Purification of Carrier-Free 47Sc of Biomedical Interest: Selective Separation Study from natCa(n,γ)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
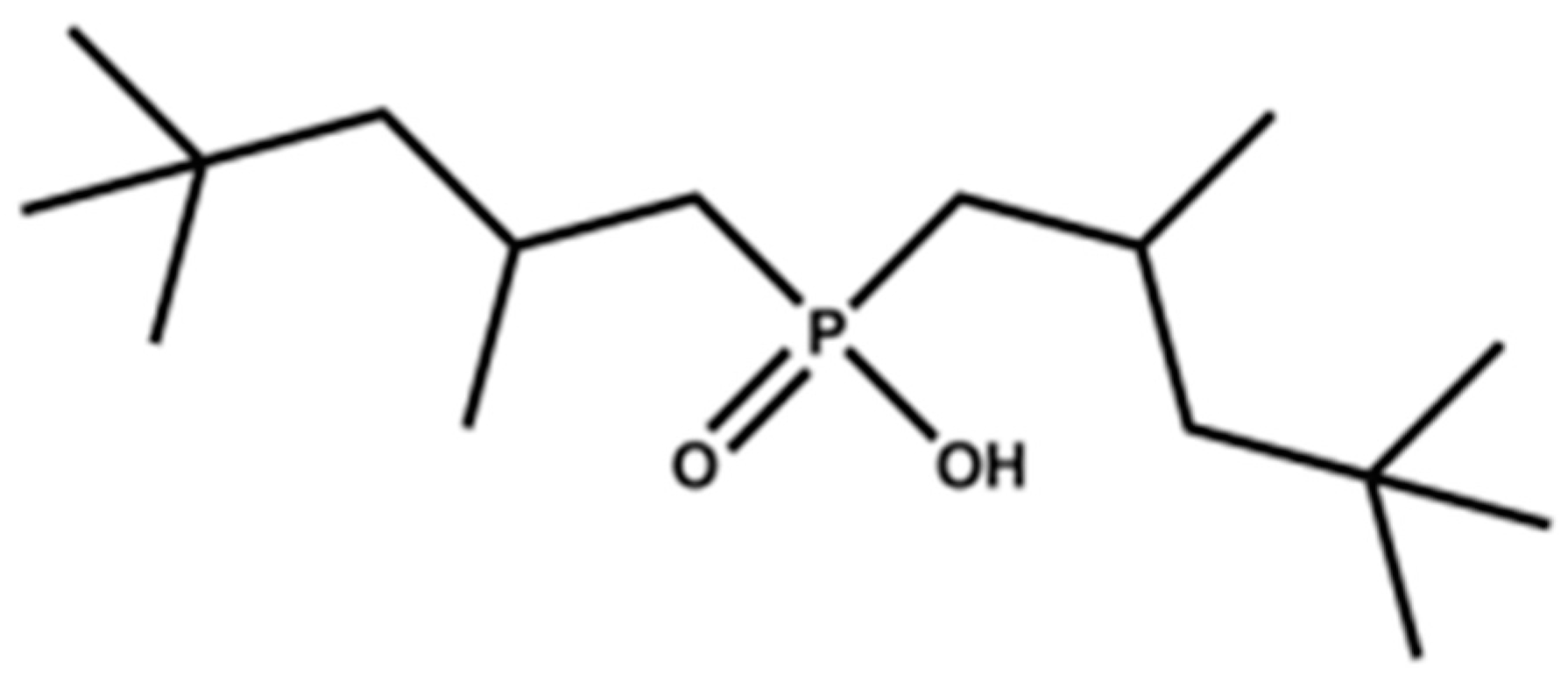
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. 47Sc Radioisotope Production
2.3. Batch Experiment Study
2.4. Radiometric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production of 47Sc from Calcium Target
3.2. Solvent Extraction of 47Sc from 47Ca
3.2.1. Effect of pH
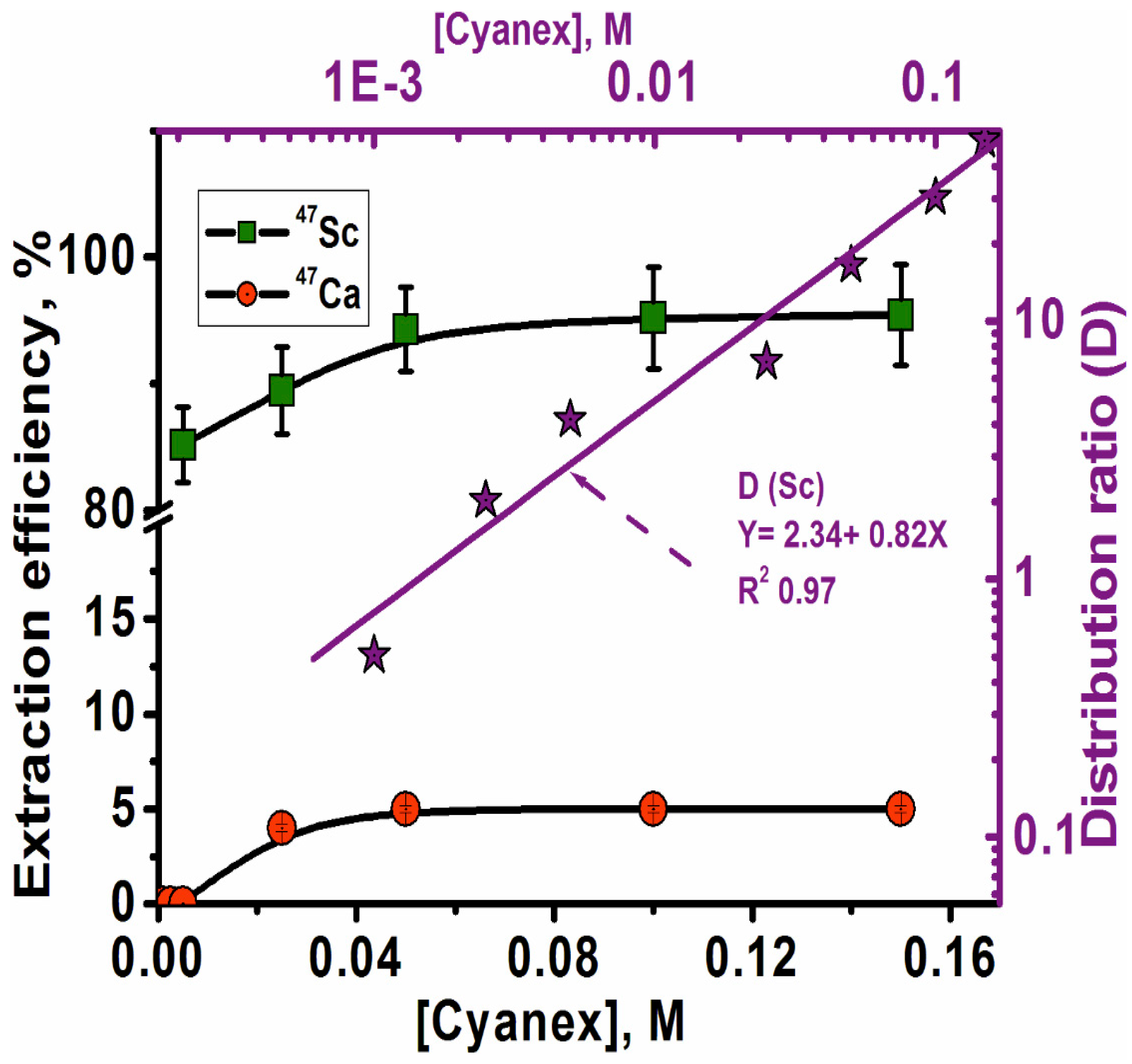
3.2.2. Effect of Cyanex 272 Concentration
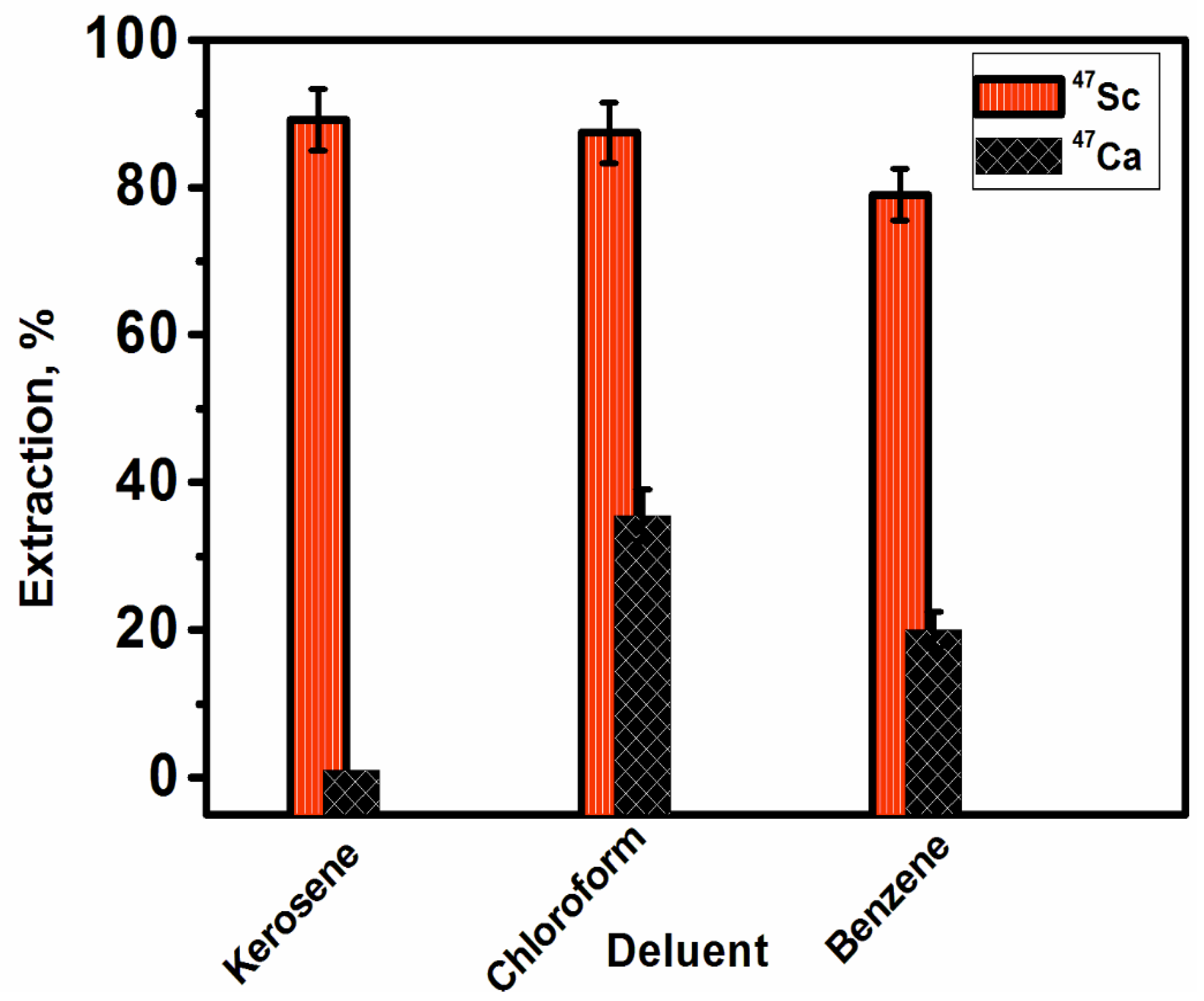
3.2.3. Effect of Diluent Type
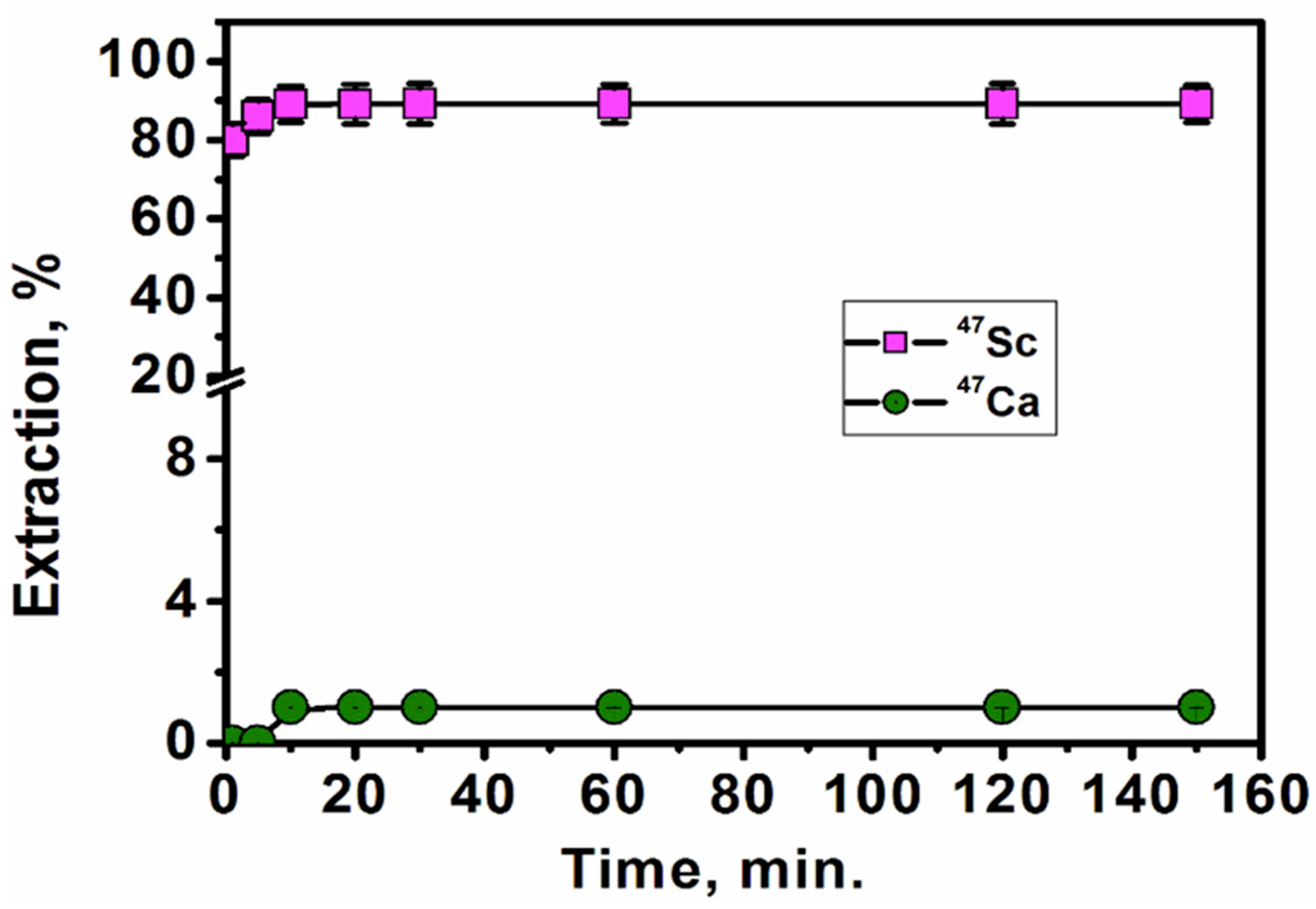
3.2.4. Effect of Extraction Time
3.2.5. Effect of Metal Concentration
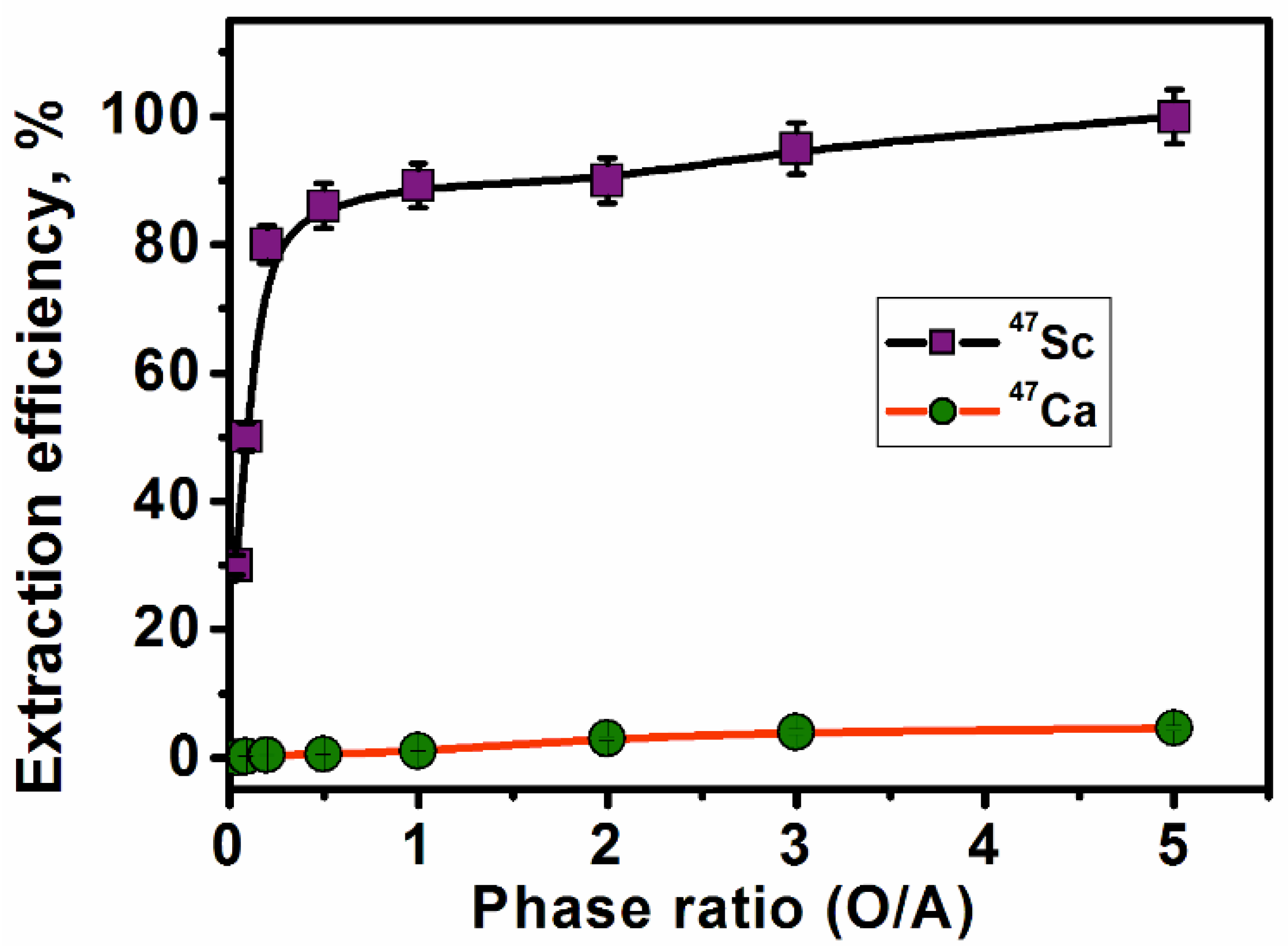
3.2.6. Effect of Phase Ratio
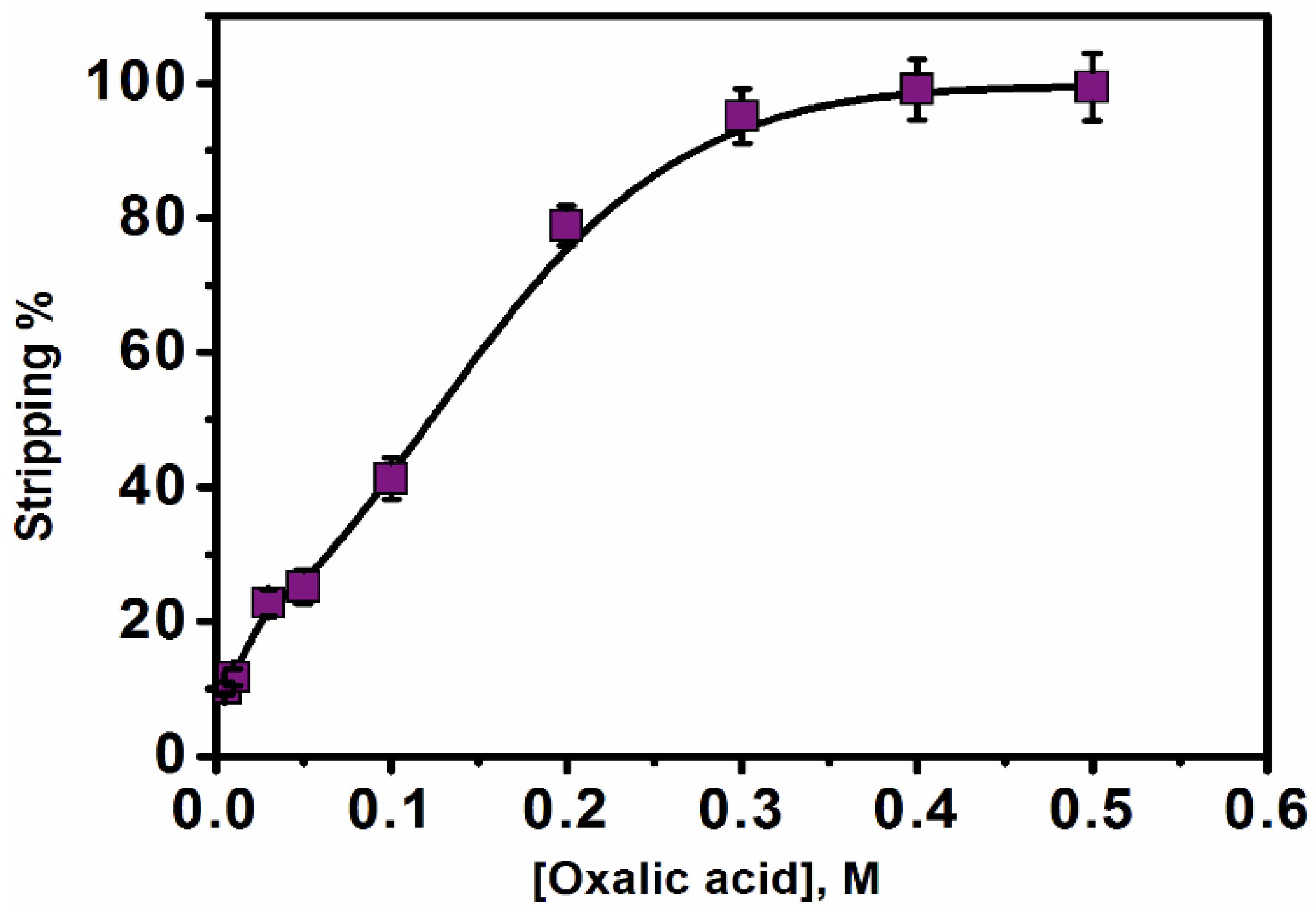
3.3. Stripping Procedure
3.4. Quality Control Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attallah, M.F.; Shahr El-Din, A.M.; Gizawy, M.A.; Ali, A.M.I. Efficient trace-scale extraction method of reactor produced 199Au adequate for nuclear medicine applications. Radiochim. Acta 2021, 109, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizawy, M.A.; Shamsel-Din, H.A.; Attallah, M.F. Purification development of carrier-free 47Sc produced from natTi(n,p) reaction for radiotheranostic applications. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 328, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Gizawy, M.A.; Labib, S. Separation of 47Sc produced from natCa(n, γ) reaction for potential medical applications by a synthesized raspberry-like structure of metal-organic framework material. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 52, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Loveless, C.S.; Blanco, J.R.; Diehl, G.L.I.I.I.; Elbahrawi, R.T.; Carzaniga, T.S.; Braccini, S.; Lapi, S.E. Cyclotron Production and Separation of Scandium Radionuclides from Natural Titanium Metal and Titanium Dioxide Targets. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, W.; Hoffman, T.J. Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2269–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barto´s, B.; Majkowska, A.; Kasperek, A.; Krajewski, S.; Bilewicz, A. New separation method of no-carrier-added 47Sc from titanium targets. Radiochim. Acta 2012, 100, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Bunka, M.; Haller, S.; UlliKöster Groehn, V.; Bernhardt, P.; Meulen Nvd Türler, A.; Schibli, R. Promising Prospects for 44Sc-/47Sc-Based Theragnostics: Application of 47Sc for Radionuclide Tumor Therapy in Mice. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misiak, R.; Walczak, R.; Wąs, B.; Bartyzel, M.; Mietelski, J.W.; Bilewicz, A. 47Sc production development by cyclotron irradiation of 48Ca. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 313, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domnanich, K.A.; Müller, C.; Benešová, M.; Dressler, R.; Haller, S.; UlliKöster Ponsard, B.; Schibli, R.; Türler, A.; Meulen, N.v.d. 47Sc as useful β—Emitter for the radiotheragnostic paradigm: A comparative study of feasible production routes. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2017, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolsky, K.L.; Joshi, V.; Mausner, L.F.; Srivastava, S.C. Radiochemical purification of no-carrier-added scandium-47 for radioimmunotherapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1998, 49, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A.; Ahmed, I.; Abd-Elhamid, A.; Aly, H.F.; Attallah, M.F. Selective sorption of 134Cs and 60Co radioisotopes using synthetic nanocopper ferrocyanide-SiO2 materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Hassan, H.S.; Youssef, M.A. Synthesis and sorption potential study of Al2O3-ZrO2-CeO2 composite material for removal of some radionuclides from radioactive waste effluent. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 147C, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Cho C-Wa Kim, S.; Song, M.-H.; Bediako, J.K.; Yun, Y.-S. Selective recovery of Au(III), Pt(IV), and Pd(II) from aqueous solutions by liquid–liquid extraction using ionic liquid Aliquat-336. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Rizk, S.E.; Shady, S.A. Separation of 152+154Eu, 90Sr from radioactive waste effluent using liquid–liquid extraction by polyglycerol phthalate. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahr El-Din, A.M.; Borai, E.H.; Abd El-Ghany, M.S. Selective separation of thorium from rare earth elements liquor during the alkaline processing of Egyptian monazite concentrate. Main Group Chem. 2018, 17, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrelli, L.; Mausner, L.F.; Kolsky, K.L. Separation of carrier- free 47Sc from titanium targets. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1992, 157, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.F.; El-Haggan, M.A. Production of carrier-free scandium radioisotopes from a neutron-irradiated potassium titanium oxalate target. Microchim. Acta 1971, 59, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.R. LLX separation of carrier free 47Sc, 48V and 48, 49, 51Cr produced in α-particle activated titanium with HDEHP. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1996, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, H.E.; El-Nadi, Y.A.; El-Hefny, N.E. Extractive Separation of Scandium from Strongly Alkaline Solution by Quaternary Ammonium Salt. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2020, 38, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hefny, N.E.; El-Nadi, Y.A.; Daoud, J.D. Equilibrium and mechanism of samarium extraction from chloride medium using sodium salt of CYANEX 272. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Malik, A.; Deep, A. Solvent extraction and separation of tervalent lanthanides and yttrium using CYANEX 923. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2003, 21, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Radhika, S.; Kumar, B.N.P. Liquid–liquid extraction studies of trivalent yttrium from phosphoric acid solutions using TOPS 99 as an extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 45, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Mohamed, G.Y.; Breky, M.M.E. Production and subsequent separation of 47Sc of nuclear medicine applications using neutron-induced reactions on different natural targets. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 331, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.F.A.; Mansur, M.B. Competing solvent extraction of calcium and/or nickel with Cyanex 272 and/or Brazilian. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Tonga, S.; Li, Z.; Zhoua, W.; Li, H.; Meng, S. Solvent extraction of rare earth elements with mixtures of sec-octylphenoxy acetic acid and bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) dithiophosphinic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, W. Extraction of Scandium (III) using ionic liquids functionalized solvent impregnated resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelchuk, K.; Szczepanski, P.; Shrotre, A.; Haddada, M.; Chagnes, A. Effects of structural changes of new organophosphorus cationic exchangers on a solvent extraction of cobalt, nickel and manganese from acidic chloride media. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Behera, S.S.; Murmub, B.M.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Mandal, D.; Samantraya, R.; Parhia, P.K.; Senanayakec, G. Extraction of Scandium (III) from acidic solutions using organo-phosphoric acid reagents: A comparative study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, D. Extraction mechanism of Sc(III) and separation from Th(III), Fe(III) and Lu(III) with bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid in N-hexanefromsulphuric acid solutions. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1994, 12, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Kotekar, M.K.; Singh, H. Development of a solvent extraction process for production of nuclear grade dysprosium oxide from a crude concentrate. Desalination 2008, 232, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhao, X.; Song, N.; Jia, Q.J.; Zhou, W.; Liao, W. Solvent extraction study of rare earth elements from chloride medium by mixtures of sec-nonylphenoxy acetic acid with Cyanex301 or Cyanex302. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 100, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Ji, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Li, D.Q. A novel ammonium ionic liquid-based extraction strategy for separating scandium from yttrium and lanthanides. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, N.K.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, M.S. Solvent extraction of praseodymium(III) from chloride solutions by a mixture of Cyanex 301 and LIX 63. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borai, E.H.; Shahr El-Din, A.M.; El Afifi, E.M.; Aglan, R.F.; Abo-Aly, M.M. Subsequent Separation and Selective Extraction of Thorium (IV), Iron (III), Zirconium (IV) and Cerium (III) from Aqueous Sulfate Medium. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2016, 69, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlobina, E.; Ismailova, A.; Tassibekov, K. Extractive Separation of Scandium from Rare Earth Elements. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 96, 00001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharafa, M.; Yoshidaa, W.; Kubotaa, F.; Goto, M. Selective Extraction of Scandium by a Long Alkyl Chain Carboxylic Acid/Organophosphonic Ester Binary Extractant. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2018, 36, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, C. Solvent extraction of Scandium III by Cyanex 923/and Cyanex 925. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, D.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Solvent Extraction of Scandium(III) by an Aqueous Biphasic System with a Nonfluorinated Functionalized Ionic Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 8988–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| pH | DSc | DCa | SF = DSc/DCa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.93 | 0.01 | 193 |
| 1 | 3.988 | 0.01 | 398 |
| 1.8 | 6.98 | 0.01 | 698 |
| 2 | 9.33 | 0.0412 | 222.14 |
| 2.5 | 9.7 | 0.0412 | 230.95 |
| 3 | 10.71 | 0.0412 | 255 |
| 3.5 | 11.543 | 0.0412 | 274.8 |
| 4.5 | 12.51 | 0.0412 | 297.863 |
| Extractant Name | Extractant Concentration, M | Capacity, mg/L | Experimental Condition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 TOPO-kerosene | 0.001 | 7.7 | 0.5 M HNO3 | [35] |
| 2 TABAC-3 D2EHPA-heptane | 0.01 | 40 | 1 M HNO3 | [35] |
| 4 PC88A-n-dodecane | 0.001 | ~9 | 0.1 M HNO3 | [36] |
| (PC88A/5 Versatic10)-n-dodecane | 0.001(PC88A) + 0.1 (Versatic10) | ~9 | 0.1 M HNO3 | [36] |
| Cyanex 272–kerosene | 0.025 | 410 | pH 1.8 (~ 0.01 M HCl) | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahr El-Din, A.M.; Rizk, H.E.; Attallah, M.F. Purification of Carrier-Free 47Sc of Biomedical Interest: Selective Separation Study from natCa(n,γ). Separations 2023, 10, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010008
Shahr El-Din AM, Rizk HE, Attallah MF. Purification of Carrier-Free 47Sc of Biomedical Interest: Selective Separation Study from natCa(n,γ). Separations. 2023; 10(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahr El-Din, Ahmed M., Hoda E. Rizk, and Mohamed F. Attallah. 2023. "Purification of Carrier-Free 47Sc of Biomedical Interest: Selective Separation Study from natCa(n,γ)" Separations 10, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010008
APA StyleShahr El-Din, A. M., Rizk, H. E., & Attallah, M. F. (2023). Purification of Carrier-Free 47Sc of Biomedical Interest: Selective Separation Study from natCa(n,γ). Separations, 10(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10010008








