathanasis, E. The effects of particle size, density and shape on margination of nanoparticles in microcirculation. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.H.; Sun, H.W.; Charmchi, M.; Wang, P.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Faghri, M. Modeling of micro/nano particle separation in microchannels with field-flow fractionation. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.M.; Liu, J.; Hackley, V.A. Fractionation and Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Gold Nanorods Using Asymmetric-Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Chromatography 2015, 2, 422-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030422
Nguyen TM, Liu J, Hackley VA. Fractionation and Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Gold Nanorods Using Asymmetric-Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Chromatography. 2015; 2(3):422-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030422
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thao M., Jingyu Liu, and Vincent A. Hackley. 2015. "Fractionation and Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Gold Nanorods Using Asymmetric-Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry" Chromatography 2, no. 3: 422-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030422
APA StyleNguyen, T. M., Liu, J., & Hackley, V. A. (2015). Fractionation and Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Gold Nanorods Using Asymmetric-Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Chromatography, 2(3), 422-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030422