Abstract
Flavonoids, a ubiquitous class of plant secondary metabolites, are increasingly pivotal as chemical markers for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of herbal medicines (HMs). Their broad distribution, biological activities, and detectability make them ideal for this role. This comprehensive review critically examines current trends and analytical perspectives regarding flavonoids in HM quality control. We first explore advanced quality control strategies that move beyond single-compound quantification, including chemical fingerprinting, metabolomics, network pharmacology, and the innovative concept of Q-markers. The review then provides an in-depth analysis of the analytical techniques central to flavonoid analysis, from the routine use of HPTLC and HPLC-UV to advanced hyphenated systems like UHPLC-QTOF-MS, highlighting their applications in authentication, standardization, and adulteration detection. Furthermore, we emphasize the growing importance of modern data analysis workflows, particularly the integration of chemometrics and molecular networking, for interpreting complex datasets and identifying robust, bioactivity-relevant markers. By synthesizing recent research (2017–2024), this work underscores a paradigm shift towards holistic, multi-marker approaches and data-driven methodologies. It concludes that the synergistic application of advanced analytical techniques with sophisticated data modeling is essential for the future of HM quality control, ensuring reliable and standardized herbal products for global consumers.
1. Introduction
Traditional herbal medicines have been used for the prevention and treatment of human diseases for thousands of years and remain the preferred healthcare approach in many developing countries. Developed countries have also experienced an increase in sales of plant-based health products [1,2,3]. Herbal medicines (HMs), including herbs, herbal materials, herbal preparations, and finished herbal products, have become an increasingly important part of the global healthcare system, especially for primary healthcare in communities [2,3,4]. HMs have shown promising efficacy. However, most raw materials used in plant-based traditional medicines remain untested and their use unmonitored. For this reason, they are not fully accepted in some countries, as safety and efficacy evaluation data are considered insufficient regarding the criteria required by regulatory authorities [1,2].
HM quality is affected by several factors, such as growing conditions, harvest timing, and post-harvest treatments, including drying processes, extraction methods, solvent choices, and storage conditions. Indeed, these may lead to variations in chemical composition and stability, resulting in significant batch-to-batch differences and subsequent modulations in therapeutic effects [1,2]. Regulatory authorities should focus on screening, standardization, packaging, labeling, registration, and licensing to ensure that consumers use safe and effective products [1].
Quality control is an important and essential step in manufacturing herbal preparations to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicines. It may be applied to herbal drugs, herbal derivatives (raw materials), and finished products [3]. In existing regulatory systems and pharmacopeias, quantitative quality assessment is usually based on the determination of a few intrinsic marker compounds [2]. In this context, flavonoids are widely distributed in plants and represent an important class of bioactive chemicals [5]. They are also extensively used as markers for quality control of many HMs. For example, the Ginkgo biloba L. standardized extract named EGb 761 contains, as markers, 24% flavone glycosides (primarily quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin) and 6% terpene lactones (2.8–3.4% ginkgolides A, B, and C, and 2.6–3.2% bilobalide) [6]. Another renowned species that contains flavonoids as markers is Passiflora incarnata L., whose leaves contain 1.5% flavonoids (expressed as vitexin) [7]. Therefore, it is essential to determine the presence and content of these compounds in their matrices to control product quality and bioactive efficacy [8].
Flavonoids are a large class of common secondary metabolites that occur naturally and have countless recognized pharmacological activities [9]. Researchers have become interested in understanding how these compounds can positively influence human body functions. Regarding their chemistry, flavonoids exist in the form of aglycones or glycosides, with different substitution patterns such as methylation and prenylation. These patterns generate complexity and diversity in flavonoid structures. In addition, they play essential biological roles in plant development, growth, and ripening, as well as in mediating responses to biological and non-biological environmental factors, such as resistance to various biotic and abiotic stresses, including herbivores, bacteria, fungi, and stressors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation [5,8,10,11].
Flavonoids have received increasing research interest over the years. Furthermore, with the worldwide increase in regulations regarding HM use, these secondary metabolites have become important for HM quality control, since they are easily detected by UV-based methods, facilitating their role as markers. In addition, some clinical trials and reviews have demonstrated their potential therapeutic benefits, especially for treating inflammation-associated chronic diseases [5,8,10,11]. Therefore, taking into consideration all these elements, i.e., the importance of detecting, extracting, and quantifying these plant-derived compounds, as well as their nutritional and health potential, the aim of the present review is to focus on the role of flavonoids as molecules of interest for quality control of HM quality control.
Given the widespread distribution and therapeutic interest in flavonoids, it is not surprising that investigations have been conducted on cultivation conditions such as seasonal variations, comparisons of different plant parts, species authentication, differentiation of species within the same genus or family or even chemotypes, plant age, adulteration and raw material origin (wild collection or cultivation). Processing steps were also evaluated as the way for obtaining raw material (drying or extraction methods), evaluation of collection timing, chemical/bioactive differences in materials collected from different geographical locations and evaluation of agro-industrial residues. Flavonoids in phytotherapeutic formulas as Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) have been studied to determine their potential role as pharmacological, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic markers.
Indeed, many studies have demonstrated the importance of methods for analyzing flavonoids in HM quality control (QC) to maintain the qualitative consistency of these materials [12]. In recent years, research has pursued holistic approaches and integrated evaluation models. These efforts have sought to extend beyond the basics of classical quantification by incorporating three key aspects in quality control research for herbal medicines focused on flavonoid markers: metabolite identification, multivariate analysis, and validated quantitative analytical methods. When possible, studies have been associated with pharmacological assays to prove therapeutic effects, understand the mechanisms of action of compounds, or record pharmacokinetic profiles. All these endeavors have employed new data mining methodologies, making it easier to interpret the integrated results. This review explores the analytical methods used in HM quality control, with a focus on flavonoids and extending to their use as chemotaxonomic and bioactive markers [12]. The literature search, presented in Figure 1, was conducted using the term “flavonoids” in combination with the terms “chromatography,” “herbal medicine quality control,” and/or “marker” in the PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Web of Science databases. Articles were selected according to the general objective of the present review. They were included based on the following criteria: (i) use of analytical chromatographic techniques for the analysis of extracts and fractions enriched in flavonoids or their quantification, (ii) recent research articles published between January 2017 and October 2024, and (iii) presentation and discussion of the impacts and contributions of the results obtained. We did not include all articles that matched the inclusion criteria in this review due to the large number of publications. In addition to the publications obtained from the database search, other relevant documents on the subject were added to support discussions on concepts, information, and details regarding analytical instrumentation and flavonoids.
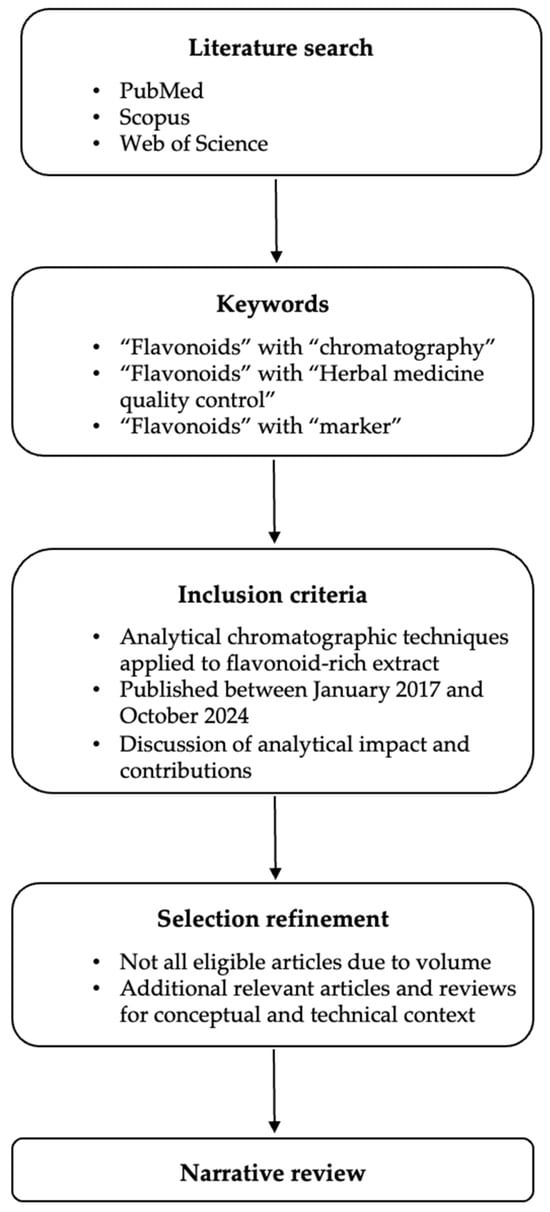
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework of the literature search and selection process.
Our review is therefore divided into three subtopics discussed below: (i) trends in quality control strategies, (ii) analytical techniques and their importance for the quality control of HM, and (iii) trends in data analysis with a focus on the contribution of multivariate analysis.
2. Trends in Quality Control Strategies
Four usual strategies in HM quality control studies focusing on flavonoids are discussed below and summarized in Table 1: (a) fingerprints, (b) metabolomic approaches, (c) network pharmacology and (d) Q-markers.

Table 1.
Quality control strategies for herbal medicine.
2.1. Fingerprint
Usually, quantitative quality assessment is based on the determination of marker compounds. However, this process neglects the potential synergistic effects of the multiple components present in most HM. In general, two main pharmacopoeia tests are required: identification (qualitative analysis) and quantification (quantitative analysis) for plant material, botanical extracts, and finished products. For qualitative analysis, a chromatographic profile based on one to three markers using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is required. For quantitative analysis, it is recommended to quantify at least one marker compound [12]. The challenge lies in how to guarantee the therapeutic effects of herbal products by relying on a single marker without accounting for the chemical complexity of the extracts.
Techniques for overall quality evaluation based on non-targeted approaches have been proposed. They aim to provide a comprehensive chemical description of HM, known as a “chemical fingerprint” [2]. A chemical fingerprint is a unique pattern that indicates the presence of multiple chemical markers within a sample [12]. Chemical fingerprinting has been demonstrated to be a powerful technique for HM quality control. The World Health Organization (WHO), along with regulatory boards worldwide such as the Chinese State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) of Korea, have accepted the concept of fingerprinting to evaluate the quality of HM [2,13,14].
Quality evaluation of HM has always been a challenging task due to their complex phytochemistry. Although chromatographic fingerprinting has attracted high recognition as a preferred tool in HM quality evaluation, samples with high chemical similarity values do not always show equivalent efficacies [15]. Modern analytical instruments play a great role in the quality control and standardization of HM. More specifically, spectroscopic and chromatographic methods mainly contribute to quality control and analytical validation of herbal preparations [3].
Chromatographic fingerprint investigation has been used as a realistic and practical method for quality assessment and species authentication of various traditional medicines [16,17]. This chromatographic fingerprint of natural products can then be used to identify the presence or absence of markers of concern, as well as the ratios of all detectable compounds [16]. Fingerprint validation by chromatographic methods can be combined with other required quality control parameters, such as the relative standard deviations (RSDs) of peak areas, retention times (Rt) or retention factors (Rf), molecular weights, or UV spectra of the selected peaks with their retention times [18], as well as precision (intra- and inter-day) and stability [19,20,21,22,23]. This approach is routinely used to carry out batch-to-batch quality control for single HM extracts, as well as for complex mixtures (including those used in the TCM tradition) [24,25].
Similarity analysis is thus carried out to determine the degree of similarity or dissimilarity among samples [13]. The fingerprints of 49 batches of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (RS), wine-processed RS, and carbonized RS samples were matched automatically using the Similarity Evaluation System for Chromatographic Fingerprint of Traditional Chinese Medicine software [26]. The same strategy used to validate chromatographic fingerprints and flavonoid quantification was adopted to analyze 57 batches of Sophora japonica L. flower samples [15]. This software, which automatically matches fingerprints by similarity, has been used in many studies to analyze TCM products [20,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. The Digitized Evaluation System for Super-Information Characteristics of TCM/HP Chromatographic Fingerprint 3.0 (Software certificate No. 0407573, China) is another software used for fingerprint similarity analysis [21,34]. Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Fourier Transform Infrared), UV, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) fingerprints were used for Keteling capsules (KCs). This TCM was explored with chromatographic fingerprinting and flavonoid quantification via the strategy called three-dimensional quantum fingerprint (QFP), proposed by Professor Guoxiang Sun. The fingerprints were processed by the “TCM Spectrum Quantum Profiling Consistency Digitized Evaluation System 4.0” (TCM-SQPC-DES 4.0, Certificate No. 7037415, China) [35].
An interesting strategy in biomarker discovery is the concept of fingerprint-efficacy relationship analysis for identifying key health-relevant biomarkers in quality assessment, especially for samples showing subtle differences in their chemical composition and bioactivity [36].
Fingerprint studies are key to both regulatory and research aspects of the HM field. Despite this, they have some limitations, including a degree of specificity that restricts the exhaustive characterization of the landscape present in HM extracts obtained through this type of approach [37].
Flavonoids are informative yet complex markers for herbal medicine quality control, and chemical fingerprinting offers a robust approach for their standardization and authentication. Unlike single-marker assays, fingerprinting captures the full chemical profile, enabling species authentication and batch comparison [2,38]. Common flavonoids like quercetin are routinely quantified by HPLC, while metabolomic fingerprinting has identified marker sets in different species used in TCM such as Sophora flavescens and Puerariae sp. [3,39,40].
However, fingerprinting has limitations. High chemical similarity does not guarantee equivalent efficacy, and multivariate analysis is often needed to interpret complex profiles (Wenhui Cheng et al., 2022) [41]. Commercial samples may vary significantly in composition. For instance, in Xinmeng Shi et al. (2022) study, Apocynum venetum L. leaves showed two-fold differences in flavonoid content with RSDs up to 75% [42]. Thus, while fingerprinting enhances representativeness, further methodological refinement is needed for it to become a standardized predictive QC tool [43].
2.2. Metabolomics Approach
Metabolomics is an interdisciplinary field that integrates capabilities from several areas of research, including biology, analytical chemistry, statistics, and biochemistry. It provides strategies for understanding qualitative and quantitative changes in metabolite levels [10]. There are two main approaches to metabolomics analysis: targeted, which focuses on a few metabolites from one or different pathways, and untargeted, which is based on the whole metabolome of an organism or sample. The methodology and theory of metabolomics have been applied in HM quality control research to characterize chemical compositions from different origins or harvest seasons, vegetative periods, and to identify chemical markers for discriminating between raw and processed products, as well as investigating adulteration [44].
An untargeted metabolomic study was performed to discriminate differences in phenolic compounds among brocade orange samples from different maturity levels [45]. A metabolomics approach based on UPLC-QTOF-MS (ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry) was demonstrated to be an effective method for differentiating Citrus reticulata Blanco and ‘Chachi’, as well as ‘Chachi’ samples from different years of storage, in terms of flavonoids [46]. A strategy integrating UPLC/Q-TOF-MS in-depth profiling, untargeted metabolomics, and selected detection was established and exemplarily applied to authenticate Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.-related products, showing that flavonoids can serve as potential markers [47]. Untargeted metabolomics workflows based on UHPLC/QTOF-MSE profiling by ESI+ (electrospray ionization) and chemometrics analysis were successfully performed to achieve complete differentiation of Gleditsiae Sinensis Fructus (GSF), Gleditsiae Fructus Abnormalis (GFA), and Gleditsiae Spina (GS) (all derived from Gleditsia sinensis L.) in terms of flavonoid and other compound compositions [48]. Other examples of metabolomic approaches applied to HM quality control with a focus on flavonoids can be found in the literature [32,49]. Metabolomics studies still present important challenges, including the unambiguous identification of metabolites, data reproducibility, and data processing [37,50]. The latter is likely to benefit from rapid advances in large dataset handling [51].
Metabolomics provides a powerful yet complex approach for assessing flavonoids in herbal medicine quality control. By enabling LC–MS or GC–MS profiling of numerous metabolites, it delivers a more integrated view of chemical variability and potential bioactivity [52] In Sophora flavescens, for instance, an integrated metabolomics workflow identified six major flavonoids (i.e., kurarinone, norkurarinone, kuraridin, kushenol N, trifolirhizin, and genistein) as key quality markers [39]. A similar metabolomics-based evaluation of a traditional cardiotonic formulation detected compositional inconsistencies that conventional assays had overlooked [53] highlighting its superior discriminative power.
Despite these strengths, routine application remains limited by complex plant matrices, costly instrumentation, and the absence of standardized data-processing pipelines [37]. Pattern-oriented models show promise for capturing overall compositional trends [43] but still require harmonized validation before regulatory adoption.
2.3. Network Pharmacology
The rational development and utilization of medicinal resources is also an important strategy for biomarker discovery in current research. Network pharmacology offers a framework for drug discovery that simultaneously addresses efforts to improve clinical efficacy and understand side effects and toxicity, by combining chemistry and pharmacology, thereby facilitating the identification of biomarkers in HM quality control. It allows: (i) the establishment of a pragmatic network model and prediction of drug targets based on public databases or available data from earlier research and (ii) the reconstruction of a “drug-target-disease” network prediction model using high-throughput screening technology and bioinformatics methods [54,55]. The process in network pharmacology research involves: (i) data collection and validation, and (ii) network analysis and visualization [55]. Nowadays, an increasing number of researchers are applying network pharmacology techniques in quality control studies to ensure quality, safety, and efficacy.
Chromatographic fingerprint analysis coupled with chemometrics and network pharmacology was used to compare the chemical constituents and explore the effects of these differentiated markers on the pharmacodynamics of leaves and twigs from Murraya exotica and Murraya paniculata L. The results showed that 7-methoxycoumarins were higher in M. exotica, while M. paniculata was richer in polymethoxylated flavonoids. However, the network pharmacology analysis revealed that these discriminating markers acted via many common targets and metabolic pathways, indicating the possibility of similar pharmacological effects [56]. Flavonoids were identified and detected in Lonicera rupicola Hook.f. & Thomson for the first time using UPLC-MS/MS, with predictions of the core target proteins acting on ulcerative colitis and their potential molecular mechanisms made with the assistance of a network pharmacology bioinformatics platform [57]. Other works have also used this approach for the identification of chemical markers and medicinal potential [23,42,58,59,60,61,62].
Network pharmacology complements chromatographic and metabolomic approaches by offering a systems-level framework to identify flavonoid quality markers through compound–target–disease associations [63]. It facilitates the prioritization of bioactive constituents and prediction of pharmacological mechanisms in complex herbal formulas. For instance, a double-network analysis of Shenxian-Shengmai herbal preparation identified 26 potential antiarrhythmic compounds [58] while studies on the Tangshen formula revealed 13 key flavonoids relevant to diabetic nephropathy, including naringin, daidzein, and genistein [64].
Despite its integrative potential, network pharmacology relies heavily on computational predictions and heterogeneous databases. Limitations include insufficient experimental validation, lack of standardized workflows, and limited consideration of bioavailability and pharmacokinetics [65]. While it is a valuable exploratory tool for marker discovery, its current methodological constraints limit its suitability for routine or regulatory quality control.
2.4. “Q-Markers”
Quality markers (Q-markers) of herbs, pieces, extracts, single herbs, or compound formulations represent a novel concept first clarified by the academician Changxiao Liu [66]. This approach may provide novel insights for further investigations into the quality control of Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) and their processing mechanisms. It has been proposed as a new concept for quality evaluation and standard elaboration of TCM [67,68,69]. Q-markers are defined as chemical constituents that comply with five elements: traceability and transitivity, measurability, effectiveness, specificity, and prescription compatibility [70]. In other words, they are related to effectiveness and safety. Appropriate Q-markers can characterize chemical changes during pharmaceutical processes, as well as ensure the clinical efficacy of TCM. This means that pharmaceutical industries can monitor the entire production process of TCM by determining its corresponding Q-markers [68,71,72]. Nowadays, metabolomics combined with systems pharmacology has proven to be a potent strategy for discovering Q-markers to distinguish between raw and processed TCM [71,73]. Q-markers can be selected by combining chemical profiling and network pharmacology to identify them for Chinese medical preparation (CMP) quality control [23,58].
A multi-dimensional “radar chart” mode was developed based on multiple characteristics related to Q-markers, including the compatibility contribution of HM, content, bioactivity, in vivo predicted bioavailability, and the degree of network pharmacology of candidate components in the TCM prescription [74]. This type of study investigated the metabolism of Xiao-Cheng-Qi decoction (XCQD) by human intestinal bacteria and discovered flavonoids as one of the active component combinations contributing to the anti-inflammatory activity of XCQD [75]. A strategy called the “Spider-web” mode was proposed to discriminate and identify Q-markers by comprehensively integrating the “content-stability-pharmacokinetics-pharmacology” aspects of candidate compounds. The authors hope it could provide a valuable reference and alternative for quality assessment of HM, contributing to the modernization and globalization of TCM [76]. This strategy was used to identify flavonoids as Q-markers in Mailuoshutong pill, a TCM preparation made from 9 plant drugs, by developing a new multi-dimensional network strategy based on “Content-Pharmacokinetics-Pharmacology” [77].
Flavonoids are among the most extensively studied Q-markers, owing to their wide distribution and pharmacological relevance [41] For example, their quantification in preparations such as Ginkgo biloba and Herba epimedii (derived from Epimedium species used for kidney tonification) illustrates how bioactive constituents can serve as measurable indicators of efficacy and batch consistency [78].
However, the practical application of Q-markers in industrial quality control remains challenging. Flavonoid content is highly sensitive to extraction methods, storage conditions, and matrix effects, which can compromise reproducibility and restrict standardization Moreover, relying on a single marker rarely reflects the multicomponent, multitarget nature of herbal formulations. Compared to fingerprinting or metabolomics, Q-marker strategies require more complex workflows, including bioactivity validation and systems pharmacology integration, which may not be feasible in routine manufacturing environments. Additionally, regulatory frameworks for Q-marker-based standards are still evolving, and their incorporation into pharmacopeial monographs remains limited. Therefore, while the Q-marker framework provides a valuable link between chemistry and pharmacological activity, its implementation should be complemented by robust fingerprinting, bioactivity-guided assays, and harmonized validation protocols to ensure reliable and scalable quality control of complex herbal medicines [79].
3. Analytical Techniques and Their Importance for the Quality Control of Herbal Medicines
Analytical instruments play a crucial role in the quality control and standardization of HM, particularly spectroscopic and chromatographic methods [3]. The literature highlights the need to develop authenticated and validated chromatographic protocols for the identification and estimation of phytomarkers that are robust, precise, and cost-effective. In addition, the methods developed must be regulatory compliant to achieve global approval [80].
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC, or its high-performance version, HPTLC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, or its ultra-high-performance versions, UPLC or UHPLC), coupled with various spectroscopic methods (mainly UV), are widely used as qualitative and quantitative techniques for biomarker/marker discovery and in pharmacopeia quality control monographs that feature flavonoids as markers. Table 2 and Table 3 provide some examples of the application of flavonoids as markers in Pharmacopeia quality control monographs, respectively, in the Brazilian Pharmacopeia 6th edition and the European Pharmacopeia 11th edition. Given the importance of TLC and HPLC techniques for analyzing flavonoid composition as markers, some examples will be discussed in the following subsections.

Table 2.
Examples of selected application of flavonoids as markers in quality control in Brazilian Pharmacopoeia 6th edition monographs.

Table 3.
Examples of selected application of flavonoids as markers in quality control European Pharmacopoeia 11th edition monographs.
Although TLC is still widely used in the HM field, it has several limitations that are largely overcome by HPTLC, making the latter technique more suitable for obtaining high-quality results. As shown by Karthika and Paulsamy [81] in their analysis of Solena amplexicaulis (Lam.) Gandhi stem samples, HPTLC provides superior sensitivity and resolution compared to TLC. A side-by-side comparison of the two techniques presented by Gunjal and Dighe [82] clearly highlights the superiority of HPTLC over TLC in the field of HM studies, particularly in terms of sensitivity, quantification, reproducibility, and throughput.
TLC and HPLC/UPLC are used not only for flavonoid identification and quantification but also for obtaining fingerprints. They have been shown to be valuable tools for the chemical analysis of complex matrices and for evaluating quality control, as well as the authenticity, of herbal drugs [14,83,84]. The HPTLC and HPLC methods developed by Bezerra et al. provide helpful and simple tools for quality (fingerprint) evaluation, both qualitatively and quantitatively, of raw materials and extracts from leaves of Eugenia uniflora [83]. Some studies have already explored the integration of these two techniques coupled with MS (mass spectrometry) using an interface for the analysis of flavonoids and other compounds. A two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography/high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TLC/HPLC/ESI-TOF-MS) system was developed to analyze flavonoids (quercetin, astragalin, afzelin, and other components) and distinguish extracts from fruits of Eryngium amethystinum and Eryngium planum [85].
Other methods can be used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonoids. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and infrared (IR, with NIR standing for near-infrared or FT-IR for Fourier-transform infrared) are the most commonly cited for establishing fingerprints or metabolic profiles. For example, the impact of different extraction methods (decoction, infusion, and maceration) on Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx and epicalyx was compared using quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy, revealing that cold maceration is optimal for preserving anthocyanins [86]. 1H NMR was used to analyze the chemical profiling of extracts in a semi-targeted context to identify flavonoids as chemotaxonomic markers in Gnaphalium species that compose “Mexican gordolobo” [87]. According to Tsujimoto et al., 13C-NMR spectra-based metabolic fingerprinting can serve as a strategy for classifying crude drugs with various constituents [88] that contain flavonoids as markers. HPTLC and NMR fingerprints were used to demonstrate the feasibility of identifying and classifying Glycyrrhiza species [17].
FT-IR or NIR can also be used for metabolite fingerprinting [30,89,90]. A sequential integrated NIR-HPTLC image multivariate analysis strategy for the bioprofiling of Egyptian propolis was developed for authenticity and quality assessment [36]. FT-IR and HPLC-DAD combined with chemometrics methods showed that rutin, hyperoside, and luteoside are differential markers between Lonicera species [30]. Quality control of Zanthoxylum nitidum using five major compounds, among which is a flavonoid (hesperidin), by UPLC coupled with NIRS has the potential to discriminate different tissue powders (e.g., root and stem) of Z. nitidum and make a quick distinction between Z. nitidum and its related species [90].
Electrochemical analysis techniques are now emerging as promising applications for obtaining electrochemical fingerprint-based HM QC strategies, due to their low cost and fast analysis processes. They appear to be smart and reliable evaluation methods [91].
An interesting observation from recent works focused on HM QC is the use of “pooled quality control samples” [18,49,92,93]. This strategy is employed when the research objective is to obtain a chromatographic method that can be used to analyze different samples as universally as possible and compare them. This is achieved by mixing equal quantities (mass, volume, or concentration) of samples to determine the stability of the analytical system.
3.1. High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC)
TLC is the most widely used technique for separating phytochemical compounds in botanical extracts. It is a classic method for the quality control (QC) of herbal products and is required for all pharmacopeia assays. It is a simple, efficient, and low-cost methodology to implement [84,94]. HPTLC is a robust and reliable technique for detecting adulteration. It can demonstrate phytochemical differences between products, adulteration with other species, and potential chemotypes within the same species [95]. For legitimate companies aiming to produce high-quality products, HPTLC can provide important information about raw material acquisition, product development, control of intermediate processing steps, and regulatory compliance of the final product [96].
Although HPTLC has a few limitations, such as low plate efficiency and narrow developing distance compared to GC and HPLC, it remains a valuable tool for quality assessment of herbal products due to its ease of use. It has been profitably used to develop chromatographic fingerprints for various natural products, herbal drugs, and commercial herbal formulations [16].
Previous studies [80] investigated the identification of bioactive phytochemical markers in selected medicinal plants, namely the fruits of Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb. and Terminalia chebula Retz, and their HM. The results indicated that HPTLC method development complies with global guidelines, thereby leading to better acceptability of this tool as the preferred method for herbal analysis. In addition, regression values, quantification thresholds, and validation parameters demonstrated that the HPTLC method is an optimal alternative to tedious, complex, and costly methods such as HPLC, LC-MS, and GC–MS. Therefore, HPTLC may be used as a preferred routine method for quality control and related analyses [80].
A study conducted by Wosch et al. collected leaf samples different locations of twelve Passiflora taxa (i.e., ten species and two forms of P. edulis Sims): P. actinia Hook, P. alata Curtis, P. amethystina J.C.Mikan, P. capsularis L., P. cincinnata Mast., P. edulis f. flavicarpa, P. edulis f. edulis, P. incarnata L., P. morifolia Mast., P. urnifolia Rusby, P. coccinea Sol., and P. setacea DC. Their chromatographic profiles were obtained via TLC. These were compared to the flavonoid C-glycosides iso-orientin, orientin, vitexin, and iso-vitexin as reference compounds. It was ultimately possible to establish specific profiles for each species [97].
A simple and precise validated HPTLC method was successfully applied to the simultaneous determination of curcumin and galangin (a flavonoid) in a commercial polyherbal formulation [16]. A single HPTLC method for the simultaneous separation and estimation of selected markers, including galangin, apigenin, pinocembrin, luteolin, and other compounds, was also developed for Indian propolis [98]. Similarly, a simple and sensitive method for the simultaneous detection and quantification of ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid and rutin in Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Royle was proposed by Siddiqui et al. [99]. Booker et al. performed a study to evaluate phytochemical variations among commercial finished St. John’s wort products (Hypericum perforatum L.) [95]. The authors demonstrated that HPTLC was able to identify adulterations between licensed and unlicensed marketed products [95]. An HPTLC method was also validated and demonstrated to be highly accurate for identifying and quantifying kaempferol, as well as quercetin, in six genotypes of Setaria italica (L.) P.Beauv [100].
Likewise, in parallel with HPLC fingerprinting, HPTLC has also proven adequate for determining a characteristic fingerprint for herbal drugs [17,27,84]. It has been coupled with mass spectrometry to provide sensitive and specific analysis [94,101]. An HPTLC method provided a good fingerprint for Croton gratissimus Burch. species authentication through direct band comparison and could clearly confirm the presence of iso-orientin and kaempferol-3-β-D-(6″-O-trans-p-coumaroyl) glucopyranoside [102]. Comprehensive HPTLC fingerprinting could provide information beyond the identification of ginkgo products, thereby avoiding additional chromatographic tests to detect adulterations. Molecular markers included rutin and quercetin or herbal extracts rich in these compounds [96].
In addition to all these applications, the HPTLC technique has been used for bioactivity screening assays to measure (i) antioxidant activity using DPPH as a free radical reagent [80,85] or (ii) acetylcholinesterase inhibition through bioautographic enzyme assays [103].
High-performance thin-layer chromatography continues to serve as a rapid and cost-effective method for flavonoid analysis, offering minimal sample preparation and the ability to process multiple extracts simultaneously [104]. It generates clear, image-like fingerprints that facilitate visual comparison and support adulteration detection [105]. Recent studies have demonstrated its quantitative precision: Kobakhidze et al. [106] quantified rutin in violet herb extracts, showing solvent-dependent yields of 3.08% and 1.59% for 96% and 70% ethanol extractions, respectively. Likewise, a validated HPTLC-densitometric method for Cassia occidentalis quantified luteolin with recoveries between 88% and 101%, confirming the method’s reproducibility for routine quality control. Notably, HPTLC has been validated in multiple pharmacopeias and offers a robust alternative to more complex chromatographic methods, particularly for preliminary screening and fingerprinting [82].
However, its quantitative accuracy remains dependent on optimized sample application, solvent composition, and densitometric calibration. Compared to LC or MS-based techniques, HPTLC is less suited for absolute quantification but excels in accessibility and throughput. Overall, it provides a reliable platform for routine herbal quality control, best used in combination with complementary analytical methods to ensure regulatory compliance and analytical depth.
3.2. Liquid Chromatography
Liquid Chromatography (LC) techniques, including UPLC, UHPLC, and HPLC, when coupled with various detectors (e.g., UV, Diode Array Detection (DAD), Photodiode Array (PDA), and Mass Spectrometry (MS)), are essential methods for flavonoid quantification. These methods are of particular interest because they can be validated according to the guidelines of regulatory agencies worldwide. This is one of the reasons why they are often included in pharmacopeia monographs. Consequently, most of the analytical work focused on flavonoid quantification employs this approach [20,83,89,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116]. While MS detectors can be used for biomarker discovery and routine quality control (QC), UV detectors remain a frequent choice. As a result, LC methodologies are widely used to develop and validate the chemical fingerprints of herbal medicines (HMs) [20,117].
Coupling LC with different detector types offers several benefits. This approach enhances detection sensitivity, enables more accurate quantification of flavonoids with diverse chemical structures, facilitates the identification of novel flavonoids and their derivatives, and improves analytical throughput and reproducibility—a significant challenge in the field of natural products. Specifically, DAD allows for the simultaneous detection of compounds at multiple wavelengths. MS provides the advantage of detecting flavonoids that might be missed by UV detection due to low abundance or a weak spectral signature. Indeed, quantification via MS can be more reliable, whereas UV-based quantification can sometimes be misleading. Consequently, LC-DAD, LC-MS, and simultaneous LC-DAD-MS are extremely useful for identifying unknown flavonoids and characterizing their subclasses. Performing multiple detection methods in a single LC run significantly increases throughput. For a review of recent advances in coupling multiple detectors to LC, see Verma et al. [118].
For instance, HPLC-DAD quantification has been used to demonstrate seasonal variations in plant flavonoid content, revealing higher summer levels of tricin-7-O-diglucuronide, the major flavonoid in Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br [119]. As secondary metabolites, flavonoids also have proven taxonomic value. A study by Napoli et al. (2018) [120] utilized HPLC-DAD-MS to identify five flavonoids across eleven Hypericum species, linking them to the species’ antioxidant properties. The metabolites quercetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-galactoside, quercitrin, quercetin, and biapigenin were found in all analyzed species. Additionally, myricitrin was identified in H. perfoliatum, and quercetin-3-O-rutinoside was found in H. calycinum L. and H. aegypticum L [120]. Similarly, UHPLC-QTOF-MS and UHPLC-PDA were used to identify and quantify marker compounds in Agastache rugosa at different growth stages, finding that flavonoids of the tilianin group were the predominant substances [121]. In another application, TLC and HPLC-DAD were employed to compare the flavonoid composition in the leaves of two Jatropha L. species (Jatropha gossypiifolia L. and Jatropha mollissima (Pohl) Baill)), which are used interchangeably to treat snakebites. The C-glycoside flavonoids isoorientin, isovitexin, orientin, and vitexin were identified as differential chemical markers for these species [122].
Flavonoids are crucial for differentiating between authentic herbal drugs, their adulterants, and related species. For example, a validated UHPLC-DAD method was successfully applied to distinguish Verbena officinalis from its most common adulterant, Aloysia citriodora Paláu, proving to be a useful and reliable tool for rapid quality control [111]. In another study, Wosch et al. [97] collected leaf samples from twelve Passiflora taxa from different locations and generated their chromatographic profiles using HPLC-DAD. By using the C-glycoside flavonoids isoorientin, orientin, vitexin, and isovitexin as reference compounds, they were able to establish specific profiles for each species and differentiate between them [97].
An HPLC fingerprinting method was developed for the analysis of alkaloid and flavonoid constituents in Sophora flavescens Aiton (SFR) and Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep (STR). The results showed that flavonoid constituents could serve as diagnostic markers to differentiate between SFR and STR, a difference that might be attributed to their distinct therapeutic effects [29]. In another study, Tewari et al. [123] addressed the QC of Saraca asoca (Roxb.) Willd. bark extracts by analyzing marker compounds (flavonoids and polyphenols) using RP-HPLC-PDA-RI, revealing that flavonoids can serve as differential markers for samples from different geographical locations [123].
Apigenin derivatives were used to develop an innovative green HPLC-DAD chromatographic method. This method, based on experimental design and green chemistry principles, was created for the qualitative and quantitative analysis and standardization of hydroethanolic leaf extracts of Serjania marginata Casar [124].
HPLC-DAD has also been employed to understand the chemical complexity of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and other herbal preparations. For example, twelve phenolic compounds, including nine flavonoids, were simultaneously quantified in different batches of Longxuetongluo Capsule (the dried red resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis) using HPLC-DAD [108]. This technique was similarly used to characterize the Xiao-Cheng-Qi decoction [75] and the Buyang Huanwu decoction [19].
Advanced MS methods are frequently used for detailed plant analysis. A UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS method was developed to investigate flavonoids in the leaf, rhizome, and bud of both natural and tissue-cultured Epimedium alpinum L. [125]. A validated UPLC-MS/MS method identified numerous compounds, particularly flavonoids, in the root, rhizome, stem, leaf, and flower of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus Bunge [126]. Furthermore, a validated UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method was developed to simultaneously quantify chemical compounds, including flavonoids, in Yiqi Jiangzhi Granules, a formula composed of 10 different TCM herbs [127]. Similarly, a validated UPLC-TQ-MS/MS method was used to qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate samples of Hibiscus mutabilis L. folium, a TCM herb. This study recorded differences in flavonoid, coumarin, and organic acid content based on when the samples were harvested and how they were dried [128].
LC-MS/MS is a workhorse technique for the chemical profiling of complex matrices, especially when compounds have weak ultraviolet absorption, are present in low concentrations, or are easily obscured by impurities [108]. Specifically, the LC-MS/MS multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode is a highly suitable analytical method for the quality evaluation of HM [129,130]. Among the various MS scan modes, MRM is considered a reliable method for detecting specific constituents of interest and can be used to develop MRM-based fingerprints [131].
New techniques are emerging in LC, such as Online Extraction (OLE) technology. Ferreira et al. developed a simple, efficient, and economical extraction procedure where a solid sample is inserted into a micro-column, and its components are extracted and transferred online to the HPLC system [132]. This strategy was used to develop a novel OLE–HPLC–DAD–QTOF-MS/MS system for the rapid, efficient, and sensitive analysis of interglycosidic linkage isomers (hesperidin and neohesperidin) in Citrus paradisi cv. Changshan-Huyou [133].
Preparative LC techniques have also been used for marker discovery. Researchers developed a broadly applicable methodology to investigate and differentiate bioactive components in HM using preparative HPLC (prep-HPLC) combined with a selective “knock-out” strategy. This strategy involves selectively removing individual components from an herbal extract, determining their structures, evaluating their bioactivities, and analyzing the data to determine the contribution of each component to the extract’s overall bioactivity. This approach was applied to investigate the main bioactive components in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) and to distinguish their respective contributions. The results suggest that flavonoid glycoside compounds containing a C7-OH group can be considered chemical markers for the QC of safflower [134]. This methodology could be useful for investigating the bioactive constituents of other medicinal herbs.
Liquid chromatography, particularly reversed-phase HPLC, remains the leading technique for identifying and quantifying flavonoid markers in herbal medicine due to its high sensitivity, selectivity, and compatibility with multiple detection systems [135]. Recent LC-MS/MS applications have demonstrated their precision and versatility. For example, Seo et al. [129] developed a nine-marker method for Gungha-tang, a traditional Korean herbal decoction used to treat inflammatory and respiratory conditions, detecting compounds such as liquiritin apioside, naringin, and hesperidin at nanogram levels with recoveries ranging from 89% to 118%. Similarly, Juszczak et al. [136] used HPLC to separate luteolin and its glycosides from several plant species, highlighting the method’s capacity to distinguish structurally related flavonoids.
LC analysis, however, requires extensive sample preparation, careful optimization of mobile-phase and detection conditions, and rigorous matrix-specific validation [3]. Thus, while LC offers unparalleled analytical depth for flavonoid profiling, its technical complexity and resource demands may limit routine use, reinforcing the value of simpler complementary screening tools in industrial herbal quality control.
4. Trend in Data Analysis: Multivariate Analysis Contribution
Data generated by analytical methods requires suitable processing. A review of the literature from our search strategy shows that in the last five years, data analysis has advanced considerably in quality control studies of HM. This progress is largely due to the use of multivariate analysis to facilitate information mining. Modern phytochemical studies and their analytical workflows are developing rapidly, particularly with advances in data treatment and analysis, such as molecular networking for data visualization and multivariate analysis using chemometric techniques. Although these techniques are not yet routinely used for quality control in the HM industry, they play an important role in analyzing the complex datasets generated by HM quality control studies, as well as in identifying and validating more suitable markers. Some chosen markers may not accurately reflect the quality and consistency of the herbal product. In this regard, further studies are necessary to characterize metabolic alterations that plant material may undergo due to abiotic conditions or raw material processing. Multivariate strategies are powerful tools for processing the resulting data and simplifying the interpretation of the results.
4.1. Chemometrics and Molecular Networking Contribution in Herbal Quality Control Workflow
After collection and pre-processing, data from HM samples are analyzed using molecular networking (MN) for feature extraction, structural elucidation, and pattern recognition. Subsequently, or concurrently, various multivariate analysis techniques are applied, including Support Vector Machine (SVM), Grey Relational Analysis (GRA), Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR), Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares (MCR−ALS) [137].
In the context of natural product quality control, MN organizes molecules based on structural similarity. This process facilitates subsequent chemometric analysis, which provides several key outcomes:
Complexity reduction: Achieved with unsupervised methods like PCA or clustering.
Class prediction: used to identify categories, such as adulterated samples, with models like SVM, ANNs, or PLS.
Identification of similarities and outliers: performed using techniques such as GRA.
Integration with molecular networking: allows for the quantification of relationships between compound clusters and biological activities.
In summary, for HM quality control, multivariate analysis is a powerful tool for detecting adulteration, authenticating samples, and ranking product quality [138]. Recent studies illustrate the practical potential of these integrated approaches. Arbianto et al. [139] applied UHPLC-QTOF/MS-based molecular networking coupled with multivariate analysis to distinguish Epimedium koreanum extracts from four South Korean regions, revealing location-specific flavonoid clusters. Yuan et al. [140] integrated Orbitrap-MS/MS with chemometrics to identify 21 quality markers among more than 10,000 molecular features in Chrysanthemum species. Similarly, Seo et al. mapped glucuronidated metabolites of quercetin and kaempferol in Cudrania tricuspidata using molecular networking, demonstrating its value for detailed metabolite profiling [129].
Taken together, chemometrics and molecular networking provide powerful yet complex frameworks for identifying and quantifying flavonoid markers in herbal medicine quality control. Molecular networking enables rapid visualization of structurally related flavonoid clusters, improving spectral interpretation and biomarker discovery, while chemometric methods address analytical challenges such as co-eluting peaks, instrumental drift, and multivariate variability [141,142]. Despite these strengths, both approaches remain computationally demanding and rely on robust spectral libraries and standardized workflows. Their gradual integration into quality-control pipelines marks a significant step toward data-driven standardization of complex herbal preparations. However, broader adoption in industrial settings will require simplified user interfaces, regulatory harmonization, and improved training in data interpretation. These tools therefore complement rather than replace conventional chromatographic methods, offering enhanced resolution and insight for flavonoid marker discovery and validation.
4.2. Molecular Networking
Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS) platforms are widely used for drug discovery as well as the quality control of HM and food supplements. The large datasets generated during LC–MS analysis contain valuable information that can be extracted and processed using various data mining and statistical tools [143]. In this context, the molecular networking (MN) approach has emerged as a powerful tool for processing tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) data [144].
MN is based on the premise that compounds with similar chemical structures produce similar mass spectral fragments, enabling their automatic clustering within the Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) platform. MN incorporates multivariate statistical analysis to avoid false positives and provides a reliable method for identifying chemical markers in HMs and their associated products [92,143,145]. The GNPS platform facilitates the characterization of natural products and accelerates drug discovery [144]. This approach, either alone or combined with other multivariate techniques, can be used to detect and quantify flavonoids as quality markers, thereby improving authenticity studies and HM quality control.
For example, An et al. used a molecular networking strategy to identify complex chemical constituents and markers in different colored varieties of Cassia angustifolia Vahl and C. acutifolia Delile [92]. Wang et al. (2022) [146] presented an integrative approach combining comprehensive 2D-LC/IM−QTOF−MS, automatic peak annotation, molecular networking, and collision cross-section prediction. This method improved the resolution and reliability of metabolite characterization in the seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lam., whose constituents are vital to its pharmacological activities [146]. In another study, chemical compounds, including flavonoids, were comprehensively characterized in the roots, stems, leaves, and seeds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. using an LC−MS workflow that integrated MN, spectral matching, MS2LDA-based substructure recognition, and comparison with reference standards [147]. Finally, an untargeted metabolomics approach combining UPLC−MS/MS-based MN with conventional isolation and NMR methods profiled the phytochemistry of Crescentia cujete L. fruit pulp, identifying 15 flavonoids [148].
Molecular networking offers a powerful computational framework for identifying and characterizing flavonoid markers in herbal medicine quality control. By visualizing spectral similarities among MS/MS fragments, it enables rapid dereplication of flavonoid molecular families and efficient annotation of unknown compounds [141]. Feature-based molecular networking further enhances precision by resolving closely related flavonoid isomers and facilitating large-scale spectral comparisons [149]. Recent applications have demonstrated its analytical depth: MN has been used to characterize 222 compounds in Paris polyphylla, including four novel flavonoids and to differentiate botanical components in a ten-herb TCM formula based on distinct flavonoid signatures [150,151].
Despite these strengths, MN remains dependent on curated spectral libraries and high-quality fragmentation data, and its interpretation requires expert oversight to avoid misclassification [149]. When integrated with conventional LC–MS or NMR workflows, however, MN significantly enhances metabolite coverage and annotation reliability, representing a key advance toward standardized, data-driven quality control of complex herbal preparations [139].
4.3. Chemometric Methods
Chemometric methods are increasingly applied to quality control research for HM. They bring solutions to a variety of analytical issues. Techniques such as similarity analysis, exploratory learning, and classification algorithms are used for qualitative analysis. For quantitative analysis, multivariate calibration algorithms can be employed to explore the relationships between independent and dependent variables [2,143].
Chemometric analyses are performed to discriminate between samples, differentiate species, classify cultivation methods or plant parts, and verify the authenticity of HM. Common methods include Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Partial Least Squares (PLS), Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS−DA), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Grey Relational Analysis (GRA), Similarity Analysis (SA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and heat mapping.
Several studies demonstrate the potential of these techniques. For instance, PCA and OPLS−DA were used to identify chemical markers for different quality grades (green, yellow, and diseased) of Sennae Mill., revealing that flavonoid concentrations increased as leaf quality declined [92]. These same methods helped establish key quality control indicators, including seven flavonoids, for licorice samples based on age, harvest season, and production area [152]. Using PCA, researchers found that the flavonoid luteolin-7,4′-O-diglucoside, present in variable amounts in different Lantana camara L. cultivars, could serve as a species marker and potential biomarker due to its link with biological activity [153]. Furthermore, PCA and OPLS−DA of LC−MS data confirmed that flavonoids are effective markers for discriminating between Hibiscus sabdariffa L. cultivars [86].
Chemometrics is also crucial for establishing the relationship between a plant’s chemical fingerprint and its biological activity. Applying these methods to fingerprint data can uncover hidden information through mathematical modeling, making it a promising approach for the comprehensive quality assessment of HM [2,143].
Indeed, PCA and OPLS−DA were used to compare the chemical fingerprints of non-fumigated and sulfur-fumigated Smilax glabra Roxb. samples. This analysis identified flavonoids like astilbin as major constituents and pinpointed newly formed sulfur-containing compounds as key markers for distinguishing the fumigated samples [154]. In another study, PCA and HCA investigated the relationship between the chemical composition of Harconia speciosa Gomes extracts and their bioactivities, showing a strong correlation with flavonoids [116].
Similarity Analysis (SA) and HCA have also been widely used. This combination showed that flavonoid profiles could serve as diagnostic markers to differentiate Sophorae species [29]. A comprehensive method using HPLC fingerprinting combined with SA, HCA, and PCA was established to assess the quality of Emilia prenanthoidea DC. from different regions, identifying chlorogenic acid, hyperoside, and quercitrin as reliable chemical markers [20]. Likewise, HCA and PCA revealed that the anticoagulant activity of Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br ex Britton & P. Wilson accessions results from a synergy between flavonoids and phenylpropanoids [155].
Finally, heat mapping is another valuable tool, particularly in metabolite annotation studies. It is used to distinguish samples based on plant part, cultivation conditions, collection season, or geographic origin. This tool is especially useful because it provides valuable semi-quantitative information [71,93,153,156].
Overall, chemometric methods provide a sophisticated yet demanding framework for herbal medicine quality control. Their advanced statistical capabilities enable resolution of multifactorial challenges such as sample-preparation optimization, instrumental calibration, and co-eluting peak correction [142]. By integrating pattern-recognition and variable-selection algorithms, chemometric models support comprehensive assessment of plant materials and finished products, identifying variables most strongly associated with pharmacological or compositional properties [157]. Recent applications underscore their wide applicability across herbal matrices and analytical platforms: Rohman et al. (2020) [158] authenticated Curcuma longa and C. xanthorrhiza using combined spectroscopic and chromatographic data, while Rebiai et al. (2021) [159] reviewed over ninety studies integrating chemometrics with HPLC, GC-MS, UV-Vis, FTIR, and NMR workflows. These examples highlight chemometrics’ capacity to extract hidden patterns related to plant part, developmental stage, processing, or geographic origin [158,159].
On the other hand, chemometric workflows demand proper statistical control and data preprocessing to prevent overfitting. They are most effective when combined with chromatographic or spectrometric analyses, ensuring consistent and reproducible quality assessment of herbal products [158].
5. Conclusions
In summary, this review underscores the pivotal role of flavonoids as versatile and reliable markers in the quality control of herbal medicines. The journey from classical pharmacopeial techniques to sophisticated, integrated strategies reflects a significant evolution in the field. Traditional chromatographic methods such as high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC-DAD) remain the bedrock of routine analysis due to their robustness, accessibility, reproducibility, and regulatory acceptance. These classical methods provide clear quantitative data and form the basis of many pharmacopeial standards; however, they offer limited insight into the complex multicomponent interactions within herbal formulations.
Therefore, the paradigm in quality assessment is decisively shifting toward more holistic, system-level approaches that can capture the entire phytochemical matrix and its biological relevance. Emerging strategies such as chemical fingerprinting, metabolomics, network pharmacology, and the “Q-marker” concept link the chemical composition of an herbal medicine to its bioactivity in a comprehensive manner, moving beyond single-compound quantification to characterize synergistic effects and the broader metabolic profile of putative remedies. This integration of classical and modern methodologies positions flavonoids (chemically stable and pharmacologically potent metabolites) as major indicators in an evolving analytical framework that connects chemical profiles with clinical efficacy.
The integration of advanced analytical technologies with cutting-edge data analysis tools has been a game-changer for flavonoid-based quality control. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC–HRMS) now enables high sensitivity associated with the identification of a wide spectrum of flavonoid metabolites, while hyphenated techniques (e.g., HPLC–DAD–MS or HPLC–NMR) provide multi-dimensional insights into complex extracts. Furthermore, combining these powerful methodologies with modern computational data mining tools is transforming raw data into meaningful, actionable information. For example, chemometric methods and molecular networking can visualize hidden relationships within large metabolomic datasets, reduce analytical bias, and extract latent chemical information that would be missed by univariate analyses. This synergy is proving crucial for authenticating botanical species, detecting adulteration or quality inconsistencies, linking chemical fingerprints to biological activities, and discovering novel efficacy-related markers.
Nonetheless, despite these advancements, significant challenges remain before such integrated approaches become routine in industrial quality control. The selection of appropriate quality markers is often context-dependent, complicating the efforts to establish universal standards. Many of the most advanced techniques require expensive high-resolution instrumentation and specialized bioinformatic expertise, creating practical barriers for widespread adoption. In addition, a lack of standardized reference materials and curated spectral libraries for plant metabolites, coupled with the use of non-standardized data-processing workflows, can lead to reproducibility issues and inconsistent results between different laboratories. Importantly, regulatory frameworks have not yet fully recognized algorithm-driven analyses (such as chemometric models or molecular network-based markers) in official quality specifications, and harmonized validation protocols for these novel tools are largely absent. These factors collectively limit the current industrial uptake of emerging methodologies and underscore the need for collaborative solutions.
Future concerted efforts should focus on bridging the gap between cutting-edge research innovations and practical, regulatory-compliant quality control of herbal medicines.
First, developing streamlined, miniaturized, greener, and cost-effective analytical workflows will be essential to make advanced techniques more accessible for routine use. Such methods should retain the robustness of classical chromatography while incorporating the depth of metabolomic profiling, thereby ensuring scalability beyond specialized research settings.
Second, harnessing artificial intelligence and machine learning for data processing and biomarker discovery could automate complex analyses, improving throughput and reducing the requirement for expert intervention in interpreting large datasets.
Third, promoting the integration of multi-omics data (combining metabolomic, genomic, and transcriptomic information) will facilitate a true systems-level understanding of herbal medicine quality, shedding light on how genetic and environmental factors influence phytochemical profiles and therapeutic outcomes.
Fourth, and critically, the community must establish international consensus on the validation and application of these novel strategies. This includes building open-access spectral databases and curated libraries of plant metabolites, standardizing chemometric and molecular networking protocols, and developing clear guidelines for their validation and regulatory acceptance.
By achieving harmonization in how advanced analytical data are interpreted and reported, it may be possible to enhance reproducibility and foster regulatory confidence in these next-generation quality control tools.
Ultimately, the most promising path forward is to combine the proven reliability of classical chemical analysis with the interpretive depth of computational and metabolomic approaches, all anchored in biological relevance. Such integration can transform flavonoid-based quality control from basic chemical profiling into a more predictive, standardized, and insightful approach. By addressing the current challenges through technological innovation, capacity-building, and regulatory collaboration, the scientific community may strengthen the global framework for herbal medicine quality control, thereby effectively bridging the gap between research and regulation, and ensuring that consumers worldwide receive herbal products that are safe, effective, and consistent in quality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.F., S.M.Z. and P.P.; methodology, J.M.F.; validation, J.M.F., S.M.Z., F.V. and P.P.; investigation, J.M.F., C.S. and P.P.; data curation, J.M.F., C.S., J.A., F.V. and A.E.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.F., C.S., J.A. and P.P.; writing—review and editing, S.M.Z., C.S., J.A., A.E., F.V. and P.P.; visualization, J.M.F., C.S., S.M.Z. and P.P.; supervision, S.M.Z., F.V. and P.P.; funding acquisition, P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- van Wyk, A.S.; Prinsloo, G. Health, Safety and Quality Concerns of Plant-Based Traditional Medicines and Herbal Remedies. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 133, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yao, C.; Guo, D. Quality Assessment of Herbal Medicines Based on Chemical Fingerprints Combined with Chemometrics Approach: A Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawad, P.; Gharge, S.; Jivaje, K.; Hiremath, S.I.; Suryawanshi, S.S. Quality Control and Standardization of Quercetin in Herbal Medicines by Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Techniques. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. General Guidelines for Methodologies on Research and Evaluation of Traditional Medicine; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; 71p. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Jiang, Y. New Insights on Bioactivities and Biosynthesis of Flavonoid Glycosides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adis R&D Profile. EGb 761: Ginkgo Biloba Extract, Ginkor. Drugs RD 2003, 4, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, M.; Busse, W.R.; Goldberg, A.; Gruenwald, J.; Hall, T.; Riggins, C.W.; Rister, R.S. The Complete German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Guide to Herbal Medicines; American Botanical Council: Austin, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sammani, M.S.; Clavijo, S.; Cerdà, V. Recent, Advanced Sample Pretreatments and Analytical Methods for Flavonoids Determination in Different Samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 138, 116220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turatbekova, A.; Babamuradova, L.; Tasheva, U.; Saparbaeva, N.; Saibnazarova, G.; Turayeva, M.; Yakubov, Y. A Brief Review on Biological and Chemical Activities of Flavonoids in Plants. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 434, 03026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant Flavonoids: Classification, Distribution, Biosynthesis, and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Fraga, C.G. Research Trends in Flavonoids and Health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 646, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Han, Q.; Qiao, C.; Song, J.; Cheng, C.L.; Xu, H. Chemical Markers for the Quality Control of Herbal Medicines: An Overview. Chin. Med. 2008, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Su, J.; Nian, H.; Shen, H.; Zhai, X.; Xin, H.; Qin, L.; Han, T. Chemical Fingerprint and Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids for Quality Control of Sea Buckthorn Leaves by HPLC and UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Oketch-Rabah, H.; Kim, N.-C.; Monagas, M.; Bzhelyansky, A.; Sarma, N.; Giancaspro, G. Quality Specifications for Articles of Botanical Origin from the United States Pharmacopeia. Phytomedicine 2018, 45, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xiong, Z.-Y.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Gao, W.; Li, H.-J. From Chemical Consistency to Effective Consistency in Precise Quality Discrimination of Sophora Flower-Bud and Sophora Flower: Discovering Efficacy-Associated Markers by Fingerprint-Activity Relationship Modeling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharat, S.; Namdeo, A.; Mehta, P. Development and Validation of HPTLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Curcumin and Galangin in Polyherbal Capsule Dosage Form. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Adams, S.J.; Lee, J.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Avula, B.; Ali, Z.; Raman, V.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; et al. Metabolite Variation and Discrimination of Five Licorice (Glycyrrhiza) Species: HPTLC and NMR Explorations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 220, 115012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.-X.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, G.-D.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, Z.-F.; Xu, L.; Duan, R.; Tsim, K.W.K.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.-T. Discrimination of Three Siegesbeckiae Herba Species Using UPLC-QTOF/MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Yu, A.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Meng, Y.; He, D.; Shen, X.; Wang, L. Identification of Active Ingredients Mediating Anti-Platelet Aggregation Effects of BuyangHuanwu Decoction Using a Platelet Binding Assay, Solid Phase Extraction, and HPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gong, X.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X. Quantification and Efficient Discovery of Quality Control Markers for Emilia Prenanthoidea DC. by Fingerprint-Efficacy Relationship Modelling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 156, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, W.; Sun, G. Quality Consistency Evaluation of Isatidis Folium Combined with Equal Weight Quantified Ratio Fingerprint Method and Determination of Antioxidant Activity. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1095, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; Yao, M.; Wang, N.; Peng, D. Spectrum-Effect Relationship between UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Fingerprint and Anti-AUB Effect of Clinopodium chinense (Benth.) O. Kuntze. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 217, 114828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Luo, J.; Lyu, M.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, W. An Integrated Approach to Q-Marker Discovery and Quality Assessment of Edible Chrysanthemum Flowers Based on Chromatogram–Effect Relationship and Bioinformatics Analyses. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Song, Q.; Luo, H.; Wang, R.; Fang, C. Quality Evaluation of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Moutan Cortex Based on UPLC Fingerprinting and Chemometrics Analysis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhao, W.; Pu, X.; Zhong, X.; Tao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, D. UPLC Fingerprinting Combined with Quantitative Analysis of Multicomponents by a Single Marker for Quality Evaluation of YiQing Granules. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1632033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Z.-Y.Y.; Gao, W.; Li, P.; Li, H.-J.J. Discovery of Discriminatory Quality Control Markers for Chinese Herbal Medicines and Related Processed Products by Combination of Chromatographic Analysis and Chemometrics Methods: Radix Scutellariae as a Case Study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Mondal, S.; Ramakrishna, K. Pharmacobotanical, Physicochemical and Phytochemical Characterisation of a Rare Salt-Secreting Mangrove Aegialitis rotundifolia Roxb., (Plumbaginaceae) Leaves: A Comprehensive Pharmacognostical Study. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, Y.; Sun, G.-X.; Jin, Y.; Xie, X.-M.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ma, D.-D.; Zhang, J.; GAO, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-F. Holistic Evaluation of San-Huang Tablets Using a Combination of Multi-Wavelength Quantitative Fingerprinting and Radical-Scavenging Assays. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.-L.; He, C.-M.; Cheng, Z.-H.; Chen, D.-F. Flavonoids Rather than Alkaloids as the Diagnostic Constituents to Distinguish Sophorae Flavescentis Radix from Sophorae Tonkinensis Radix et Rhizoma: An HPLC Fingerprint Study. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Wu, H. Comprehensive Chemical Analysis of the Flower Buds of Five Lonicera Species by ATR-FTIR, HPLC-DAD, and Chemometric Methods. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yin, Y.-H.H.; Miao, L.-Y.Y.; Zheng, X.; Gao, W.; Chen, X.-D.D.; Wei, M.; Chen, S.-J.J.; Li, S.; Xin, G.-Z.Z.; et al. Integrating Chemical Similarity and Bioequivalence: A Pilot Study on Quality Consistency Evaluation of Dispensing Granule and Traditional Decoction of Scutellariae Radix by a Totality-of-the-Evidence Approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Linghu, K.-G.; Xiao, L.; Hua, T.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, S.; Shen, L.; Yu, J.; Hou, X.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory/Anti-Oxidant Properties and the UPLC-QTOF/MS-Based Metabolomics Discrimination of Three Yellow Camellia Species. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, C.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Tian, Y.W.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Qin, K.M.; Li, W.D. Quality Evaluation of Crude and Salt-Processed Cuscutae Semen through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Multiple Components Using HPLC Combined with Chemometrics. Separations 2022, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, G. Multiple Wavelengths Maximization Fusion Fingerprint Profiling for Quality Evaluation of Compound Liquorice Tablets and Related Antioxidant Activity Analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, H.; Ling, G.; Sun, G. Evaluating the Quality Consistency of Keteling Capsules by Three-Dimensional Quantum Fingerprints and HPLC Fingerprint. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 270, 120820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, E.; Ibrahim, R.S. Bioprofiling for the Quality Control of Egyptian Propolis Using an Integrated NIR-HPTLC-Image Analysis Strategy. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1095, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X. Application of Metabolomics in Quality Control of Traditional Chinese Medicines: A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1463666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Li, H.; Ding, X.; Liu, Z.; He, D.; Kowah, J.A.H.; Wang, L.; Yuan, M.; Liu, X. A Review of The Application of Spectroscopy to Flavonoids from Medicine and Food Homology Materials. Molecules 2022, 27, 7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shao, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology strategy for ascertaining the quality marker of flavonoids for Sophora flavescens. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xu, K.; Yan, Q.; Sui, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Han, F. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of Flos Puerariae by using chemical fingerprint in combination with chemometrics method. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 12, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, S.; Han, J.; Su, J.; Cai, W. Supermolecules as a quality markers of herbal medicinal products. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Long, F.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhou, J.; Shen, H.; Zhou, S.S.; Xu, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.L. Integrating Serum Pharmacochemistry and Network Pharmacology to Identify Chemical Markers for Quality Control of Apocyni Veneti Folium. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Junior, L.C.; de Souza, M.R.; Viaene, J.; Bresolin, T.M.B.; de Gasper, A.L.; Henriques, A.T.; Heyden, Y.V. Quality Control of Herbal Medicines: From Traditional Techniques to State-of-the-art Approaches. Planta Medica 2021, 87, 964–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, M.; Koçak, E.; Gonulalan, E.M.; Demirezer, L.O.; Kır, S.; Nemutlu, E. Metabolomics Analysis Insight into Medicinal Plant Science. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Feng, X.; Huang, P.; Du, M.; Zalán, Z.; Kan, J. Distribution and Natural Variation of Free, Esterified, Glycosylated, and Insoluble-Bound Phenolic Compounds in Brocade Orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) Peel. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Huang, K.-E.E.; Li, D.-X.X.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.-Q.Q.; Ke, X.-H.H. Discrimination of Citrus reticulata Blanco and Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’ as Well as the Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’ within Different Storage Years Using Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Based Metabol. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 171, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yao, C.; An, Y.; Wei, W.; Yao, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Qu, H.; et al. In-Depth Profiling, Nontargeted Metabolomic and Selective Ion Monitoring of Eight Chemical Markers for Simultaneous Identification of Different Part of Eucommia Ulmoides in 12 Commercial Products by UPLC/QDa. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, B.; Lou, J.; Wang, H.H.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Jing, Q.; Jiang, M.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis to Unveil the Chemical Markers for the Differentiation among Three Gleditsia Sinensis-Derived Herbal Medicines by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokwuru, C.P.; Tankeu, S.; van Vuuren, S.; Viljoen, A.; Ramaite, I.D.I.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Combrinck, S. Unravelling the Antibacterial Activity of Terminalia sericea Root Bark through a Metabolomic Approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, L.K.; Kellogg, J.J.; Kvalheim, O.M.; Cech, N.B. Opportunities and Limitations for Untargeted Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics to Identify Biologically Active Constituents in Complex Natural Product Mixtures. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, L.M.; Shomron, N. AI/ML-Driven Advances in Untargeted Metabolomics and Exposomics for Biomedical Applications. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Singh, M.; Punetha, S.; Pradhan, S. Recent Advancement in Metabolomic Research: Applications and Limitations. In Ethnopharmacology and OMICS Advances in Medicinal Plants Volume 2; Nandave, M., Joshi, R., Upadhyay, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Jia, W.; Xie, G. A Metabolomics-Based Strategy for the Quality Control of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Shengmai Injection as a Case Study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 836179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology: The next Paradigm in Drug Discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.B.; Li, Q.Y.; Chen, Q.L.; Su, S.B. Network Pharmacology: A New Approach for Chinese Herbal Medicine Research. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 621423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-Z.; Du, Z.-Y.; Yuan, S.; Lu, M.-Q.; Xing, J.-Y.; Ma, Q.; Han, Z.-Z.; Tu, P.-F.; Jiang, Y. Comparison of Murraya exotica and Murraya paniculata by Fingerprint Analysis Coupled with Chemometrics and Network Pharmacology Methods. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhai, S.; Tan, M.; Guan, K.; Huang, Z.; Chen, C. Lonicera Rupicola Hook.f.et Thoms Flavonoids Ameliorated Dysregulated Inflammatory Responses, Intestinal Barrier, and Gut Microbiome in Ulcerative Colitis via PI3K/AKT Pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Suo, T.-C.; Yu, H.; Li, A.-P.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, C.-H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z. A New Strategy for Choosing “Q-Markers” via Network Pharmacology, Application to the Quality Control of a Chinese Medical Preparation. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.M.A.; Rahman, A.; Hossen, A.; Reza, A.S.M.A.; Islam, S.; Rashid, M.; Rafi, K.J.; Siddiqui, T.A.; Al-Noman, A.; Uddin, N. Epiphytic Acampe ochracea Orchid Relieves Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Upregulating Antioxidant Genes in in Vivo and Virtual Screening. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.-Y.; Si, N.; Li, M.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.-J.; Wei, X.-L.; Bian, B.-L.; Zhao, H.-Y. The Integrated Study on the Chemical Profiling and in Vivo Course to Explore the Bioactive Constituents and Potential Targets of Chinese Classical Formula Qingxin Lianzi Yin Decoction by UHPLC-MS and Network Pharmacology Approaches. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 272, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qu, B.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.F. A New Strategy to Investigate the Efficacy Markers Underlying the Medicinal Potentials of Orthosiphon Stamineus Benth. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 748684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xun, G.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ge, J.; Liu, F.; Qian, Q.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. An Integrated Approach for Investigating Pharmacodynamic Material Basis of Lingguizhugan Decoction in the Treatment of Heart Failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 295, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, T.; Li, Y.; Liao, M.; Zhang, H.; Hou, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, C. Prediction of quality markers of traditional Chinese medicines based on network pharmacology. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, P. A novel and comprehensive strategy for quality control in complex Chinese medicine formula using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and UHPLC-MS/MS combined with network pharmacology analysis: Take Tangshen formula as an example. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1183, 122889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Niu, L.; Yin, T.; Li, L.; Gao, S.; Yuan, D.; Hu, M. A novel strategy for screening bioavailable quality markers of traditional Chinese medicine by integrating intestinal absorption and network pharmacology: Application to Wu Ji Bai Feng Pill. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2020, 76, 153226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Hou, W.; Huang, L.; Xu, H. A New Concept on Quality Marker for Quality Assessment and Process Control of Chinese Medicines. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Hai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, C.; Liu, C.; et al. Exploring the Q-Marker of “Sweat Soaking Method” Processed Radix Wikstroemia Indica: Based on the “Effect-Toxicity-Chemicals” Study. Phytomedicine 2018, 45, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Bai, G.; Han, Y.; Xu, J.; Gong, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. The Method of Quality Marker Research and Quality Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Drug Properties and Effect Characteristics. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Ma, S.; et al. Identifying Potential Quality Markers of Xin-Su-Ning Capsules Acting on Arrhythmia by Integrating UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap, ADME Prediction and Network Target Analysis. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, D.-a.; Liu, L. Quality Transitivity and Traceability System of Herbal Medicine Products Based on Quality Markers. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Lan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Bao, B.; Yao, W.; Cao, Y.; Shan, M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. Discovery of Processing-Associated Q-Marker of Carbonized Traditional Chinese Medicine: An Integrated Strategy of Metabolomics, Systems Pharmacology and in Vivo High-Throughput Screening Model. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, M.; Deng, L.; Xie, X.; Zhang, M. Investigation on the Q-Markers of Bushen Huoxue Prescriptions for DR Treatment Based on Chemometric Methods and Spectrum-Effect Relationship. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Su, H.; Liang, Y.; Shi, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Gong, L.; Huang, Z.; Qiu, X. Screening of Quality Markers During the Processing of Reynoutria Multiflora Based on the UHPLC-Q-Exactive Plus Orbitrap MS/MS Metabolomic Method. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 695560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Zou, Z.; Fan, C.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Yao, X. The Discovery of Q-Markers of Qiliqiangxin Capsule, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure, Based on a Novel Strategy of Multi-Dimensional “Radar Chart” Mode Evaluation. Phytomedicine 2021, 82, 153443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.-Q.; Yu, B.-Y.; Liu, J.-H. Identification of Active Compound Combination Contributing to Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Xiao-Cheng-Qi Decoction via Human Intestinal Bacterial Metabolism. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Discrimination and Identification of Q-Markers Based on ‘Spider-Web’ Mode for Quality Control of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Chu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, L.; Kang, J.; Cheng, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, S. Discovery of Quality Markers for Mailuoshutong Pill Based on “Spider Web” Mode of “Content-Pharmacokinetics-Pharmacology” Network. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chau, F.T.; Chan, H.Y.; Cheung, C.Y.; Lau, T.Y.; Wei, S.; Mok, D.K.; Chan, C.O.; Liang, Y. Recent advances in the compound-oriented and pattern-oriented approaches to the quality control of herbal medicines. Chin. Med. 2008, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, C. Approaches to establish Q-markers for the quality standards of traditional Chinese medicines. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2017, 7, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidikar, C.M.; Hurkadale, P.J.; Nandanwadkar, S.M.; Hegde, H.V. A Validated Spectro Densitometric Regulatory Compliant USP-HP-TLC Protocol for Quantification of Polyphenols and Antioxidants from Polyherbal Formulations Containing Terminalia Species. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1207, 123379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, K.; Paulsamy, S. TLC and HPTLC Fingerprints of Various Secondary Metabolites in the Stem of the Traditional Medicinal Climber, Solena Amplexicaulis. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjal, S.B.; Dighe, P.R. Analysis of Herbal Drugs by HPTLC: A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2022, 10, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, I.C.F.; Ramos, R.T.d.M.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Soares, L.A.L. Chromatographic Profiles of Extractives from Leaves of Eugenia uniflora. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blainski, A.; Antonelli-Ushirobira, T.M.; Godoy, G.; Leite-Mello, E.V.S.; Mello, J.C.P. Pharmacognostic Evaluation, and Development and Validation of a HPLC-DAD Technique for Gallocatechin and Epigallocatechin in Rhizomes from Limonium Brasiliense. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtanowski, K.K.; Mroczek, T. Study of a Complex Secondary Metabolites with Potent Anti-Radical Activity by Two Dimensional TLC/HPLC Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Bioautography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1029, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, D.M.; Porzel, A.; Frolov, A.; El Seedi, H.R.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Farag, M.A. Comparative Analysis of Hibiscus Sabdariffa (Roselle) Hot and Cold Extracts in Respect to Their Potential for α-Glucosidase Inhibition. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontiveros-Rodríguez, J.C.; Serrano-Contreras, J.I.; Villagómez-Ibarra, J.R.; García-Gutiérrez, H.A.; Gerardo Zepeda-Vallejo, L. A Semi-Targeted NMR-Based Chemical Profiling of Retail Samples of Mexican Gordolobo. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 212, 114651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Yoshitomi, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hakamatsuka, T.; Uchiyama, N. 13C-NMR-Based Metabolic Fingerprinting of Citrus-Type Crude Drugs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 161, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaei, A.; Saeed, M.A.A.; Hamil, M.S.R.; Ismail, Z. Application of High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Techniques for Evaluating the Stability of Orthosiphon Aristatus Ethanolic Extract and Its Nano Liposomes. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wu, Q.W.; Li, L.L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.F.; Ma, X.J.; Shu, J.; Zhang, K.; Ma, D.M. Determination of Quality Markers for Quality Control of Zanthoxylum Nitidum Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with near Infrared Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, D.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, G.; Guo, P. Electrochemical-Based Quantitative Fingerprint Evaluation Strategy Combined with Multi-Markers Assay by Monolinear Method for Quality Control of Herbal Medicine. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wang, L.; Ding, X.-Y.; Shen, Y.-J.; Hao, S.-H.; Li, W.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, T.; Zhan, Z.-L.; Zheng, Y.-G.; et al. Validation of Sennae Folium Specification Grade Classification Based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Spectrum-Effect Relationship. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Kong, J.; Yue, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Application of UHPLC-Q-TOF MS Based Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Variation and Correlation amongst Different Tissues of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-C.; Bhat, S.M.; Lee, C.-W.; Shiea, J. Thin Layer Chromatography Combined with Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Characterizing Herbal Compounds. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 434, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, A.; Agapouda, A.; Frommenwiler, D.A.; Scotti, F.; Reich, E.; Heinrich, M. St John’s Wort (Hypericum Perforatum) Products—An Assessment of Their Authenticity and Quality. Phytomedicine 2018, 40, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommenwiler, D.A.; Booker, A.; Vila, R.; Heinrich, M.; Reich, E.; Cañigueral, S. Comprehensive HPTLC Fingerprinting as a Tool for a Simplified Analysis of Purity of Ginkgo Products. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosch, L.; Santos, K.C.d.; Imig, D.C.; Santos, C.A.M. Comparative Study of Passiflora Taxa Leaves: II. A Chromatographic Profile. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhana, N.; Lohidasan, S.; Mahadik, K.R. Marker-Based Standardization and Investigation of Nutraceutical Potential of Indian Propolis. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 15, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.A.; Mothana, R.A.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Alam, P.; Yousaf, M.; Ahmed, S.; Alatar, A. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Based Concurrent Estimation of Biomarkers Ent-Phyllanthidine and Rutin in the Dried Aerial Parts of Flueggea Virosa. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Lawrence, K.; Singh, S.; Ercisli, S.; Choudhary, R. In-Vivo Hyperglycemic, Antioxidant, Histopathological Changes, and Simultaneous Measurement of Kaempferol Verified by High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography of Setaria italica in Streptozotocin -Induced Diabetic Rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3772–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Li, L.N.; Xu, R.; Li, F.; Gu, L.H.; Liu, H.W.; Wang, Z.T.; Yang, L. Characterization of Natural Herbal Medicines by Thin-Layer Chromatography Combined with Laser Ablation-Assisted Direct Analysis in Real-Time Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudumo, J.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Chen, W.; Viljoen, A.; Vermaak, I.; Veale, C.G.L. HPTLC Fingerprinting of Croton Gratissimus Leaf Extract with Preparative HPLC-MS-Isolated Marker Compounds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 114, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, U.C.; Sahoo, A.K. In Vitro Antioxidant Assessment and a Rapid HPTLC Bioautographic Method for the Detection of Anticholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Geophila Repens. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 15, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramu, B.; Chittela, K.B. High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography and Its Role Pharmaceutical Industry: Review. Open Sci. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Frommenwiler, D.A.; Kim, J.; Yook, C.S.; Tran, T.T.T.; Cañigueral, S.; Reich, E. Comprehensive HPTLC Fingerprinting for Quality Control of an Herbal Drug—The Case of Angelica gigas Root. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobakhidze, T.; Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Gegechkori, V.I.; Chugaev, D.; Ramenskaya, G.V. Quantitative analysis of rutin in flavonoid-rich plant raw material by HPTLC. Farmaciya 2024, 73, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, K.C.; Guex, C.G.; Reginato, F.Z.; Haas da Silva, A.R.; Cassanego, G.B.; Lhamas, C.L.; Boligon, A.A.; Lopes, G.H.H.; de Freitas Bauermann, L. Safety Assessment of Morus nigra L. Leaves: Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity Studies in Wistar Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Tu, P.; et al. Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Derivatives in Longxuetongluo Capsule by HPLC-DAD-IT-TOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais Fernandes, J.; Ortiz, S.; Padilha, M.; Tavares, R.; Mandova, T.; Araújo, E.R.D.; Andrade, A.W.L.; Michel, S.; Grougnet, R.; Zucolotto, S.M. Bryophyllum Pinnatum Markers: CPC Isolation, Simultaneous Quantification by a Validated UPLC-DAD Method and Biological Evaluations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garayev, E.; Di Giorgio, C.; Herbette, G.; Mabrouki, F.; Chiffolleau, P.; Roux, D.; Sallanon, H.; Ollivier, E.; Elias, R.; Baghdikian, B. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and UHPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS Quantification of Potential Anti-Inflammatory Phenolic Compounds from Flowers of Inula montana L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 226, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibitz-Eisath, N.; Eichberger, M.; Gruber, R.; Sturm, S.; Stuppner, H. Development and Validation of a Rapid Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Diode Array Detector Method for Verbena officinalis L. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.W.; Kim, K.-A.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, S.J.; Kang, T.K.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, T.-J.; Oh, S.-R.; Jung, S.H. A Standardized Extract of Rhynchosia Volubilis Lour. Exerts a Protective Effect on Benzalkonium Chloride-Induced Mouse Dry Eye Model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 215, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Lee, K.D.; Song, C.E.; Ilavenil, S.; Srigopalram, S.; Arasu, M.V.; Choi, K.C. Quantification of Major Phenolic and Flavonoid Markers in Forage Crop Lolium Multiflorum Using HPLC-DAD. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardakci, H.; Acar, E.T.; Kırmızıbekmez, H. Simultaneous Quantification of Six Flavonoids in Four Scutellaria Taxa by HPLC-DAD Method. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.; Barroso, M.F.; De Simone, A.; Emriková, E.; Dias-Teixeira, M.; Pereira, J.P.; Chlebek, J.; Fernandes, V.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Multi-Target Neuroprotective Effects of Herbal Medicines for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 290, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.B.D.; Gomes, J.H.d.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Pádua, R.M.d.; Côrtes, S.F.; Sena, M.M.; Braga, F.C. Definition of Chemical Markers for Hancornia Speciosa Gomes by Chemometric Analysis Based on the Chemical Composition of Extracts, Their Vasorelaxant Effect and α-Glucosidase Inhibition. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 299, 115692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Du, X.; Han, L.; Lv, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y. Nuciferine and Paeoniflorin Can Be Quality Markers of Tangzhiqing Tablet, a Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, Based on the Qualitative, Quantitative and Dose-Exposure-Response Analysis. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Chattopadhaya, A.; Gupta, P.; Tiwari, H.; Singh, S.; Kumar, L.; Gautam, V. Integration of Hyphenated Techniques for Characterizing and Chemical Profiling of Natural Products. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202500234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.F.; Almeida, M.P.; Leite, M.F.; Schwaiger, S.; Stuppner, H.; Halabalaki, M.; Amaral, J.G.; David, J.M. Seasonal Variation in the Chemical Composition of Two Chemotypes of Lippia Alba. Food Chem. 2019, 273, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Siracusa, L.; Ruberto, G.; Carrubba, A.; Lazzara, S.; Speciale, A.; Cimino, F.; Saija, A.; Cristani, M. Phytochemical Profiles, Phototoxic and Antioxidant Properties of Eleven Hypericum Species—A Comparative Study. Phytochemistry 2018, 152, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Yuk, H.J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Nho, C.W.; Lee, D.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.-R. Evaluation of Phytochemicals in Agastache rugosa (Fisch. & C.A.Mey.) Kuntze at Different Growth Stages by UPLC-QTof-MS. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Silva, J.; Gomes, J.A.S.S.; Fernandes, J.M.; Moura, A.K.C.C.; Menezes, Y.A.S.S.; Santos, E.C.G.G.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Zucolotto, S.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F. Comparison of Two Jatropha Species (Euphorbiaceae) Used Popularly to Treat Snakebites in Northeastern Brazil: Chemical Profile, Inhibitory Activity against Bothrops Erythromelas Venom and Antibacterial Activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, R.; Gupta, M.; Ahmad, F.; Rout, P.K.; Misra, L.; Patwardhan, A.; Vasudeva, R. Extraction, Quantification and Antioxidant Activities of Flavonoids, Polyphenols and Pinitol from Wild and Cultivated Saraca Asoca Bark Using RP-HPLC-PDA-RI Method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 103, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, A.C.; Borges, M.S.; Mannochio-Russo, H.; Heredia-Vieira, S.C.; Campaner dos Santos, L.; Rinaldo, D.; Vilegas, W. Green Chromatography as a Novel Alternative for the Quality Control of Serjania marginata Casar. Leaves. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilepić, K.H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Mihaljević, S.; Li, S.P. Flavonoids in Natural and Tissue Cultured Materials of Epimedium Alpinum Identified by Using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 434, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Yu, J.-Q.; Duan, J.-A. Comparative Analysis of Twenty-Five Compounds in Different Parts of Astragalus membranaceus Var. mongholicus and Astragalus membranaceus by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, B. Quantitative Determination of Multi-Class Bioactive Constituents for Quality Control of Yiqi Jiangzhi Granules. Chin. Herb. Med. 2022, 14, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Long, F.; Zhang, W.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.-D.; Zhou, S.-S.; Li, S.-L. Holistic Quality Evaluation of Hibisci Mutabilis Folium by Integrating UPLC–QTOF–MS/MS Chemical Profiling and UPLC–TQ–MS/MS Quantification Approaches. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 218, 114869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.S.; Shin, H.K. Simultaneous Analysis for Quality Control of Traditional Herbal Medicine, Gungha-Tang, Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, V.; Parisi, V.; D’Ambola, M.; Sinisgalli, C.; Monne, M.; Milella, L.; Russo, R.; Severino, L.; Braca, A.; De Tommasi, N. Chemical Profiling of Astragalus membranaceus Roots (Fish.) Bunge Herbal Preparation and Evaluation of Its Bioactivity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liao, J.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y. An Ultra-Robust Fingerprinting Method for Quality Assessment of Traditional Chinese Medicine Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.G.; Leme, G.M.; Cavalheiro, A.J.; Funari, C.S. Online Extraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography Analysis (OLE-LC): Eliminating Traditional Sample Preparation Steps in the Investigation of Solid Complex Matrices. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8421–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Tong, X.; Shi, S.; Guo, K. Rapid Discrimination and Quantification of Isomeric Flavonoid-O-Diglycosides in Citrus paradisi Cv. Changshanhuyou by Online Extraction–Quadrupole Time-of Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 165, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lin, H.; Shang, E.-X.; Tang, Y.-P.; Yue, S.-J.; Jin, Y.; Tao, W.-W.; Li, S.-P.; Hua, Y.-Q.; et al. Hierarchical Identification of Bioactive Components in a Medicinal Herb by Preparative High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Selective Knock-out Strategy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 135, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrayanto, G. Recent Development of Quality Control Methods for Herbal Derived Drug Preparations. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczak, A.M.; Zovko-Končić, M.; Tomczyk, M. Recent Trends in the Application of Chromatographic Techniques in the Analysis of Luteolin and Its Derivatives. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Parekh, N.; Kaur, G.; Sharma, S.; Buttar, H.S.; Chauhan, R.; Kaur, D.; Tuli, H.S.; Jairoun, A.A.; Shahwan, M. Chemometric Perspective on Herbal Medicine Evaluation: Tools, Techniques, and Trends. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmaier, M.P.; Bernart, M.W.; Brinckmann, J.A. Advanced Methodologies for the Quality Control of Herbal Supplements and Regulatory Considerations. Phytochem. Anal. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbianto, A.D.; Kim, M.; Oh, S.M.; Jang, H.-J.; Ryu, H.W.; Paik, J.-H.; Oh, S.-R.; Ahn, J. Regional comparison study of Epimedium koreanum using UHPLC-QTOF/MS-based metabolomics approach. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xie, Q.; Liang, L.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, W. An Efficient Workflow for Quality Control Marker Screening and Metabolite Discovery in Dietary Herbs by LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS and Chemometric Methods: A Case Study of Chrysanthemum Flowers. Foods 2024, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.A.; Norazhar, A.I.; Che Zain, M.S. Integrating LC-MS/MS and Molecular Networking for Advance Analysis and Comprehensive Flavonoids Annotation. J. Sep. Sci. 2025, 48, e70230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhou, Y. How to identify “Material basis-Quality markers” more accurately in Chinese herbal medicines from modern chromatography-mass spectrometry data-sets: Opportunities and challenges of chemometric tools. Chin. Herb. Med. 2020, 13, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrianidi, A. A Classification of Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Techniques for Evaluation of Chemical Composition and Quality Control of Traditional Medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and Community Curation of Mass Spectrometry Data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-R.; Li, M.-N.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; Gao, W. Rapid Characterization of Chemical Markers for Discrimination of Moutan Cortex and Its Processed Products by Direct Injection-Based Mass Spectrometry Profiling and Metabolomic Method. Phytomedicine 2018, 45, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, B.; Jiang, M.; Qi, J.; Li, X.; et al. A Multi-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography/High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Approach Combined with Computational Data Processing for the Comprehensive Characterization of the Multicomponents from Cuscuta Chinensis. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1675, 463162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yi, Y.; Li, K.; Qiao, X.; Ye, M. Comparative Bioactivity Evaluation and Chemical Profiling of Different Parts of the Medicinal Plant Glycyrrhiza uralensis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 215, 114793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Mondragón, A.; Tuenter, E.; Ortiz, O.; Sakavitsi, M.E.; Nikou, T.; Halabalaki, M.; Caballero-George, C.; Apers, S.; Pieters, L.; Foubert, K. UPLC-MS/MS-Based Molecular Networking and NMR Structural Determination for the Untargeted Phytochemical Characterization of the Fruit of Crescentia Cujete (Bignoniaceae). Phytochemistry 2020, 177, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Tao, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, J. Integrated molecular networking strategy enhance the accuracy and visualization of components identification: A case study of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Xiang, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Wu, A.; Zhang, C.; Rong, L. Structural characterization and discrimination of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis by a molecular networking strategy coupled with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2020, 34, e8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houriet, J.; Allard, P.M.; Queiroz, E.F.; Marcourt, L.; Gaudry, A.; Vallin, L.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, R.; Kuchta, K.; et al. A Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolite Profiling Workflow for Selecting Abundant Specific Markers and Their Structurally Related Multi-Component Signatures in Traditional Chinese Medicine Multi-Herb Formulae. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 578346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, X.-L.; Li, L.-F.; Dai, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D.; Li, M.-H.; Guo, X.-H.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.-C. A General Procedure for Establishing Composite Quality Evaluation Indices Based on Key Quality Attributes of Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 207, 114415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.S.; El-Banna, A.A.; Ghareeb, D.A.; El-Hosseny, M.F.; Seadawy, M.G.; Dawood, H.M. Chemical Profiling and Unraveling of Anti-COVID-19 Biomarkers of Red Sage (Lantana camara L.) Cultivars Using UPLC-MS/MS Coupled to Chemometric Analysis, in Vitro Study and Molecular Docking. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Yuan, M.; Dong, G.; Luo, P.; Yan, Z. Rapid Discrimination of Raw and Sulfur-Fumigated Smilax Glabra Based on Chemical Profiles by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, P.M.; Miranda, A.P.N.; Amorim, J.M.; Santos, L.B.; Duarte, R.C.F.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Viccini, L.F.; Faraco, A.A.G.; Graças Carvalho, M.d.; Castilho, R.O. Correlation of Chemical Composition and Anticoagulant Activity in Different Accessions of Brazilian Lippia Alba (Verbenaceae). J. Herb. Med. 2022, 34, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; Chang, W.-Q.; Zhou, J.-L.; Yin, Y.-H.; Xia, W.-R.; Liu, J.-Q.; Liu, L.-F.; Xin, G.-Z. Comparison of Three Officinal Species of Callicarpa Based on a Biochemome Profiling Strategy with UHPLC-IT-MS and Chemometrics Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaião Calixto, M.; Alves Ramos, H.; Veríssimo, L.S.; Dantas Alves, V.; Medeiros, A.C.D.; Alencar Fernandes, F.H.; Veras, G. Trends and Application of Chemometric Pattern Recognition Techniques in Medicinal Plants Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 53, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Rawar, E.A.; Sudevi, S.; Nurrulhidayah, A.F.; Windarsih, A. The use of chemometrics in combination with molecular spectroscopic and chromatographic methods for authentication of Curcuma species: A Review. Food Res. 2020, 4, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebiai, A.; Hemmami, H.; Zeghoud, S.; Ben Seghir, B.; Kouadri, I.; Eddine, L.S.; Elboughdiri, N.; Ghareba, S.; Ghernaout, D.; Abbas, N. Current Application of Chemometrics Analysis in Authentication of Natural Products: A Review. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2022, 25, 945–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).