An Improved Analytical Approach Based on µ-QuEChERS Combined with LC-ESI/MS for Monitoring the Occurrence and Levels of Patulin in Commercial Apple Juices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Samples
2.3. Standard Solutions
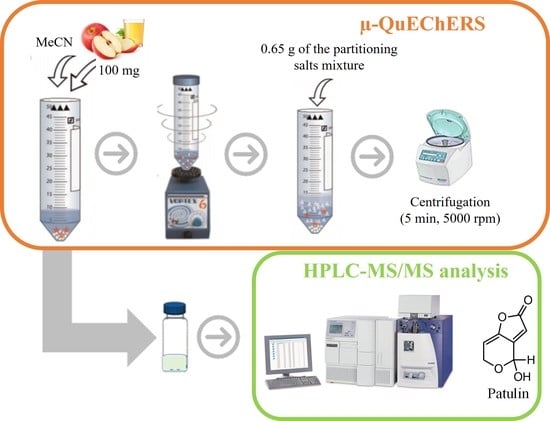
2.4. µ-QuEChERS Extraction
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Method Validation
3.2. Quantification of Patulin in Apple Juice
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinde, R.; Dhanshetty, M.; Lakade, A.; Elliott, C.T.; Banerjee, K. Development and Validation of a Liquid Chromatographic Tandem Mass Spectrometric Method for the Analysis of Patulin in Apple and Apple Juice. Mycotoxin Res. 2021, 37, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadok, I.; Szmagara, A.; Krzyszczak, A. Validated QuEChERS-Based UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS Method for the Postharvest Control of Patulin (Mycotoxin) Contamination in Red-Pigmented Fruits. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayashree, G.V.; Krupashree, K.; Rachitha, P.; Khanum, F. Patulin Induced Oxidative Stress Mediated Apoptotic Damage in Mice, and Its Modulation by Green Tea Leaves. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2017, 7, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussabbeh, M.; Ben Salem, I.; Neffati, F.; Najjar, M.F.; Bacha, H.; Abid-Essefi, S. Crocin Prevents Patulin-Induced Acute Toxicity in Cardiac Tissues via the Regulation of Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Singh, N.; Ansari, K.M. Toxicological Effects of Patulin Mycotoxin on the Mammalian System: An Overview. Toxicol. Res. Camb. 2017, 6, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, M.A.A.; Tabana, Y.M.; Musa, K.B.; Sandai, D.A. Effects of Different Mycotoxins on Humans, Cell Genome and Their Involvement in Cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puel, O.; Galtier, P.; Oswald, I.P. Biosynthesis and Toxicological Effects of Patulin. Toxins 2010, 2, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artigot, M.P.; Loiseau, N.; Laffitte, J.; Mas-Reguieg, L.; Tadrist, S.; Oswald, I.P.; Puel, O. Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of Two CYP619 Cytochrome P450s Involved in Biosynthesis of Patulin in Aspergillus Clavatus. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comission, E. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Available online: https://leap.unep.org/countries/eu/national-legislation/commission-regulation-ec-no-18812006-setting-maximum-levels (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Mahfoud, R.; Maresca, M.; Garmy, N.; Fantini, J. The Mycotoxin Patulin Alters the Barrier Function of the Intestinal Epithelium: Mechanism of Action of the Toxin and Protective Effects of Glutathione. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 181, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dou, X.W.; Zhang, C.; Logrieco, A.F.; Yang, M.H. A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines. Toxins 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha, S.C.; Faria, M.A.; Pereira, V.L.; Oliveira, T.M.; Lima, A.C.; Pinto, E. Patulin Assessment and Fungi Identification in Organic and Conventional Fruits and Derived Products. Food Control 2014, 44, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioates Negut, C.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; van Staden, J.F. Minireview: Current Trends and Future Challenges for the Determination of Patulin in Food Products. Anal. Lett. 2023, 56, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.; Biziuk, M. Determination of Pesticide Residues in Food Matrices Using the QuEChERS Methodology. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Choi, K.; Kim, B. Development of Isotope Dilution-Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry as a Candidate Reference Method for the Accurate Determination of Patulin in Apple Products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Shao, H.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, M.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Hacımüftüoğlu, A.; Yan, F.; et al. The Determination of Patulin from Food Samples Using Dual-Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1125, 121714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Determination of Patulin in Apple Juice by Single-Drop Liquid-Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa da Silva, C.; Tonial Simões, C.; Kobs Vidal, J.; Reghelin, M.A.; Araújo de Almeida, C.A.; Mallmann, C.A. Development and Validation of an Extraction Method Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry to Determine Patulin in Apple Juice. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşpınar, H.; Elik, A.; Kaya, S.; Altunay, N. Optimization of Green and Rapid Analytical Procedure for the Extraction of Patulin in Fruit Juice and Dried Fruit Samples by Air-Assisted Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Solidified Homogeneous Liquid Phase Microextraction Using Experimental Design And. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Decision 2002/657—2002/657/EC: Commission Decision of 12 August 2002 Implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC Concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results (Notified under Document Number C(2002) 3044)—EU. Available online: https://www.eumonitor.eu/9353000/1/j9vvik7m1c3gyxp/vi8rm2yoqlym (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Leite, M.; Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Ramos, F. Comprehensive Assessment of Different Extraction Methodologies for Optimization and Validation of an Analytical Multi-Method for Determination of Emerging and Regulated Mycotoxins in Maize by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, H.; Juan, C.; Mañes, J.; Mercader, J.V.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Green Derivatization Strategy Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (QTOF-MS) for Patulin Monitoring in Fruit Products. Talanta 2023, 253, 124061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Barda, O.; Zakin, V.; Reifen, R.; Sionov, E. Rapid Detection and Quantification of Patulin and Citrinin Contamination in Fruits. Molecules 2021, 26, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Linear Range (µg/kg) | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | LOD (µg/kg) a | LOQ (µg/kg) b | Accuracy c | Precision c (%RSD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (% ± SD) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |||||
| 2–50 | 0.999 | 0.32 | 1.15 | LL | 98 ± 8 | 3.78 | 5.10 |
| ML | 92 ± 4 | 4.58 | 6.85 | ||||
| HL | 103 ± 1 | 2.67 | 4.73 | ||||
| Sample Amount | Extraction Procedure | Analytical Method | LOD (µg/kg) | LOQ (µg/kg) | Rec (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | LLE (10 mL MeCN) | LC-MS/MS | 0.5 | 4 | 87–100 | [19] |
| 1 g | LLE (2 mL ethyl acetate) | LC-PDA | 6 | 18 | 55–97 | [24] |
| 0.5 g | ID-MIP-SPE (10 mL H2O:AcA (99:1 v/v) | LC-MS/MS | 0.33 | 1.10 | 98–102 | [16] |
| 5 g | - | LC-MS/MS | 0.5 | 2 | 94–98 | [23] |
| 2 mL | AA-NADES-SH-LPME (410 µL NADES solvent) | UV-Vis | 3.5 | 10 | 94–104 | [20] |
| 10 g | QuEChERS (10 mL ethyl acetate) | UHPLC-MS/MS | - | 0.65–3.01 | 96–109 | [2] |
| 10 g | QuEChERS-dSPE (10 mL ethyl acetate) | LC-MS/MS | - | 5 | 90–95 | [1] |
| 0.1 g | µ-QuEChERS (1 mL MeCN) | LC-MS/MS | 0.32 | 1.15 | 92–103 | This work |
| Number of Samples | 30 |
|---|---|
| Incidence a (%) | 10 (3 of 30) |
| Concentration range (µg/kg) | 1.94–7.15 |
| Mean ± SD (µg/kg) | 4.38 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Câmara, J.S.; Fernandes, P.; Barros, N.; Perestrelo, R. An Improved Analytical Approach Based on µ-QuEChERS Combined with LC-ESI/MS for Monitoring the Occurrence and Levels of Patulin in Commercial Apple Juices. Separations 2023, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030149
Câmara JS, Fernandes P, Barros N, Perestrelo R. An Improved Analytical Approach Based on µ-QuEChERS Combined with LC-ESI/MS for Monitoring the Occurrence and Levels of Patulin in Commercial Apple Juices. Separations. 2023; 10(3):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030149
Chicago/Turabian StyleCâmara, José S., Paulo Fernandes, Nelson Barros, and Rosa Perestrelo. 2023. "An Improved Analytical Approach Based on µ-QuEChERS Combined with LC-ESI/MS for Monitoring the Occurrence and Levels of Patulin in Commercial Apple Juices" Separations 10, no. 3: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030149
APA StyleCâmara, J. S., Fernandes, P., Barros, N., & Perestrelo, R. (2023). An Improved Analytical Approach Based on µ-QuEChERS Combined with LC-ESI/MS for Monitoring the Occurrence and Levels of Patulin in Commercial Apple Juices. Separations, 10(3), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10030149