Possibilities for the Environmental Processing of Gold-Bearing Ores
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- I.
- The absence of harmful gaseous emissions;
- II.
- Low energy consumption (low temperature and pressure);
- III.
- An increase in gold extraction from low-grade ores while reducing the consumption of chemical reagents;
- IV.
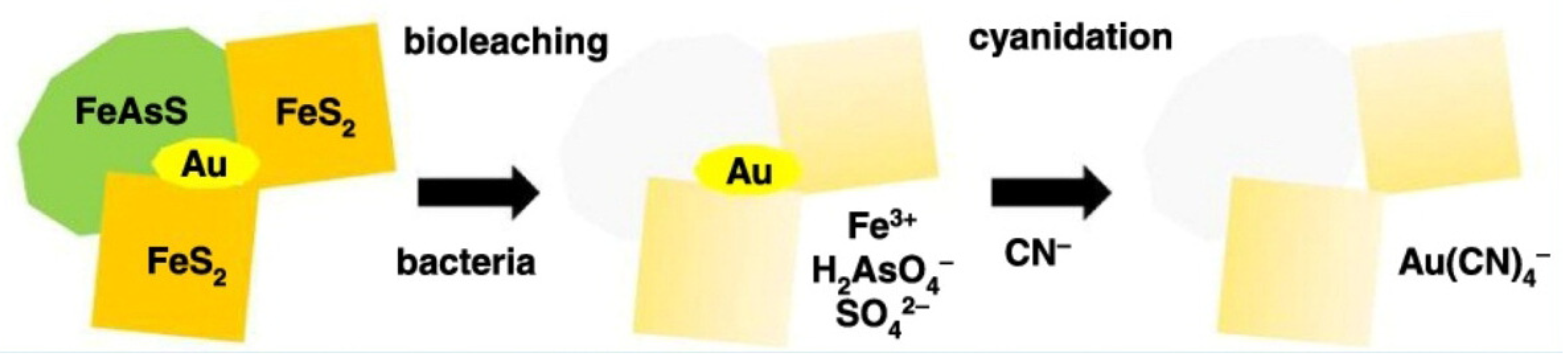
- The tailings produced from bio-mining processes are less chemically and biologically active, as they are already biologically leached [23].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Comparison of the Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.H. Environmental Science and Policy. In Mining, the Environment, and Indigenous Development Conflicts; University of Arizona Press: Tuscon, AZ, USA, 2009; Volume 54, pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wijewardena, R.; Takama, T.; Wijesekara, R.S. Environmental and Social Impacts of Mining and Mineral Processing in the Western Province of Sri Lanka. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 84, 732–742. [Google Scholar]
- Hilson, G. The Environmental Impact of Small-Scale Gold Mining in Ghana: Identifying Problems and Possible Solutions. Geogr. J. 2014, 168, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylmore, M.G. Alternative lixiviants to cyanide for leaching gold ores. Dev. Miner. Process. 2005, 15, 501–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Lyu, X. A review of gold extraction using alternatives to cyanide: Focus on current status and future prospects of the novel eco-friendly synthetic gold lixiviants. Miner. Eng. 2022, 176, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Taylor, M.P. Alternative lixiviants to cyanide for leaching gold ores. Dev. Miner. Process. 2016, 15, 383–415. [Google Scholar]
- Kratochvíl, M. Gold-Bearing Ore Treatment Technologies. Diploma Thesis, University of Mining—Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Müezzinoğlu, A. A Review of environmental considerations on gold mining and production. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 33, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.K.; Pownceby, M.I.; Ram, R. Hydrometallurgy. Metals 2016, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, M. (Ed.) Advances in gold ore processing. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, p. 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrometallurgy. Available online: https://chem.libretexts.org/@go/page/91360 (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Hydrometallurgy. Available online: https://medium.com/@bicspuc/hydrometallurgy-237ad568732d (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, G.J.; Woodcock, J.T. Cyanide and other lixiviant leaching systems for gold with some practical applications. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1995, 14, 193–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.; Monhemius, A.J. Alternatives to cyanide in the gold mining industry: What prospects for the future? J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylmore, M.G. Alternative lixiviants to cyanide for leaching gold ores. In Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 447–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, L. Hydrothermal Processes at the Osborne Fe-Oxide-Cu-Au Deposit, NW Queensland: Integration of Multiple Micro-Analytical Data Sets to Trace Ore Fluid Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, James Cook University, Douglas, QLD, Australia, 2007. Available online: https://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/4782/3/03Chapters4-6.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2008).
- Li, J.; Miller, J.D. A review of gold leaching in acid thiourea solutions. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2006, 27, 177–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H.; Zhang, L. A systematic review of gold extraction: Fundamentals, advancements, and challenges toward alternative lixiviants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy metal pollution from gold mines: Environmental effects and bacterial strategies for resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaksonen, A.H.; Mudunuru, B.M.; Hackl, R. The role of microorganisms in gold processing and recovery—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 142, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B. Biomining—Biotechnologies for extracting and recovering metals from ores and waste materials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, F.; Lengke, M.F.; Falconer, D.; Craw, D.; Southam, G. The geomicrobiology of gold. ISME J. 2007, 1, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, İ.; Celep, O.; Paktunç, D.; Thibault, Y. Influence of potassium hydroxide pretreatment on the extraction of gold and silver from a refractory ore. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver and Gold-Bearing Tetrahedrite. Available online: https://www.mindat.org/min-26626.html (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Ghisani, F.; Timmo, K.; Altosaar, M.; Mikli, V.; Pilvet, M.; Kaupmees, R.; Krustok, J.; Grossberg, M.; Kauk-Kuusik, M. Characterization of tetrahedrite Cu10Cd2Sb4S13 monograin materials grown in molten CdI2 and LiI. Thin Solid Films 2021, 739, 138980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.W.; Craig, J.R. Tetrahedrite-tennantite series compositional variations in the Cofer Deposit, Mineral District, Virginia. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 227–234. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/msa/ammin/article-abstract/68/1-2/227/41451 (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Biagioni, C.; George, L.L.; Cook, N.J.; Makovicky, E.; Moëlo, Y.; Pasero, M.; Sejkora, J.; Stanley, C.J.; Welch, M.D.; Bosi, F. The tetrahedrite group: Nomenclature and classification. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 2020, 105, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Mao, J.; Cao, D.; Shen, X.; Volinsky, A.A. The role of trivalent arsenic in removal of antimony and bismuth impurities from copper electrolytes. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 125, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.A.; Ayinla, K.I.; Adekola, F.A.; Ghosh, M.K.; Ayanda, O.S.; Bale, R.B.; Sheik, A.R.; Pradhan, S.R. A review on novel techniques for chalcopyrite ore processing. Int. J. Min. Eng. Miner. Process. 2012, 1, 1–16. Available online: https://digitalknowledge.cput.ac.za/bitstream/11189/7612/1/A%20Review%20on%20Novel%20Techniques%20for%20Chalcopyrite%20Ore.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, H.; Malfliet, A.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. A review of the technologies for antimony recovery from refractory ores and metallurgical residues. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2022, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, S.A.; Sandström, Å. Selective leaching of arsenic and antimony from a tetrahedrite rich complex sulphide concentrate using alkaline sulphide solution. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, S.; Abdollahi, H.; Gharabaghi, M.; Mirmohammadi, M. Selective leaching of antimony from tetrahedrite rich concentrate using alkaline sulfide solution with experimental design: Optimization and kinetic studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 119, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M.J.N.; Carvalho, J.R.; Monhemius, A.J. The leaching of tetrahedrite in ferric chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 57, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, S.A. Hydrometallurgical Upgrading of a Tetrahedrite-Rich Copper Concentrate. Doctoral Dissertation, Luleå Tekniska Universitet, Luleå, Sweden, 2010. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:998811/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Awe, S.A.; Samuelsson, C.; Sandström, Å. Dissolution kinetics of tetrahedrite mineral in alkaline sulphide media. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.G.; Twidwell, L.G. The alkaline sulfide hydrometallurgical separation, recovery and fixation of tin, arsenic, antimony, mercury and gold. Lead Zinc 2008, 2008, 121–132. Available online: https://www.saimm.co.za/Conferences/PbZn2008/121–132_Anderson (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Spasova, I.; Nicolova, M.; Veglio, F.; Groudev, S. Leaching of gold from a polymetallic sulphide ore. Annu. Univ. Min. Geol. Sodia. 2006, 49, 213–216. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stoyan-Groudev/publication/267788510_LEACHING_OF_GOLD_FROM_A_POLYMETALLIC_SULPHIDE_ORE/links/54ba25d40cf24e50e93dd7f3/LEACHING-OF-GOLD-FROM-A-POLYMETALLIC-SULPHIDE-ORE.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Sasvári, T.; Kondela, J.; Ľuboslav, M.; Slowakiewicz, M. Indície Pt-PGE Mineralizácie na žile Strieborná av širšej Oblasti Rožňavského Rudného Poľa (Spišsko-Qemerské Rudohorie, Západné Karpaty). 2003. Available online: http://gse.vsb.cz/2003/XLIX-2003–1-129–136.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Sasvári, T.; Mat’o, L. Charakteristika rožňavského rudného pol’a vo vzt’ahu k štruktúrno-tektonickej analýze a mineralizácie, na príklade ložiskových pomerov žily Strieborná. Acta Montan. Slovaca 1998, 3, 33–117. Available online: http://actamont.tuke.sk/pdf/1998/n5/6sasvari.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
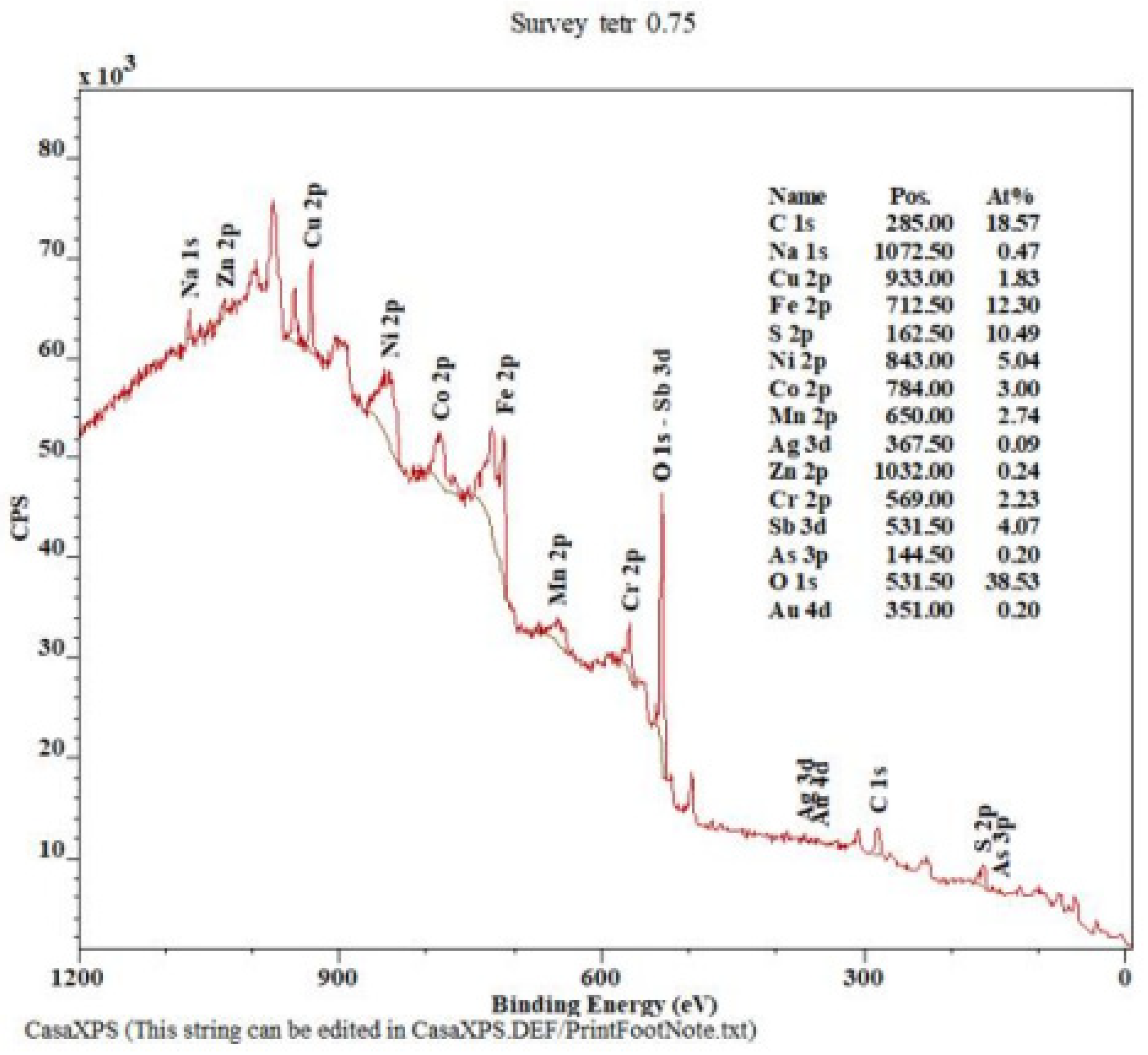
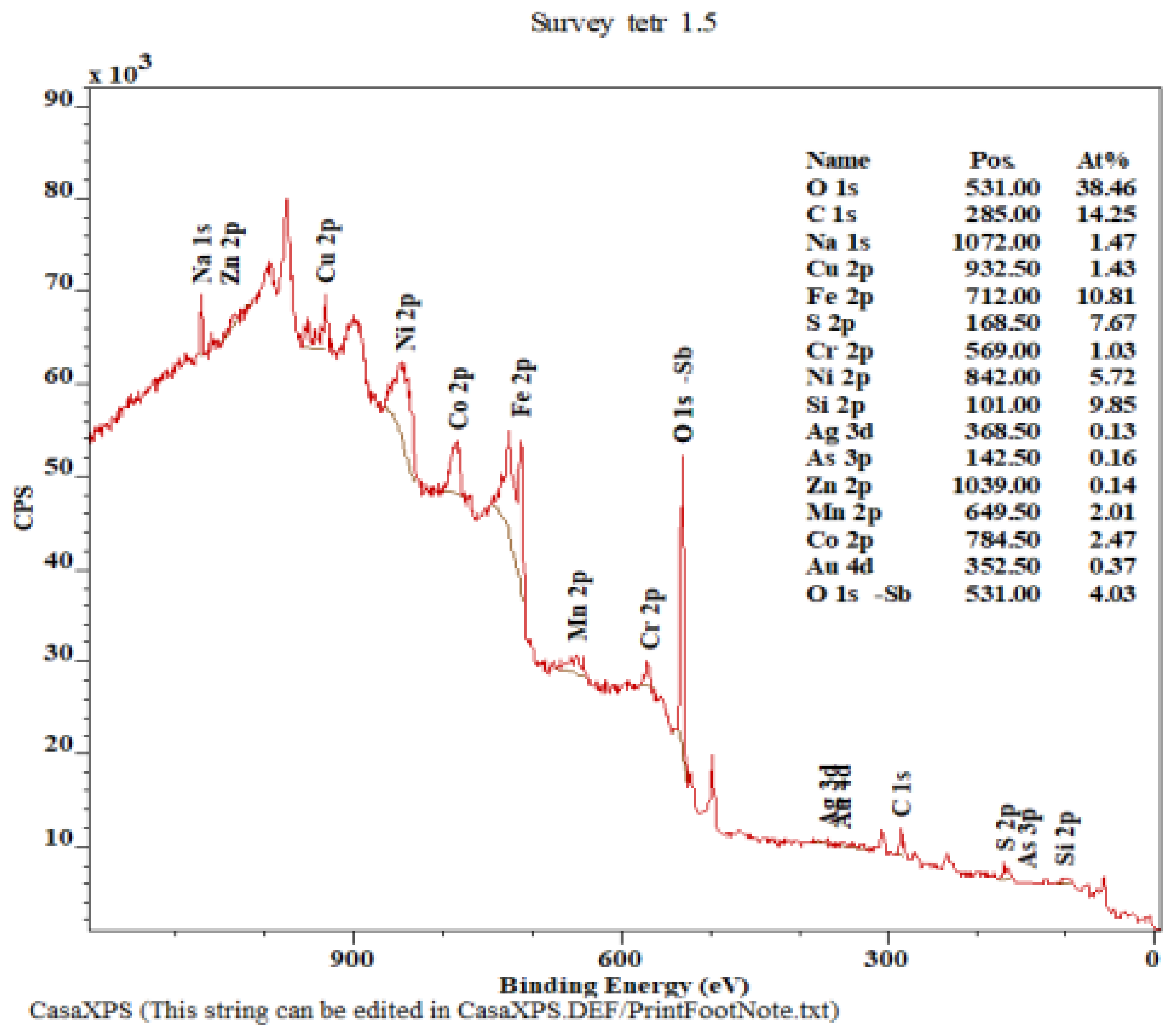
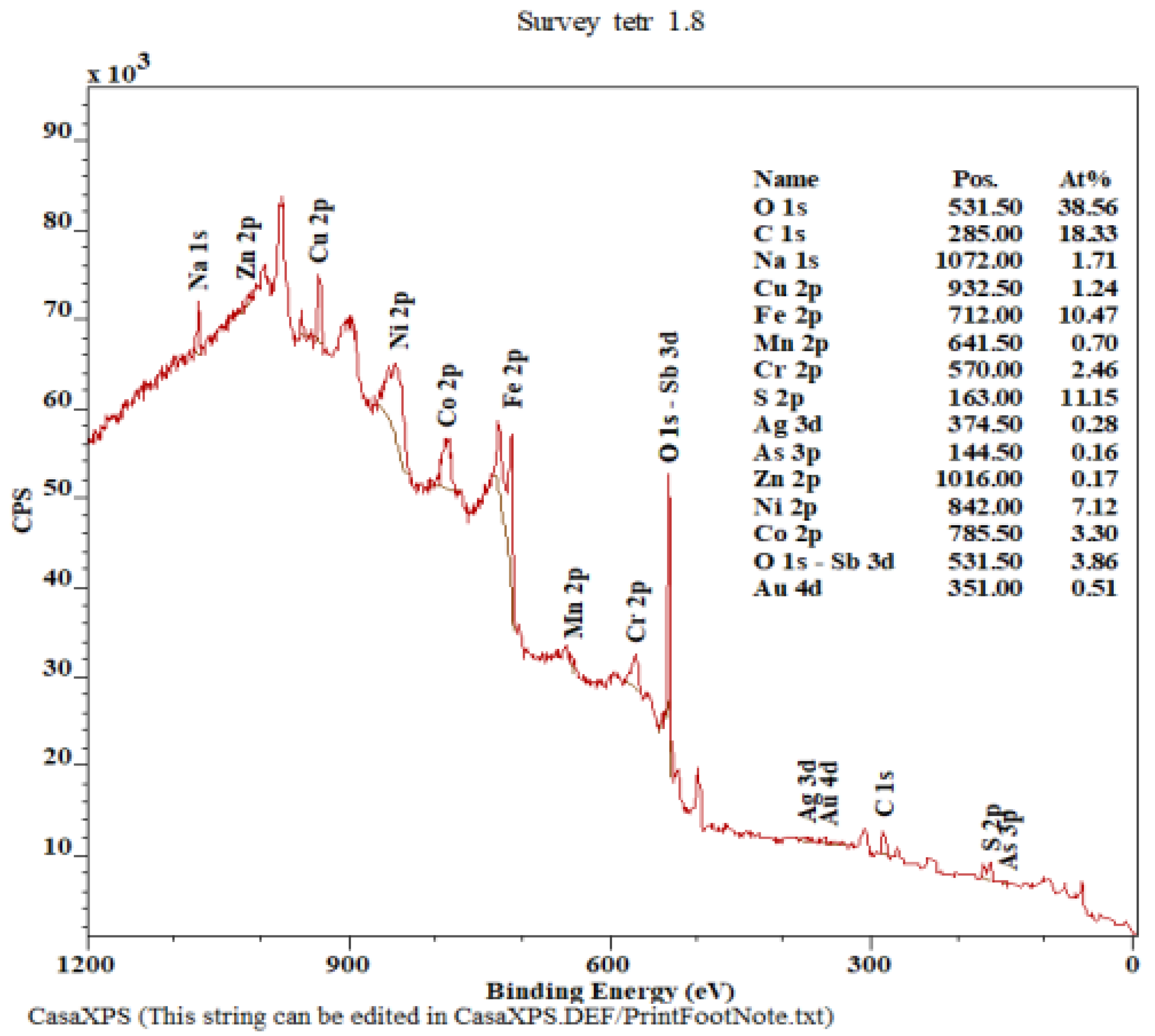


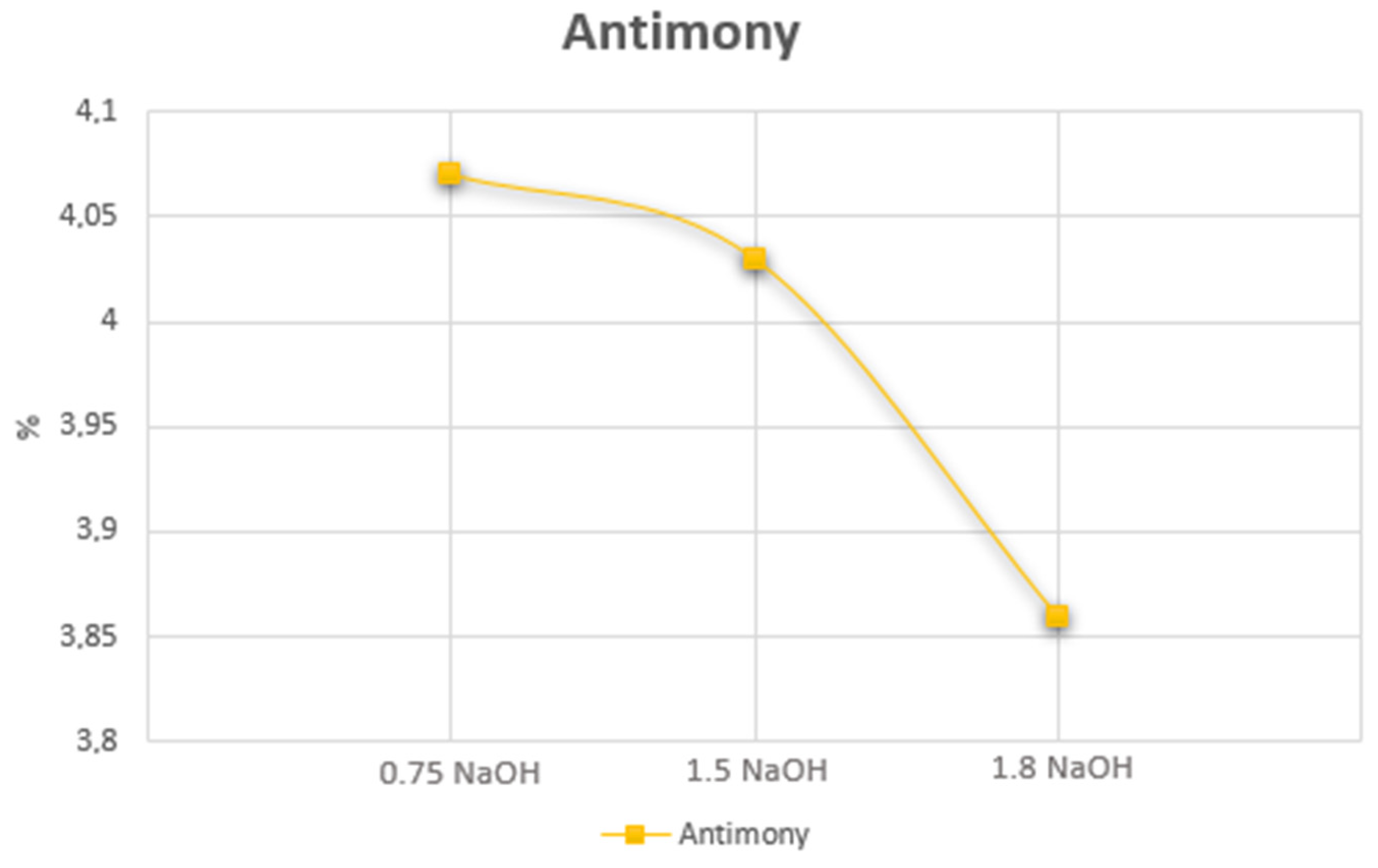
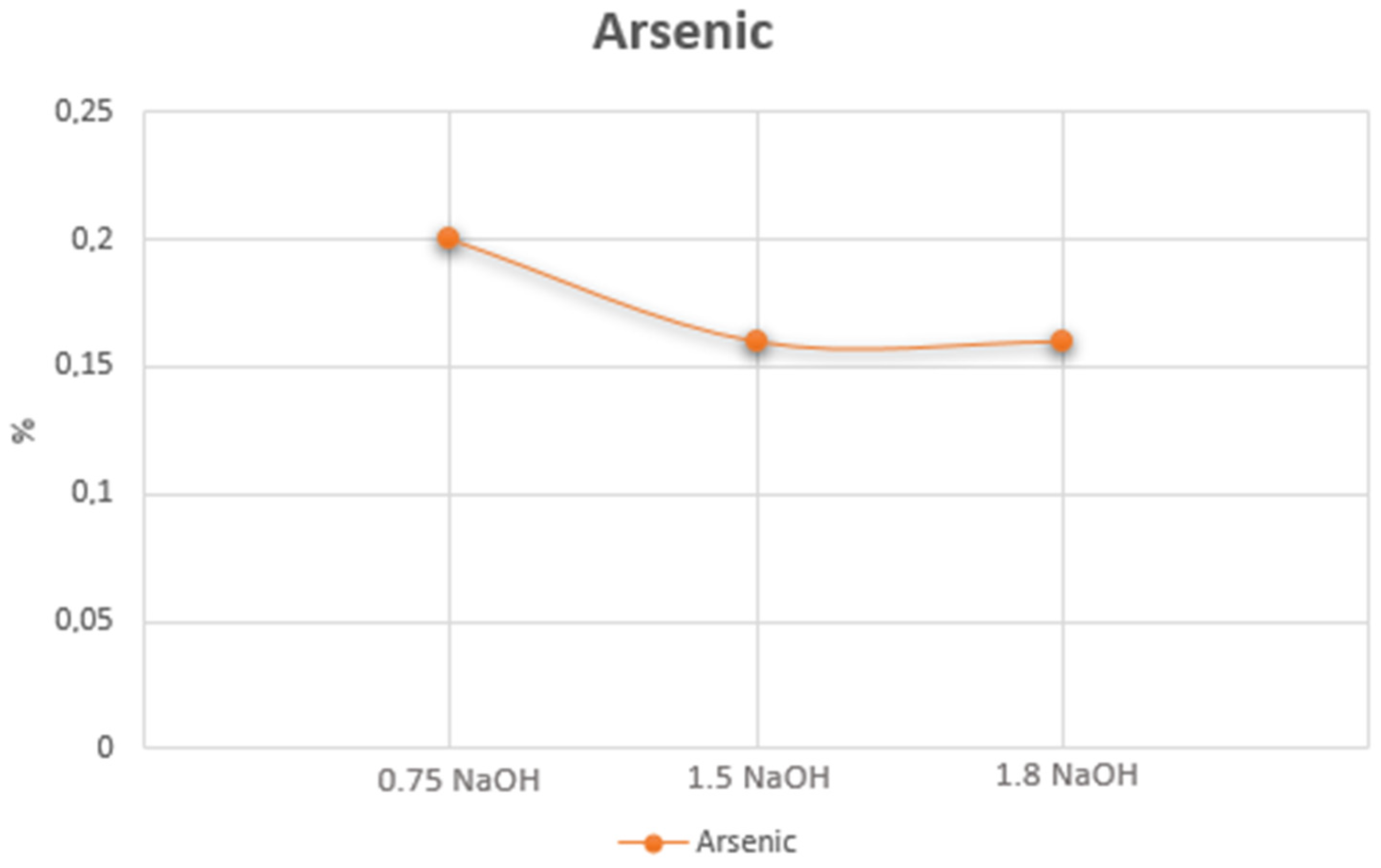

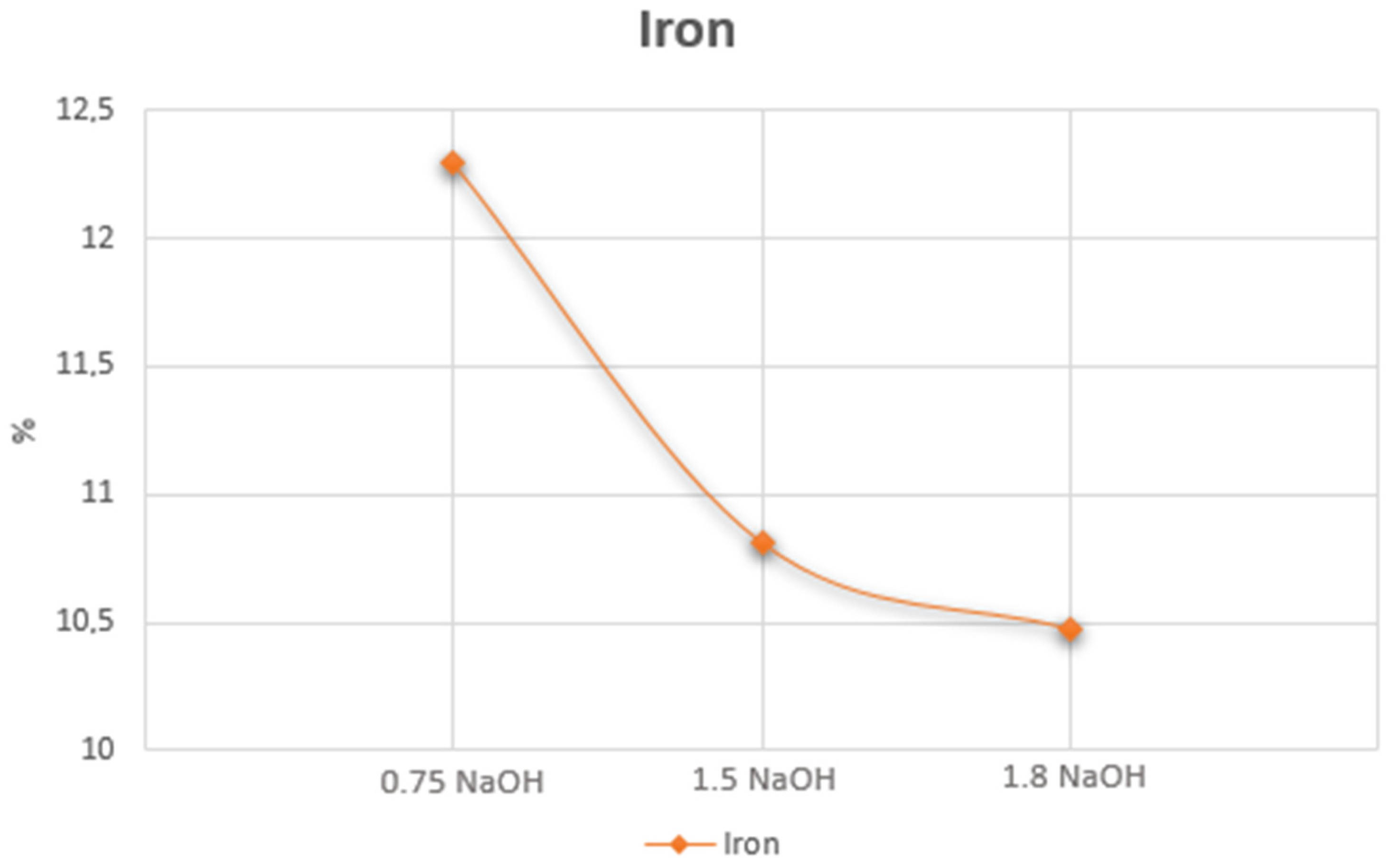

| Cu (%) | Ag (g.t−1) | Au (g.t−1) | Fe (%) | Sb (%) | As (%) | Bi (%) | Hg (%) | Co (%) | Cr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.8–3.5 | 4000–7050 | 5–10 | 8–10 | 12–14 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.2–0.4 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.05–1 |
| mg L−1 | 0.75 M NaOH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 24 |
| As | 2.31 | 2.30 | 3.05 | 2.69 | 3.25 | 2.67 | 3.52 | 7.79 |
| Sb | 6.81 | 7.51 | 8.66 | 9.37 | 10.31 | 11.66 | 12.95 | 21.39 |
| Cu | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| Fe | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| mg L−1 | 1.5 M NaOH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 24 |
| As | 3.31 | 4.24 | 4.37 | 4.91 | 4.65 | 5.05 | 9.37 | 22.43 |
| Sb | 11.31 | 11.52 | 13.21 | 15.41 | 16.54 | 17.13 | 20.44 | 51.14 |
| Cu | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Fe | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.3 |
| mg L−1 | 1.8 M NaOH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 24 |
| As | 3.44 | 4.12 | 4.40 | 4.53 | 4.77 | 5.08 | 9.11 | 14.59 |
| Sb | 9.78 | 14.11 | 14.80 | 16.69 | 19.52 | 21.24 | 55.85 | 66.21 |
| Cu | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Fe | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sudova, M.; Kanuchova, M.; Sisol, M.; Kozakova, L.; Marcin, M.; Holub, T. Possibilities for the Environmental Processing of Gold-Bearing Ores. Separations 2023, 10, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070384
Sudova M, Kanuchova M, Sisol M, Kozakova L, Marcin M, Holub T. Possibilities for the Environmental Processing of Gold-Bearing Ores. Separations. 2023; 10(7):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070384
Chicago/Turabian StyleSudova, Michaela, Maria Kanuchova, Martin Sisol, Lubica Kozakova, Michal Marcin, and Tomas Holub. 2023. "Possibilities for the Environmental Processing of Gold-Bearing Ores" Separations 10, no. 7: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070384
APA StyleSudova, M., Kanuchova, M., Sisol, M., Kozakova, L., Marcin, M., & Holub, T. (2023). Possibilities for the Environmental Processing of Gold-Bearing Ores. Separations, 10(7), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070384







