Abstract
Ferulic acid is a widespread phenolic compound that occurs in seeds and leaves, both in its free form and conjugated to polysaccharides, carbohydrates, glycoproteins and lignins in the plant cell walls. It exhibits various biological activities, like antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, and antiviral activity, and it modulates enzyme activity. Given these wide potential health benefits, ferulic acid has attracted considerable research interest and may be considered a biomolecule with strong prospects as a functional food ingredient. Great attempts have been made to enhance its extraction process and recovery from natural matrices and agro-industrial wastes for its various applications relating to human health and nutrition. This review presents the recently available information on the extraction methods for quantifying ferulic acid in different samples, along with its bioavailability and stability in processing foods and biological activities.
1. Introduction
Ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, FA) belongs to the group of hydroxycinnamic acids, the class of phenolic compounds. Its name is derived from the genus Ferula, referring to the giant fennel (Ferula communis). As a by-product of the metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine, it is found in all plants. FA is abundant in numerous cereals and grains (such as rice, barley, wheat, and maize), fruits and vegetables (bananas, citrus fruits, eggplant, and cabbage), some beverages (coffee and beer) as well as in monocot plants [,,,,]. It is a component of plant cell walls and forms a three-dimensional structure with cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin []. The contents of FA (101.99–884.68 μg/g dry weight) determined in commonly consumed vegetables in China were mainly found in leafy vegetables [].
Ferulic acid has low toxicity and exerts a wide range of biological functions. It presents potential therapeutic effects useful in treating cancer, diabetes, and lung cardiovascular diseases, and it is an important active component of many traditional Chinese medicines [,,,,]. Its antioxidant properties are mainly manifested through the effective scavenging of oxygen-reactive species by phenolic hydroxyl groups and this effect is much stronger than vanillic, coumaric, and cinnamic acids [,,]. FA is quickly absorbed by the organism and remains for longer in the blood compared to other phenolic acids [].
In addition to being widely used in medicine, some countries have approved it as a food additive to prevent lipid peroxidation []. Ferulic acid is also used for the production of vanillin [,] and preservatives [] and as a cross-linking agent for the preparation of gels and edible films used in food industries [,]. It is widely applied in the cosmetic industry to protect skin from UV-induced damage [,]. Adding FA to the mixture containing ascorbic acid and tocopherol improved the chemical stability of these vitamins and enhanced skin photoprotection under solar-simulated irradiation [].
Given its potential health benefits and several applications, ferulic acid has attracted considerable research interest and may be considered a biomolecule with strong prospects as a functional food ingredient. Great attention is paid to its extraction from natural matrices and agro-industrial wastes for its various applications relating to human health and nutrition, particularly to achieve greater efficiency in the isolation of the free-form FA from plant materials and to increase its bioavailability. This review presents the recently available information on the extraction methods for quantifying ferulic acid in different samples, along with its bioavailability and stability in processing foods. The biological activities of FA are also described.
2. Extraction and Preconcentration of Ferulic Acid
In plant materials, ferulic acid is present in three forms: as soluble-free, soluble-conjugated (esterified to sugars and other low molecular mass compounds), and insoluble-bound FA as a constituent of arabinoxylan and lignocellulosic complexes (Figure 1) []. The FA content and distribution can vary a lot between the different varieties of plants, but most of this phenolic acid exists in the insoluble-bound form. Recovery of FA from natural sources requires the use of the appropriate extraction conditions with high quality and purity of the final product. Moreover, a detailed knowledge of the ferulic acid content in foods and pharmaceuticals is important to understand its potential for human health. The methods used for its determination have some limitations due to both spectral and background interferences, and often the low content of FA. To improve the detection capability and selectivity of analytical methods, the separation and preconcentration of FA from matrix samples are usually necessary before the final quantification.
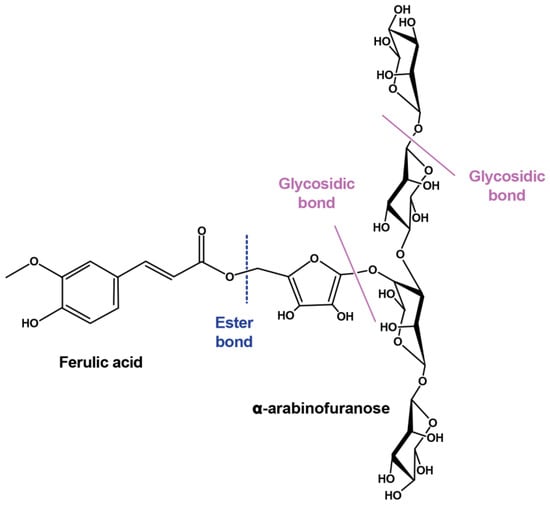
Figure 1.
The structure of ferulic acid linked to arabinoxylans. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [] 2021 Elsevier.
2.1. Recovery of Ferulic Acid from Natural Sources
Typical Soxhlet extraction is increasingly being replaced by advanced techniques to enhance its efficiency and selectivity. These techniques are generally faster and have higher automation levels. Several methodologies based on accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), ultrasound-assisted extraction (USE), subcritical water extraction (SWE), and pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) have been used for the isolation of FA from plant materials, particularly from wheat-based foods [,,,,,]. Application of mathematical and statistical methods to the analysis of chemical data, like experimental design, response surface analysis and principal component analysis, has often been used for determining the optimum extraction conditions as this process is influenced by several factors, such as the solvent type, temperature, extraction time, and liquid–solid ratio [,].
Free ferulic acid and its ester forms can be directly extracted using pressurized hot water or aqueous ethanol solution [,,,]. Pressurized water at 200 °C for 3.5 min extracted 17% of FA-free form from destarched wheat bran and the rest was covalent ester-bounded to arabinoxylans []. In terms of the extraction yield, no significant effect was observed with microwave heating used to intensify this process. However, it was stated that microwave power enhanced the FA extraction from tomatoes using 80% methanol []. Buranov et al. reported that using the SWE method resulted in higher amounts of FA being extracted from corn bran (432 ± 3 mg/100 g) compared to wheat bran (115 ± 5 mg/100 g) and flax shives (7.9 ± 3 mg/100 g) []. Papadaki et al. investigated the release and recovery of FA from wheat bran using hydrothermal treatment []. The best results were obtained when 10% of either citric acid or sodium carbonate (90 °C for 24 h) was applied. Based on chromatographic analysis, it was found that Na2CO3 extraction afforded products enriched in free ferulic acid, but the use of citric acid gave extracts enriched in a ferulate pentose ester [].
Conjugated ferulic acid bound to the cell wall via an ester bond can be extracted using alkaline hydrolysis [,,,,,,]. This process can cleave the lignin/phenolic-carbohydrate complexes structure, resulting in a phenolic portion, soluble sugars, insoluble lignin, and carbohydrates. Similar results were reported for pressurized and non-pressurized alkaline extractions using 0.5 M NaOH solution for wheat and corn bran []. The purification of FA from alkaline extracts was usually performed by its adsorption on a surface of a different solid material [,,,,]. Ren et al. found that among the four tested carbon adsorbents, mesoporous carbon showed the highest adsorption capacity (238.5 mg/g of carbon) due to its high mesopore volume in comparison with powdered active charcoal (220 mg/g) and XAD-4 resin (49.98 mg/g) []. However, the purification methods using solid sorbents are expensive for industrial use; thus, purification of extracted FA by precipitation method is recommended where oily substances and hemicelluloses can be precipitated after ethanol addition [].
Harsh chemicals and high temperatures are usually used for alkaline hydrolysis, thus representing the main limitation of its use in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. For this reason, enzymatic processes as alternative hydrolysis methods for the extraction of FA (in the free and conjugated forms) were applied []. The enzymes used differ in their specification in the degradation of plant cells. Feruloyl esterases, the most commonly used enzyme for the release of ferulic acid from agro-industrial by-products, cause the hydrolysis of the ester bond between FA and α-L-arabinofuranose in hemicellulose [,,,]. Commercial enzyme preparations are also used [,,]. For instance, the enzymatic hydrolysis was performed by sequential biorefining, applying four hydrolytic enzymes under optimal conditions for each enzyme []. Among the enzymes tested, the superiority of multi-enzyme complex Viscozyme® L has been highlighted, as the maximal yield of 11.3 and 8.6 g/kg from rye and wheat bran was obtained, respectively []. To increase the accessibility of the enzymes and increase the dissolution of the plant structure, some preliminary steps before enzymatic hydrolysis have been explored, mostly by applying high temperatures and pressures (hydrothermal pretreatment) [,,,,]. However, the main disadvantages of enzymatic hydrolysis are the cost of the enzymes and/or the reaction time. Additionally, for the process to be efficient, control of the reaction temperature and pH is required []. Table 1 presents recent examples of the extraction conditions for the isolation of ferulic acid from different natural sources.

Table 1.
Recent examples of the extraction of ferulic acid from natural sources.
2.2. Preconcentration of Ferulic Acid for Analytical Determination
Among the different techniques that can be used for the determination of ferulic acid, solid-phase extraction (SPE) using various solid sorbents has been developed [,,,]. Besides the preconcentration, it can also be used for the matrix removal necessary in some procedures. SPE methods are considered to be superior to liquid–liquid extraction in terms of the simplicity, rapid phase separation, high enrichment factor, and the ability to combine them with different detection techniques. Moreover, they offer the possibility of direct combination with the final chromatographic analysis. The imprinted polymer coupled with HPLC was used for the selective enrichment and determination of ferulic acid in traditional Chinese medicine and biological samples [] and in orange peels []. Dil et al. applied also molecularly imprinted polymer, albeit based on syringe-to-syringe magnetic solid-phase microextraction for FA preconcentration from pomegranate, grape, and orange samples [].
Recently, room temperature ionic liquids (ILs) and deep eutectic solvents (DESs) were introduced as a new kind of alternative solvents for the preconcentration and/or purification of bioactive compounds [,,]. ILs represent organic salts with a melting point generally below 100 °C, that consist entirely of ions, relatively bulky organic cations (imidazolium, pyridinium) with different tailorable characteristics, and small inorganic anions (Cl−, Br−, BF4−, PF6−). DESs, formed from Lewis or Brönsted acids and bases, exhibit physicochemical properties similar to ILs, such as negligible volatility and high thermal and chemical stabilities, but they are less toxic and more biodegradable. In a study by Wang et al., four hydrophobic ionic liquids with a PF6− anion and different cations based on imidazolium derivatives were examined []. The experimental results showed that the extraction efficiency of FA increased with the increase in the alkyl chain length from butyl to hexyl. The DES of choline chloride-acetic acid was used for ferulic acid isolation and preconcentration from palm-pressed fiber with microwave assistance [].
3. Bioavailability of Ferulic Acid
The bioavailability of nutrients is an important factor as it is directly proportional to the positive effects they have on overall health. The bioavailable fraction is defined as the amount of ingested nutrients that are absorbed, distributed to organs and tissues, and then transformed into a biochemically active form that is effectively used by the organism [,,,]. For assessing the bioavailability, most science researchers investigated the main factors that affect bioavailability, such as the bioaccessibility, absorption, and potential transformation of a provides biomolecules. The term bioaccessibility refers the fraction of an ingested biocomponent that is potentially available for absorption and used for storage and metabolic function. As bioaccessibility falls within the scope of bioavailability and both concepts are similar, it has been suggested that. they could be grouped in a broader definition as bioefficiency [].
Several procedures were applied for the evaluation of the nutrients’ bioavailability, including in vitro methodologies (simulated gastrointestinal digestion, Caco-2 cell assay) and in vivo approaches such as measuring their levels in the blood or tissues [,]. Only compounds that are released from the food matrix by the action of digestive enzymes (small intestine) and bacterial microflora (large intestine) are available for absorption, e.g., potentially bioavailable [,].
Ferulic acid is mostly bound to arabinoxylans and other indigestible polysaccharides and its bioavailability is limited due to the poor intrinsic distribution rate [,,]. Anson et al. investigated the bioaccessibility of ferulic acid from different wheat fractions and bread using a dynamic system that simulates the upper gastrointestinal transit []. The results showed the low bioaccessibility of FA from the wheat fractions and bread (<1%). However, the bioaccessibility was high (~60%) when free FA was added to flour. Raj and Singh reported that the presence of lipids had a considerable effect on the bioavailability of drugs containing FA due to their pH-dependent solubility profile []. Simulated in vitro upper gastrointestinal digestion increased the percentage of free FA for bread (3.12% to 15.44%), cookies (6.00% to 17.55%), and pasta (1.78% to 8.62%) []. This increase in the potential bioaccessibility was noticeable within the first hour of this process.
The bioavailability of the bioactive compounds is also influenced by food processing, such as mechanical or thermal treatment, extrusion cooking, and bioprocessing, which alters the matrix [,,,,,,]. The thermal action of boiling increased the extractability of FA, possibly through the loosening of the food matrix and breaking the bonds between phenolic acid and the cell wall components. The content of free FA in whole-grain, hulless raw barley varieties in the range of 5.39–8.16 µg/g dry weight, while after boiling for 40 min the range of 7.94–12.58 µg/g was determined []. After simulated gastric digestion (with α-amylase, pepsin, and pancreatin), the major bioaccessible phenolic was ferulic acid. Its bioaccessibility (calculated as the amount of FA in the digested samples divided by its amount in boiled samples) ranged from 131 to 173%. Thus, boiling enhanced the extractability of bound phenolic acid, while digestion increased its free-form content.
Pumpkin leaves were subjected to different household cooking methods (boiling, microwaving, steaming, and stir-frying) to evaluate their effect on the phenolic compounds, antinutrients (tannins, phytates, and oxalates), and antioxidant properties []. All the used cooking methods significantly reduced the antinutrients (oxalates by more than 50%, tannins by 47%, and phytates by 79%) and antioxidant activities, whilst the content of ferulic acid was significantly increased. Steaming (91.8 mg/kg) and boiling (103.90 mg/kg) resulted in the highest concentrations of FA compared to the other cooking methods.
Kongkachuichai et al. studied the effect of different processing conditions such as germination, parboiling, and polishing on the ferulic acid content in various landrace brown rice varieties from Thailand []. The ferulic content ranged from 9.94 to 14.98 mg/100 g for raw rice, 10.35 to 16.30 mg/100 g for parboiled rice, 10.24 to 17.77 mg/100 g for germinated parboiled rice, and 3.06 to 5.19 mg/100 g for polished samples, respectively. According to this study, the polishing process strongly removed 65–73% of ferulic acid as it is mostly located in the outer layer of rice grain. The effect of the parboiling hydrothermal process on the ferulic acid content was not significant, but together with germination, it reduced the glycemic index (GI); thus, it could be beneficial for health promotion. The changes in the FA contents were also not significant during the whole wheat bread-making process []. The use of low temperatures during the fluidized bed-drying process of paddy black rice is essential for obtaining a low glycemic index, but this process does not favor the bioaccessibility of ferulic acid in the rice grains [].
Generally, food-processing treatment under high temperature and pressure increased the content of the bound form of ferulic acid and free FA, but to a much lesser extent due to the partial decomposition of the plant matrix. The degree of this effect depends on the cell wall structure and its chemical composition [,]. During these processes, the content of other compounds is also changing. It has an impact on the antioxidant activity of the obtained hydrolysate. On one side, food processing could liberate more compounds with significant antioxidant activity, but on the other side, it is well known that polyphenolic compounds can be degraded under these treatments. Mashitoa et al. reported that all household cooking methods reduced the total antioxidant activities of pumpkin extracts [], while opposite results were obtained for cooking rice under high pressure []. Although some research has been conducted on the effects of different kinds of processing methods on the contents of phenolic compounds, including FA, little work has described the impacts of its bioavailability. Even with a high content of FA being determined in raw or cooked cereal and rice grains, only a small fraction was available for absorption in the gut [,].
4. Biological Activity
The biological and pharmacological properties of ferulic acid have been extensively studied to reveal its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antiallergic, and antiviral effects, protective properties against cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative properties, among others [,,]. This wide range of biological activities has strong beneficial effects on the human body and is mostly attributed to the powerful free radical scavenging activity of FA. Examples of its main biological activities are presented in Figure 2. Interested readers can find more specific information regarding the biological activities of ferulic acid and the results of the preclinical studies in the recent review papers [,,].
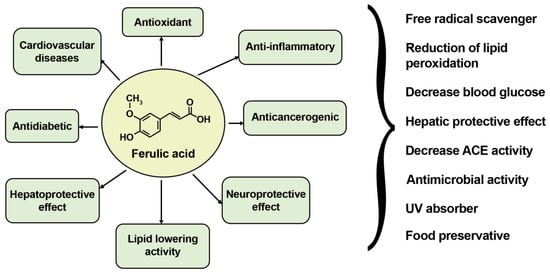
Figure 2.
Main biological activities of ferulic acid.
4.1. Free Radical Scavenging
Several researchers have examined the antioxidant activity of FA using various assays [,,,,,]. Its antioxidant properties are mainly expressed by direct free radical scavenging or indirectly by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, or glutathione peroxidase []. In a living organism, reactive oxygen species (ROS) can contribute to oxidative stress, i.e., an imbalance between ROS production and the ability of cells to detoxify the reactive intermediates []. The increase in ROS is positively related to the pathology of many diseases. As a secondary antioxidant, ferulic acid and its derivatives can also bind transition metal ions, such as iron and copper, preventing the formation of toxic hydroxyl radicals, which lead to cell membrane peroxidation. Thus, some methods that are used to study the antioxidant activity of a given compound or a natural sample are concerned with electron or radical screening, whereas others are focused on their reducing ability []. Zhang et al. reported that the presence of different ester derivatives does not greatly change the antioxidant capacity of ferulic acid []. The extracts after hydrothermal treatment in the presence of citric acid (enriched in the ferulate pentose ester) were more active in antiradical activity than water or 60% ethanol extracts [].
Das et al. evaluated the properties of FA for free radical scavenging, reducing activity, and iron chelation using different assays (Figure 3) []. FA at low concentrations had much higher DPPH radical-scavenging power than ascorbic acid (as control), while at concentrations below 200 µM, both compounds showed similar effects (Figure 3A). The reducing activities of FA and ascorbic acid were comparable (Figure 3B). The hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of ferulic acid at a concentration of up to 150 µM was higher than quercetin, which was reversed at higher concentrations (Figure 3C). FA had fairly higher NO scavenging activity as compared to quercetin (Figure 3D) and also higher iron chelating ability in comparison to EDTA (Figure 3E).
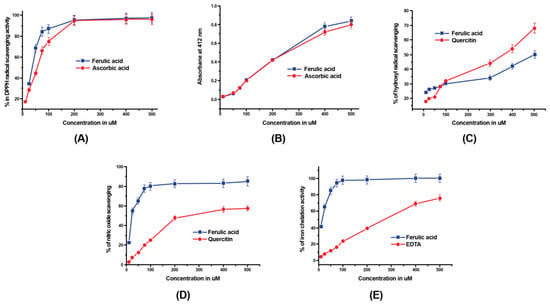
Figure 3.
In vitro antioxidant activity of ferulic acid. (A) DPPH radical-scavenging activity of FA in comparison to ascorbic acid control. (B) Reducing activity of FA in comparison to ascorbic acid control. (C) Hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of FA compared to quercetin control. (D) NO-scavenging activity of FA in comparison to quercetin. (E) Iron chelation activity of FA compared to the EDTA control. p < 0.05 was considered significant (error bars represent the SEM values of four independent experiments) []. Reprinted with permission from ref. []. 2016 Taylor & Francis.
However, while the antioxidant capacity of ferulic acid is limited by its relatively low solubility in hydrophobic media, several research efforts are being made to enhance the therapeutic benefits of ferulic acid. Adeyemi et al. synthesized ester and amide derivatives of ferulic acid, showing that these compounds had excellent antioxidant capacity and demonstrated strong inhibitory potential []. Another approach is to entrap ferulic acid in solid lipid nanoparticles or bind it to other therapeutic agents through organic moieties, which serve as carriers [,,,,].
4.2. Anticancer Activity
Ferulic acid shows anticancer activity by inhibiting the proliferation and migration of various malignant tumors [,,]. FA can cause mitochondrial apoptosis by inducing the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species, acting on a series of intracellular and extracellular targets, and being involved in the regulation of tumor cell signaling pathways. Gao et al. found that FA can significantly inhibit proliferation and invasion in Hela and Caski cervical cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner []. The combination of ferulic acid and some known chemotherapeutic drugs exhibits maximum therapeutic efficiency, minimal side effects, and overcomes drug resistance [,].
The administration of FA to male adult rats showed a dose-dependent protective effect against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity, indicating a biphasic response (hormetic effect), where being pro-oxidant at lower concentrations and antioxidant at higher concentrations promoted chemoresistance []. The lowest dose of 75 mg/kg had no protective effect, whereas starting from the dose of 150 mg/kg, FA attenuated cisplatin-induced hearing loss. The evidence of an FA-induced hormetic dose response in the treatment of inflammation was also discussed by Barreiro-Sisto et al. [].
Nanocarriers can overcome the restriction of anticancer drug action by body barriers (such as the blood-brain barrier and blood–eye barriers), reduce drug doses, and improve availability [,,,]. Lipids, polysaccharides, polymers, dendrimers, and certain enzymes are the most common base materials used for the production of novel formulations with FA []. Sweed et al. obtained polymeric mixed micelles loaded with FA and investigated their potential concerning colon cancer []. The results reported by El-Gregory et al. revealed that both polymeric and lipidic nanocapsules of FA showed favorable anticancer properties []. The lipidic nanomaterial was smaller in size and presented a higher cumulative percent release of FA on the cellular level.
4.3. Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a global term used for the group of diseases affecting the heart and/or blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, congenital heart disease, hypertension, heart failure, and stroke []. Consumption of various plant infusions rich in hydroxycinnamic acids has been associated with a lower risk of CVD due to their anti-hypertensive effect, capacity to reduce blood viscosity, and modulation of platelet function [,].
The cardioprotective effects of ferulic acid against various drugs and toxic agents (such as isoproterenol, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, streptozotocin, and arsenic species) demonstrated in animals and cell-line models have recently been summarized by Pandi et al. []. For example, the modulatory role of FA against arsenic-induced cardiotoxicity could be due to its ability to improve antioxidants, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels, and modulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Modulation of oxidative stress, together with inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, calcium homeostasis, and renin, also played a major role in the cardioprotective efficacy of FA against doxorubicin.
4.4. Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a multisystem disease mainly characterized by high glucose levels in the blood (termed hyperglycemia), deficiency of insulin secretion, or insulin resistance. Too high a level of sugar in the blood can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and other diabetic complications []. Thus, the multisystem pathophysiology of diabetes requires a multifaceted approach to treatment that combines therapies with complementary mechanisms of action [,]. New therapeutics as well as medicinal natural products with high efficiency and negligible toxic effects are constantly in demand []. As ferulic acid defends against free radical damage and inflammation, it was also suggested that it plays a crucial role in controlling DM and its complications [,,].
Ferulic acid could be used as a potential therapeutic drug in diabetic nephropathy (denotes disease or damage of the kidney) [], neuropathy (when nerve damage leads to pain, numbness and tingling in the feet or hands) [], cardiomyopathy that affects the heart muscle [], retinopathy (involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina) [] and hypertension [].
4.5. Other Activities
Ferulic acid also has neuropharmacological applications due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and antiapoptotic effects, among others []. The neuroprotective effect of ferulic acid has been studied in many diseases, like epilepsy, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Sgarbbossa et al. presented the role of ferulic acid as an inhibitor or disaggregating agent of amyloid structures, which play a central role in the development and progress of Alzheimer’s disease, both in oligomer and fibril forms [].
Ferulic acid has a protective role in relation to the main skin structures, such as keratinocytes, fibroblasts, collagen, and elastin. It inhibits melanogenesis, enhances angiogenesis, and accelerates wound healing. The applications of FA on the skin mainly aim for protection from aging, sun damage, and skin cancer [].
5. Conclusions
Ferulic acid is a widespread phenolic phytochemical present in the seeds, leaves, and fruits, both in its free form and conjugated to the plant cell wall polysaccharides, carbohydrates, glycoproteins and lignins. The amount of ingested FA that is potentially available for adsorption is greatly dependent on its release from the food matrix. Bound forms of ferulic acid are converted by the intestinal microflora for adsorption and further metabolized in the liver. Similarly, the effective recovery of free ferulic acid from natural sources and agro-industrial waste requires the use of hydrothermal treatment, alkaline or enzymatic hydrolysis, and probiotic fermentation due to its covalently linking to lignins and other biopolymers. The intensification of these processes in terms of the extraction yields needs further investigation. The combination of treatment methods under optimized conditions seems to have great potential in the extraction of ferulic acid from natural sources.
The regular intake of whole grains of cereals, maize or rice, which are rich in FA, can reduce the risk of many chronic diseases. Ferulic acid has demonstrated antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, and antibacterial activities according to several cited studies. Its ability to remove free radicals by balancing unpaired electrons, reduce substances by giving either an electron or a hydrogen atom, and interfere with numerous oxidative reactions are examples of its health-promoting properties. Although a variety of reported studies have confirmed the efficacy of FA in the management of several human disorders, only a few studies were carried out in humans, mostly using foods containing this compound [,]. Thus, the clinical effects of ferulic acid need to be tested in the future for the complete evaluation of its therapeutic potential in chronic diseases.
The still limited therapeutic use of FA is a result of its poor pharmacokinetic properties after oral administration, such as the short resistance duration, quick renal clearance, low plasma levels and low bioavailability. The strategies proposed to overcome this problem mostly apply to the inclusion of FA in a nanocarrier, which improves its stability and controls release. A wide range of nano-formulations with lipids, polymers or chitosan conjugate have been investigated and developed, trying to maximize the effects of ferulic acid [].
As ferulic acid is a naturally occurring potent antioxidant, dietary supplementation seems to be an effective strategy to delay ageing, for example. Many such products are commercially available without a prescription. However, taking into consideration the potential of FA as a diet supplement, attention should be paid to its dose as its excessive and uncontrolled consumption may induce negative effects. Truzzi et al. reported high FA contents in two supplements as 1.3695 ± 0.140 mg/g and 1.8494 ± 0.180 mg/g, which contain dry blueberry extract and dry extract from an apple, respectively []. They were higher than the relative contents found in fruit and flour. In addition, it was shown using three different cell lines in an in vitro cell model that ingestion of ferulic acid at the dose of ≥40 mg/L could induce negative effects on the intestinal wall’s integrity.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Soycan, G.; Schair, M.Y.; Kristek, A.; Boberska, J.; Aksharif, S.N.S.; Corona, G.; Shewry, P.R.; Spencer, J.P.E. Composition and content of phenolic acids and avenanthramides in commercial oat products: Are oats important polyphenol source for consumers? Food Chem. X 2019, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Pruthi, V. Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manusco, C.; Santangelo, R. Ferulic Acid: Pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dędek, K.; Rosicka-Kaczmarek, J.; Nebesny, E.; Kowalska, G. Characteristics and biological properties of ferulic acid. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 83, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Boz, H. Ferulic acid in cereals—A review. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2015, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zduńska, K.; Dana, A.; Kolodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Antioxidant Properties of Ferulic Acid and Its Possible Application. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liang, K.; Zhang, F.; Xu, T.; Wang, M.; Song, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, B. Determination of phenolic acid profiles by HPLC-MS in vegetables commonly consumed in China. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Hu, P.; Feng, L.P.; Huang, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Xiong, J.; Xio, H.L. Protective Effects of Ferulic Acid on Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Tan, Y.; Tang, G.; Wu, Z.; Li, A.; Qin, X.; Li, S.; Liao, H.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.; et al. Neuroprotective potentials of ferulic acid against intracerebral hemorrhage COVID-19 through using network pharmacology approach and molecular docking analysis. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Li, W.; Jia, R.; Meng, D.; Zhang, H.; Xia, L. Molecular mechanism of ferulic acid and its derivatives in tumor progression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishtiaq, I.; Zeb, A.; Badshah, H.; Alattar, A.; Alshaman, R.; Koh, P.O. Enhanced cardioprotective activity of ferulic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle in an animal model of myocardial injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 476, 116657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A. Anti-hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Yu, J. Dietary ferulic acid supplementation improves antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism in weaned piglets. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, N.D.; Singh, D. A critical appraisal on ferulic acid: Biological profile, biopharmaceutical challenges and nano formulations. Health Sci. Rev. 2022, 5, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luziatelli, F.; Brunetti, L.; Ficca, A.G.; Ruzzi, M. Maximizing the Efficiency of Vanillin Production by Biocatalyst Enhancement and Process Optimization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério, R.; Torres, C.; Brazinha, C.; Gomes da Silva, M.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Purification of ferulic acid from corn fibre alkaline extracts for bio-vanillin production using an adsorption process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, H. The Applications of Ferulic-Acid-Loaded Fibrous Films for Fruit Preservation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-García, E.; Vargas, M.; Chiralt, A. Effect of active phenolic acids on properties of PLA-PHBV blend films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, Y. Preparation, characterization and application of SPI-based blend film with antioxidant activity. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 27, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zduńska-Pęciak, K.; Kołodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Two Superior Antioxidants: Ferulic Acid and Ascorbic Acid in Reducing Signs of Photoaging—A Split-face Comparative Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, E.; Pinheiro, M.; Nowak, A.; Kucharska, E.; Świątek, E.; Podolak, N.; Perużyńska, M.; Piotrowska, K.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; et al. New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Gupta, R.D.; Tournas, J.A.; Burch, J.A.; Selim, M.A. Ferulic acid stabilizes a solution of vitamins C and E and doubles its photoprotection of skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazo-Cepeda, M.V.; Aspromonte, S.G.; Alonso, E. Extraction of ferulic acid and feruloylated arabinoxylo-oligosaccharides from wheat bran using pressurized hot water. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazo-Cepeda, V.; Benito-Román, Ó.; Navarrete, A.; Alonso, E. Valorization of Wheat Bran: Ferulic Acid Recovery Using Pressurized Aqueous Ethanol Solutions. Waste Biomass Valor. 2022, 11, 4701–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, D. Comparison of six modification methods on the chemical composition, functional properties and antioxidant capacity of wheat bran. LWT 2021, 149, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Dye, L.; Mackie, A. The impact of processing on the release and antioxidant capacity of ferulic acid from wheat: A systematic review. Food Res. Inter. 2023, 164, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibhatu, H.K.; Jabasingh, A.; Yimam, A.; Ahmed, S. Ferulic acid production from brewery spent grains, and agro-industrial waste. LWT 2021, 135, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Ukaegbu, C.I. Extraction of phenolic compounds: A review. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 14, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentkowska, A.; Ivanova-Petropulos, V.; Pyrzynska, K. What Can Be Done to Get More—Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Plant Materials. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltacıoğlu, H.; Baltacıoğlu, C.; Okur, I.; Tanrıvermiş, A.; Yalıç, M. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from tomato: Characterization by FTIR and HPLC and comparison with conventional solvent extraction. Vib. Spectrosc. 2021, 113, 103204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranov, A.U.; Mazza, G. Extraction and purification of ferulic acid from flax shives, wheat and corn bran by alkaline hydrolysis and pressurised solvents. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento-Silva, A.; Vaz Pattoa, M.C.; do Rosário Bronze, M. Relevance, structure and analysis of ferulic acid in maize cell walls. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, E.; Grigorakis, S.; Palaiogiannis, D.; Lalas, S.I.; Mitlianga, P. Hydrothermal Treatment of Wheat Bran under Mild Acidic or Alkaline Conditions for Enhanced Polyphenol Recovery and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2024, 29, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideia, P.; Sousa-Ferreira, I.; Castilho, P.C. A Novel and Simpler Alkaline Hydrolysis Methodology for Extraction of Ferulic Acid from Brewer’s Spent Grain and its (Partial) Purification through Adsorption in a Synthetic Resin. Foods 2020, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alana, M.M.; Adalberto Pessoa-Junior, M.; Roberto, I.C. Extraction of hydroxycinnamic acids (ferulic and p-coumaric) from rice straw alkaline black liquor using Pluronic F-127 for potential applications in the cosmetics industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 201, 11691. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Dai, K.; Kou, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. Selective adsorption of ferulic acid and furfural from acid lignocellulosic hydrolysate by novel magnetic lignin-based adsorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wei, W.; Qin, G. Recovery of ferulic acid from corn bran by adsorption on mesoporous carbon. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44, e13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q. Adsorption of ferulic acid from an alkali-pretreated hydrolysate using a new effective adsorbent prepared by a thermal processing method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, I.; Sapountzaki, E.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. Ferulic Acid from Plant Biomass: A Phytochemical with Promising Antiviral Properties. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 777576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério, R.; Serra, A.T.; Baixinho, J.; Cardeira, M.; Fernández, N.; Bronze, M.R.; Duarte, L.C.; Tavares, M.L.; Brazinha, C. Combined hydrothermal pre-treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of corn fibre: Production of ferulic acid extracts and assessment of their antioxidant and antiproliferative properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferria, M.; Happel, A.; Zanaroli, G.; Bertolini, M.; Chiesa, S.; Commisso, M.; Guzzo, F.; Tassoni, A. Advances in combined enzymatic extraction of ferulic acid from wheat bran. New Biotechnol. 2020, 56, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Guan, T.; Li, L.; Diao, E.; Fan, J.; Siyu Chen, S.; Liang, X. Efficient production of ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid from reed straws via combined enzymatic hydrolysis and hydrothermal pretreatment. Food Bioprod. Process 2023, 140, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhnevica-Radenkova, K.; Kviesis, J.; Moreno, D.A.; Seglina, D.; Vallejo, F.; Valdovska, A.; Radenkovs, V. Highly-Efficient Release of Ferulic Acid from Agro-Industrial By-Products via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Cellulose-Degrading Enzymes: Part I—The Superiority of Hydrolytic Enzymes versus Conventional Hydrolysis. Foods 2021, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shwafy, K.W.A.; Chadni, M.; Abg Zamari, M.H.H.; Ioannou, I. Enzymatic extraction of ferulic acid from brewer’s spent grain: Effect of physical pretreatments and optimization using design of experiments. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 51, 102779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Gao, S.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Diao, E.; Chang, W.; Liang, X.; Xie, P.; Jin, C. Effects of combined enzymatic hydrolysis and fed-batch operation on efficient improvement of ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid production from pretreated corn straws. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 366, 12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapini, T.; Maicon, S.; dos Santos, M.N.S.; Bonatto, C.; Wancura, J.H.; Mulinari, J.; Camargo, A.F.; Klanovicz, N.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V.; et al. Hydrothermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for hemicellulose recovery. Biores. Technol. 2021, 342, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowska-Sieprawska, A.; Rafińska, K.; Walczak-Skierska, J.; Buszewski, B. The Influence of Plant Material Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Extraction Conditions on the Polyphenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts: A Green and Efficient Approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, G.Y.; Hou, Y.Y.; Qin, L. Extraction of ferulic acid and vanilla acid by hydrophobic ionic liquid 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3508–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Ren, L.; Tang, L.; Shan, W. Magnetic carbon nanotubes-molecularly imprinted polymer coupled with HPLC for selective enrichment and determination of ferulic acid in traditional Chinese medicine and biological samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1180, 122870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffon, E.; Stradiotto, N.R. A molecularly imprinted polymer on reduced graphene oxide-gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrode for selective determination of ferulic acid in orange peels. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dil, E.A.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Mehrabi, F.; Shokrollahi, A.; Matin, A.A.; Tayebi, L. Magnetic dual-template molecularly imprinted polymer based on syringe-to-syringe magnetic solid-phase microextraction for selective enrichment of p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid from pomegranate, grape, and orange samples. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126902. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, G.; Li, N. Ionic liquid solutions as a green tool for the extraction and isolation of natural products. Molecules 2018, 23, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for valuable flavonoids from natural sources. Appl. Sci. 2019, 29, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Vázquez, J.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Boczkaj, G.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Latest insights on novel deep eutectic solvents (DES) for sustainable extraction of phenolic compounds from natural sources. Molecules 2021, 26, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.H.; Nulman, A.H. Investigation on the use of deep eutectic solvent with microwave assistance for the extraction of ferulic acid from palm pressed fibre. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Colombo, F.; Biella, S.; Stockley, C.; Restani, P. Polyphenols and Human Health: The role of Bioavailability. Nutrients 2021, 3, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of food bioactive compounds; overview and assessment by in vitro methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowski, M.; Rodrigues, D.; Marques, M.C.; Hacke, A.; Filho, P.S.L.; Cazarin, C.B.; Barros Mariutti, L.R. Trust your gut: Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of dietary compounds. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Nechifor, A.; Dima, S.; Li, Y.; Jafari, S.M. Oral bioavailability of bioactive compounds; modulating factors, in vitro analysis methods, and enhancing strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.; Afonso, C.; Lourenço, H.; Costa, S.; Nunes, M.L. Bioaccessibility assessment methodologies and their consequences for the risk-benefit evaluation of food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, N.M.; van den Berg, R.; Havenaar, R.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M. Bioavailability of ferulic acid is determined by its bioaccessibility. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Teng, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, M. The intestinal delivery systems of ferulic acid: Absorption, metabolism, influencing factors, and potential applications. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1126–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Hu, R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Potential bioaccessibility of phenolic acids in whole wheat products during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and probiotic fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drawbridge, P.C.; Apea-Bah, F.; Silveira Hornung, P.; Beta, T. Bioaccessibility of phenolic acids in Canadian hulless barley varieties. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashitoa, F.M.; Manhivi, V.; Slabbert, R.M.; Shai, J.L.; Sivakumar, D. Changes in antinutrients, phenolics, antioxidant activities and in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in pumpkin leaves (Cucurbita moschata) during different domestic cooking methods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Kongkachuichai, R.; Charoensiri, R.; Meekhruerod, A.; Kettawan, A. Effect of processing conditions on bioactive compounds and glycemic index of the selected landrace rice variety in pre-diabetes. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 94, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Chen, G.; Tilley, M.; Li, Y. Changes in phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities during the whole wheat bread-making process. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Lindemann, I.; Lambrecht Dittgen, C.; de Souza Batista, C.; dos Santos, J.P.; Pinheiro Bruni, G.; Cardoso Elias, M.; Vanier, N.L. Rice and common bean blends: Effect of cooking on in vitro starch digestibility and phenolics profile. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.H.; Lindemann, I.S.; Goebel, J.T.; Ferreira, C.D.; Acunha, T.S.; de Oliveira, M. Fluidized-bed drying of black rice grains: Impact on cooking properties, in vitro starch digestibility, and bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Zhou, L. Effect of cooking pressure on phenolic compounds, gamma-aminobutyric acid, antioxidant activity and volatile compounds of brown rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 97, 103127. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, R.; Mandal, S.; Das, P.; Ashraf, G.J.; Dua, T.K.; Paul, P.; Nandi, G.; Khanra, R. The bioavailability, health advantages, extraction method, and distribution of free and bound phenolics of rice, wheat, and maize: A review. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stompor-Gorący, M.; Machaczka, M. Recent Advances in Biological Activity, New Formulations and Prodrugs of Ferulic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanshita, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Odeku, O.A.; Singh, I. Ferulic acid’s therapeutic odyssey: Nano formulations, pre-clinical investigations, and patent perspective. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-López, E.G.; Reina, M.; Hernández-Ayala, L.F.; Galano, A. Rational Design of Multifunctional Ferulic Acid Derivatives Aimed for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Li, C.; Huang, R.; Qu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y. Ferulic acid enhanced resistance against blue mold of Malus domestica by regulating reactive oxygen species and phenylpropanoid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 202, 112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadão, V.S.J.; Ishimoto, E.Y.; Cruz, R.J.; Seabra Pereira, C.D.; Torres, E.A. Increase of the activity of Phase II antioxidant enzymes in rats after a single dose of coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10887–10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kıran, T.R.; Otlu, O.; Karabulut, A.B. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in health and disease. J. Lab. Med. 2023, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Inter. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, R.; Fu, Z.M.; Chen, D.F. Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of ferulic acid derivatives: Effect of ester groups at the end of the carbon side chain. LWT 2020, 120, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Manna, K.; Khan, A.; Sinha, M.; Biswas, S.; Sengupta, A.; Chakraborty, A.; De, S. Ferulic acid (FA) abrogates c-radiation induced oxidative stress and DNA damage by up-regulating nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and activation of NHEJ pathway. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 51, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers of natural phenolic compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiamphun, S.; Chaiyana, W. Enhancing Skin Delivery and Stability of Vanillic and Ferulic Acids in Aqueous Enzymatically Extracted Glutinous Rice Husk by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.; Nandi, N.K.; Singh, B.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B.; Narang, R.K.; Charan Singh, C. Ferulic acid-loaded drug delivery systems for biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 75, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, Ç.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Ilbasmis-Tamer, S.; Değim, I.T. Ferulic acid-loaded aspasomes: A new approach to enhance the skin permeation, anti-aging and antioxidant effects. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2023, 86, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweed, N.M.; Dawoud, M.H.S.; Aborehab, N.M.; Ezzat, S.M. An approach for an enhanced anticancer activity of ferulic acid-loaded polymeric micelles via MicroRNA-221 mediated activation of TP53INP1 in caco-2 cell line. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.Q.; Xu, Y. The inducing effects of ferulic acid on the apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and its influence on COX-2, survivin, XIAP and p53. West. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Singh Tuli, H.; Kumar, A.; Ramniwas, S.; Coudhary, R.; Aggarwal, D.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, U.; Chaturvedi Parashar, N.; Haque, S.; Sak, K. Ferulic Acid: A Natural Phenol That Inhibits Neoplastic Events through Modulation of Oncogenic Signaling. Molecules 2022, 7, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Manochakian, R.; James, L.; Azzouqa, A.G.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lou, Y. Emerging therapeutic agents for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Guo, W.; Kong, Y.; Gu, I.; Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. The anticancer effects of ferulic acid is associated with induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell. Int. 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.X.; Wang, Z.F.; Qin, Q.P.; Zou, B.Q.; Liang, H. Complexes of oxoplatin with rhein and ferulic acid ligands as platinum(IV) prodrugs with high anti-tumor activity. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.; Manna, K.; Adhikary, A.; Mishra, S.; Saha, K.D.; Sharma, R.D.; Majumder, B.; Dey, S. Ferulic acid enhances the radiation sensitivity of lung and liver carcinoma cells by collapsing redox homeostasis: Mechanistic involvement of Akt/p38 MAPK signalling pathway. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 944–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Agathokleous, E.; Calabrese, V. Ferulic acid and hormesis: Biomedical and environmental implications. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 198, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro-Sisto, U.; Fernández-Fariña, S.; González-Noya, A.M.; Pedrido, R.; Maneiro, M. Enemies or Allies? Hormetic and Apparent Non-Dose-Dependent Effects of Natural Bioactive Antioxidants in the Treatment of Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.; Borkar, S.B.; Nandanwar, S.K.; Panda, P.K.; Choi, E.H.; Kumar Kaushik, N. Nanocarrier cancer therapeutics with functional stimuli-responsive mechanisms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gogary, R.I.; Nasr, M.; Rahsed, L.R.; Hamzawy, M.A. Ferulic acid nanocapsules as a promising treatment modality for colorectal cancer: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo appraisal. Life Sci. 2022, 298, 120500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto-Neves, E.M.; da Silva Maia Bezerra Filho, C.; Dejani, N.N.; de Sousa, D.P. Ferulic Acid and Cardiovascular Health: Therapeutic and Preventive Potential. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, D.S.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Mao, J.L.; He, J.H. The treatment of cardiovascular diseases: A review of ferulic acid and its derivatives. Pharmazie 2021, 76, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baeza, G.; Bachmair, E.M.; Wood, S.; Mateos, R.; Bravo, L.; de Roos, B. The colonic metabolites dihydrocaffeic acid and dihydroferulic acid are more effective inhibitors of in vitro platelet activation than their phenolic precursors. Food Func. 2017, 8, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, A.; Raghu, M.H.; Chandrashekar, N.; Kalappan, V. Cardioprotective effects of ferulic acid against various drugs and toxic agents. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubiak, G.K.; Lejawa, K.M.; Osadnik, T.; Goławski, M.; Lewandowski, P.; Pawlas, N. ”Obesity and insulin resistance” is the component of the metabolic syndrome most strongly associated with oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2020, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, G.W.; Parvez, S.H. The multi-systemic nature of diabetes mellitus: Genotype or phenotype? N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 2, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, F.; Chu, C.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, W. Use of Ferulic Acid in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Molecules 2020, 27, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, R.; Matafome, P.; Freitas, M.; García-Conesa, M.T. Updated Information of the Effects of (Poly)phenols against Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus in Humans: Reinforcing the Recommendations for Future Research. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J.; Pinho, A.; Carvalho, E. The Role of Nutraceutical Containing Polyphenols in Diabetes Prevention. Metabolites 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.Y.; Wang, X.T.; Xu, H.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, B. Protective effect of ferulic acid on STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3706–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, J.; Dhaliwal, N.; Akhtar, A.; Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Beneficial effects of ferulic acid alone and in combination with insulin in streptozotocin induced diabetic neuropathy in Sprague Dawley rats. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salau, V.F.; Erukainure, O.L.; Olofinsan, K.A.; Msomi, N.Z.; Ijomone, O.K.; Islam, M.S. Ferulic acid mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy via modulation of metabolic abnormalities in cardiac tissues of diabetic rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Ferulic acid alleviates retinal neovascularization by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the ROS/NF-κB axis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 976729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surbhi, S.; Richmond, A.; Shubham, U.; Kumar, P. Ferulic acid ameliorates neurodegeneration via the Nrf2/ARE signalling pathway: A Review. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 5, 100190. [Google Scholar]
- Sgarbossa, A.; Giacomazza, D.; Di Carlo, M. Ferulic Acid: A Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy from Plants. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5764–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zduńska-Pęciak, K.; Dębowska, R.; Kołodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Ferulic acid—A novel topical agent in reducing signs of photoaging. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 35, 15543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.E.; Flury, A.; Marmet, C.; Poquet, L.; Rimoldi, S.F.; Sartori, C.; Rexhaj, E.; Brenner, R.; Allemann, Y.; Zimmermann, D.; et al. Mediation of coffee-induced improvements in human vascular function by chlorogenic acids and its metabolites: Two randomized, controlled, crossover intervention trials. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Feliciano, R.P.; Boeres, A.; Weber, T.; Dos Santos, C.N.; Ventura, M.R.; Heiss, C. Cranberry (poly)phenol metabolites correlate with improvements in vascular function: A double-blind, randomized, controlled, dose-response, cross-over study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2130–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Valerii, M.C.; Tibaldi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Abduazizova, V.; Spisni, E.; Dinelli, G. Are Supplements Safe? Effects of Gallic and Ferulic Acids on In Vitro Cell Models. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).