Development and Validation of an Ecofriendly, Rapid, Simple and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Entrectinib Quantification in Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Stock Solution, Calibration Standards, and Quality Control Sample Preparation
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Chromatographic Conditions
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. In Vitro Metabolic Stability
2.8. Evaluation of the Greenness of the Method
3. Results
3.1. UPLC-MS/MS Parameters Optimization
3.2. Optimization of the Chromatographic Separations
3.3. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure
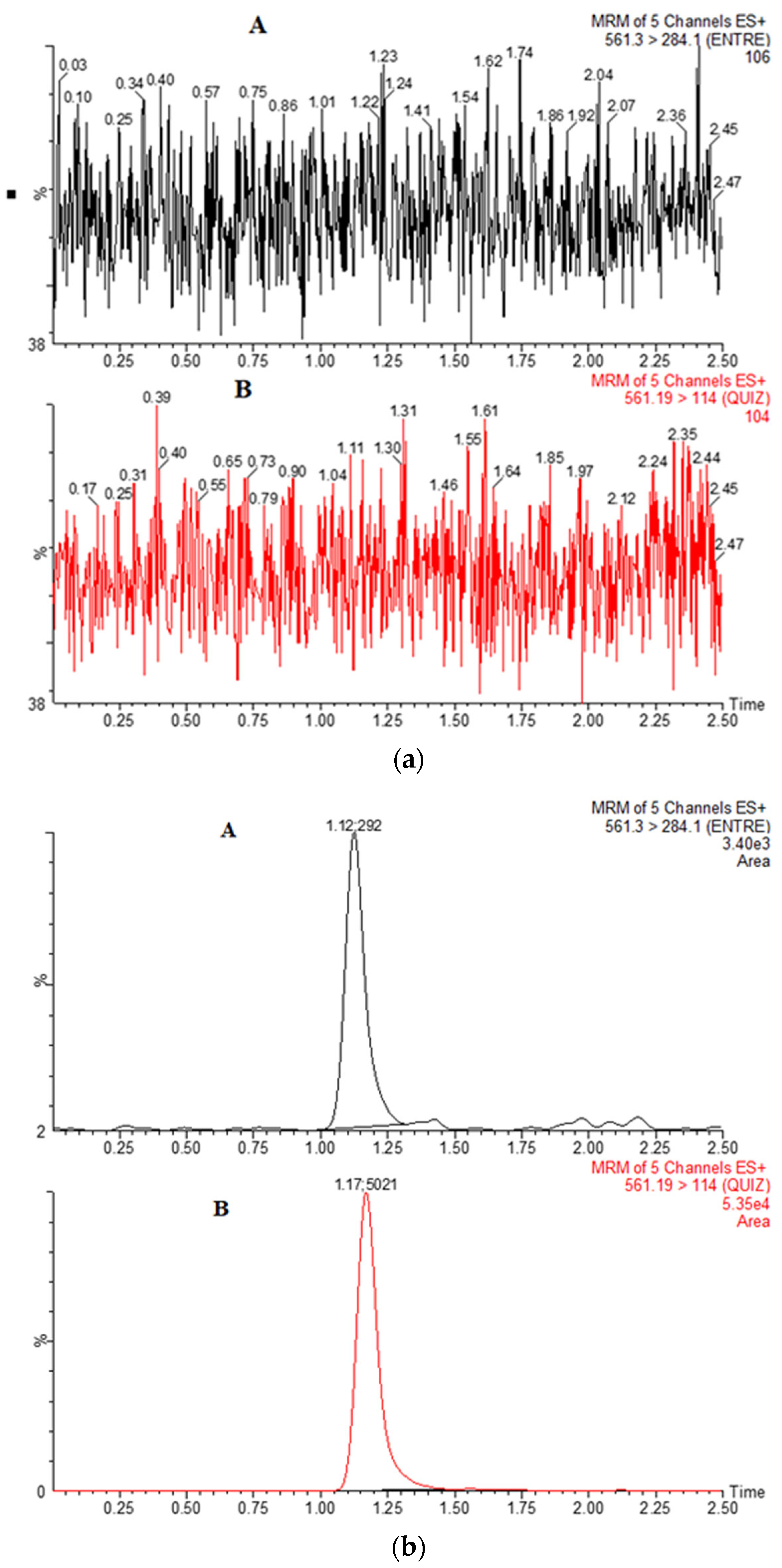
3.4. Selectivity and Sensitivity
3.5. Precision and Accuracy
3.6. Recovery and Matrix Effects
3.7. Stability
3.8. Linearity and Calibration Curves
3.9. In Vitro Metabolic Stability Study
3.10. The Greenness of the Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menichincheri, M.; Ardini, E.; Magnaghi, P.; Avanzi, N.; Banfi, P.; Bossi, R.; Buffa, L.; Canevari, G.; Ceriani, L.; Colombo, M.; et al. Discovery of Entrectinib: A New 3-Aminoindazole as a Potent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK), c-ros Oncogene 1 Kinase (ROS1), and Pan-Tropomyosin Receptor Kinases (Pan-TRKs) Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3392–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salama, Z.T.; Keam, S.J. Entrectinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Takeda, M. Current Status of Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Cancer Genome Profiling Tests in Japan and Prospects for Liquid Biopsy. Life 2021, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azelby, C.M.; Sakamoto, M.R.; Bowles, D.W. ROS1 Targeted Therapies: Current Status. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratake, N.; Seto, T. NTRK Fusion-positive Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: The Diagnosis and Targeted Therapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Pean, E.; Melchiorri, D.; Migali, C.; Josephson, F.; Enzmann, H.; Pignatti, F. The European Medicines Agency review of entrectinib for the treatment of adult or paediatric patients with solid tumours who have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase gene fusions and adult patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ROS1 rearrangements. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.; Bui, N.Q.; Seetharam, M. Evolving Role of Entrectinib in Treatment of NTRK-Positive Tumors. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Offin, M.; Harnicar, S.; Li, B.T.; Drilon, A. Entrectinib: An Orally Available, Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of NTRK, ROS1, and ALK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, G.; Groff, M.; Iadeluca, L.; Daniele, P.; Wilner, K.; Wiltshire, R.; Bartolome, L.; Usari, T.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Camidge, D.R. Effectiveness of Crizotinib versus Entrectinib in ROS1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Using Clinical and Real-World Data. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Antoniou, M.; Bhutani, M.K.; Aziez, A.; Daigl, M. Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison: Entrectinib versus Crizotinib in ROS1 Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2020, 9, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Garcia, A.; Torrens-Fontanals, M.; Stepniewski, T.M.; Grau-Expósito, J.; Perea, D.; Ayinampudi, V.; Waldhoer, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Buzón, M.J.; Genescà, M.; et al. Entrectinib-A SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitor in Human Lung Tissue (HLT) Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziadziuszko, R.; Krebs, M.G.; De Braud, F.; Siena, S.; Drilon, A.; Doebele, R.C.; Patel, M.R.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, S.V.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Updated integrated analysis of the efficacy and safety of entrectinib in locally advanced or metastatic ROS1 fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Chiu, C.H.; Fan, Y.; Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Ahn, M.J.; Krebs, M.G.; Liu, S.V.; John, T.; Otterson, G.A.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Entrectinib in ROS1 Fusion-Positive NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; De Braud, F.; Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Patel, M.R.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, S.V.; Ahn, M.J.; Chiu, C.H.; Lin, J.J.; et al. Updated Integrated Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Entrectinib in Patients with NTRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, L.; Donoghue, M.; Aungst, S.; Myers, C.E.; Helms, W.S.; Shen, G.; Zhao, H.; Stephens, O.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Entrectinib for the Treatment of NTRK gene Fusion Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.; Chen, D.H.; Walker, J.M.; Ghosh, A.K. Entrectinib-related myocarditis in a young female patient with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e243946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, D.S.; DuBois, S.G. The Evolving Diagnostic and Treatment Landscape of NTRK-Fusion-Driven Pediatric Cancers. Paediatr Drugs 2020, 22, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Misale, S.; Wei, G.; Siravegna, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Lazzari, L.; Corti, G.; Rospo, G.; Novara, L.; Mussolin, B.; et al. Acquired Resistance to the TRK Inhibitor Entrectinib in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Li, G.; Dogan, S.; Gounder, M.; Shen, R.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Hyman, D.M.; Hechtman, J.; Wei, G.; et al. What Hides behind the MASC: Clinical Response and Acquired Resistance to Entrectinib after ETV6-NTRK3 Identification in a Mammary Analogue Secretory Carcinoma (MASC). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, B.M.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.J. Entrectinib Resistance Mechanisms in ROS1-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarland, S.P.; Naraparaju, K.; Iyer, R.; Guan, P.; Kolla, V.; Hu, Y.; Tan, K.; Brodeur, G.M. Mechanisms of Entrectinib Resistance in a Neuroblastoma Xenograft Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebli, N.; Buchheit, V.; Parrott, N.; Guerini, E.; Cleary, Y.; Fowler, S.; Frey, N.; Yu, L.; Mercier, F.; Phipps, A.; et al. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling of Entrectinib Parent and Active Metabolite to Support Regulatory Decision-Making. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 46, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sales, M.; Djebli, N.; Meneses-Lorente, G.; Buchheit, V.; Bonnefois, G.; Tremblay, P.O.; Frey, N.; Mercier, F. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of entrectinib in pediatric and adult patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors: Support of new drug application submission. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, P.N.; Cleary, Y.; Sturm-Pellanda, C.; Guerini, E.; Abt, M.; Donzelli, M.; Vazvaei, F.; Balas, B.; Parrott, N.; Yu, L. Effect of Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Alectinib. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Label. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Meneses-Lorente, G.; Bentley, D.; Guerini, E.; Kowalski, K.; Chow-Maneval, E.; Yu, L.; Brink, A.; Djebli, N.; Mercier, F.; Buchheit, V.; et al. Characterization of the pharmacokinetics of entrectinib and its active M5 metabolite in healthy volunteers and patients with solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Pizzutilo, E.G.; Marrapese, G.; Tosi, F.; Cerea, G.; Siena, S. Entrectinib for the treatment of metastatic NSCLC: Safety and efficacy. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2020, 20, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Ullah, M.; de la Cruz, C.C.; Hunsaker, T.; Senn, C.; Wirz, T.; Wagner, B.; Draganov, D.; Vazvaei, F.; Donzelli, M.; et al. Entrectinib, a TRK/ROS1 inhibitor with anti-CNS tumor activity: Differentiation from other inhibitors in its class due to weak interaction with P-glycoprotein. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Banfi, P.; Bosotti, R.; De Ponti, C.; Pulci, R.; Ballinari, D.; Ciomei, M.; Texido, G.; Degrassi, A.; et al. Entrectinib, a Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor with Activity in Multiple Molecularly Defined Cancer Indications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Ou, S.H.; Patel, M.; Ahn, M.J.; Lee, J.; Bauer, T.M.; Farago, A.F.; Wheler, J.J.; Liu, S.V.; et al. Safety and antitumor activity of the multitargeted Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor entrectinib: Combined results from two Phase I trials (ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1). Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Scholar, E.M. Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, E.; Iqbal, M.; Asiri, Y.A.; Sayed, A.Y.A.; Alsalahi, R. Eco-Friendly UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of a Fostamatinib Metabolite, Tamatinib, in Plasma: Pharmacokinetic Application in Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzeldin, E.; Asiri, Y.A.; Iqbal, M. Effects of green tea extracts on the pharmacokinetics of quetiapine in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 615285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.W.; Kadi, A.A. Sapitinib: Reactive intermediates and bioactivation pathways characterized by LC-MS/MS. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32995–33006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.W.; Abdelhameed, A.S.; Al-Shakliah, N.S.; Kadi, A.A. LC-MS/MS Estimation of the Anti-Cancer Agent Tandutinib Levels in Human Liver Microsomes: Metabolic Stability Evaluation Assay. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4439–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwa, M.W.; Darwish, H.W.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Kadi, A.A. Investigation of metabolic degradation of new ALK inhibitor: Entrectinib by LC-MS/MS. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2018, 485, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70858/download (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2019. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M10_Step4_Guideline_2019_1204.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Leahy, D.E. Integrating In Vitro ADMET Data through Generic Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Von Mehren, M.; Blanke, C.D.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Eisenberg, B.; Roberts, P.J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Tuveson, D.A.; Singer, S.; Janicek, M. Efficacy and Safety of Imatinib Mesylate in Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, J.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Gotlib, J.; Stover, E.H.; Legare, R.D.; Cortes, J.; Kutok, J.; Clark, J.; Galinsky, I.; Griffin, J.D. A Tyrosine Kinase Created by Fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 Genes as a Therapeutic Target of Imatinib in Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Marć, M.; Gałuszka, A.; Namieśnik, J. Green Chemistry Metrics with Special Reference to Green Analytical Chemistry. Molecules 2015, 20, 10928–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE-Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | ENT | Quizartinib |
|---|---|---|
| I. Compound Parameters | ||
| Precursor | 561.23 | 561.19 |
| Product ion | 284.18 | 114.0 |
| Dwell time (s) | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| Cone voltage (V) | 82 | 52 |
| Collision energy eV | 82 | 82 |
| II. Instrument Parameters | ||
| Collision gas flow rate (mL/min) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Nitrogen flow rate | 600 L/h | 600 L/h |
| Conc. (ng/mL) | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Precision (CV %) | Accuracy (%) | Mean ± SD | Precision (CV %) | Accuracy (%) | |
| 0.5 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | 3.64 | 82.24 | 673.74 ± 78.86 | 11.70 | 89.83 |
| 1.5 | 1.40 ± 0.12 | 11.56 | 93.33 | 132.89 ± 19.65 | 14.78 | 85.59 |
| 150 | 134.49 ± 12.88 | 9.51 | 89.66 | 125.2 ± 0.09 | 7.33 | 83.82 |
| 350 | 320.08 ± 9.4 | 9.45 | 91.54 | 318.42 ± 20.4 | 6.42 | 90.97 |
| 750 | 641.57 ± 60.89 | 9.49 | 85.54 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 7.97 | 84.97 |
| Compound | Nominal Conc. (ng/mL) | Extraction Recovery | Matrix Effects | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | RSD | Mean | RSD | ||
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | ||
| Entrecitinib | 15 | 89.09 | 11.22 | 92.11 | 5.15 |
| 150 | 87.06 | 6.20 | 91.50 | 13.90 | |
| 350 | 89.43 | 1.78 | 90.48 | 3.92 | |
| 750 | 81.40 | 13.30 | 89.61 | 9.10 | |
| IS | 100 | 89.50 | 6.22 | 89.10 | 13.94 |
| Stability | Nominal Con. (ng/mL) | Measured Con. (ng/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term | 1.5 | 1.34 ± 0.06 | 4.16 | 89.26 |
| 350 | 314.50 ± 6.26 | 1.99 | 89.86 | |
| 750 | 610.50 ± 44.00 | 7.20 | 87.21 | |
| Long-term | 1.5 | 1.35 ± 0.18 | 13.86 | 90.48 |
| 350 | 318.75 ± 8.06 | 2.53 | 90.90 | |
| 750 | 625.23 ± 11.49 | 1.19 | 89.31 | |
| Thaw and freeze | 1.5 | 1.33 ± 0.02 | 7.96 | 86.58 |
| 350 | 314.67 ± 8.39 | 2.67 | 89.90 | |
| 750 | 647.524 ± 73.69 | 11.38 | 86.33 | |
| Auto-sampler (24) h | 1.5 | 1.39 ± 0.09 | 0.09 | 86.46 |
| 350 | 315. ± 5.0 | 1.59 | 90.00 | |
| 750 | 660.75 ± 59.12 | 8.95 | 88.07 |
| Parameter | Value | Penalty Points |
|---|---|---|
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | <10 mL (g) | 1 |
| Acetonitrile | <10 m L (g) | 4 |
| Methanol | <10 mL (g) | 6 |
| Ammonium acetate | <10 mL (g) | 1 |
| Methyl tert-butyl ether | <10 mL (g) | 3 |
| Waste | <1.0 mL/run (g) | 3 |
| Instrument energy | More than 1.5 kw/h | 2 |
| Total penalty points | 20 | |
| Eco-Scale score | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, E.A.; Iqbal, M.; Mostafa, G.A.E.; Al Salahi, R. Development and Validation of an Ecofriendly, Rapid, Simple and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Entrectinib Quantification in Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Separations 2023, 10, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090494
Ali EA, Iqbal M, Mostafa GAE, Al Salahi R. Development and Validation of an Ecofriendly, Rapid, Simple and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Entrectinib Quantification in Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Separations. 2023; 10(9):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090494
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Essam A., Muzaffar Iqbal, Gamal A. E. Mostafa, and Rashad Al Salahi. 2023. "Development and Validation of an Ecofriendly, Rapid, Simple and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Entrectinib Quantification in Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring" Separations 10, no. 9: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090494
APA StyleAli, E. A., Iqbal, M., Mostafa, G. A. E., & Al Salahi, R. (2023). Development and Validation of an Ecofriendly, Rapid, Simple and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Entrectinib Quantification in Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Separations, 10(9), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090494







