The Simultaneous Determination of Nine Furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica Using UPLC Combined with the QAMS Approach and Novel Health Risk Assessment Based on the Toxic Equivalency Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Condition
2.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.4. Preparation of BZ Samples
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Theory of QAMS
2.7. Quantification of AD Samples
2.8. Healthy Risk Assessment
2.8.1. Assessment of Daily Intake of AD Based on the EQF
2.8.2. Risk Characterization Based on Health-Based Guidance Values
3. Results and Discussion
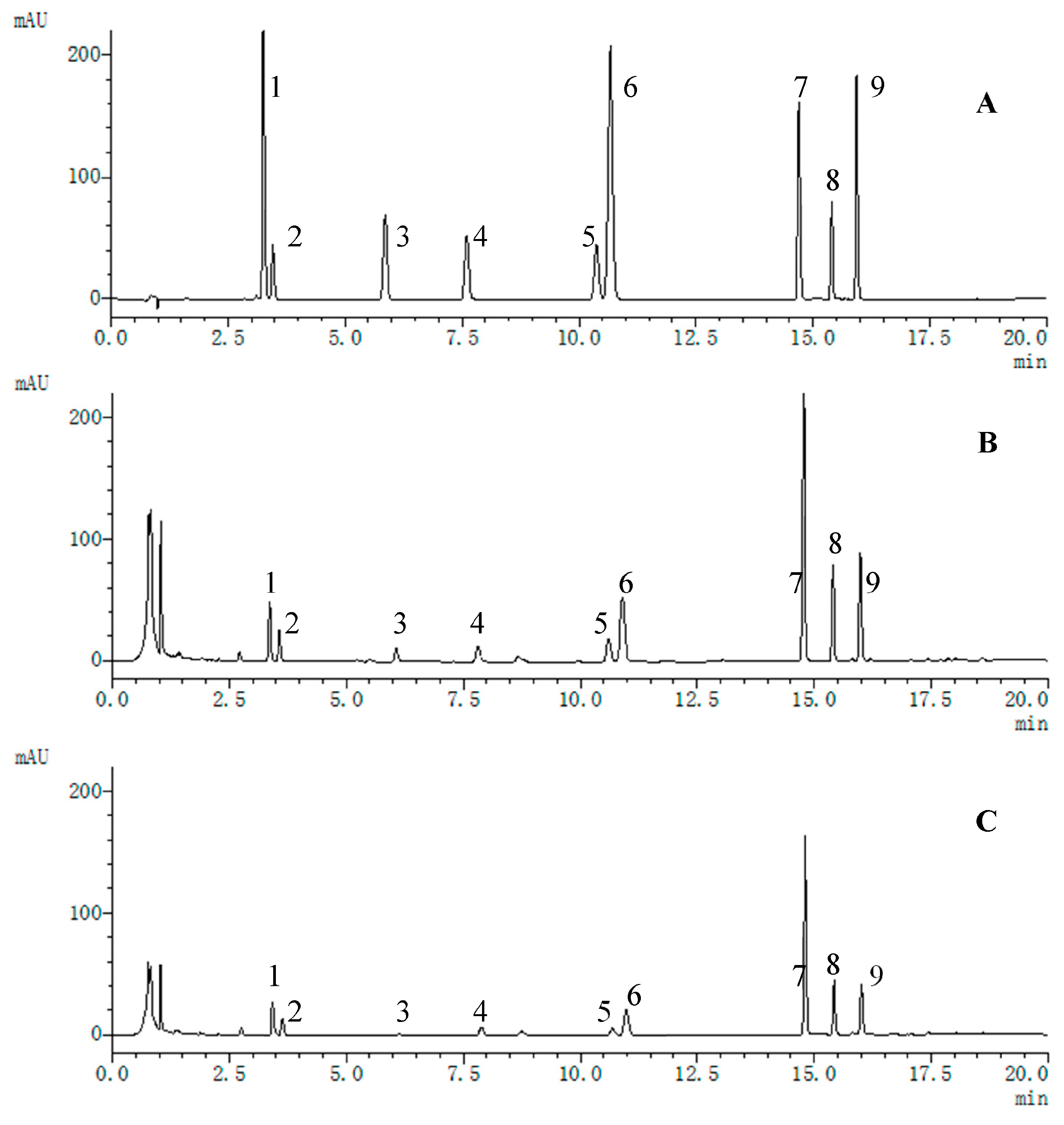
3.1. Extraction Procedures and UPLC Condition Optimization
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. Quantitative Analyses of Multiple Components via Single Marker
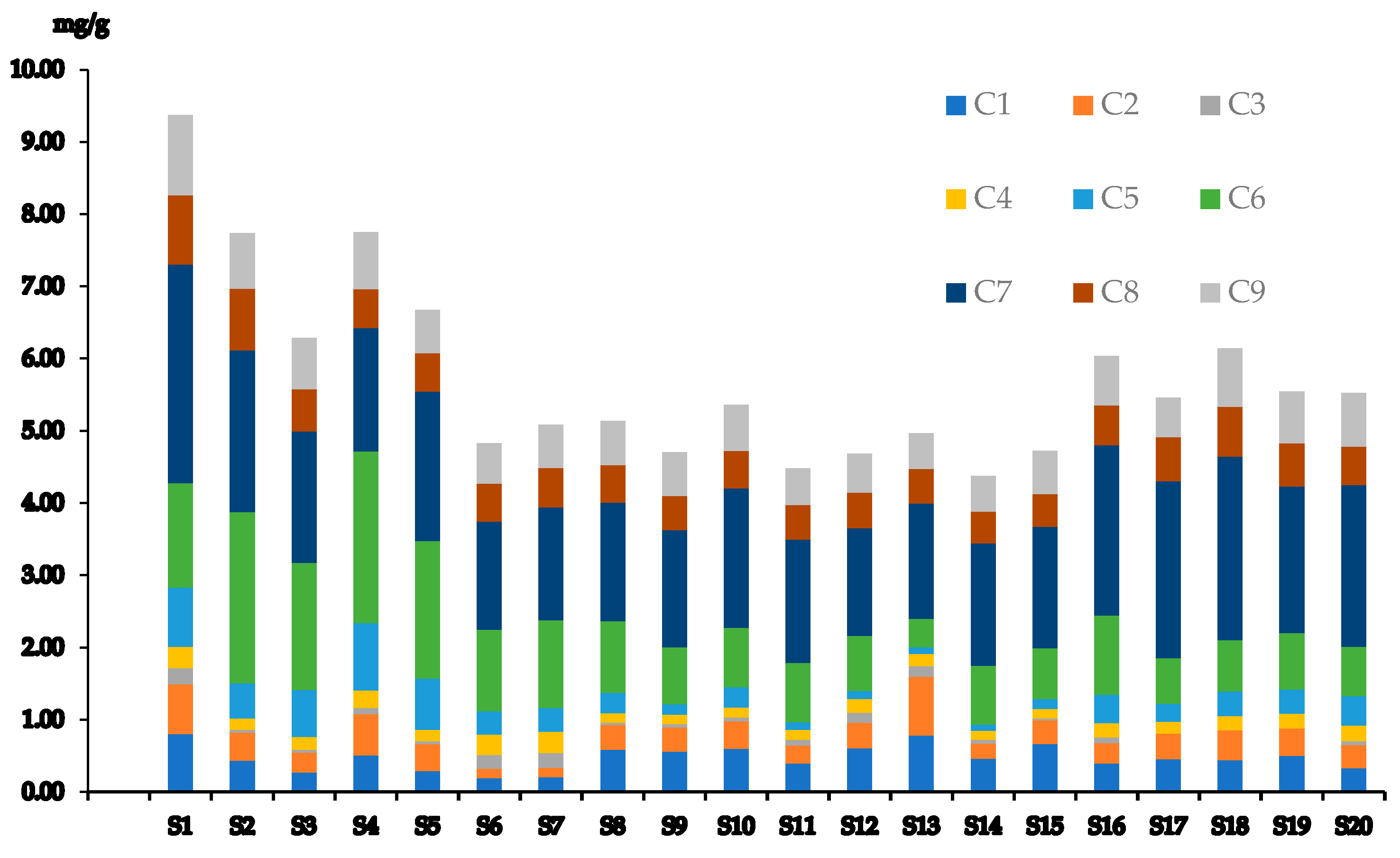
3.4. Quantification and Method Assessment
3.5. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melough, M.M.; Cho, E.; Chun, O.K. Furocoumarins: A review of biochemical activities, dietary sources and intake, and potential health risks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Roleira, F.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F. Furocoumarins in medicinal chemistry. Synthesis, natural occurrence and biological activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3239–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.R.; Pathak, M.A.; Mohn, G.R. Molecular and genetic basis of furocoumarin reactions. Mutat. Res. 1976, 39, 29–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, R.M.; Dowdy, J.C. The increase in melanoma: Are dietary furocoumarins responsible? Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.W.; Cho, E.; Feskanich, D.; Li, W.Q.; Sun, Q.; Han, J.L.; Qureshi, A.A. Citrus consumption and risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.W.; Han, J.L.; Feskanich, D.; Cho, E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Qureshi, A.A. Citrus Consumption and Risk of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; Wöhrlin, F.; Lindtner, O.; Heinemeyer, G.; Lampen, A. Toxicology and risk assessment of coumarin: Focus on human data. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Kasper, P.; Kersten, B.; Zhang, J. Photochemical genotoxicity and photochemical carcinogenesis—Two sides of a coin? Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 102–103, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, N.; Kohtai, S.; Nakagaki, R. Molecular aspects of furocoumarin reactions: Photophysics, photochemistry, photobiology, and structural analysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2005, 6, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, F. Photochemical and photobiological properties of furocoumarins and homologues drugs. Int. J. Photoenergy 1999, 1, 761394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Q.; Yamazoe, Y. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 by furanocoumarins in grapefruit juice and herbal medicines. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Reflection Paper on the Risk Associated with Furocoumarins Contained in Preparations of Angelica archangelica L. EMEA/HMPC/317913/2006 [EB/OL]. 2007. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/final-reflection-paper-risks-associated-furocoumarins-contained-preparations-angelica-archangelica-l_en.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2021).
- Raquet, N.; Schrenk, D. Relative photomutagenicity of furocoumarins and limettin in the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase assay in V79 cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Chemical Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, S.G.; Xiang, Z.D.; Dong, W.C.; Li, X.Y.; Wei, Y.M.; Gao, P.; Dai, L. A review of the historical records, chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and edibility of Angelica dahurica. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 1878–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, M.; Guo, J.; Su, S.L.; Yu, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Z. Angelica dahurica Extracts Attenuate CFA Induced Inflammatory Pain via TRPV1 in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 4684830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, T.; Fan, G.; Wu, Y. An efficient strategy based on MAE, HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS and 2D-prep-HPLC-DAD for the rapid extraction, separation, identification and purification of five active coumarin components from Radix Angelicae Dahuricae. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, T.; Yu, J. The Angelica dahurica: A Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 896637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, P.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, D.W.; Duan, J.A. Analysis and evaluation of coumarins and polysaccharides in Angelica dahurica from different habitats. Acta. Univ. Med. 2015, 31, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Na, L. Research progress on medicinal and food homology of Angelica dahurica. Asian-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2022, 18, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.Y.; Jing, Y.S.; Zheng, Y.G.; Wu, L.F. Chemical constituents of Angelica dahurica and its therapeutic effect on nervous system diseases. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 690–691. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z. Skin phototoxicity study of radix Angelicae dahuricae water extract using rats by oral administration. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2018, 44, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Han, J.; Guo, D.A. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis and characterization of furocoumarins in the roots of Angelica dahurica by HPLC/DAD/ESI-MSn technique. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, C.G.; Lv, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Chai YFZhang, G.Q. Rapid separation and identification of furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection, time-of-flight mass spectrometry and quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Q.; Zhu, Z.X.; Song, Y.L.; Qi, B.W.; Wang, J.; Su, C.; Tu, P.F.; Shi, S.P. Dimeric furanocoumarins from the roots of Angelica dahurica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, P.; Li, J.P.; Fei, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.Q.; Yu, M.Z.; Liu, A.Q.; Niu, H.Y.; Zou, S.M.; Wei, X.L.; Ju, Z.Y.; et al. Isolation, structure elucidation, tyrosinase inhibitory, and antioxidant evaluation of the constituents from Angelica dahurica roots. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, C.; Raquet, N.; Schrenk, D. Application of the concept of relative photomutagenic potencies to selected furocoumarins in V79 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raquet, N.; Schrenk, D. Application of the equivalency factor concept to the phototoxicity and -genotoxicity of furocoumarin mixtures. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion of the panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food on a request from the European Commission on Coumarin in flavourings and other food ingredients with flavouring properties. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 793–808. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yin, L.; Dong, L.; Quan, H.F.; Chen, R.; Hua, S.Y.; Ma, J.H.; Guo, D.Y.; Fu, X.Y. Quality evaluation for Radix Astragali based on fingerprint, indicative components selection and QAMS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, 4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, M.; Zou, J.; Liu, Z. Analysis of the HPLC fingerprint and QAMS for Sanhuang gypsum soup. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 5890973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, X. Simultaneous determination of seven phenylethanoid glycosides in Cistanches Herba by a single marker using a new calculation of relative correction factor. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.T.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Nie, J.; Chen, B.L.; Fang, C.F.; Xue, J.; Bi, X.Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Innovative health risk assessment of heavy metals in Chinese herbal medicines based on extensive data. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104987–104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). 5-Methoxypsoralen [A]//IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.H.; Cao, Y.X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.W.; He, J.Y.; Cao, L.Q. Research on chronic toxicology of Compound Radix Angelicae Dahuricae capsule. J. Shanxi Med. Univ. 2006, 37, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Lu, X.L.; Hai, M.Z.; Guo, P.L. Effect of sulfuring on the acute toxicity of the angelica extract. Pharm. Clin. Chin. Mater. Medica 2012, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kortenkamp, A.; Evans, R.; Faust, M.; Kalberlah, F.; Scholze, M.; Wolz, S.U. Investigation of the state of the science on combined actions of chemicals in food through dissimilar modes of action and proposal for science-based approach for performing related cumulative risk assessment. EFSA Support. Publ. 2012, 9, 1–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to Flavouring Group Evaluation 6 (FGE.06): Straight-and branched-chain aliphatic unsatured primary alcohols, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and esters from chemical groups 1 and 4. EFSA J. 2004, 2, 108. [Google Scholar]

| Analytes | Calibration Curves | r | /μg·mL−1 | /μg·mL−1 | /μg·mL−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Y = 24489800X + 4561.67 | 0.9999 | 1.270–158.7 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| 2 | Y = 16185800X + 850.89 | 0.9999 | 0.3970–49.60 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Y = 31411100X + 1986.14 | 0.9999 | 0.4580–57.28 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Y = 29319800X + 1010.05 | 0.9999 | 0.4290–53.65 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 5 | Y = 16335500X + 1443.08 | 0.9999 | 0.7210–90.15 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| 6 | Y = 26801600X + 5930.63 | 0.9999 | 2.070–258.8 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| 7 | Y = 27494800X + 3435.56 | 0.9999 | 0.8160–102.0 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 8 | Y = 28897035X + 1351.04 | 0.9999 | 0.8000–100.50 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| 9 | Y = 28331800X + 597.95 | 0.9999 | 0.8200–102.50 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Analytes | Precision (RSD/%, n = 6) | Stability (RSD/%, n = 6) | Repeatability (RSD/%, n = 6) | Recoveries (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean/% | RSD/% | ||||
| 1 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 2.01 | 97.57 | 2.98 |
| 2 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 1.89 | 107.9 | 2.59 |
| 3 | 0.52 | 1.10 | 2.75 | 107.9 | 2.98 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 1.14 | 2.07 | 106.9 | 2.91 |
| 5 | 0.23 | 1.07 | 1.93 | 90.07 | 2.98 |
| 6 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 1.91 | 92.09 | 2.66 |
| 7 | 0.01 | 1.04 | 1.97 | 93.76 | 3.00 |
| 8 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 2.10 | 101.5 | 2.62 |
| 9 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 1.98 | 91.97 | 2.16 |
| RCF | Calculated by Slope | a | b | c | d | e | f | Mean | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f7/1 | 0.891 | 0.890 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.892 | 0.891 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.17 |
| f7/2 | 0.589 | 0.574 | 0.583 | 0.585 | 0.587 | 0.588 | 0.589 | 0.585 | 0.91 |
| f7/3 | 1.142 | 1.124 | 1.131 | 1.136 | 1.137 | 1.140 | 1.142 | 1.136 | 0.58 |
| f7/4 | 1.066 | 1.016 | 1.025 | 1.041 | 1.054 | 1.060 | 1.061 | 1.046 | 1.85 |
| f7/5 | 0.594 | 0.568 | 0.584 | 0.589 | 0.590 | 0.593 | 0.593 | 0.587 | 1.57 |
| f7/6 | 0.975 | 0.961 | 0.965 | 0.967 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.971 | 0.968 | 0.46 |
| f7/8 | 1. 051 | 1.055 | 1.053 | 1.052 | 1.049 | 1.048 | 1.051 | 1. 051 | 0.25 |
| f7/9 | 1.030 | 1.008 | 1.009 | 1.011 | 1.012 | 1.014 | 1.018 | 1.015 | 0.76 |
| Conditions | Items | f7/1 | f7/2 | f7/3 | f7/4 | f7/5 | f7/6 | f7/8 | f7/9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class | Column 1 | 0.898 | 0.582 | 1.110 | 1.051 | 0.599 | 0.973 | 1.055 | 1.018 |
| Column 2 | 0.890 | 0.541 | 1.125 | 1.082 | 0.547 | 0.967 | 1.049 | 1.042 | |
| Column 3 | 0.881 | 0.591 | 1.041 | 1.045 | 0.597 | 0.966 | 1.062 | 1.021 | |
| Shimadzu UPLC Instrument (LC-30AD) | Column 1 | 0.891 | 0.585 | 1.136 | 1.046 | 0.587 | 0.968 | 1.051 | 1.015 |
| Column 2 | 0.878 | 0.523 | 1.121 | 1.103 | 0.571 | 0.978 | 1.048 | 1.038 | |
| Column 3 | 0.902 | 0.576 | 1.064 | 1.045 | 0.590 | 0.994 | 1.049 | 1.016 | |
| Mean | 0.890 | 0.566 | 1.100 | 1.062 | 0.582 | 0.974 | 1.052 | 1.025 | |
| RSD (%) | 1.05 | 4.88 | 3.47 | 2.32 | 3.39 | 1.10 | 0.51 | 1.16 | |
| Column temperature (°C) | 23 | 0.890 | 0.603 | 1.141 | 1.024 | 0.577 | 0.971 | 1.0518 | 1.018 |
| 25 | 0.891 | 0.585 | 1.136 | 1.046 | 0.587 | 0.968 | 1.050 | 1.015 | |
| 27 | 0.891 | 0.582 | 1.122 | 1.053 | 0.594 | 0.962 | 1.0475 | 1.014 | |
| Mean | 0.891 | 0.590 | 1.133 | 1.041 | 0.586 | 0.967 | 1.050 | 1.016 | |
| RSD (%) | 0.07 | 1.92 | 0.87 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.21 | |
| Flow rates (mL/min) | 0.28 | 0.872 | 0.569 | 1.114 | 1.041 | 0.579 | 0.966 | 1.049 | 1.006 |
| 0.30 | 0.891 | 0.585 | 1.136 | 1.046 | 0.587 | 0.968 | 1.050 | 1.015 | |
| 0.32 | 0.925 | 0.601 | 1.151 | 1.052 | 0.595 | 0.971 | 1.0524 | 1.034 | |
| Mean | 0.896 | 0.585 | 1.134 | 1.046 | 0.587 | 0.968 | 1.051 | 1.018 | |
| RSD (%) | 3.00 | 2.74 | 1.64 | 0.53 | 1.36 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 1.41 |
| Instrument | Column | t7/1 | t7/2 | t7/3 | t7/4 | t7/5 | t7/6 | t7/8 | t7/9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class | ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 | 0.225 | 0.239 | 0.401 | 0.509 | 0.701 | 0.730 | 1.049 | 1.087 |
| ZORBAX Eclipse plus C18 | 0.221 | 0.235 | 0.397 | 0.517 | 0.706 | 0.725 | 1.051 | 1.084 | |
| ACQUITY UPLC HSS, T3 | 0.223 | 0.235 | 0.399 | 0.529 | 0.703 | 0.719 | 1.064 | 1.081 | |
| Shimadzu UPLC Instrument (LC-30AD) | ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 | 0.229 | 0.241 | 0.414 | 0.511 | 0.705 | 0.726 | 1.052 | 1.089 |
| ZORBAX Eclipse plus C18 | 0.222 | 0.236 | 0.398 | 0.518 | 0.706 | 0.726 | 1.052 | 1.084 | |
| ACQUITY UPLC HSS, T3 | 0.223 | 0.234 | 0.398 | 0.522 | 0.698 | 0.728 | 1.063 | 1.083 | |
| mean | 0.224 | 0.237 | 0.401 | 0.518 | 0.703 | 0.726 | 1.055 | 1.085 | |
| RSD/% | 1.29 | 1.14 | 1.61 | 1.41 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.27 |
| Batch No. | Source | Species | EDI1 | EDI2 | EDI3 | EDI4 | EDI5 | EDI6 | EDI7 | EDI8 | EDI9 | ΣEDI Based on TEF | ΣEDI without TEF | HI Values Based on TEF | HI Values without TEF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | Bozhou, Anhui | 1 | 0.00084 | 0.00005 | 0.00029 | 0.00194 | 0.00005 | 0.00072 | 0.00298 | 0.00006 | 0.00109 | 0.0080 | 0.0613 | 0.80 | 6.13 |
| B2 | Anguo, Hebei | 1 | 0.00045 | 0.00003 | 0.00005 | 0.00105 | 0.00003 | 0.00118 | 0.00220 | 0.00006 | 0.00075 | 0.0058 | 0.0506 | 0.58 | 5.06 |
| B3 | Anguo, Hebei | 1 | 0.00028 | 0.00002 | 0.00006 | 0.00116 | 0.00004 | 0.00087 | 0.00179 | 0.00004 | 0.00069 | 0.0050 | 0.0411 | 0.50 | 4.11 |
| B4 | Anguo, Hebei | 1 | 0.00053 | 0.00004 | 0.00011 | 0.00157 | 0.00006 | 0.00118 | 0.00168 | 0.00004 | 0.00077 | 0.0060 | 0.0507 | 0.60 | 5.07 |
| B5 | Anguo, Hebei | 1 | 0.00030 | 0.00002 | 0.00005 | 0.00103 | 0.00005 | 0.00095 | 0.00203 | 0.00003 | 0.00059 | 0.0050 | 0.0436 | 0.50 | 4.36 |
| B6 | Jiaozuo, Hebei | 1 | 0.00020 | 0.00001 | 0.00025 | 0.00185 | 0.00002 | 0.00056 | 0.00147 | 0.00003 | 0.00055 | 0.0049 | 0.0316 | 0.49 | 3.16 |
| B7 | Hong Kong | 1 | 0.00021 | 0.00001 | 0.00027 | 0.00194 | 0.00002 | 0.00060 | 0.00153 | 0.00004 | 0.00059 | 0.0052 | 0.0333 | 0.52 | 3.33 |
| B8 | Hong Kong | 1 | 0.00062 | 0.00002 | 0.00005 | 0.00085 | 0.00002 | 0.00049 | 0.00161 | 0.00003 | 0.00060 | 0.0043 | 0.0336 | 0.43 | 3.36 |
| B9 | Hong Kong | 1 | 0.00058 | 0.00002 | 0.00006 | 0.00083 | 0.00001 | 0.00039 | 0.00160 | 0.00003 | 0.00059 | 0.0041 | 0.0308 | 0.41 | 3.08 |
| B10 | Hong Kong | 1 | 0.00063 | 0.00002 | 0.00007 | 0.00086 | 0.00002 | 0.00041 | 0.00189 | 0.00003 | 0.00062 | 0.0046 | 0.0351 | 0.46 | 3.51 |
| B11 | Shehong, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00041 | 0.00002 | 0.00010 | 0.00092 | 0.00001 | 0.00041 | 0.00167 | 0.00003 | 0.00050 | 0.0041 | 0.0293 | 0.41 | 2.93 |
| B12 | Suining, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00063 | 0.00002 | 0.00018 | 0.00125 | 0.00001 | 0.00038 | 0.00147 | 0.00003 | 0.00053 | 0.0045 | 0.0306 | 0.45 | 3.06 |
| B13 | Suining, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00082 | 0.00005 | 0.00019 | 0.00112 | 0.00001 | 0.00019 | 0.00157 | 0.00003 | 0.00048 | 0.0045 | 0.0325 | 0.45 | 3.25 |
| B14 | Suining, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00048 | 0.00001 | 0.00007 | 0.00081 | 0.00001 | 0.00040 | 0.00166 | 0.00003 | 0.00048 | 0.0040 | 0.0286 | 0.40 | 2.86 |
| B15 | Suining, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00070 | 0.00002 | 0.00004 | 0.00083 | 0.00001 | 0.00035 | 0.00164 | 0.00003 | 0.00059 | 0.0042 | 0.0309 | 0.42 | 3.09 |
| B16 | Suining, Sichuan | 2 | 0.00041 | 0.00002 | 0.00010 | 0.00130 | 0.00003 | 0.00054 | 0.00232 | 0.00004 | 0.00067 | 0.0054 | 0.0395 | 0.54 | 3.95 |
| B17 | Hong Kong | 2 | 0.00048 | 0.00002 | 0.00000 | 0.00108 | 0.00002 | 0.00031 | 0.00241 | 0.00004 | 0.00053 | 0.0049 | 0.0357 | 0.49 | 3.57 |
| B18 | Hong Kong | 2 | 0.00046 | 0.00003 | 0.00000 | 0.00129 | 0.00002 | 0.00035 | 0.00250 | 0.00004 | 0.00079 | 0.0055 | 0.0402 | 0.55 | 4.02 |
| B19 | Hong Kong | 2 | 0.00052 | 0.00003 | 0.00000 | 0.00130 | 0.00002 | 0.00039 | 0.00199 | 0.00004 | 0.00070 | 0.0050 | 0.0363 | 0.50 | 3.63 |
| B20 | Hong Kong | 2 | 0.00034 | 0.00002 | 0.00007 | 0.00140 | 0.00003 | 0.00034 | 0.00219 | 0.00004 | 0.00073 | 0.0052 | 0.0361 | 0.52 | 3.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zan, K.; Hu, X.-W.; Kang, S.; Li, H.-L.; Zuo, T.-T.; Jin, H.-Y.; Ma, S.-C. The Simultaneous Determination of Nine Furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica Using UPLC Combined with the QAMS Approach and Novel Health Risk Assessment Based on the Toxic Equivalency Factor. Separations 2023, 10, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090508
Wang Z, Zan K, Hu X-W, Kang S, Li H-L, Zuo T-T, Jin H-Y, Ma S-C. The Simultaneous Determination of Nine Furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica Using UPLC Combined with the QAMS Approach and Novel Health Risk Assessment Based on the Toxic Equivalency Factor. Separations. 2023; 10(9):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090508
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhao, Ke Zan, Xiao-Wen Hu, Shuai Kang, Hai-Liang Li, Tian-Tian Zuo, Hong-Yu Jin, and Shuang-Cheng Ma. 2023. "The Simultaneous Determination of Nine Furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica Using UPLC Combined with the QAMS Approach and Novel Health Risk Assessment Based on the Toxic Equivalency Factor" Separations 10, no. 9: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090508
APA StyleWang, Z., Zan, K., Hu, X. -W., Kang, S., Li, H. -L., Zuo, T. -T., Jin, H. -Y., & Ma, S. -C. (2023). The Simultaneous Determination of Nine Furocoumarins in Angelica dahurica Using UPLC Combined with the QAMS Approach and Novel Health Risk Assessment Based on the Toxic Equivalency Factor. Separations, 10(9), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090508






