Facial Emotion Recognition Using Hybrid Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The proposed framework is characterized by the compact representation of spatial information [3] that effectively encodes emotion information. The strengths of both face detection and emotion classification are integrated into a unified framework. The framework summarizes the local structure of the facial image considering the mutual relationship of neighboring regions.
- The framework is modular in nature based on three components including face detection, visual representation, and emotion classification. Therefore, any individual component can be replaced with any of the latest state-of-the-art algorithms. Furthermore, the individual components can be trained offline. Hence, the framework is suitable for handheld devices including smartphones.
2. Related Work
2.1. Speech Signal Based Emotion Classification
2.2. Physiological Signal Based Emotion Classification
2.3. Visual Signal Based Emotion Classification
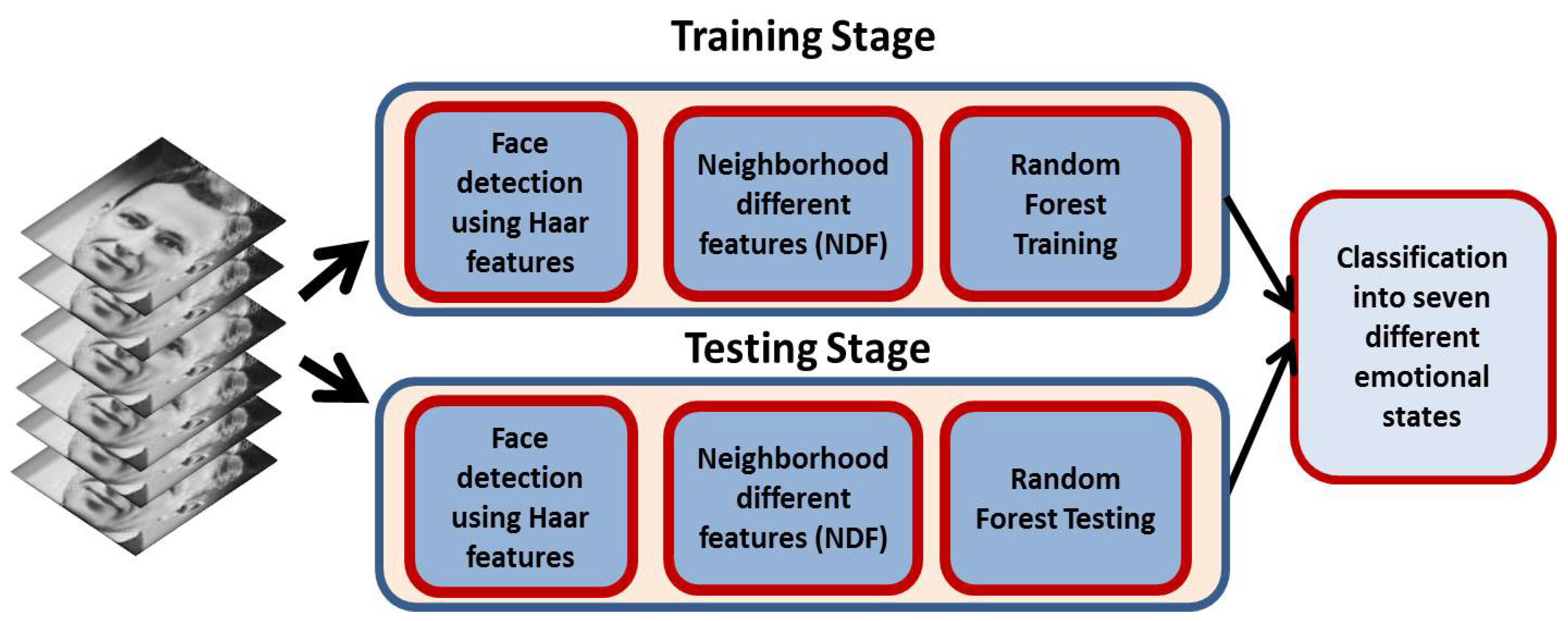
3. Proposed Method
- Face detection,
- Extraction of NDF features,
- Emotion state classification.
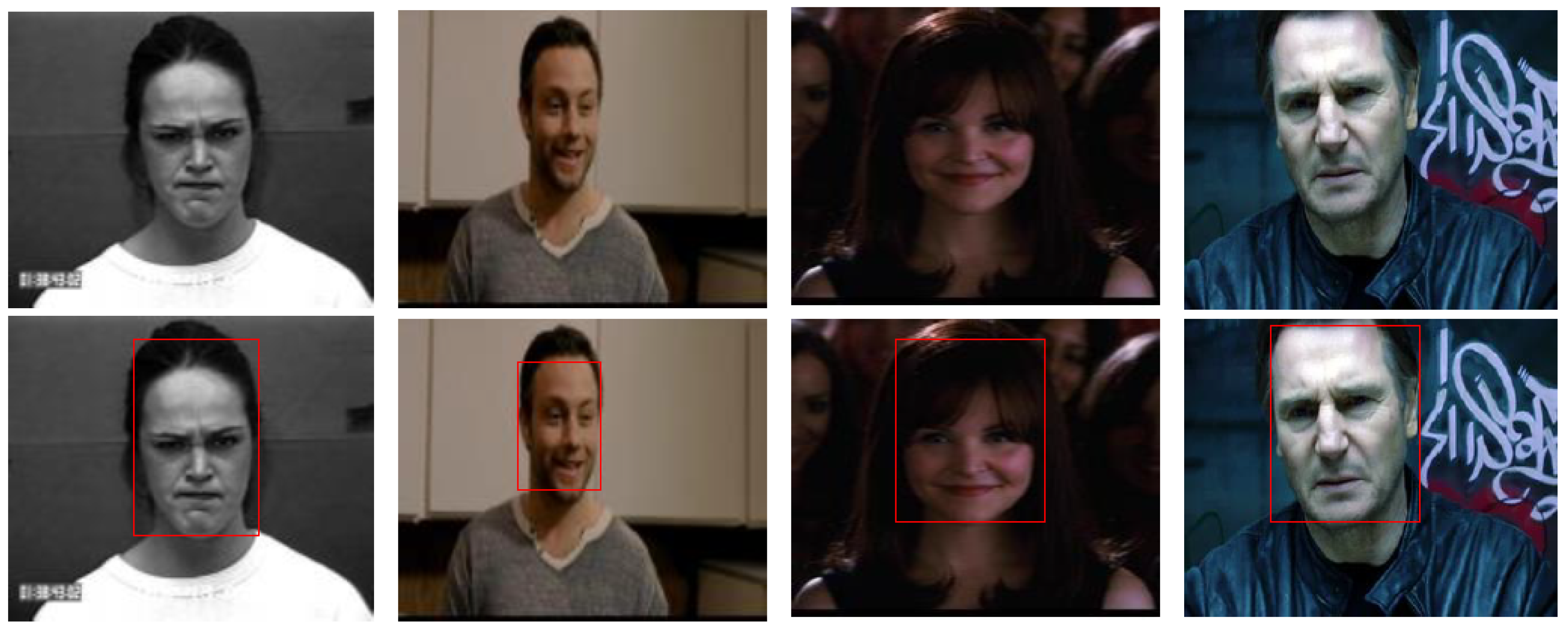
3.1. Face Detection
3.2. Neighborhood Difference Features
3.3. Emotion Classification
4. Experiments and Results
Performance Metric
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDF | Neighborhood difference features |
| LSM | Liquid state machine |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| BEL | Brain emotional learning |
| SNN | Spiking neural network |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| MCML | Maximally collapsing metric learning |
| BWT | Bionic wavelet transform |
| MFCC | Mel frequency cepstral coefficient |
References
- Shojaeilangari, S.; Yau, W.Y.; Nandakumar, K.; Li, J.; Teoh, E.K. Robust representation and recognition of facial emotions using extreme sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2140–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.E.; Sim, K.B. Development of a Facial Emotion Recognition Method based on combining AAM with DBN. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW), Singapore, 20–22 October 2010; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.; Raman, B. Local neighborhood difference pattern: A new feature descriptor for natural and texture image retrieval. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 11843–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariyanidi, E.; Gunes, H.; Cavallaro, A. Automatic analysis of facial affect: A survey of registration, representation, and recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 1113–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likitha, M.; Gupta, S.R.R.; Hasitha, K.; Raju, A.U. Speech based human emotion recognition using MFCC. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 20–24 March 2017; pp. 2257–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfidereshgi, R.; Gournay, P. Biologically inspired speech emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 5135–5139. [Google Scholar]
- Durrieu, J.L.; Richard, G.; David, B.; Févotte, C. Source/filter model for unsupervised main Melody extraction from polyphonic audio signals. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verstraeten, D.; Schrauwen, B.; Stroobandt, D.; Van Campenhout, J. Isolated word recognition with the liquid state machine: A case study. Inf. Process. Lett. 2005, 95, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.J.; Leung, C.H.; Milani, A.; Chen, L. Emotional states associated with music: Classification, prediction of changes, and consideration in recommendation. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. TiiS 2015, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzirakis, P.; Zhang, J.; Schuller, B.W. End-to-end speech emotion recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5089–5093. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Fu, S.; Wang, F. Decision tree SVM model with Fisher feature selection for speech emotion recognition. EURASIP J. Audio, Speech Music Process. 2019, 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.T.; Xie, Q.; Wu, M.; Cao, W.H.; Mei, Y.; Mao, J.W. Speech emotion recognition based on an improved brain emotion learning model. Neurocomputing 2018, 309, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinando, H.; Seppänen, T.; Alasaarela, E. Enhancing Emotion Recognition from ECG Signals using Supervised Dimensionality Reduction. In Proceedings of the ICPRAM, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; pp. 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwal, S.; Uzair, M.; Ullah, H.; Khan, S.D.; Ullah, M.; Cheikh, F.A. An Image Based Prediction Model for Sleep Stage Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1366–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Kanjo, E.; Younis, E.M.; Ang, C.S. Deep learning analysis of mobile physiological, environmental and location sensor data for emotion detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakisa, B.; Rastgoo, M.N.; Tjondronegoro, D.; Chandran, V. Evolutionary computation algorithms for feature selection of EEG-based emotion recognition using mobile sensors. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 93, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, P.; Mishra, D.P. Analysis of EEG Signals for Emotion Recognition Using Different Computational Intelligence Techniques. In Applications of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, H.; Uzair, M.; Mahmood, A.; Ullah, M.; Khan, S.D.; Cheikh, F.A. Internal emotion classification using eeg signal with sparse discriminative ensemble. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 40144–40153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, V.; Vallverdù, J.; Milani, A. Errors, Biases and Overconfidence in Artificial Emotional Modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence-Companion Volume, Thessaloniki, Greece, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jirayucharoensak, S.; Pan-Ngum, S.; Israsena, P. EEG-based emotion recognition using deep learning network with principal component based covariate shift adaptation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 627892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Broek, E.L.; Spitters, M. Physiological signals: The next generation authentication and identification methods!? In Proceedings of the 2013 European Intelligence and Security Informatics Conference (EISIC), Uppsala, Sweden, 12–14 August 2013; pp. 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Rota, P.; Ullah, H.; Conci, N.; Sebe, N.; De Natale, F.G. Particles cross-influence for entity grouping. In Proceedings of the 21st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2013), Marrakech, Morocco, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.K.; Shamsolmoali, P.; Sehdev, P. Extended Deep Neural Network for Facial Emotion Recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 120, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Ullah, H.; Cheikh, F.A. Single shot appearance model (ssam) for multi-target tracking. Electron. Imaging 2019, 2019, 466-1–466-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Ko, B.C. Driver’s Facial Expression Recognition in Real-Time for Safe Driving. Sensors 2018, 18, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acharya, D.; Huang, Z.; Pani Paudel, D.; Van Gool, L. Covariance pooling for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, M.; Ullah, H.; Alseadonn, I.M. Human action recognition in videos using stable features. In Proceedings of the ICPRAM, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Phillips, P.; Dong, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.D. Intelligent facial emotion recognition based on stationary wavelet entropy and Jaya algorithm. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Collaborative discriminative multi-metric learning for facial expression recognition in video. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 75, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadiani, N.; Huang, G.; Cai, B.; Luo, W.; Chi, C.H.; Xiang, Y.; He, J. A review on automatic facial expression recognition systems assisted by multimodal sensor data. Sensors 2019, 19, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, N.; Li, Q.; Huan, R.; Liu, J.; Han, G. Deep spatial-temporal feature fusion for facial expression recognition in static images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 119, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.T.; de Aguiar, E.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Facial expression recognition with convolutional neural networks: coping with few data and the training sample order. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 610–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, V.; Milani, A.; Biondi, G.; Micheli, F. A Preliminary Work on Dog Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence-Companion Volume, Thessaloniki, Greece, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Communications of the ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Chi, Z.; Fu, H. Facial expression recognition in video with multiple feature fusion. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Altamimi, A.B.; Uzair, M.; Ullah, M. Anomalous entities detection and localization in pedestrian flows. Neurocomputing 2018, 290, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsi, H.; Kepuska, V.; Alshamsi, H.; Meng, H. Automated Facial Expression and Speech Emotion Recognition App Development on Smart Phones using Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 730–738. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Alhamid, M.F.; Song, B.; Al-Mutib, K. Audio-visual emotion recognition using big data towards 5G. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2016, 21, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünerbl, A.; Muaremi, A.; Osmani, V.; Bahle, G.; Oehler, S.; Tröster, G.; Mayora, O.; Haring, C.; Lukowicz, P. Smartphone-based recognition of states and state changes in bipolar disorder patients. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, H.; Rafi, M.; Kumar, M.M.; Thomas, L.; Annappa, B. Smartphone based emotion recognition and classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 Second International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India, 22–24 February 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G. An emotion recognition system for mobile applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, A.; Bouguila, N.; Hamza, A.B. Video completion using bandelet transform. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2012, 14, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, M.; Pietikäinen, M.; Schmid, C. Description of interest regions with local binary patterns. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolov, D.; Patkin, M. Real-time emotion recognition on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; p. 787. [Google Scholar]
- Perikos, I.; Paraskevas, M.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. Facial expression recognition using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACIS 17th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Singapore, 6–8 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Franzoni, V.; Biondi, G.; Milani, A. A web-based system for emotion vector extraction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Trieste, Italy, 3–6 July 2017; pp. 653–668. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, W.G.; Luna, M.A.; Moya, J.F.; Abad, V.; Parra, H.; Ruiz, H. Pedestrian detection for UAVs using cascade classifiers with meanshift. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 11th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), San Diego, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2017; pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, D.; Roth, G. Adaptive thresholding using the integral image. J. Graph. Tools 2007, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Rosset, S.; Zhu, J.; Zou, H. Multi-class adaboost. Stat. Its Interface 2009, 2, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruzzone, L.; Cossu, R. A multiple-cascade-classifier system for a robust and partially unsupervised updating of land-cover maps. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2002, 40, 1984–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.R.; Stevens, J.R. Random forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Au, T.C. Random forests, decision trees, and categorical predictors: the Absent levels problem. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2018, 19, 1737–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Joshi, J.; Sikka, K.; Gedeon, T. Emotion recognition in the wild challenge 2014: Baseline, data and protocol. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–16 November 2014; pp. 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Collecting large, richly annotated facial-expression databases from movies. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Deng, W.; Du, J. Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2852–2861. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Schuller, B. Implicit Fusion by Joint Audiovisual Training for Emotion Recognition in Mono Modality. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 5861–5865. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Yang, Z.J.; Lu, H.M.; Zhou, X.X.; Phillips, P.; Liu, Q.M.; Wang, S.H. Facial emotion recognition based on biorthogonal wavelet entropy, fuzzy support vector machine, and stratified cross validation. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 8375–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Hariharan, M.; Yaacob, S.; Adom, A.H. Facial emotion recognition based on higher-order spectra using support vector machines. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2015, 5, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, T.; Reddy, G.R.M. A hybrid bioinspired algorithm for facial emotion recognition using CSO-GA-PSO-SVM. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Gwalior, India, 4–6 April 2015; pp. 472–477. [Google Scholar]
| Predicted Facial Emotion | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger | Disgust | Fear | Happy | Neutral | Sad | Surprise | Recall | ||
| Actual Facial Emotion | Anger | 0.68 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 68% |
| Disgust | 0.20 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 55% | |
| Fear | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 49% | |
| Happy | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 51% | |
| Neutral | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 52% | |
| Sad | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 62% | |
| Surprise | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 67% | |
| Precision | 52.71% | 36.66% | 66.21% | 62.96% | 67.53 | 72.94% | 64.42% | ||
| Predicted Facial Emotion | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger | Disgust | Fear | Happy | Neutral | Sad | Surprise | Recall | ||
| Actual Facial Emotion | Anger | 0.54 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 54% |
| Disgust | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 57% | |
| Fear | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 61% | |
| Happy | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 49% | |
| Neutral | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 65% | |
| Sad | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.07 | 69% | |
| Surprise | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.58 | 58% | |
| Precision | 43.90% | 52.77% | 61.61% | 53.26% | 76.47% | 68.31% | 63.04% | ||
| Methods | SFEW | RAF |
|---|---|---|
| Total Accuracy | Total Accuracy | |
| Han et al. [57] | 56.4 | 55.7 |
| Zhang et al. [58] | 54.2 | 56.6 |
| Ali et al. [59] | 49.8 | 52.7 |
| Vivek et al. [60] | 53.5 | 54.9 |
| Verma et al. [3] | 47.6 | 48.1 |
| Prop. method | 57.7 | 59.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alreshidi, A.; Ullah, M. Facial Emotion Recognition Using Hybrid Features. Informatics 2020, 7, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics7010006
Alreshidi A, Ullah M. Facial Emotion Recognition Using Hybrid Features. Informatics. 2020; 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics7010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlreshidi, Abdulrahman, and Mohib Ullah. 2020. "Facial Emotion Recognition Using Hybrid Features" Informatics 7, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics7010006
APA StyleAlreshidi, A., & Ullah, M. (2020). Facial Emotion Recognition Using Hybrid Features. Informatics, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics7010006






