Thai Tattoo Wisdom’s Representation of Knowledge by Ontology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Implementation
3.1. Ontology Model Building
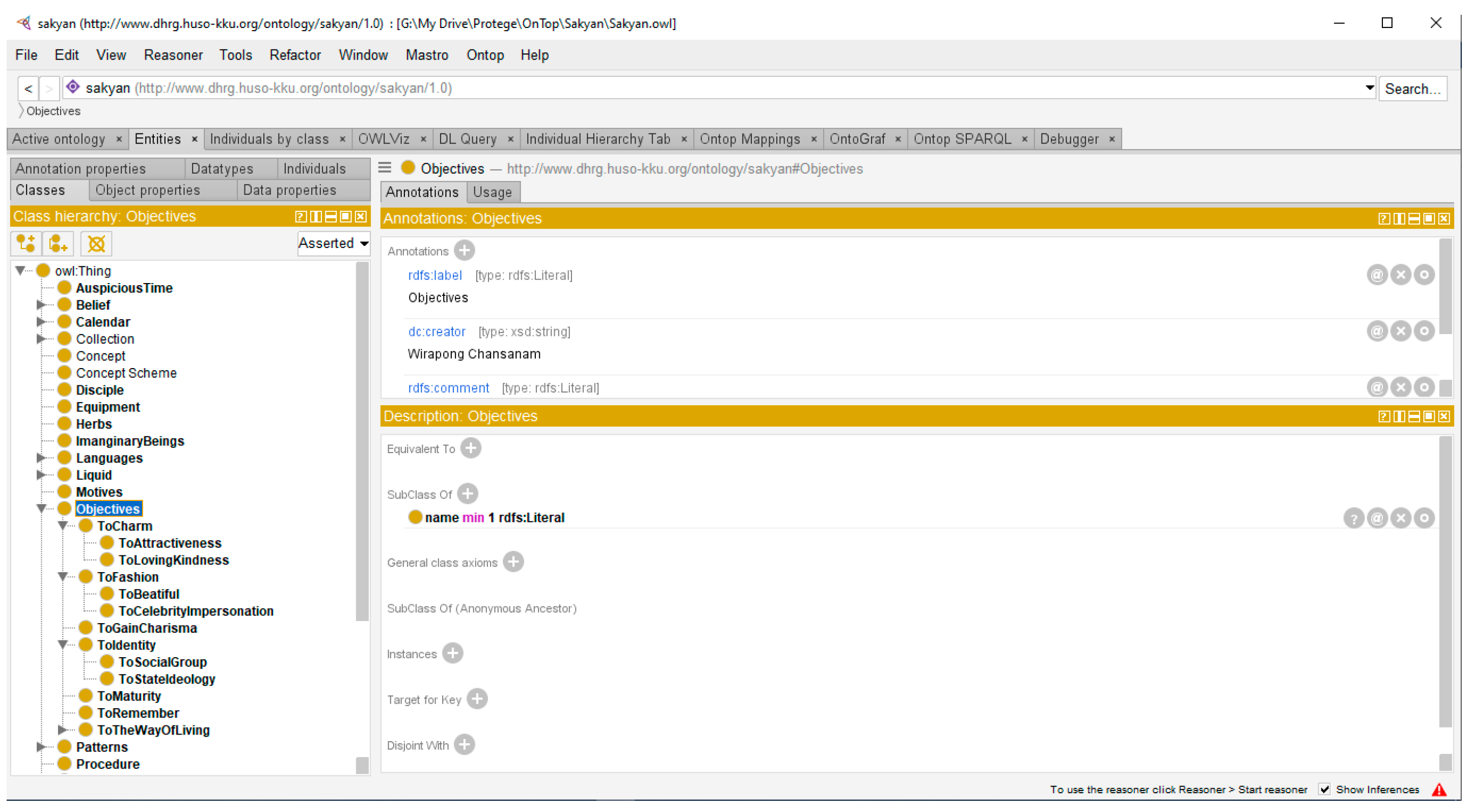
3.1.1. Class and Subclass Creation
3.1.2. Object and Data Property Identification
3.1.3. Individual or Instance Creation
3.1.4. Consistency Checking
3.2. Evaluation by OOPS!
3.3. Ontology Reparation Activity
3.4. Evaluation by Experts
- Arrange for an inquiry form for ontology evaluation by humans—It is necessary to validate and certify the ontology in an evaluation by humans. We planned an inquiry form by considering three dimensions:
- evaluator basic information;
- knowledge, structure, and representation in a variety of dimensions, such as scope, concept class, properties, instance, and reusability potential for future development and application;
- open-ended questions for recommendation.
- Arrange for evaluation by the evaluator by assigning responsibility to each group.
- Knowledge engineers—to verify a comprehensive ontology scheme for computer system agents and ontological mechanisms.
- Specialists in the yantra domain—to prove and certify correctness, consistency, properties, and hierarchical relations among concepts in ontology.
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuanchom, W. Belief in Five Columns Tattoo: A Case Study of Tattoo Group of Ajarn Noo Khanpai. Master’s Thesis, Arts Program in Sociology, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Acierno, M.; Cursi, S.; Simeone, D.; Fiorani, D. Architectural heritage knowledge modelling: An ontology-based framework for conservation process. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 24, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T. What is an ontoloty. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Liu, L., Ozsu, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Josephson, J.R. The Ontology of Tasks and Methods. AAAI 1997 Spring Symposium on Ontological Engineering, 24–26 March 1997, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA. 1997. Available online: http://web.cse.ohio-state.edu/~chandrasekaran.1/Ontology-of-Tasks-Methods.PDF (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Milton, S.; Keen, C.; Kurnia, S. “Understanding the Benefits of Ontology Use for Australian Industry: A Conceptual Study”, AIS Electronic Library (AISeL). 2010. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/acis2010/64/ (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- During, R. Cultural Heritage Discourses and Europeanisation; Thesis Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ore, C.-E.; Eide, Ø. TEI and cultural heritage ontologies: Exchange of information? Liter. Linguist. Comput. 2009, 24, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, O. The Semantic Web and Cultural Heritage: Ontologies and Technologies Help in Accessing Museum Information. Information Technoloty for the Virtual Museum. 6–7 December 2006. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/ab4f/0ee826bbea097f4d7aa4d5244b67c0caeaa6.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Koutsomitropoulos, D.; Hyvönen, E.; Papatheodorou, T. Semantic Web and reasoning for cultural heritage and digital libraries. Semant. Web 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chansanam, W.; Tuamsuk, K.; Kwiecien, K.; Ruangrajitpakorn, T.; Supnithi, T. Development of the belief culture ontology and its application: Case study of the GreaterMekong subregion. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Joint International Semantic Technology Conference, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 9–11 November 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8943, pp. 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, F.; Noah, S.A.M. Building an Event Ontology for Historical Domain to Support Semantic Document Retrieval. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2016, 6, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aloui, N.; Gargouri, F. OARLCAM: An Ontology-based Approach for Reusing and Learning through Context-aware Annotations Memory. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2014, 9, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchra, B.; Mohamed, B. Ontology and Rule-Based Recommender System for E-learning Applications. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudhana, K. The Cognitive Dimension and Course Content Modeling: An Ontological Approach. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2017, 12, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chansanam, W.; Tuamsuk, K. Development of an imaginary beings Ontology. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Digital Libraries: Knowledge, Information, and Data in an Open Access Society, Tsukuba, Japan, 7–9 December 2016; Morishima, A., Rauber, A., Liew, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 10075, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo-Ontology Editor. 2011. Available online: http://www.ei.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/hozo/eng/HozoManual_en_20140317.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Suárez-Figueroa, M.C.; de Guadalupe, A.C.; Asunción, G.-P. Lights and shadows in creating a glossary about ontology engineering. Terminol. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Issues Spec. Commun. 2013, 19, 202–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, N.F.; McGuinness, D.L. Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology. 2001. Available online: https://protege.stanford.edu/publications/ontology_development/ontology101.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Poveda-Villalón, M.; Gómez-Pérez, A.; Suárez-Figueroa, M. OOPS! (OntOlogy Pitfall Scanner!). Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst. 2014, 10, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritika, B.; Bansal, C. An Approach for Semantic Information Retrieval from Ontology in Computer Science Domain. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. (IJEAT) 2014, 4, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Biomedical Informatics Research (BMIR). A Free, Open-Source Ontology Editor and Framework for Building Intelligent Systems. Available online: http://protege.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Manola, F.; Miller, E. RDF 1.1 Primer. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-primer/ (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Chansanam, W.; Tuamsuk, K. Development of an imaginary beings knowledge structure. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the International Conference on Asian Digital Libraries, Seoul, Korea, 9–12 December 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9469, pp. 291–293. [Google Scholar]
- Villalón, M.P. Ontology Evaluation: A Pitfall-Based Approach to Ontology Diagnosis. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Artificial Intelligence, Polytechnic University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rector, A.; Drummond, N.; Horridge, M.; Rogers, J.; Knublauch, H.; Stevens, R.; Wang, H.; Wroe, C. OWL pizzas: Practical experience of teaching OWL-DL: Common errors and common patterns. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Engineering Knowledge in the Age of the Semantic Web, Whittlebury Hall, UK, 5–8 October 2004; Motta, E., Shadbolt, N.R., Stutt, A., Gibbins, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 3257, pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Horridge, M. A Practical Guide to Building OWL Ontologies using Protege 4 and CO-ODE Tools Edition 1.3; The University of Manchester: Mancherster, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Allemang, D.; Hendler, J. Semantic Web for the Working Ontologist Effective Modeling in RDFS and OWL, 2nd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler, J.; Fisher, M.; Perez-lopez, A.; Blace, R. Semantic Web Programming, Indiapolis; Wiley Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Doncel, V.; Gómez-Pérez, A.; Mihindukulasooriya, N. Rights declaration in Linked Data. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop on Consuming Linked Data (COLD), Sydney, Australia, 22 October 2013; EUR-WS.org: Aachen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Research Data Commons (ARDC). Research Data Rights Management Guide; ARDC: Caulfield East, VIC, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Poblet, M.; Aryani, A.; Manghi, P.; Unsworth, K.; Wang, J.; Hausstein, B.; Dallmeier-Tiessen, S.; Klas, C.P.; Casanovas, P.; Doncel, V.R. Assigning creative commons licenses to research metadata: Issues and cases. In AI Approaches to the Com-Plexity of Legal Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Etikan, I. Comparision of Snowball Sampling and Sequential Sampling Technique. Biom. Biostat. Int. J. 2016, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Pérez, A.; Fernández-López, M.; Corcho, O. Ontological Engineering: With Examples from the Areas of Knowledge Management, e-Commerce and the Semantic Web, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-pérez, A.; Rojas-amaya, M.D. Ontological Reengineering for Reuse. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the 11th European Workshop on Knowledge Acquisition, Modeling and Management, Dagstuhl Castle, Germany, 26–29 May 1999; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stamper, R.; Liu, K.; Hafkamp, M.; Ades, Y. Understanding the roles of signs and norms in organizations—A semiotic approach to information systems design. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2000, 19, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Palma, R.; Sure, Y.; Suarez-Figueroa, M.C.; Haase, P.; Gómez-Pérez, A.; Studer, R. Ontology metadata vocab-ulary and applications. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the OTM Confederated International Conferences “On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems, Agia Napa, Cyprus, 31 October–4 November 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 906–915. [Google Scholar]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chansanam, W.; Tuamsuk, K.; Kwiecien, K.; Sutthiprapa, K.; Supnithi, T. Thai Tattoo Wisdom’s Representation of Knowledge by Ontology. Informatics 2021, 8, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010003
Chansanam W, Tuamsuk K, Kwiecien K, Sutthiprapa K, Supnithi T. Thai Tattoo Wisdom’s Representation of Knowledge by Ontology. Informatics. 2021; 8(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleChansanam, Wirapong, Kulthida Tuamsuk, Kanyarat Kwiecien, Kittiya Sutthiprapa, and Thepchai Supnithi. 2021. "Thai Tattoo Wisdom’s Representation of Knowledge by Ontology" Informatics 8, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010003
APA StyleChansanam, W., Tuamsuk, K., Kwiecien, K., Sutthiprapa, K., & Supnithi, T. (2021). Thai Tattoo Wisdom’s Representation of Knowledge by Ontology. Informatics, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010003





