HPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Sphingosine 1-Phosphate after the Dephosphorylation by Hydrogen Fluoride
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. CKD Animal Model
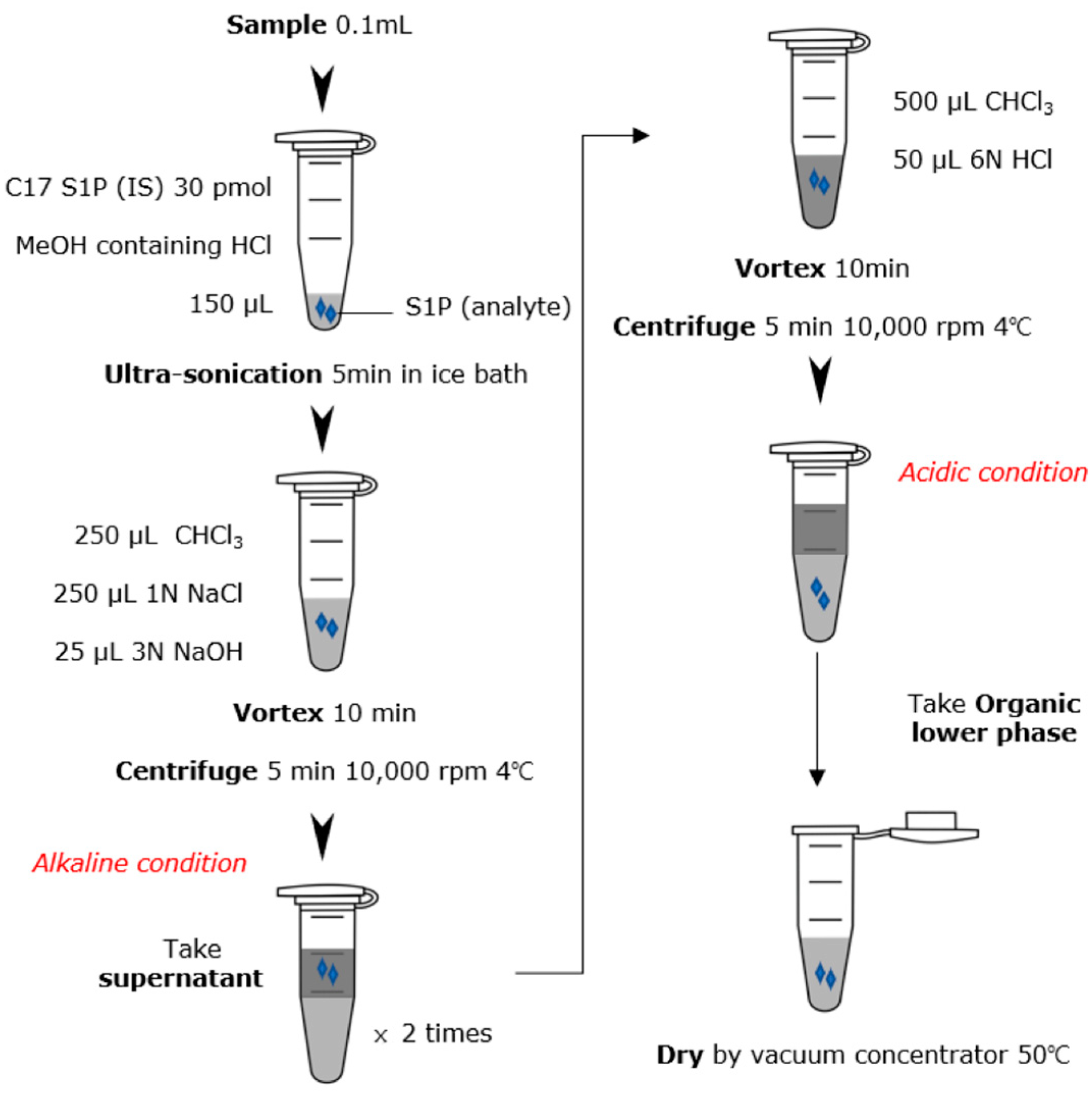
2.3. S1P Extraction
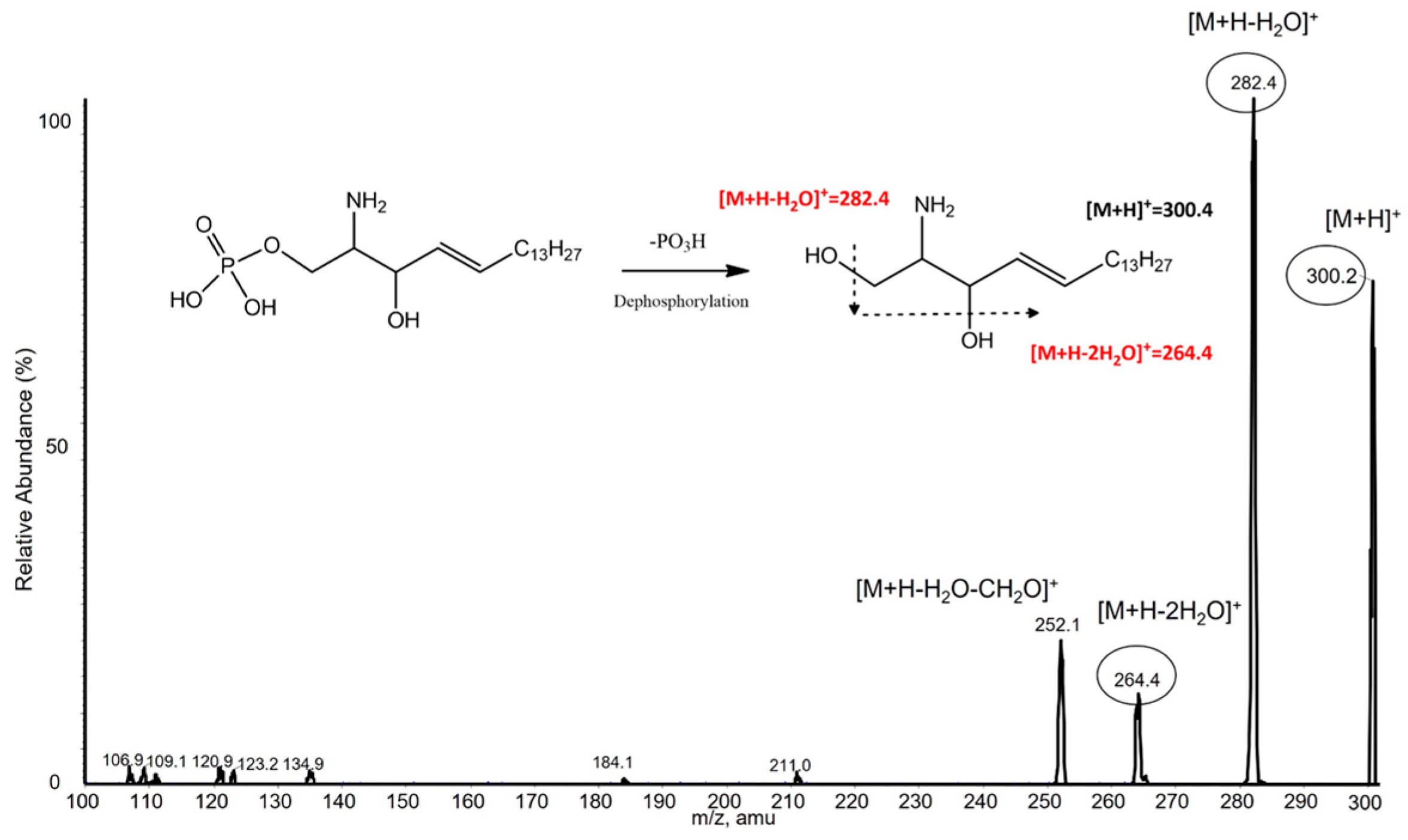
2.4. S1P Dephosphorylation
2.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Method Validation
3. Results
3.1. S1P Extraction
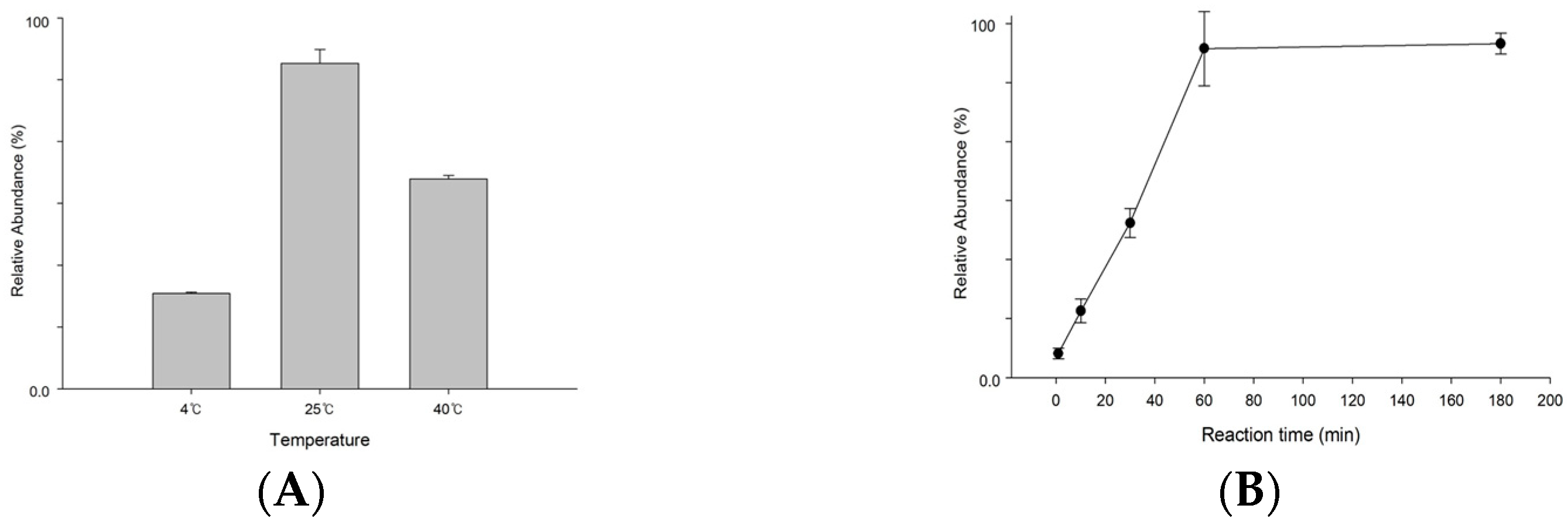
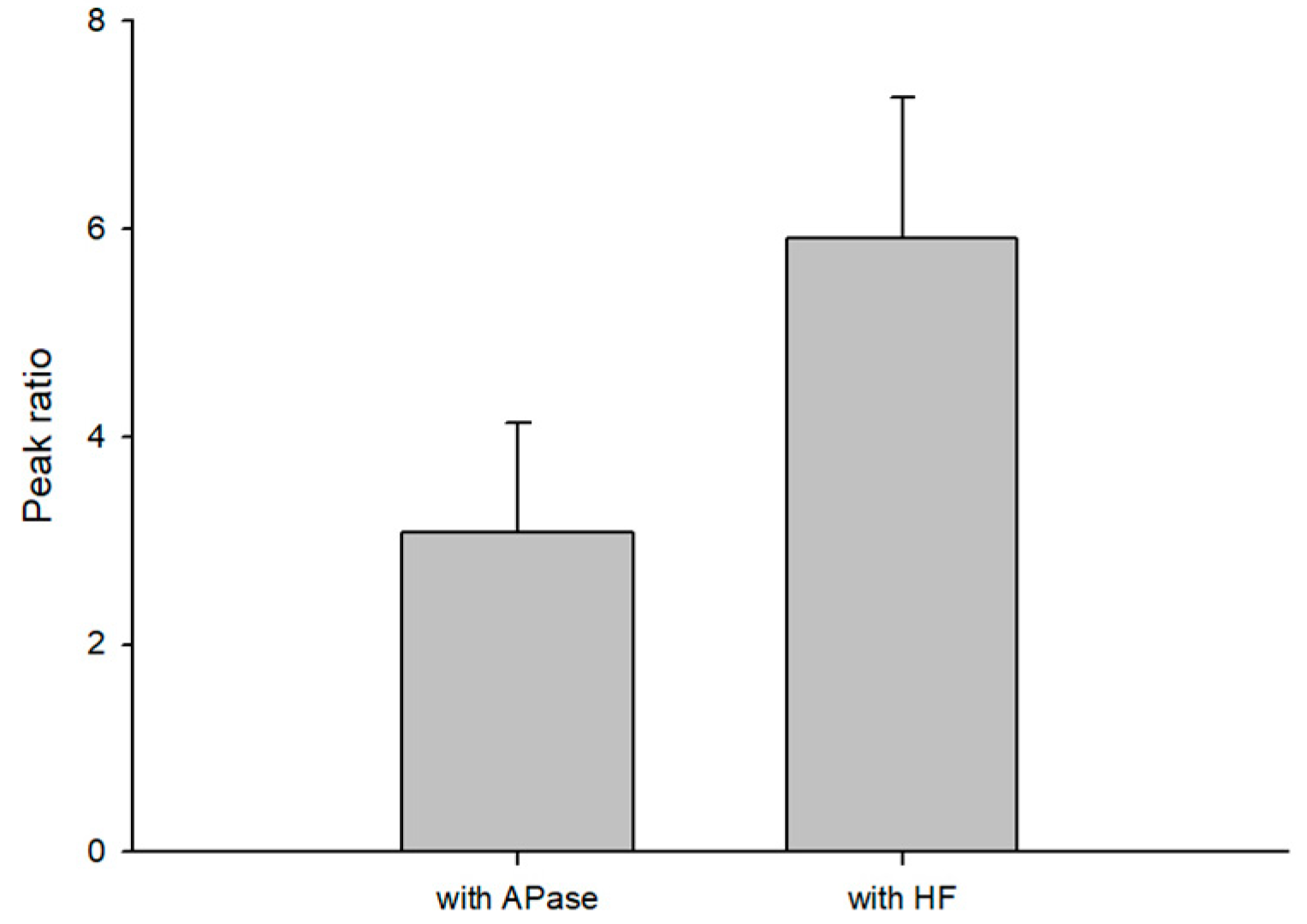
3.2. Optimization for S1P Dephosphorylation
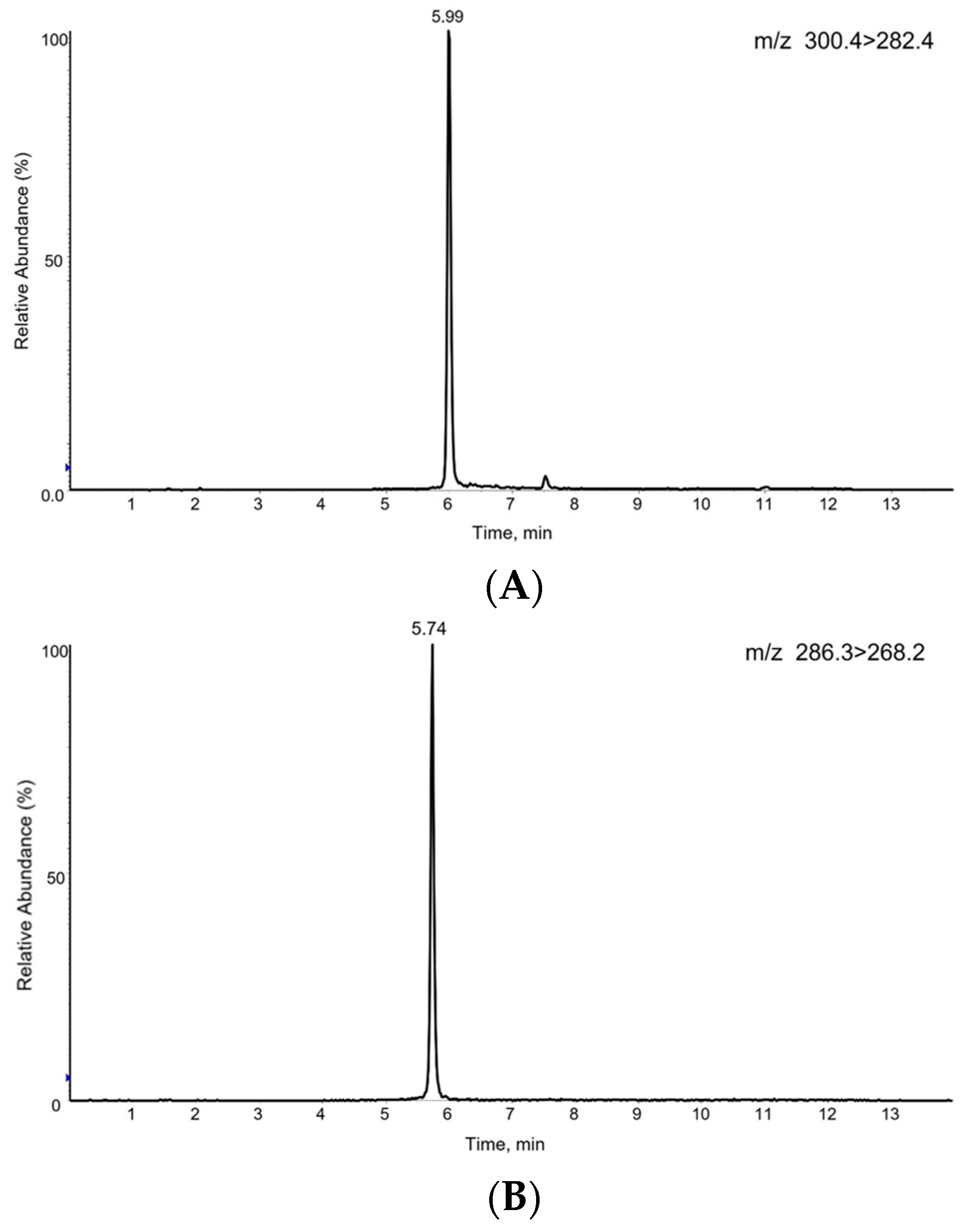
3.3. S1P Analysis by LC-MS/MS
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. S1P Levels in CKD Animal Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Vu, T.M.; Tukijan, F.; Muralidharan, S.; Foo, J.C.; Li Chin, J.F.; Hasan, Z.; Torta, F.; Nguyen, L.N. Erythrocytes efficiently utilize exogenous sphingosines for S1P synthesis and export via Mfsd2b. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, V.; Haase, R.; Akgun, K.; Ziemssen, T. S1P receptor modulators and the cardiovascular autonomic nervous system in multiple sclerosis: A narrative review. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2022, 15, 17562864221133163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luth, A.; Neuber, C.; Kleuser, B. Novel methods for the quantification of (2E)-hexadecenal by liquid chromatography with detection by either ESI QTOF tandem mass spectrometry or fluorescence measurement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 722, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielawski, J.; Pierce, J.S.; Snider, J.; Rembiesa, B.; Szulc, Z.M.; Bielawska, A. Sphingolipid analysis by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 688, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oizumi, H.; Sugimura, Y.; Totsune, T.; Kawasaki, I.; Ohshiro, S.; Baba, T.; Kimpara, T.; Sakuma, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Kawahata, I.; et al. Plasma sphingolipid abnormalities in neurodegenerative diseases. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demont, E.H.; Arpino, S.; Bit, R.A.; Campbell, C.A.; Deeks, N.; Desai, S.; Dowell, S.J.; Gaskin, P.; Gray, J.R.; Harrison, L.A.; et al. Discovery of a brain-penetrant S1P(3)-sparing direct agonist of the S1P(1) and S1P(5) receptors efficacious at low oral dose. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6724–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigusa, D.; Shiba, K.; Inoue, A.; Hama, K.; Okutani, M.; Iida, N.; Saito, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kaneko, T.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Simultaneous quantitation of sphingoid bases and their phosphates in biological samples by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frej, C.; Andersson, A.; Larsson, B.; Guo, L.J.; Norstrom, E.; Happonen, K.E.; Dahlback, B. Quantification of sphingosine 1-phosphate by validated LC-MS/MS method revealing strong correlation with apolipoprotein M in plasma but not in serum due to platelet activation during blood coagulation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8533–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Nakahashi, A.; Yamane, K.; Nakahashi, S.; Murai, Y.; Siddegowda, A.K.C.; Hammam, M.A.S.; Monde, K. Facile Chemoselective Strategy toward Capturing Sphingoid Bases by a Unique Glutaraldehyde-Functionalized Resin. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.K.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, Y.M. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of sphingoid base 1-phosphates in biological samples by o-phthalaldehyde precolumn derivatization after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 303, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, J. Reactions of proteins, carbohydrates, and related substances in liquid hydrogen fluoride. Chem. Rev. 1969, 69, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, M.; Bobrow, E. Hydrolysis of purine and pyrimidine ribosides and 2-deoxyribosides with liquid hydrogen fluoride. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 1970, 37, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuyama, H.; Toda, C.; Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nishimura, O. An efficient chemical method for dephosphorylation of phosphopeptides. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2003, 17, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwisch, L.; Schafer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. An improved high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of sphingosine-1-phosphate in complex biological materials. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2001, 363, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdyshev, E.V.; Gorshkova, I.A.; Garcia, J.G.; Natarajan, V.; Hubbard, W.C. Quantitative analysis of sphingoid base-1-phosphates as bisacetylated derivatives by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 339, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerin, D.L.; Hatcher, J.D. Hydrofluoric Acid Burns. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Beiggy, M.; Mazloum Ardekani, M. Optimization of gas chromatography using short glass capillary column with mass spectrometry for identification and evaluation of commercial heavy alkylbenzene structures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, L.; Drillich, M.; Iwersen, M. Hematology as a diagnostic tool in bovine medicine. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2014, 26, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, C.R.; Schneider, F.K.; Dos Santos, L.C. Image-based red cell counting for wild animals blood. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2010, 2010, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, P.; Andreani, P.; Graler, M.H. Erythrocytes store and release sphingosine 1-phosphate in blood. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Sunkara, M.; Salous, A.K.; Leung, S.W.; Berdyshev, E.V.; Bailey, A.; Campbell, C.L.; Charnigo, R.; Morris, A.J.; Smyth, S.S. Plasma levels of sphingosine 1-phosphate are strongly correlated with haematocrit, but variably restored by red blood cell transfusions. Clin. Sci. 2011, 121, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Ren, Y.; Yao, F.; Duan, J.; Zhao, H.; Du, Y.; Xiao, X.; Duan, H.; Shi, Y. Sphingosine kinase 1 protects renal tubular epithelial cells from renal fibrosis via induction of autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 90, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Sung, S.A.; Kim, M.G.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Jo, S.K. Sphingosine-1-phosphate reduces hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury through attenuation of endothelial injury in mice. Nephrology 2011, 16, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in renal diseases. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 31, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D.J.; Pescio, L.G.; Santacreu, B.J.; Mosca, J.M.; Sterin-Speziale, N.B.; Favale, N.O. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 plays a dual role depending on the stage of cell differentiation in renal epithelial cells. Life Sci. 2023, 316, 121404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, M.; Funao, K.; Kuratsukuri, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Chargui, J.; Touraine, J.L.; Yoshimura, N.; Yoshimura, R. Expression of sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor in rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.N.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Gao, B.; Mohammed-Ali, Z.; Lu, C.; Yum, V.; Dickhout, J.G.; Krepinsky, J.C. SREBP-1 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced TGF-beta1 Upregulation and Glomerular Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| (A) Liquid Chromatography Conditions | |||||
| Column | Inertsil ODS-3 100 × 3.0 mm, 3 μm | ||||
| Column Temp | 40 °C | ||||
| Mobile phase A | 0.1% Formic acid and 10 mM CH3COONH4 in water | ||||
| Mobile phase B | 0.1% Formic acid + 10 mM CH3COONH4 in Acetonitrile: 2-PrPanol (4:3, v/v) | ||||
| Injection volume | 20 μL | ||||
| flow rate | 0.3 mL/min | ||||
| Gradient condition | time (min) | A (vol %) | B (vol %) | ||
| 0.0~1.0 | 70 | 30 | |||
| 1.0~3.0 | 70→5 | 30→95 | |||
| 3.0~7.0 | 5→0 | 95→100 | |||
| 7.0~9.0 | 0 | 100 | |||
| 9.0~10.0 | 0→70 | 100→30 | |||
| 10.0~14.0 | 70 | 30 | |||
| 14.01 | Controller stop | ||||
| (B) Mass Spectrometer Condition | |||||
| Ionization mode | ESI (+) MRM | ||||
| Ion Source Gas 1 | 40 | ||||
| Temperature | 300 | ||||
| Ion Source Gas 2 | 50 | ||||
| Ion Spray Voltage | 5500 | ||||
| Curtain Gas (CUR) | 20 | ||||
| Collision Gas (CAD) | 5 | ||||
| Component | MRM condition | ||||
| m/z | DP (V) | CE (eV) | CXP (eV) | ||
| S1P | 300.4 > 282.4 (quantifier) | 40 | 15 | 5 | |
| 300.4 > 264.4 (qualifier) | 40 | 28 | 4 | ||
| C17 S1P | 286.3 > 268.2 | 80 | 20 | 5 | |
| Sample (n = 3) | Peak Area | Relative Amount (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without HF | With HF | ||
| FBS | 657 | 27,774 | 2.4 |
| Kidney tissue | 341 | 7257 | 4.5 |
| No. | Slope | Intercept | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0075 | 0.0760 | 0.9996 |
| 2 | 0.0074 | 0.0161 | 0.9997 |
| 3 | 0.0073 | 0.0626 | 0.9987 |
| Average | 0.0074 | 0.0516 | 0.9996 |
| S.D. | 0.0001 | 0.0314 | 0.0006 |
| Nominal Concentration (pmol/mL) | Mean (pmol/mL) | S.D. (pmol/mL) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (Recovery, %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision & Accuracy (n = 3) | 30 | 29.8 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 99.5 |
| 250 | 246.2 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 98.5 | |
| 800 | 848.1 | 46.7 | 0.1 | 106.0 | |
| Reproducibility (n = 6) | 30 | 31.4 | 1.5 | 4.7 | 104.5 |
| CKD Biomarkers | Control Group (n = 6) | CKD Group (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 1.38 ± 0.55 |
| Kynurenine (μg/mL) | 0.60 ± 0.18 | 1.01 ± 0.55 |
| Tryptophan (μg/mL) | 12.25 ± 1.42 | 7.39 ± 1.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Jung, S.-H.; Gulyamov, S.; Lee, H.-G.; Boyjigitov, O.; Lee, Y.-M. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Sphingosine 1-Phosphate after the Dephosphorylation by Hydrogen Fluoride. Separations 2024, 11, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010034
Kim H-J, Jung S-H, Gulyamov S, Lee H-G, Boyjigitov O, Lee Y-M. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Sphingosine 1-Phosphate after the Dephosphorylation by Hydrogen Fluoride. Separations. 2024; 11(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hee-Jung, Seo-Hyeon Jung, Shokhid Gulyamov, Hyun-Gy Lee, Oybek Boyjigitov, and Yong-Moon Lee. 2024. "HPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Sphingosine 1-Phosphate after the Dephosphorylation by Hydrogen Fluoride" Separations 11, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010034
APA StyleKim, H. -J., Jung, S. -H., Gulyamov, S., Lee, H. -G., Boyjigitov, O., & Lee, Y. -M. (2024). HPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Sphingosine 1-Phosphate after the Dephosphorylation by Hydrogen Fluoride. Separations, 11(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010034







