Study on the Effects of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization on Particulate Matter Emission from Industrial Coal-Fired Power Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
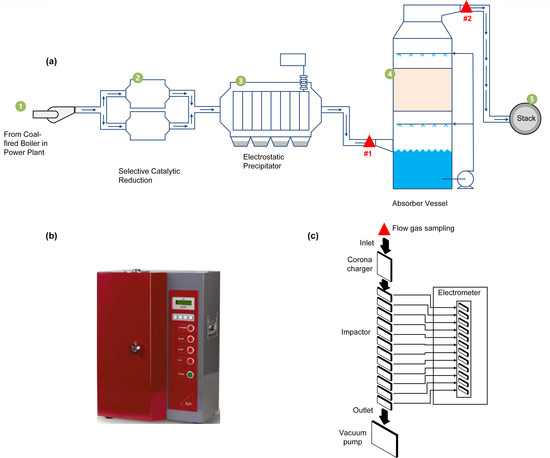
2.1. APCDs in the CFPPs
2.2. Total Particle Concentration and Flue Gas Temperature Test
2.3. PM10 Graded Concentration Test
2.4. Particle Matter Sampling Description
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of ELPI and Conventional Sampler
3.2. Characteristics of PM Emission at the Inlet and Outlet of the Industrial Boiler
3.2.1. For Plant A at 48 t/h Load
3.2.2. For Plant A at 75 t/h Load
3.3. Characteristics of PM Emission at the Inlet and Outlet of Coal-Fired Boilers
3.3.1. For Plant B with 220 MW
3.3.2. For Plant E with 135 MW
3.3.3. For Plant D with 600 MW
3.4. Influencing Factors of PM10 Emissions from Wet Desulfurization
3.4.1. The Influence of the Number of Spraying Layers
3.4.2. The Influence of the Temperature of Inlet Flue Gas
3.4.3. The Influence of the Different PM Concentrations at the Desulfurization Inlet
3.5. Summary
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The ELPI is an effective test method with more concentrated distribution, lower bias, and higher confidence in the test data of particle matter concentration than filter membrane sampler and filter cartridge sampler.
- (2)
- WFGD showed significant capture efficiency for PM10 compared to PM2.5, indicating that WFGD has particle size selectivity for the capture of particulate matter, with a better capture effect on larger particles and poorer capture effect on smaller particles.
- (3)
- The three-stage roof-type mist eliminator in the tower of WFGD had higher PM10 capture efficiency than the conventional mechanical grid mist eliminator and two-stage ridge-type mist eliminator.
- (4)
- Compared to the two-layer spray, the four-layer spray in the WFGD tower is more beneficial in reducing PM10 and PM2.5 emissions, but its capture efficiency for submicron particles is lower because more small droplets are entrained.
- (5)
- The PM10 capture efficiency of WFGD is affected by WFGD inlet flue gas temperature and particle matter concentration. Higher inlet flue gas temperature and lower inlet particle matter concentration can both increase WFGD outlet PM0.1~1 emissions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.-F.; Hao, W. Assessment method for the prevention effectiveness of PM2.5 based on the optimization development of coal-fired power generation. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Sanya, China, 21–23 November 2016; Volume 52, p. 012076. [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniewska, A.; Szramowiat, K.; Gołaś, J. An overview of some challenges in the studies in the emission of particulate matter. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Krakow, Poland, 14–17 November 2017; Volume 214, p. 012119. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, R.T.; Pope, C.A.; Ezzati, M.; Olives, C.; Lim, S.S.; Mehta, S.; Shin, H.H.; Singh, G.; Hubbell, B.; Brauer, M.; et al. An integrated risk function for estimating the global burden of disease attributable to ambient fine particulate matter exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Huo, H. Cleaning China’s air. Nature 2012, 484, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wei, C.; Mu, Q.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Carmichael, G.; et al. Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Tu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, W.; Shen, X.; Huang, D.; Gao, L.; Yan, K. Soil remediation via DBD induced multiple pollutants cleaning. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol 2004, 16, 7pp. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yue, H.; Zhang, R.; Tang, X. Environmental co-benefits of energy efficiency improvement in coal-fired power sector: A case study of Henan Province, China. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yan, B.; Liu, S.; Liang, Y.; Dong, N.; Hui, S. Ultra-fine particulate matters (PMs)formation during air and oxy-coal combustion: Kinetics study. Appl. Energy 2018, 218, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Patiño-Echeverri, D.; Zhang, J.J. Policies to promote energy efficiency and air emissions reductions in China’s electric power generation sector during the 11th and 12th five-year plan periods: Achievements, remaining challenges, and opportunities. Energy Policy 2019, 125, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Development and Reform Commission, Coal Energy Saving, Emission Reduction Upgrade and Reform Action Plan (2014–2020). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2015/content_2818468.htm (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Ruan, R.; Liu, H.; Tan, H.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Effects of APCDs on PM emission: A case study of a 660 MW coal-fired unit with ultralow pollutants emission. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 155, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagiello, D.; Erto, A.; Lancia, A.; Di Natale, F. Dataset of wet desulphurization scrubbing in a column packed with Mellapak 250 X. Data Brief 2020, 33, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.J.; Quartucy, G.C.; Cichanowiczy, J.E. Overview and status of post-combustion NOx control: SNCR, SCR and hybrid technologies. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 17, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, D.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Enhanced particle precipitation from flue gas containing ultrafine particles through precharging. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 144, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Guo, X.; Hao, J.; Duan, L.; Li, X. Characteristics of inhalable particulate matter concentration and size distribution from power plants in China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, X.; Tian, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Ke, Y.; Yan, K. The turbulent-flow-assisted electrostatic collection and alignment of recycled short-chopped carbon fiber in gaseous phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Ke, Y.; Yan, K. Development and experimental investigation of the narrow-gap coated electrostatic precipitator with a shield pre-charger for indoor air cleaning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, A.; Mo, H. Test and Study on Performance of Wet FGD Coordinated Particulate Matter Control for Ultra-Low Pollutants Emission. Electr. Power 2017, 50, 168–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; Chen, Y.; Lin, N.; Zhuo, S.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Quantification of global primary emissions of PM2.5, PM10, and TSP from combustion and industrial process sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13834–13843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Jawahar, P. Atmospheric emissions and pollution from the coal-fired thermal power plants in India. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.M.; Hassim, M.H.; Taib, R.M. Health risk assessment of emissions from a coal-fired power plant using AERMOD modelling. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, F.; Carotenuto, C.; Parisi, A.; Flagiello, D.; Lancia, A. Wet electrostatic scrubbing for flue gas treatment. Fuel 2022, 325, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, T.-A. Summary of research progress on industrial flue gas desulfurization technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ye, S.-C.; Bai, J.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Yang, Y.-F. A concise algorithm for calculating absorption height in spray tower for wet limestone–gypsum flue gas desulfurization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, J.; Huang, W.; Li, G.; Li, S.; Cui, P.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Novel product-adjustable technology using Wellman-Lord method coupled with sodium-alkali for SO2 removal and regeneration from smelting gas. Fuel 2021, 288, 119714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Valle-Zermeño, R.; Niubó, M.; Formosa, J.; Guembe, M.; Aparicio, J.; Chimenos, J. Synergistic effect of the parameters affecting wet flue gas desulfurization using magnesium oxides by-products. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, C.; Di Natale, F.; Lancia, A. Wet electrostatic scrubbers for the abatement of submicronic particulate. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Pan, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Gao, X. Field measurements on the emission and removal of PM2.5 from coal-fired power stations: 1. Case study for a 1000 MW ultrasupercritical utility boiler. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6547–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qi, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Zhou, C.; Lu, S.; Yan, J.; Li, X. Physical and chemical characteristics of condensable particulate matter from an ultralow-emission coal-fired power plant. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Norris, P.; Cao, Y.; Pan, W.P. Fine particulate matter emission and size distribution characteristics in an ultra-low emission power plant. Fuel 2016, 185, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, L.J.; Yan, J.P.; Hong, G.X.; Yang, B. Improving the removal of fine particles by heterogeneous condensation during WFGD processes. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 145, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Norris, P.; Cao, Y.; Pan, W.-P. Effects of wet flue gas desulfurization and wet electrostatic precipitator on particulate matter and sulfur oxide emission in coal-fired power plants. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 16423–16432. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China, The Determination of Particulates and Sampling Methods of Gaseous Pollutants Emitted from Exhaust Gas of Stationary Source. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/199603/t19960306_67508.shtml (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Marjamäki, M.; Lemmetty, M.; Keskinen, J. ELPI Response and data reduction I: Response functions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Ojanperä, J.; Kannosto, J.; Marjamäki, M.; Keskinen, J. Improving the nanoparticle resolution of the ELPI. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linak, W.P.; Miller, C.A.; Wendt, J.O.L. Comparison of Particle Size Distributions and Elemental Partitioning from the Combustion of Pulverized Coal and Residual Fuel Oil. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, M.; Lu, S. Emission Characteristics of Particulate Matter from Coal-Fired Power Units with Different Load Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 2022, 233, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, M.; Lu, S. Study on the control of condensable particulate matter by spraying activated carbon combined with electrostatic precipitator. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Ma, Z.; Fajardo, O.A.; Deng, J.; Duan, L. Influence of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) installations on emission characteristics of PM2.5 from coal-fired power plants equipped with selective catalytic reduction (SCR). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingjing, B.; Linjun, Y.; Jinpei, Y.; Guilong, X.; Bin, L.; Chengyun, X. Experimental study of fine particles removal in the desulfurated scrubbed flue gas. Fuel 2013, 108, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Description | Plant A | Plant B | Plant C | Plant D | Plant E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| boiler type | CFB boiler | PC boiler | PC boiler | PC boiler | CFB boiler |
| installed capacity (MW)/BMCR (t/h) | 3 × 15/75 | 4 × 220/670 | 4 × 330/1100 | 2 × 600/1900 | 2 × 135/440 |
| flue gas flow (×104 m3/h) | 10 | 45 | 110 | 145 | 88 |
| flue gas temperature (°C) | 140 | 95 | 140 (110) | - | 120 |
| mist eliminator type | Tubular type | 2nd roof ridge type | 3rd roof ridge type | 3rd roof ridge type | 3rd roof ridge type+ Mechanical grille type |
| APCDs | SCR + ESP + WFGD | SCR + LTE + ESP + WFGD | SCR + (LTE) + ESP + WFGD | SCR + ESP + WFGD | SCR + LTE + ESP + WFGD |
| Description | Range | Resolution | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling flow rate | 5~60 L/min | 0.1 L/min | ±2.5% |
| Isometric sampling flow rate | 1~45 m/s | 0.1 m/s | <±4% |
| Flue gas dynamic pressure | 0 Pa~2000 Pa | 1 Pa | <±1.5% |
| Flue gas static pressure | −20 kPa~20 kPa | 0.01 kPa | <±4% |
| Flue gas full pressure | −20 kPa~20 kPa | 0.01 kPa | <±4% |
| Pressure before flow meter | −30 kPa~0 kPa | 0.01 kPa | <±2.5% |
| Temperature before flow meter | −20 °C~100 °C | 0.1 °C | <±1.5% |
| Flue gas temperature | 0 °C~500 °C | 1 °C | ≤±3 °C |
| Dry bulb temperature | 0~100 °C | 0.1 °C | |
| Wet bulb temperature | 0~100 °C | 0.1 °C | |
| Humidity content | 0~60% | 0.1% | <±1.5% |
| Description | Range |
|---|---|
| Rated flow rate | 10 L/min |
| Range of particle size | 0.03~10 μm |
| Number of sampling trays | 12 |
| Operating temperature | 5~40 °C |
| Operating humidity | 0~60% RH |
| Flue gas temperature | −30 kPa–0 kPa |
| First stage sampling tray pressure | 100 mBar |
| Response time | <5 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, A.; Li, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yan, K. Study on the Effects of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization on Particulate Matter Emission from Industrial Coal-Fired Power Plants. Separations 2023, 10, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060356
Wang A, Li S, Zheng Q, Zhang S, Zhang S, Wang Z, Liu Z, Yan K. Study on the Effects of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization on Particulate Matter Emission from Industrial Coal-Fired Power Plants. Separations. 2023; 10(6):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060356
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Anyu, Shuran Li, Qinzhen Zheng, Shuo Zhang, Shihao Zhang, Zhihao Wang, Zhen Liu, and Keping Yan. 2023. "Study on the Effects of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization on Particulate Matter Emission from Industrial Coal-Fired Power Plants" Separations 10, no. 6: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060356
APA StyleWang, A., Li, S., Zheng, Q., Zhang, S., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Liu, Z., & Yan, K. (2023). Study on the Effects of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization on Particulate Matter Emission from Industrial Coal-Fired Power Plants. Separations, 10(6), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060356