Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s Coated Superhydrophobic Functional Materials with Efficient Oil/Water Separation Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Ionic Liquids Monomers
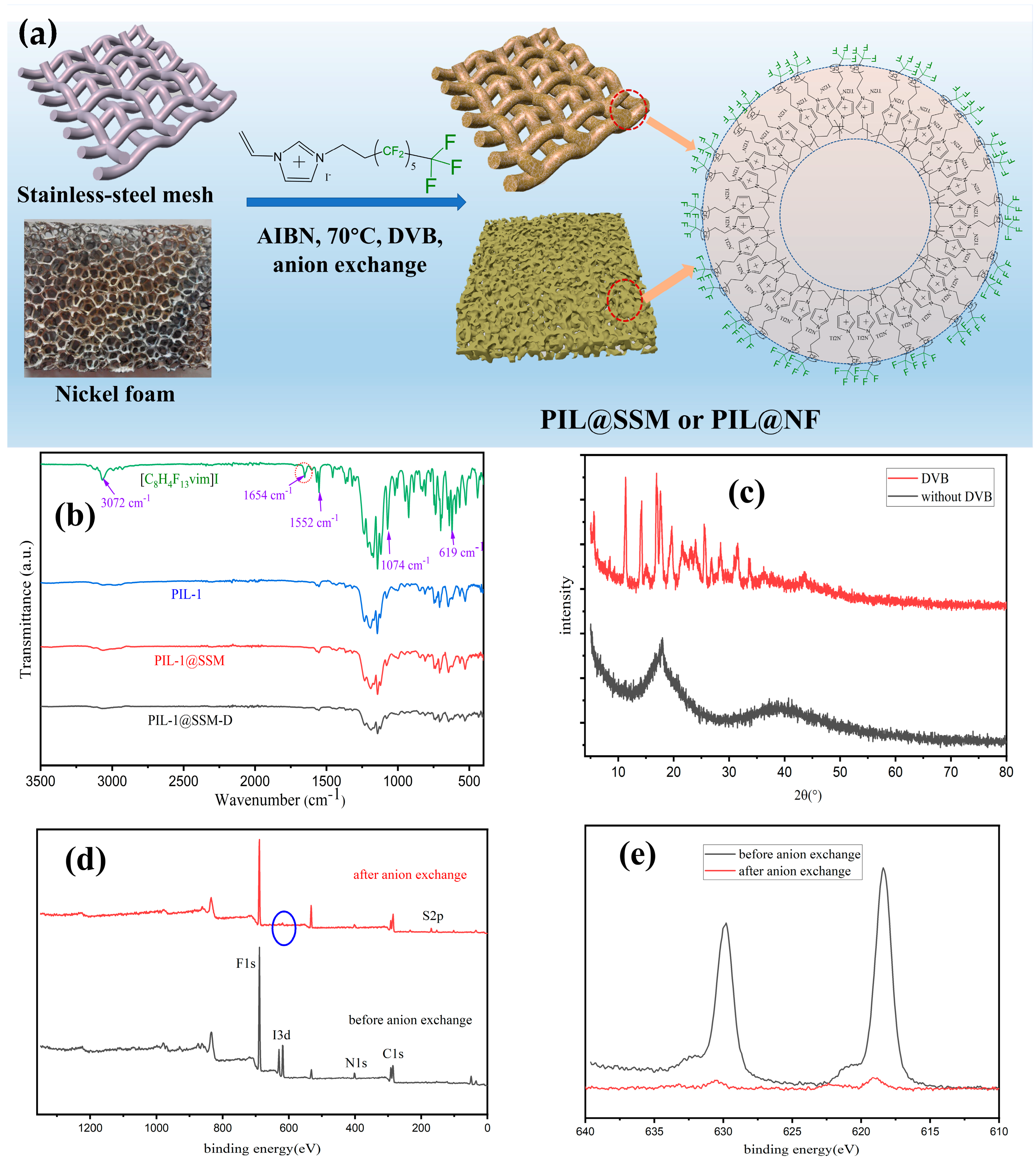
2.3. Synthesis of the Superhydrophobic Materials Coated with Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s
2.4. Characterization of the Superhydrophobic Materials
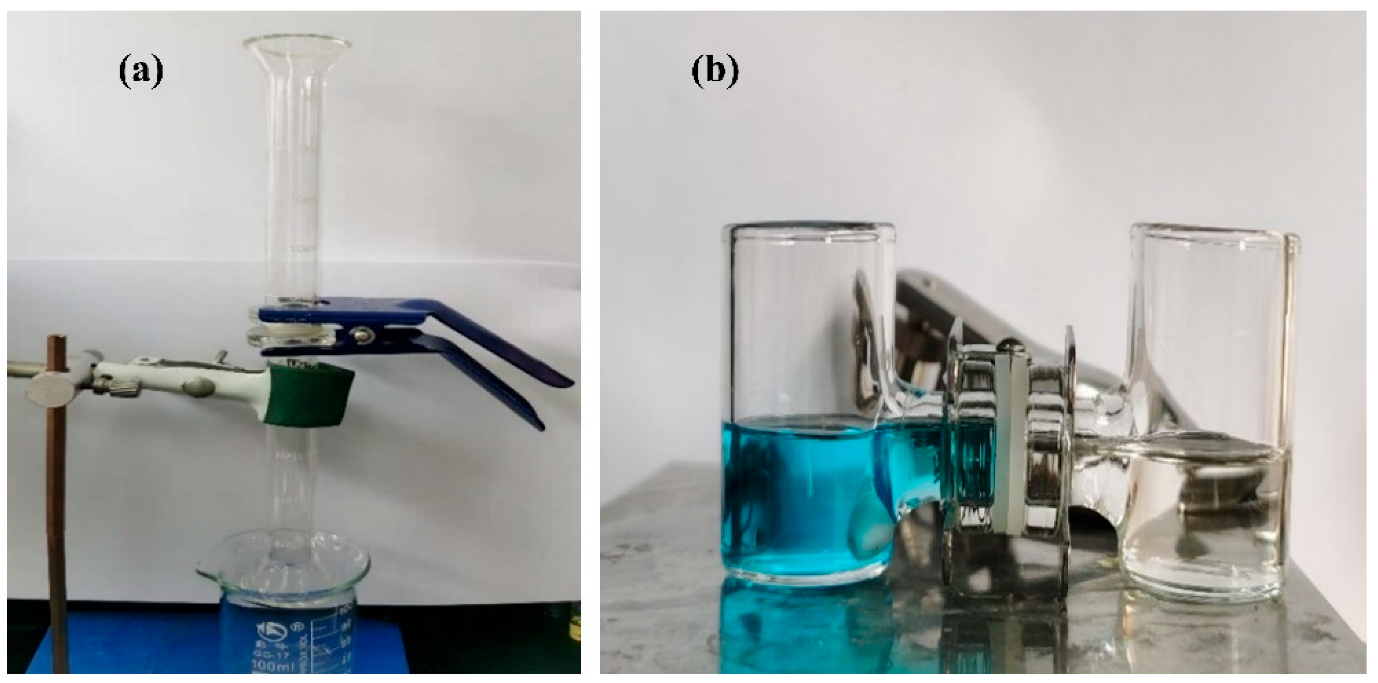
2.5. Separation Performance of the Superhydrophobic Materials
3. Results and Discussion
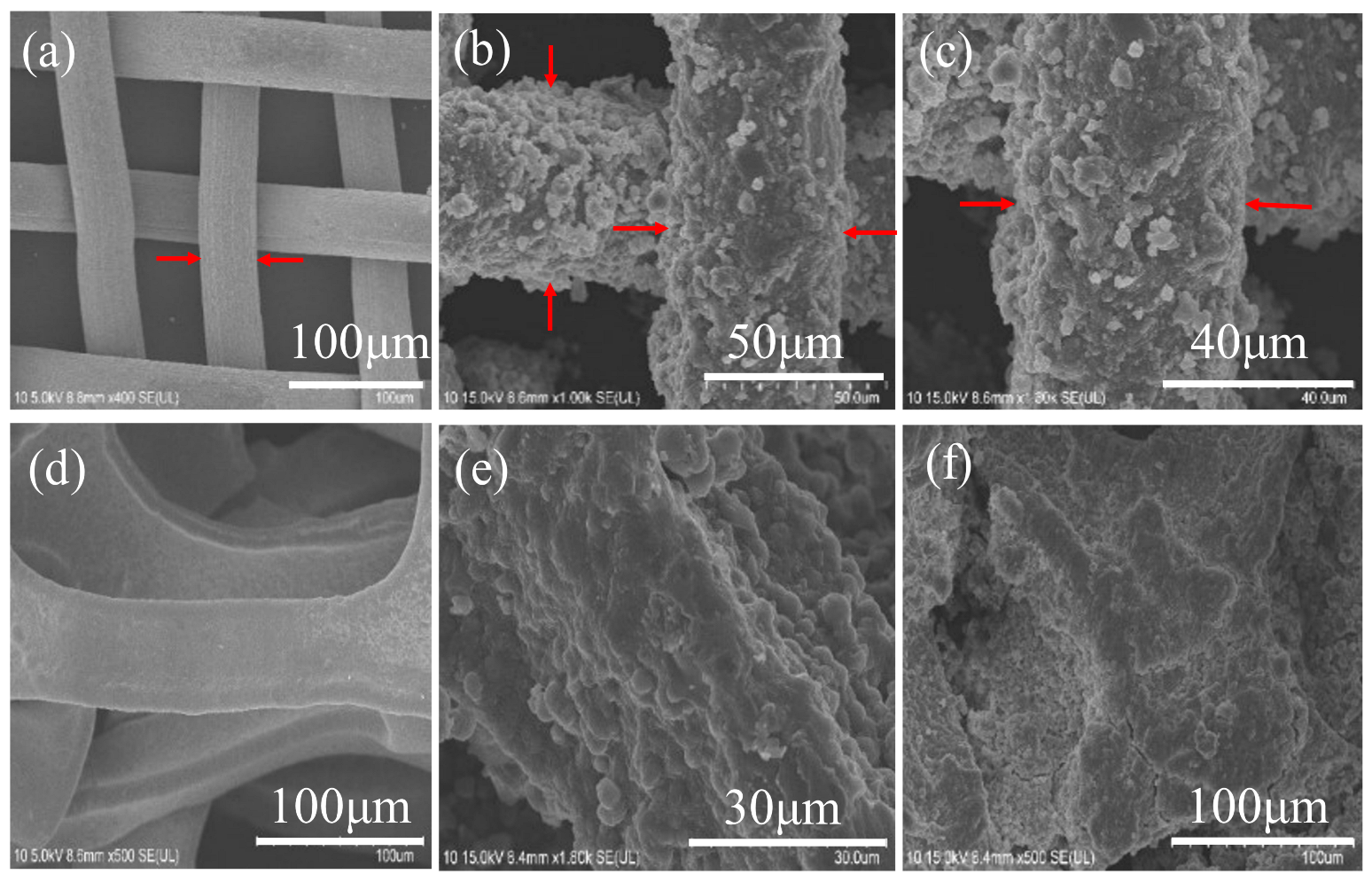
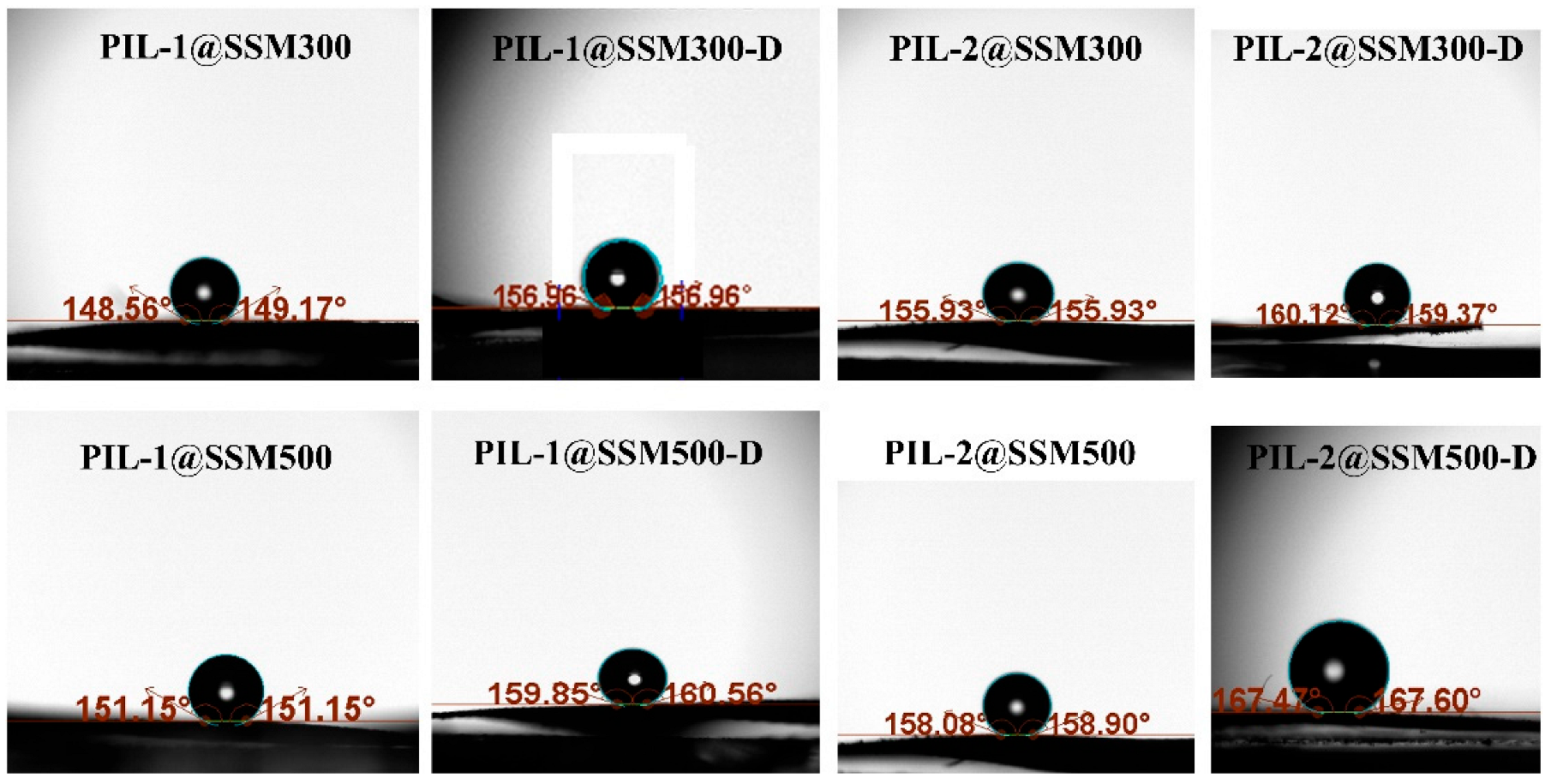
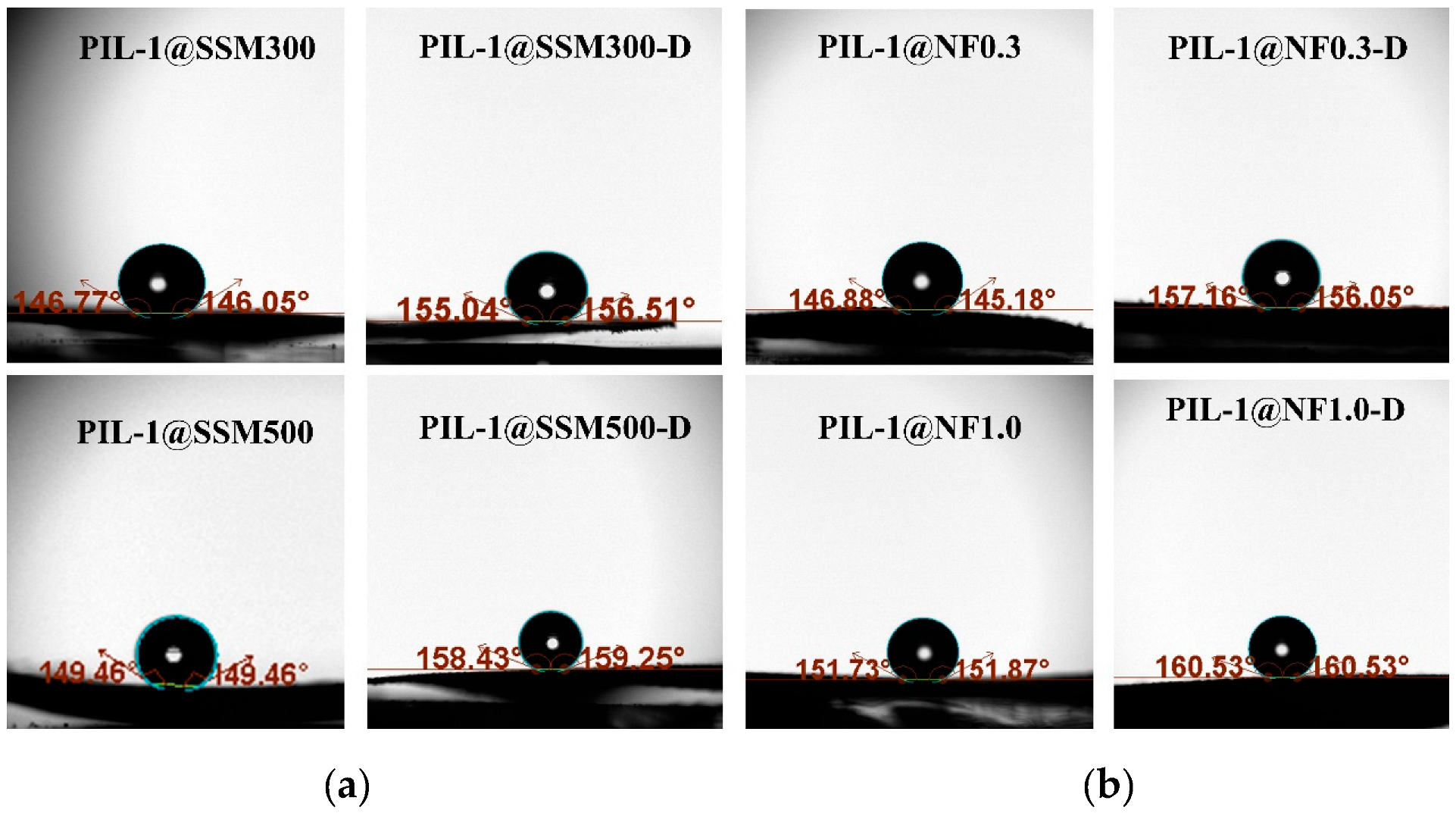
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of the PIL Coated Materials
3.2. The Permeate Flux of the Oil Phase
3.3. Oil-Water Separation Performance
3.4. Recyclability of the Superhydrophobic Material
3.5. Separation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, B.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Mu, P.; Li, J. Current research situation and future prospect of superwetting smart oil/water separation materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 20190–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Shen, Y.; Mu, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, J. Effective separation of surfactant-stabilized crude oil-in-water emulsions by using waste brick powder-coated membranes under corrosive conditions. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tiwari, B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Yap, Y.K. Water purification: Oil–water separation by nanotechnology and environmental concerns. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Seeger, S. Oil/Water Separation with Selective Superantiwetting/Superwetting Surface Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, L.T. Protonated Melamine Sponge for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, A.; Ernawati, L.; Ismayati, M.; Martak, F.; Enomae, T. Bioinspired cellulose-based membranes in oily wastewater treatment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Fu, H.; Xu, J.; Jing, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, B.; Hou, X. Efficient oil–water separation coating with robust superhydrophobicity and high transparency. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Rowe, P.; Chi, C.; Sreepal, V.; Bohn, T.; Zhou, K.-G.; Su, Y.; Prestat, E.; Pillai, P.B.; Cherian, C.T.; et al. Cation-controlled wetting properties of vermiculite membranes and its promise for fouling resistant oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Lu, T.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based materials with special wettability for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Pei, C. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals on bacterial cellulose hydrogel for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Han, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Highly efficient oil–water separation of superhydrophobic cellulose II aerogel based on dissolution and regeneration of cotton in lithium bromide system. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ji, D. Graphite powder coated polyurethane sponge hollow tube as a high-efficiency and cost-effective oil-removal materials for continuous oil collection from water surface. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Oil removal from water using biomaterials. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6594–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirzaee, M.; Abdi, J.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Schaffie, M.; Ranjbar, M.; Khataee, A. Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents for oil/water separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xi, X.; Dai, L.; Tong, S.; Chen, Z. Hydrogel as a Superwetting Surface Design Material for Oil/Water Separation: A Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H.; Lin, J.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, C.; Tan, L.; Dong, L. Room-temperature fabrication of superhydrophobic covalent organic framework (COF) decorated cotton fabric for high-flux water-in-oil emulsion separation. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 11533–11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.A.; Mohamed, M.; Deyab, N. A simple method for developing efficient room temperature reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge and cotton for oil-water separation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Luo, X.; Mi, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Ye, F.; Luo, Y. Magnetic recyclable carbon nanotubes and its demulsification performance in oily wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Design, engineering and analytical perspectives of membrane materials with smart surfaces for efficient oil/water separation. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, E.K.; Liu, J.; Lv, X. Surface engineering materials of superhydrophobic sponges for oil/water separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Abd-El-Nabey, B.A. Fabrication of a biological metal–organic framework based superhydrophobic textile fabric for efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Fan, H.; Li, C.; Caro, J.; Meng, H. Robust Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Wrinkled Microspherical MOF@rGO Composites for Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5297–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, C.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Cui, Y. Two-Dimensional Fluorinated Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Hydrophobicity for Ultrafast Oil–Water Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruidas, S.; Das, A.; Kumar, S.; Dalapati, S.; Manna, U.; Bhaumik, A. Non-Fluorinated and Robust Superhydrophobic Modification on Covalent Organic Framework for Crude-Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202210507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichiarante, V.; Milani, R.; Metrangolo, P. Natural surfactants towards a more sustainable fluorine chemistry. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdia, P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Goh, T.Y.; Jacquemin, J.; Blesic, M. A class of efficient short-chain fluorinated catanionic surfactants. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diejomaoh Abafe, O.T.; Azim, M.M.; Martincigh, B.S.; Stark, A. Cation-fluorinated ionic liquids: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and comparison with non-fluorinated analogues. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Ma, J.; Song, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Du, R. Stable nanoreactors for material fabrication using the aggregation of fluorinated ionic liquid surfactants in ionic liquid solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Ionic liquids for advanced materials. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 17, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himani; Raman, A.P.S.; Singh, M.B.; Jain, P.; Chaudhary, P.; Bahadur, I.; Lal, K.; Kumar, V.; Singh, P. An update on synthesis, properties, applications and toxicity of the ILs. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Li, Z.-Y.; Huo, F.; Dong, Y.-H.; He, H.-Y. Stimuli Responsive Ionic Liquids and the Regulation of Aggregation Structure and Phase Behavior. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Yu, Y.; Su, L.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Gao, X. Amphiphile regulated ionic-liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems with tunable LCST and extraction behavior. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 130172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jie, X.; Qin, J.; He, H. Ionic liquids enable highly efficient Knoevenagel reaction by dual-responsive emulsion microreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Mohapatra, P.K. Direct dissolution of metal oxides in ionic liquids as a smart strategy for separations: Current status and prospective. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2792–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J.; Yuan, J. Poly(ionic liquid) composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1726–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Du, R. Carboxyl functional poly(ionic liquid)s confined in metal–organic frameworks with enhanced adsorption of metal ions from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ahmed, A.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. Preparation, application and development of poly(ionic liquid) microspheres. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Feng, B.; Xiao, M.; Gai, H.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Song, H. Design of adjustable hypercrosslinked poly(ionic liquid)s for highly efficient oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Yang, B.; He, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C. Versatile and robust poly(ionic liquid) coatings with intelligent superhydrophilicity/superhydrophobicity switch in high-efficient oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Ezzat, A.O. Synthesis and application of geminal dicationic ionic liquids and poly(ionic liquids) combined imidazolium and pyridinium cations as demulsifiers for petroleum crude oil saline water emulsions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, G.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G. Poly(ionic liquid)-Coated Meshes with Opposite Wettability for Continuous Oil/Water Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6672–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wei, R.; Jin, L.; He, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Design of poly ionic liquids modified cotton fabric with ion species-triggered bidirectional oil-water separation performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mo, Z.; Arenal, R.; Li, W.; Wang, C. Efficient oil-water separation by a robust superhydrophobic coating prepared directly from commercial lacquer using silanized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as filler. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 609, 155208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; You, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Switchable and simultaneous oil/water separation induced by prewetting with a superamphiphilic self-cleaning mesh. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, J.; Yuan, W.; Jiang, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, H. Simultaneously achieving high-effective oil-water separation and filter media regeneration by facile and highly hydrophobic sand coating. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsin, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Tsai, H.; Kuo, S.; Hung, W.; Lai, J. Constructing Superwetting Membranes by Sodium Lignosulfonate-Modified Carbon Nanotube for Highly Efficient Crude Oil-In-Water Emulsions Separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, X. Smart and durable pH-responsive superhydrophobic fabrics with switchable surface wettability for high-efficiency and complex oil/water separation. Giant 2023, 14, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lv, T.; Wu, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yu, C.; Xing, G. Hydrophobic Ti3C2Tx/PU sponge prepared from commercial amphiphilic PU sponge for oil/water separation with ultrahigh flux. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Chen, S.; Hirahara, R.; Konda, T.; Aoki, T.; Ueda, T.; Shimada, I.; Cannon, J.J.; Shao, C.; Shiomi, J.; et al. Ultrafast water permeation through nanochannels with a densely fluorous interior surface. Science 2022, 376, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

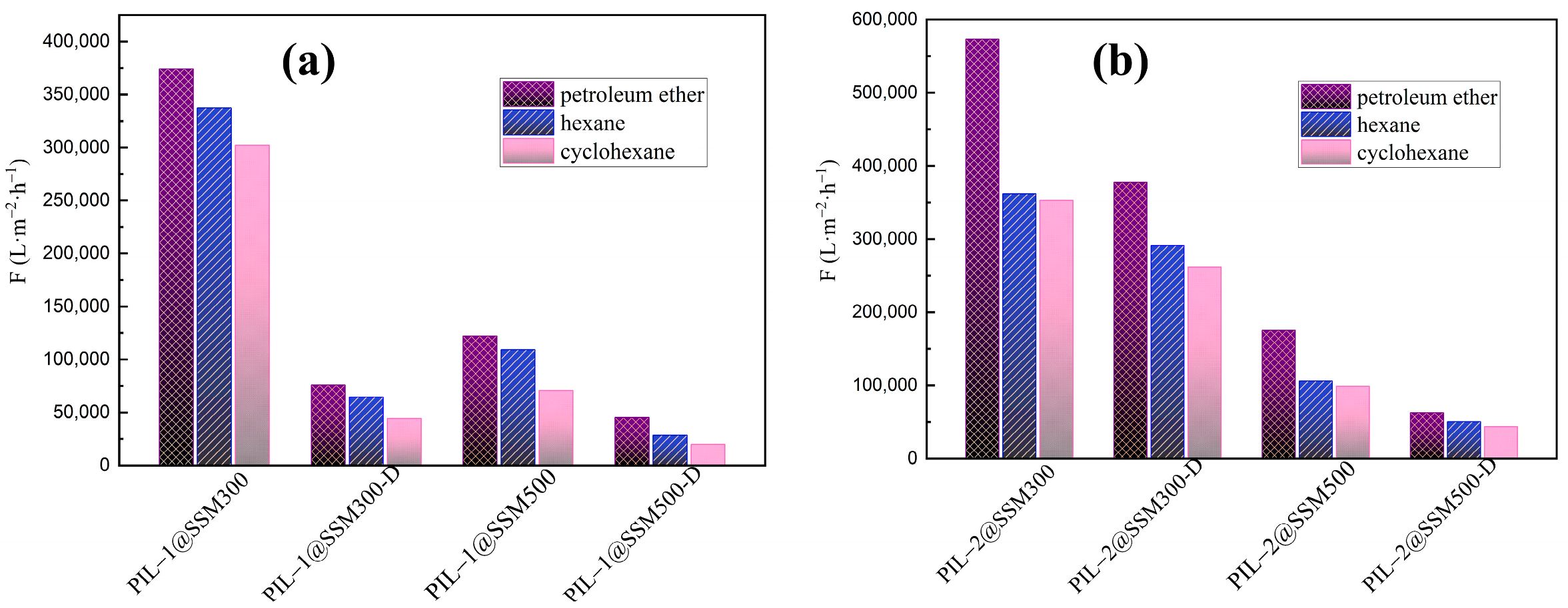


| PIL−Based Materials | Petroleum Ether | Hexane | Cyclohexane | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIL−1@SSM300 | 374,370 ± 15,310 | 337,200 ± 12,416 | 302,013 ± 9957 | |
| PIL−1@SSM300-D | 75,800 ± 1253 | 64,500 ± 910 | 44,310 ± 428 | |
| PIL−1@SSM500 | 122,000 ± 1623 | 109,060 ± 1297 | 70,608 ± 543 | |
| PIL−1@SSM500-D | 45,090 ± 440 | 28,345 ± 175 | 19,836 ± 170 | |
| PIL−2@SSM300 | 573,000 ± 35,960 | 362,000 ± 14,310 | 352,770 ± 13,591 | |
| PIL−2@SSM300-D | 377,450 ± 15,563 | 291,170 ± 9254 | 262,060 ± 7494 | |
| PIL−2@SSM500 | 175,370 ± 3354 | 105,790 ± 1220 | 98,900 ± 1066 | |
| PIL−2@SSM500-D | 62,865 ± 860 | 50,590 ± 558 | 43,660 ± 416 | |
| PIL−1@NF0.3 | 43,326 ± 409 | 41,603 ± 377 | 18,756 ± 154 | |
| PIL−1@NF0.3-D | 36,400 ± 288 | 27,330 ± 163 | 11,887 ± 110 | |
| PIL−1@NF1.0 | 37,922 ± 314 | 28,793 ± 180 | 16,046 ± 114 | |
| PIL−1@NF1.0-D | 21,325 ± 198 | 18,350 ± 146 | 5521 ± 67 | |
| PIL@cotton fabric | 69,610 | [42] | ||
| PIL@nylon fabric | 12,123 | [42] | ||
| PILM−1 or PILM−5 | 122,000 | 15,071 | [44] | |
| GO−PIL@cotton fabric | 59,000 | [45] | ||
| MWCNT@MTMS | 126,400 | [46] | ||
| TiO2@SSM | 7281 | [47] | ||
| PDMS@PMMA | 35,712 | [48] | ||
| SLS@CNT | 13,800 | 10,500 | [49] | |
| UA−co−VTMS@ | 8645 | [50] | ||
| Ti3C2Tx/PU | 328,040 | 360,340 | [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, F.; Cheng, X.; Yao, S.; Pei, Y. Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s Coated Superhydrophobic Functional Materials with Efficient Oil/Water Separation Performance. Separations 2023, 10, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070405
Shen F, Cheng X, Yao S, Pei Y. Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s Coated Superhydrophobic Functional Materials with Efficient Oil/Water Separation Performance. Separations. 2023; 10(7):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070405
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Fumin, Xuna Cheng, Shunyang Yao, and Yuanchao Pei. 2023. "Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s Coated Superhydrophobic Functional Materials with Efficient Oil/Water Separation Performance" Separations 10, no. 7: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070405
APA StyleShen, F., Cheng, X., Yao, S., & Pei, Y. (2023). Fluorinated Poly(ionic liquid)s Coated Superhydrophobic Functional Materials with Efficient Oil/Water Separation Performance. Separations, 10(7), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070405









