Potential Use of Agricultural Waste—Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a Biosorbent for Removing Boron from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
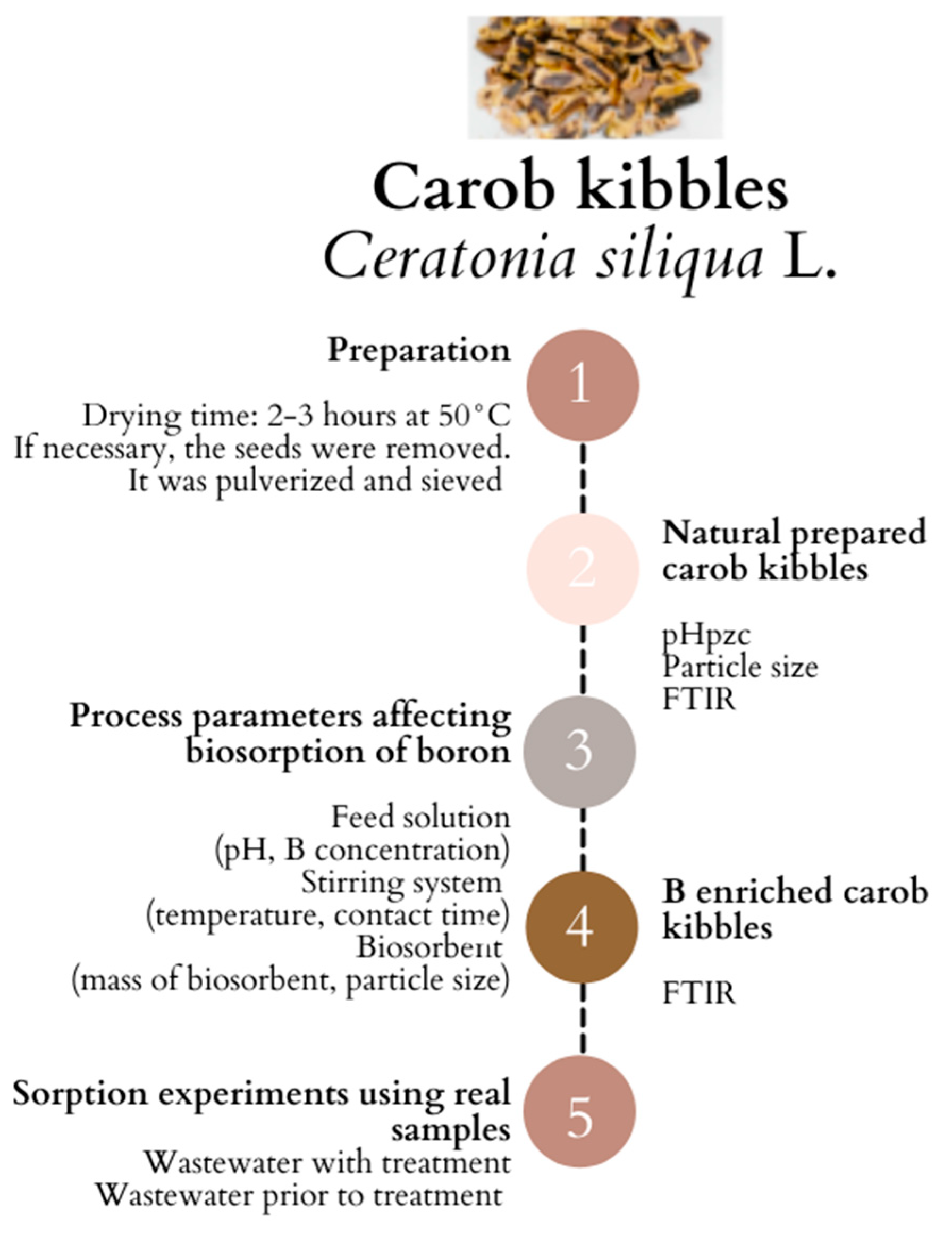
2.2. Biosorbent Preparation
2.3. Biomass Characterization
2.3.1. Isoelectric Point (pHpzc)
2.3.2. Particle Size Distribution
2.4. Batch Biosorption Experiments
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6. Sorption Experiments Using Real Wastewater Samples
2.7. Instrumental Analysis
2.8. Calculations
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
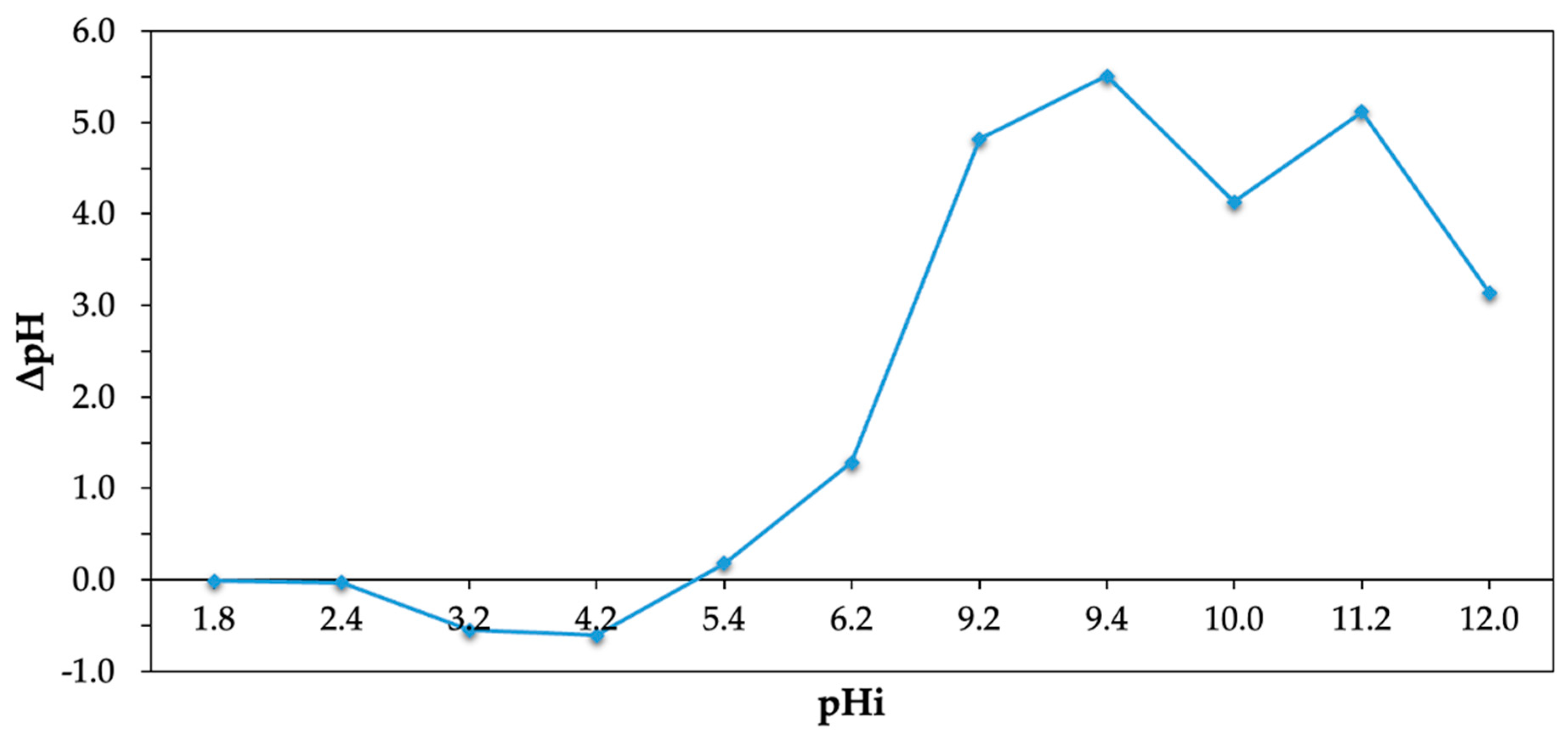
3.1. Isoelectric Point (pHpzc)
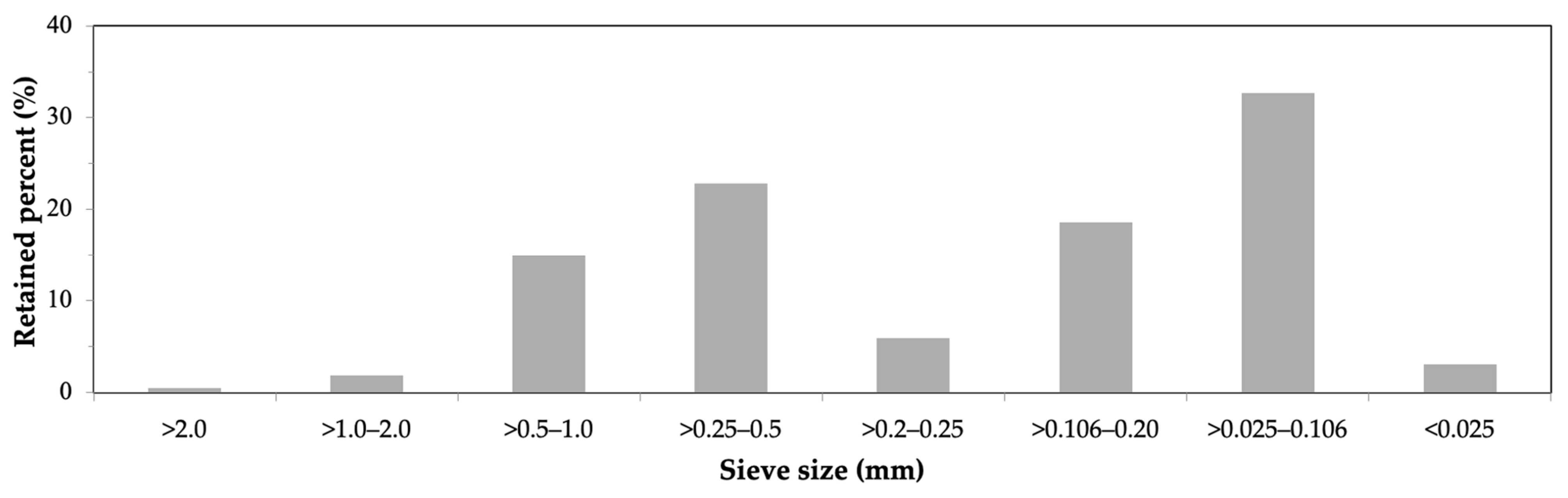
3.2. Particle Size Distribution of Biomass
3.3. Batch Biosorption Experiments
3.3.1. Kinetic Experiments
3.3.2. Influence of pH on Boron Biosorption
3.3.3. Influence of the Initial Concentration of Boron Ions in the Solution on Its Biosorption
3.3.4. Influence of Biosorbent Dose on Boron Biosorption
3.3.5. Influence of Temperature on Boron Biosorption
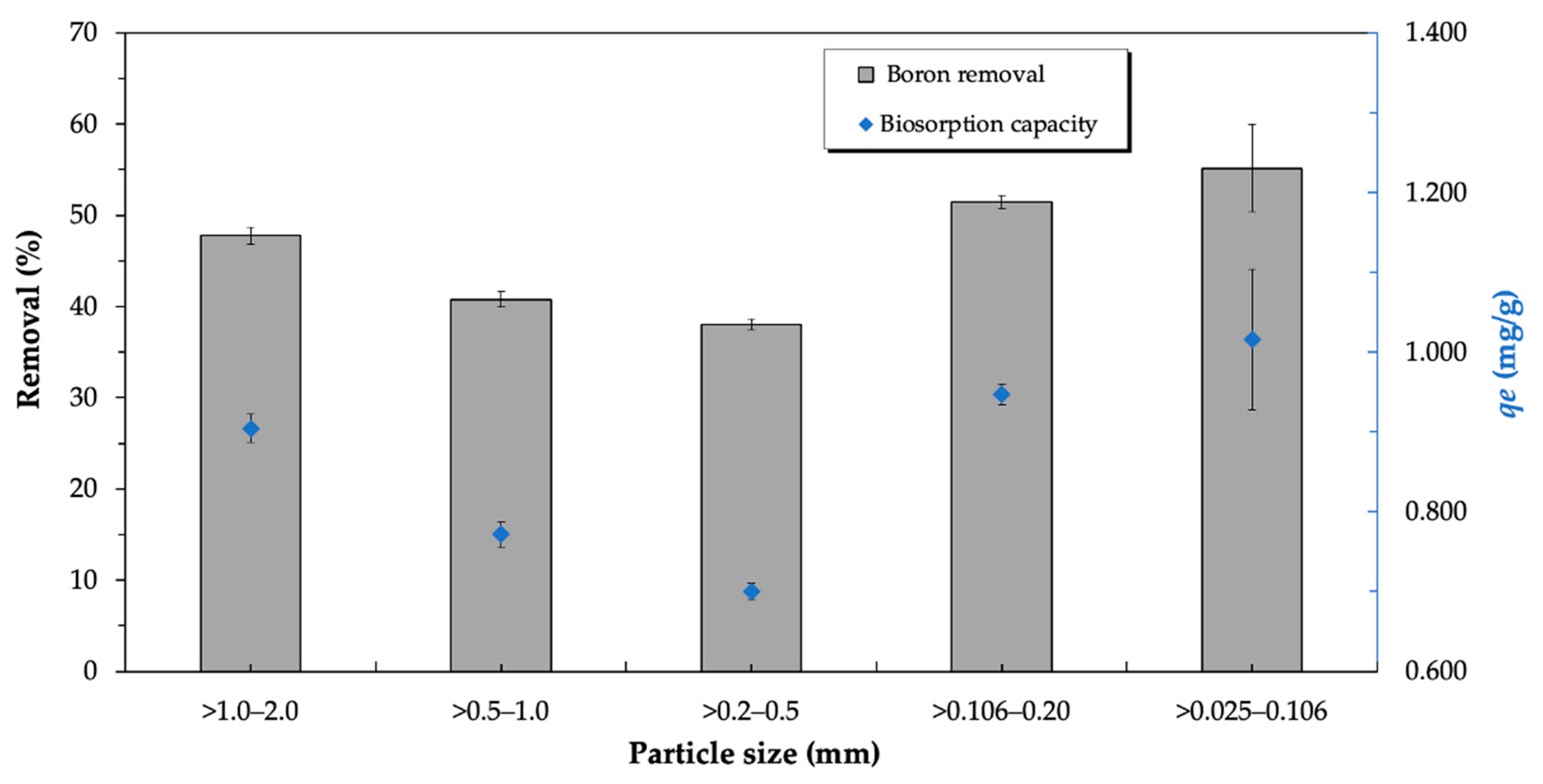
3.3.6. Influence of Particle Size
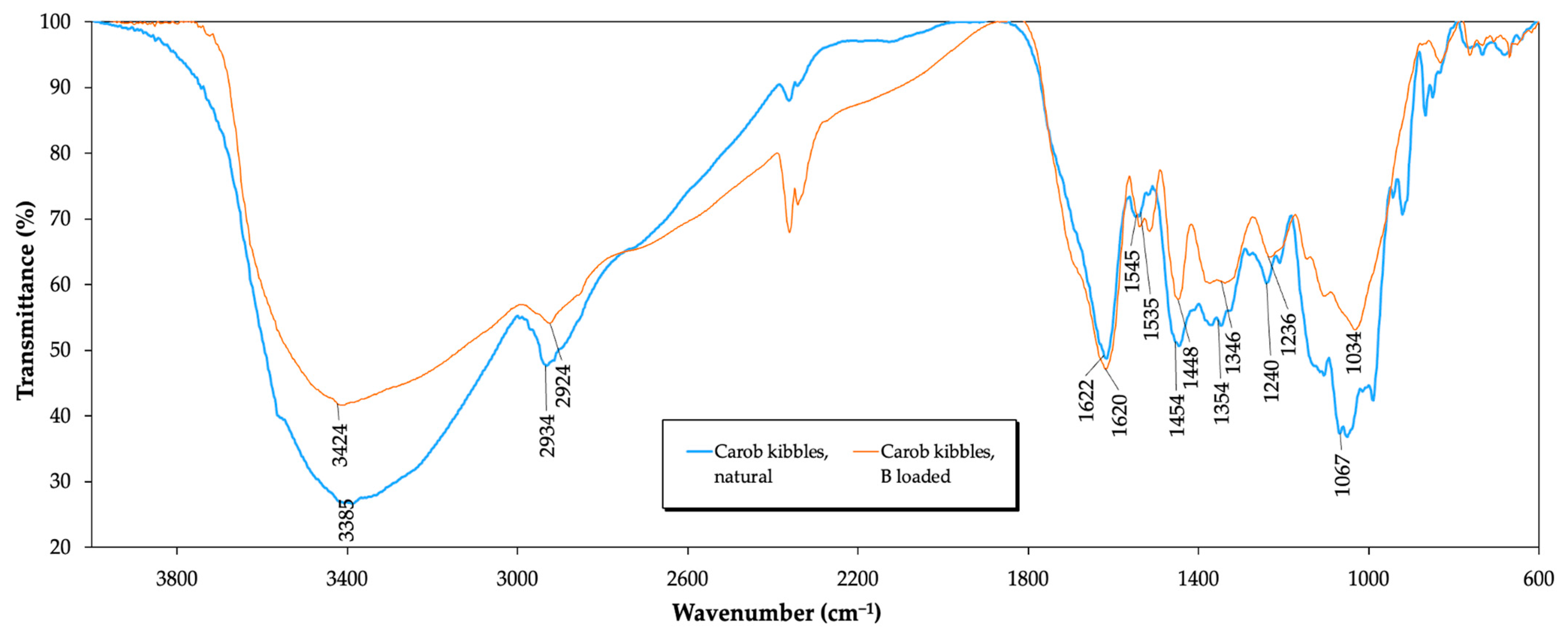
3.4. FTIR Analysis of the Biosorbent before and after Biosorption of Boron
3.5. Boron Biosorption from Real Wastewater from the Ceramic Industry: Batch Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briggs, M. Boron Oxides, Boric Acid, and Borates. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.M. Encyclopedia of Geochemistry: A Comprehensive Reference Source on the Chemistry of the Earth; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; p. 1557. [Google Scholar]
- European Chemical Society. Element Scarcity—EuChemS Periodic Table. Available online: https://www.euchems.eu/euchems-periodic-table/ (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- The Periodic Table of Endangered Elements—American Chemical Society. Available online: https://www.acs.org/greenchemistry/research-innovation/endangered-elements.html (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Chattopadhyay, D. Endangered elements of the periodic table. Resonance 2017, 22, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Schlesinger, W.H. Global biogeochemical cycle of boron. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 20-1–20-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, N.; Semiat, R.; Eisen, M.S.; Balazs, Y.; Katz, I.; Dosoretz, C.G. Boron removal from water by complexation to polyol compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Boron in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of Who Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, W. The Global Biogeochemical Cycle of Boron: Why It’s Not Boring—YouTube. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EqND28XfZ3U (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Shaaban, M.M. Role of boron in plant nutrition and human health. Am. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 5, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Nejad, S.A.G.; Nourgholipour, F.; Zoshkey, S.A. Agronomic Aspects of Boron: Fertilizers, Agronomical Strategy, and Interaction with Other Nutrients (Charpter 12) in Boron in Plants and Agriculture Exploring the Physiology of Boron and Its Impact on Plant Growth; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Dwivedi, P. Micronutrients zinc and boron enhance stevioside content in Stevia rebaudiana plants while maintaining genetic fidelity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Hussain, S.B.; Jin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Peng, S. Characteristics of boron distribution in the ‘Newhall’ navel orange plant with two root systems. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svishcheva, N.B.; Uspenskii, S.A.; Sedush, N.G.; Khaptakhanova, P.A.; Kasatova, A.I.; Buzin, A.I.; Dmitryakov, P.V.; Piskarev, M.S.; Aleksandrov, A.I.; Taskaev, S.Y. Biodegradable boron-containing poly(lactic acid) for fertilizers with prolonged action. Mater. Today 2022, 33, 104514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Mühling, K.H.; LÄuchli, A.; Brown, P.H.; Goldbach, H.E. Boron Toxicity: The importance of soluble boron. In Boron in Plant Animal Nutrition; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Trace Elements in Human Nutrition and Health: Part B; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Cristóbal, J.J.; Rexach, J.; González-Fontes, A. Boron in plants: Deficiency and toxicity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M. Competition Science Vision; Pratiyogita Darpan Gr.: Agra, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wolska, J.; Bryjak, M. Methods for boron removal from aqueous solutions—A review. Desalination 2013, 310, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, S.H.; Mohamed, M.; Nor-Anuar, A.; Muda, K.; Hassan, M.A.H.M.; Othman, M.N.; Chelliapan, S. Ceramic industry wastewater treatment by rhizofiltration system—Application of water hyacinth bioremediation. IIOAB J. 2014, 5, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, M.F.; Lee, K.P.; Chieng, H.J.; Ramli, I.I.S.B. Removal of boron from ceramic industry wastewater by adsorption-flocculation mechanism using palm oil mill boiler (POMB) bottom ash and polymer. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3326–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. 98/83/EC on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. BORON Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, S.; Nagpal, N.; Ministry of Environment Water Protection and Sustainability Branch; Environmental Sustainability and Strategic Policy Division. Water Quality Ambient Water Quality Guidelines for Boron Overview Report Prepared Pursuant to Section 2(e) of the 2003. Available online: www.gov.bc.ca/water (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- U.S. EPA. Drinking Water Health Advisory for Boron. Health and Ecological Criteria Division Office of Science and Technology Office of Water U.S.; Document Number: 822–R–08–013; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Lv, J.; Bai, P.; Guo, X. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption—A review. Desalination 2016, 383, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, J.Q. Technologies for boron removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczka, J.; Ciba, J.; Trojanowska, J.; Zolotajkin, M.; Turek, M.; Dydo, P. Removal of boron dissolved in water. Environ. Prog. 2007, 26, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, P.; Li, K.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y. Advances in Technologies for Boron Removal from Water: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasef, M.M.; Nallappan, M.; Ujang, Z. Polymer-based chelating adsorbents for the selective removal of boron from water and wastewater: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 85, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, N.; Wang, K.Y.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C.; Chung, T.S. Investigation of novel molecularly tunable thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for boron removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 620, 118887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, T.; Bai, P.P.; Lyu, J.; Guo, X. Fe3O4-loaded ion exchange resin for chromatographic separation of boron isotopes: Experiment and numerical simulation. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2021, 171, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Mahasti NN, N.; Huang, Y.H. Recent advances in adsorption and coagulation for boron removal from wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.P.; Yuwen, S.; Chung, T.S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Synthesis of hyperbranched polymers towards efficient boron reclamation via a hybrid ultrafiltration process. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 31275, Dioxane. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Dioxane (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Goren, A.Y.; Recepoglu, Y.K.; Karagunduz, A.; Khataee, A.; Yoon, Y. A review of boron removal from aqueous solution using carbon-based materials: An assessment of health risks. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, T.E.; Demiral, H.; Öztürk, N. Adsorption of boron from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from olive bagasse. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 29, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, W.; Jia, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.Y. Effect of pH on biosorption of boron onto cotton cellulose. Desalination 2007, 207, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, H.C.; Chin, W.H.; Zadeh, M.R.; Yusof, M.R.M. Adsorption potential of unmodified rice husk for boron removal. BioResources 2012, 7, 3810–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursali, E.A.; Cavas, L.; Seki, Y.; Bozkurt, S.S.; Yurdakoc, M. Sorption of boron by invasive marine seaweed. Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Rajabi, F.; Ranjbar, F. The removal of boron from aqueous solutions using natural and chemically modified sorbents. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 8278–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetgin, A.G.; Dündar, O.A.; Çakmakçı, E.; Arar, O. Removal of boron from aqueous solution by modified cellulose. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, I.A. Carob Tree. Ceratonia siliqua L. Promoting the Conservation and Use of Underutilized and Neglected Crops; Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research: Rome, Italy; Gatersleben/International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Goulas, V.; Stylos, E.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzakos, A.G. Functional components of carob fruit: Linking the chemical and biological space. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavdarova, M.; Makris, D.P. Extraction kinetics of phenolics from carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) kibbles using environmentally benign solvents. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.; Nunes, C.; Raposo, S.; Lima-Costa, M.E. Carob pulp as raw material for production of the biocontrol agent P. agglomerans PBC-1. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, A.; Salem, N.; Ahmad, A.L.; Awwad, A. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies of the biosorption of heavy metals by Ceratonia siliqua bark. Am. J. Chem. 2012, 2, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, N.; Ameh, P.; Wyasu, G.; Onwuka, J. Adsorption of cadmium(II) and chromium(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by activated locust bean husk. Int. J. Mod. Chem. 2013, 3, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, L. Biosorption Parameters: Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua) as a Potential Biosorption for Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Master’s Thesis, Erasmus Mundus Master in Quality in Analytical Laboratories (EMQAL), Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of Algarve, Faro, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.; Saddique, M.T.; Naeem, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Mustafa, S.; Alum, A. Comparison of different methods for the point of zero charge determination of NiO. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10017–10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atılgan Türkmen, B.; Karahan Özbilen, Ş.; Budak Duhbacı, T. Improving the sustainability of ceramic tile production in Turkey. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 2193–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettipathirana, T. Determination of Metals in Industrial Wastewaters by Microwave Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Available online: https://www.hpst.cz/sites/default/files/oldfiles/5990-8673en-appnote-4100mp-aes-metals-wastewaters.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Afolabi, H.K.; Nasef, M.M.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Ting, T.M.; Harun, N.Y.; Saeed, A.A.H. Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics of boron adsorption on fibrous polymeric chelator containing glycidol moiety optimized with response surface method. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczka, J.; Pudło, W.; Krukiewicz, K. Boron adsorption removal by commercial and modified activated carbons. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 147, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakade, V.E.; Ntuli, T.D.; Ofomaja, A.E. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by Macadamia nutshell powder. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3015–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Equilibrium Biosorption Performance. In Sorption and Biosorption; BV Sorbex: Saint-Lambert, QC, Canada, 2004; pp. 103–116. Available online: http://biosorption.mcgill.ca/publication/book/6.1-4w(103-16).pdf (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. The new application of biosorption properties of Enteromorpha prolifera. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1540–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnane, M.; Tounsadi, H.; Elmoubarki, R.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Elhalil, A.; Saqrane, S.; Abdennouri, M.; Qourzal, S.; Barka, N. Alkaline treated carob shells as sustainable biosorbent for clean recovery of heavy metals: Kinetics, equilibrium, ions interference and process optimization. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. State of the art for the biosorption process—A Review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1389–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Darwish, N.B.; Hilal, N. The Chemistry of Boron in Water. In Boron Separation Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Bai, P. Removal technology of boron dissolved in aqueous solutions—A review. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengeloglu, Y.; Arslan, G.; Tor, A.; Kocak, I.; Dursun, N. Removal of boron from water by using reverse osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aty, A.M.; Ammar, N.S.; Ghafar, H.H.A.; Ali, R.K. Biosorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by fresh water alga Anabaena sphaerica biomass. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qahtani, K.M. Water purification using different waste fruit cortexes for the removal of heavy metals. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2016, 10, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Choubey, S.; Verma, Y.; Pandey, M.; Kamal, S.S.K.; Chandrashekhar, K. Biosorptive removal of Ni(II) from wastewater and industrial effluent. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2007, 4, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Köse, T.E. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by ion-exchange resin: Batch studies. Desalination 2008, 227, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehal, M.; Reinert, L.; Duclaux, L. Characterization and boron adsorption capacity of vermiculite modified by thermal shock or H2O2 reaction and/or sonication. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
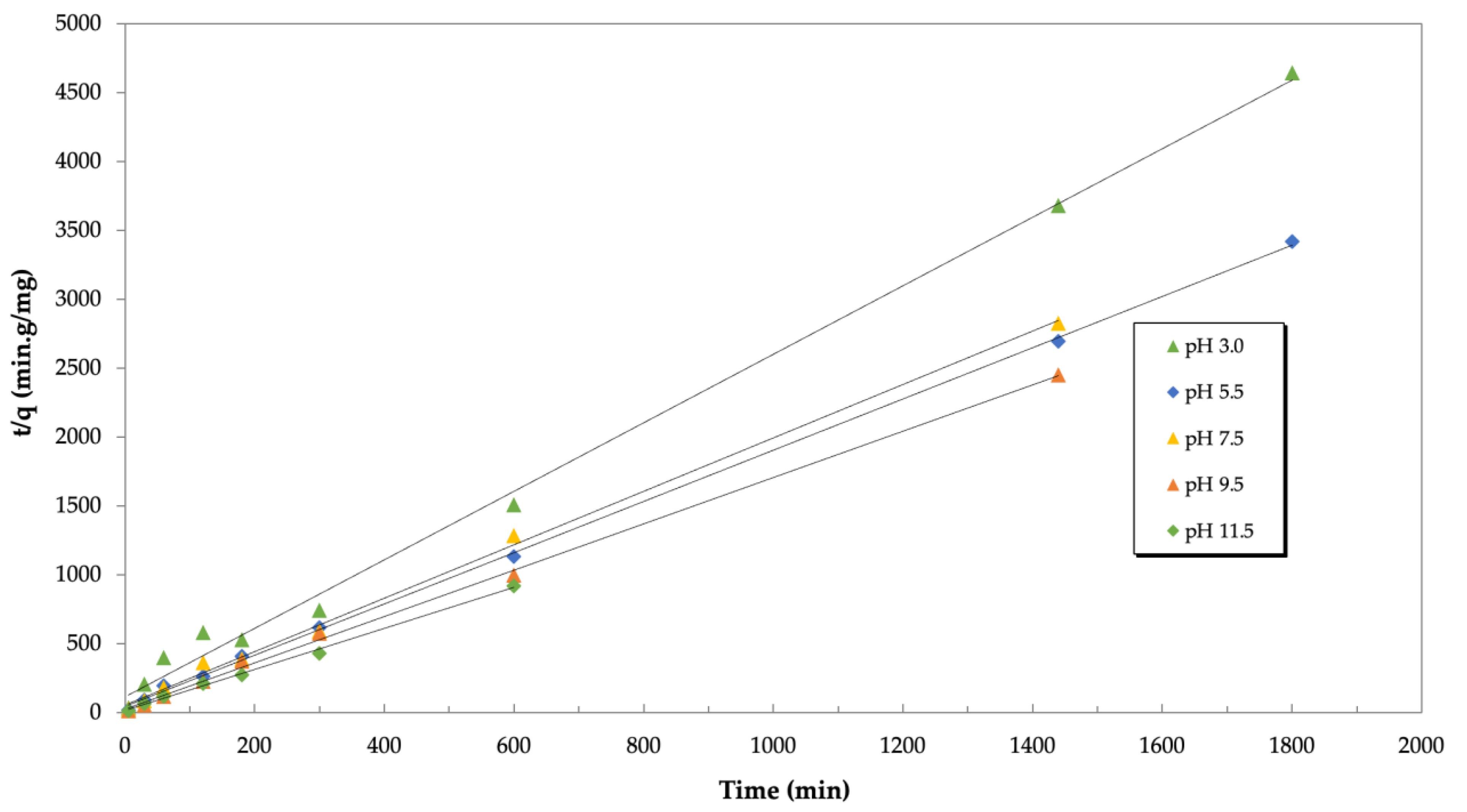
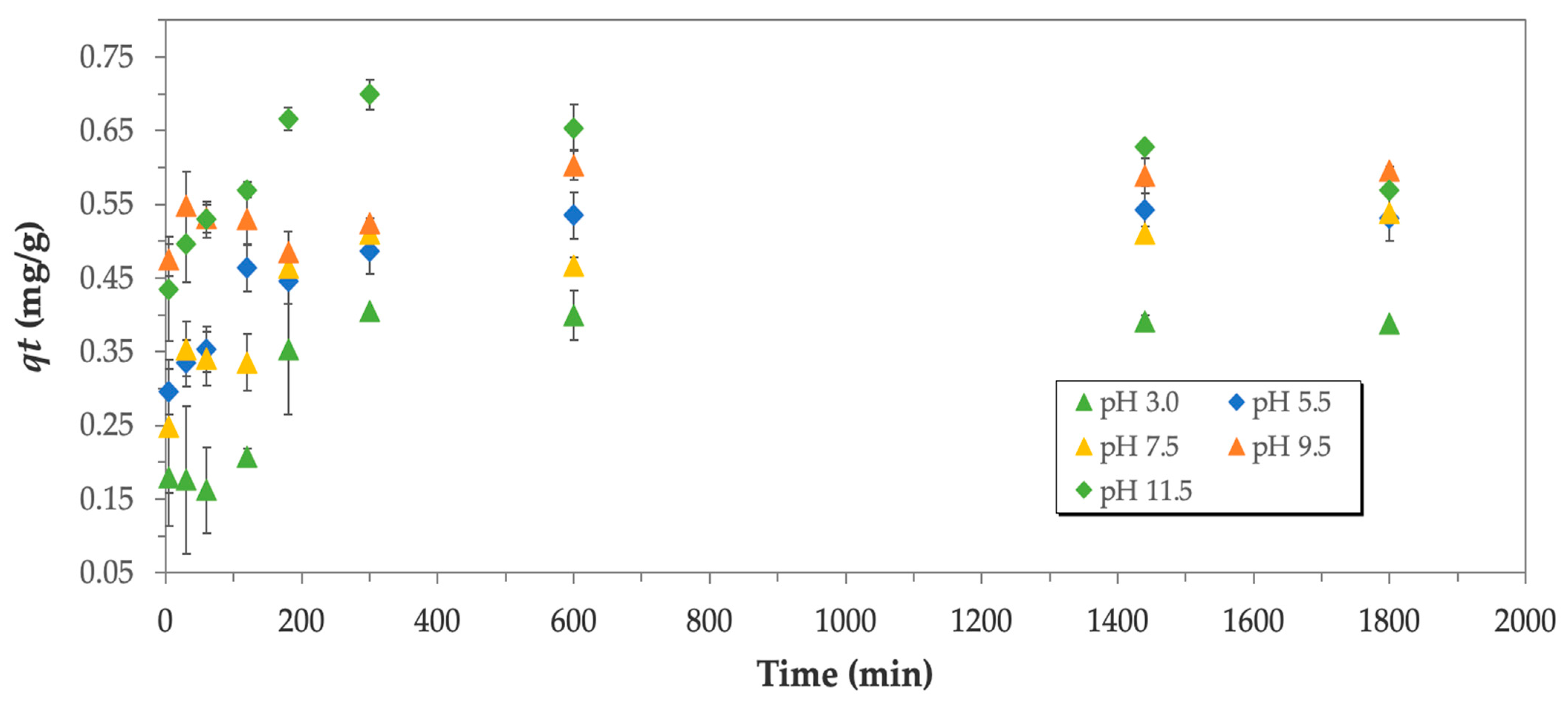
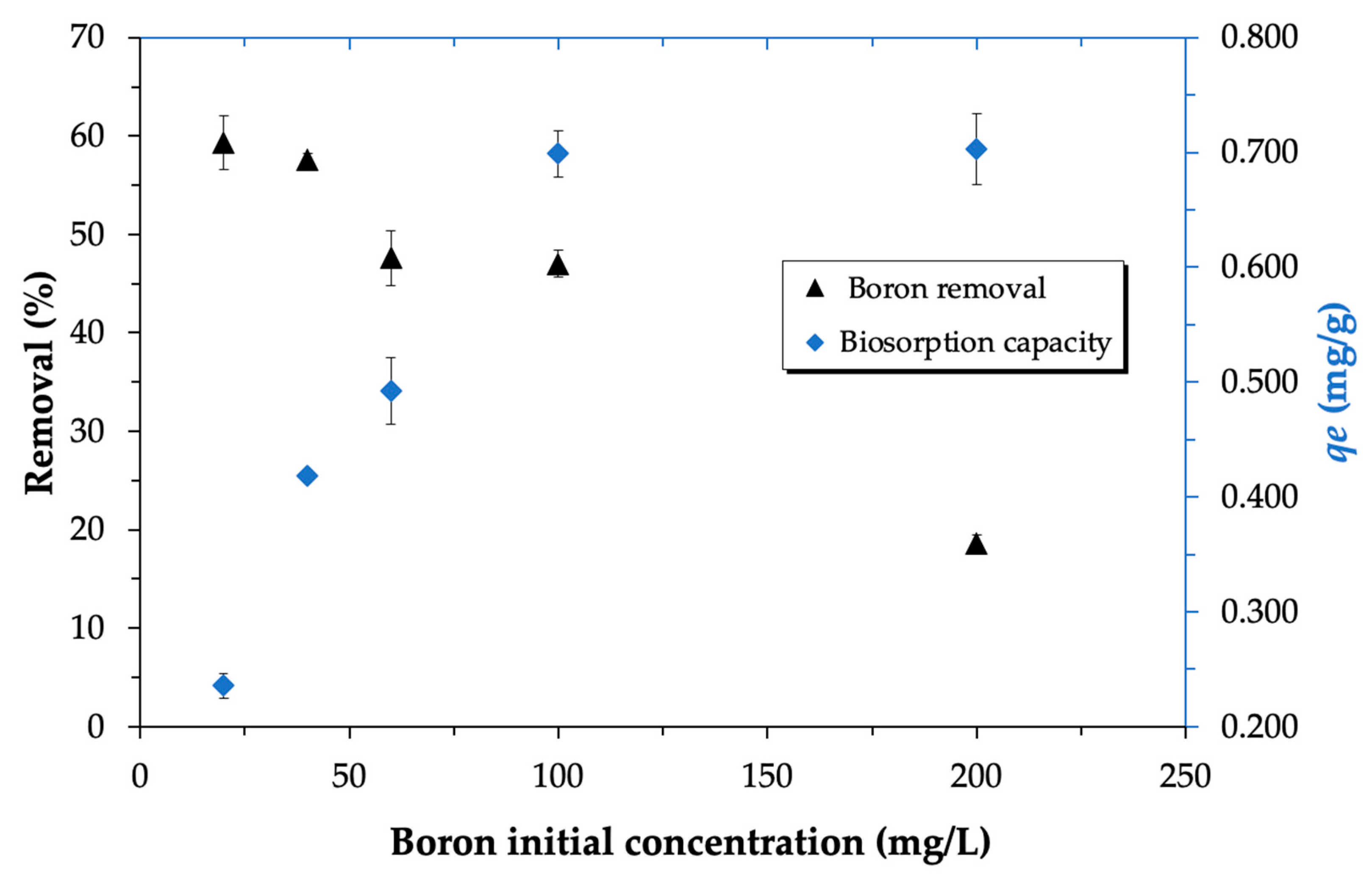
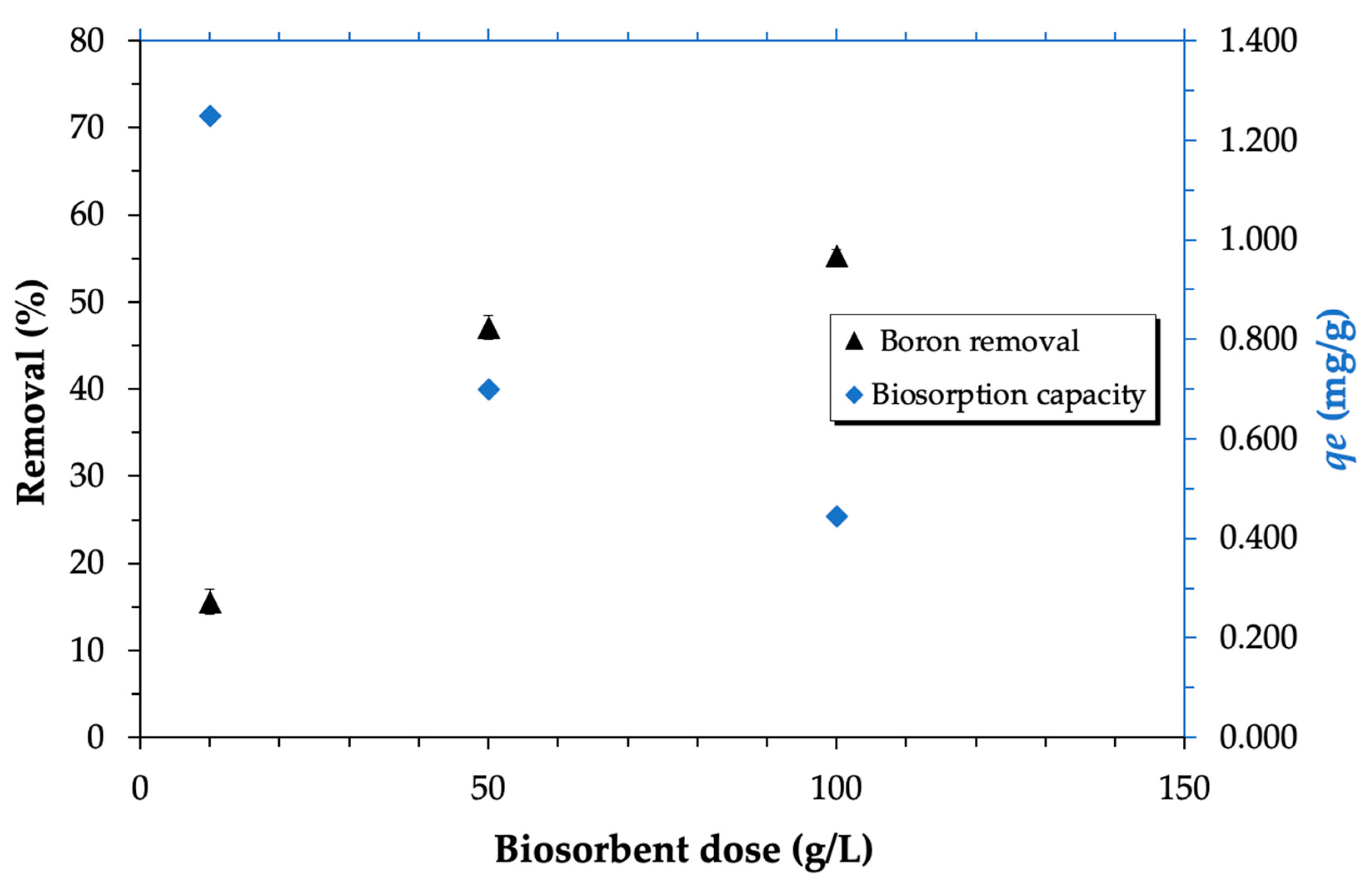
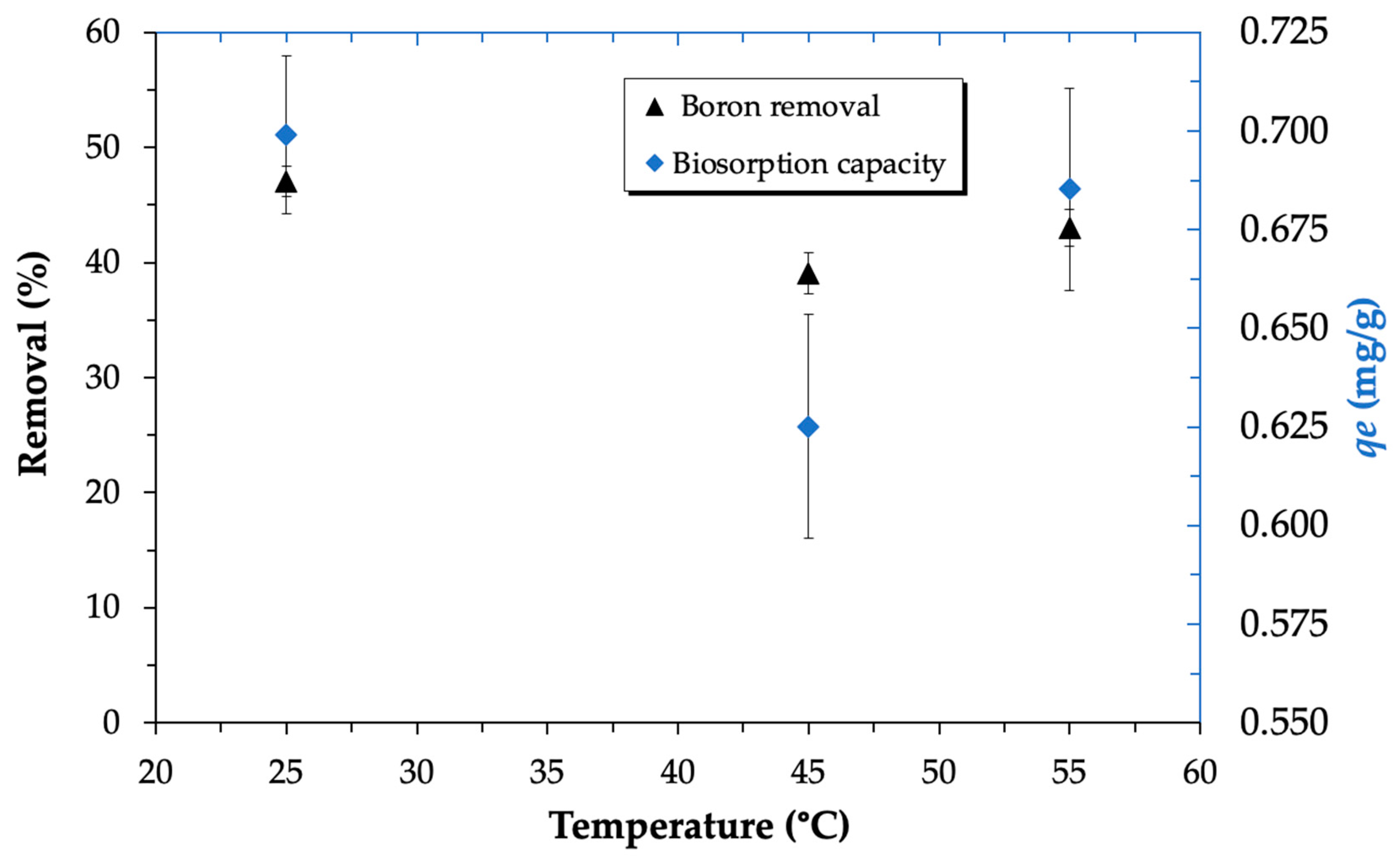
| pH | qe (mg/g) | k2 (g/mg·min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 0.402 ± 0.005 | 0.0601 ± 0.0275 | 0.995 ± 0.002 |
| 5.5 | 0.545 ± 0.091 | 0.169 ± 0.183 | 0.998 ± 0.002 |
| 7.5 | 0.516 ± 0.008 | 0.0715 ± 0.0084 | 0.997 ± 0.002 |
| 9.5 | 0.595 ± 0.024 | 0.119 ± 0.022 | 0.999 ± 0.000 |
| 11.5 | 0.672 ± 0.030 | 0.220 ± 0.137 | 0.996 ± 0.003 |
| Biosorbent | Optimal Experimental Conditions | Removal Percent (%) or Biosorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial pH | Contact Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Initial Boron Concentration (mg/L) | Biosorbent Dose (g/L) | Particle Size (mm) | |||
| Carob kibble | 11.5 | 5 | 25 | 100 | 50 | 0.025–0.106 | 55% (1.15 mg/g) | This work |
| Olive bagasse modified by pyrolysis: activation temperature of 850 °C | 5.5 | 48 | 25 | 100 | 20 | N.A. | 30% | [37] |
| Cotton cellulose modified with 0.1 M NaOH | 7 | 4 | room | 500 | 2 | N.A. | 11.3 mg/g | [38] |
| Rice husk | 5 | − | ambient | 300 | 2 | 0.425–1.00 | 119 mg/g | [39] |
| Marine seaweed: Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (0.1 M NaCl optimal ionic strength) | 7.5–8.5 | 2.5 | 45 | 8 | 8 | N.A. | 63% | [40] |
| Natural minerals Organic waste material modified with 0.1 M FeCl3 With 0.001 M CaCl2 as background electrolyte for isotherm | 9 (Waste calcite)/ 7 (Rice residues) | 24 (Mineral sorbents)/ 48 (Organic sorbents) | N.A. | 120 | 50 (Mineral sorbents)/ 2 (Organic sorbents) | N.A. | 0.24 mg/g (Waste calcite) 2.88 mg/g (Wheat residues) | [41] |
| Dowex 2 × 8 ion exchange resin modified with 2 M NaOH/48 h | 9 | 8 | 25 | 600 | 20 | N.A. | 55% | [66] |
| Functional Group | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Changes | Involved in Boron Removal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Biosorbent | Boron-Loaded Biosorbent | |||
| Alcohol; O-H | 3385 | 3424 | Intensity | Yes |
| Group; C-H | 2934 | 2924 | Intensity | No |
| Carbonyl; C=O | 1622 | 1620 | No | No |
| Amine; N-H | 1535 | 1545 | Intensity | Yes |
| Alkene; C=C | 1454 | 1448 | Intensity | Yes |
| Hydroxyl; O-H | 1354 | 1346 | Intensity | Yes |
| Phenols; C-O | 1240 | 1236 | Intensity | Yes |
| C-O phenols and C-OH | 1067 | 1034 | Intensity | Yes |
| Parameter (mg/L) | Effluent Prior to Wastewater Treatment (I) | Effluent with Wastewater Treatment (II) |
|---|---|---|
| B | 36 | 19 |
| Fe | <1.141 | <1.141 |
| Al | 1.6 | 2.9 |
| Cu | <0.531 | <0.531 |
| Zn | <0.143 | <0.143 |
| SO42− | 24 | 10.5 |
| pH (units) | 9.5 | 7.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz, L.A.; Carlier, J.D.; Michalak, I.; Costa, M.C. Potential Use of Agricultural Waste—Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a Biosorbent for Removing Boron from Wastewater. Separations 2023, 10, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090464
Díaz LA, Carlier JD, Michalak I, Costa MC. Potential Use of Agricultural Waste—Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a Biosorbent for Removing Boron from Wastewater. Separations. 2023; 10(9):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090464
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz, Luz Adriana, Jorge Dias Carlier, Izabela Michalak, and María Clara Costa. 2023. "Potential Use of Agricultural Waste—Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a Biosorbent for Removing Boron from Wastewater" Separations 10, no. 9: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090464
APA StyleDíaz, L. A., Carlier, J. D., Michalak, I., & Costa, M. C. (2023). Potential Use of Agricultural Waste—Carob Kibbles (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a Biosorbent for Removing Boron from Wastewater. Separations, 10(9), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090464








