Abstract
Rhenium metal is extensively utilized in the aerospace industry for the manufacturing of various superalloys due to its unique properties, and plays an indispensable role in the field of high technology. Rhenium resources are primarily associated with copper, molybdenum, and other metal ores. Ammonium perrhenate is predominantly derived from copper and molybdenum ore roasting flue gas scrubbers containing various impurities in the rhenium-containing contaminated acid. The complex composition of the contaminated acid renders the enrichment and purification of ammonium perrhenate more challenging, necessitating further research and development of the technology. This paper reviews the research progress in ammonium perrhenate enrichment and purification technology, encompassing chemical precipitation, adsorption, extraction, ion exchange, extraction chromatography, and recrystallization. It analyses the advantages and limitations of various methods, with the aim of providing a reference for future developments in ammonium perrhenate enrichment and purification technology. Furthermore, the paper presents a prospective view on the development of ammonium perrhenate enrichment and purification technology, focusing on the objective of obtaining more selective purification materials and more efficient purification techniques for ammonium perrhenate.
1. Introduction
Rhenium metal is extensively utilized in high-precision industries due to its unique and exceptional physicochemical properties, particularly its superior creep resistance and thermal shock resistance at elevated temperatures [1,2]. The most significant application of rhenium is in the aerospace sector for the production of various superalloys, notably the turbine blades of aero-engines and steam turbines, where it is indispensable [3]. However, the low melting and boiling point trace impurities in rhenium metal are susceptible to forming inclusion nuclei in high-temperature chemical reactions, which can serve as sources of fatigue cracks; furthermore, when trace impurity elements are inadequately controlled, deleterious phases (σ, µ phases) may precipitate, compromising the strength and toughness of the alloy [4].
Beyond its applications in the aerospace industry, rhenium can also serve as a surrogate for pertechnetate in the form of perrhenate. Technetium-99, a prominent β-decay emitter, is generated as a byproduct of the nuclear fission of 235U and the production of weapon-grade plutonium. This radionuclide presents a significant challenge in the management of legacy nuclear waste due to its exceptionally long half-life and substantial thermal neutron fission yield. In oxygenated aqueous environments, technetium predominantly exists as Tc(VII) in the form of the pertechnetate anion, TcO4−. Its notable solubility in water and limited retention in soil and natural minerals contribute to the considerable environmental mobility of TcO4−, resulting in technetium contamination in the vicinity of nuclear waste reprocessing and storage facilities [5,6]. Therefore, the perrhenate anion, ReO4−, is utilized instead.
The primary raw material for the production of rhenium metal is ammonium perrhenate, the quality of which determines the quality of rhenium metal. Currently, the extraction of ammonium perrhenate from molybdenum and copper concentrates represents the most prevalent method of rhenium extraction. The principal raw materials for extraction are derived from the soot leach solution and flue gas leaching system of copper smelters, as well as the molybdenum concentrate roasting flue gas leaching system of contaminated acid [7,8]. Copper and molybdenum ores generate substantial quantities of highly volatile Re2O7 through oxidative roasting [9,10]. The majority of this Re2O7 is collected with SO2 flue gas, while a minor portion forms particles that settle and subsequently exist in the waste acid as rhenic acid (HReO4) following the wet scrubbing process (as in Equation (1)) at a concentration of approximately 5–70 mg·L−l [11].
The rhenium content in copper and molybdenum concentrates exhibits significant variability, and the impurities present are diverse in nature. Consequently, the refining processes employed vary considerably, resulting in substantial differences in the direction and distribution of rhenium in the primary rhenium product. In the currently prevalent process, regardless of the specific methodology chosen, rhenium is initially transferred from the solid phase to the liquid phase in the form of ReO4− in solution. However, the rhenium-containing solution possesses a complex composition, characterized by high and diverse concentrations of competitive ions such as WO42− and MoO42−, and impurity ions including K+, Na+, and AsO43−. Furthermore, due to process-related factors, the rhenium concentrations span a wide range, as does the pH [12]. Therefore, to obtain high-purity ammonium perrhenate, it is imperative to investigate tainted acid solutions containing rhenium.
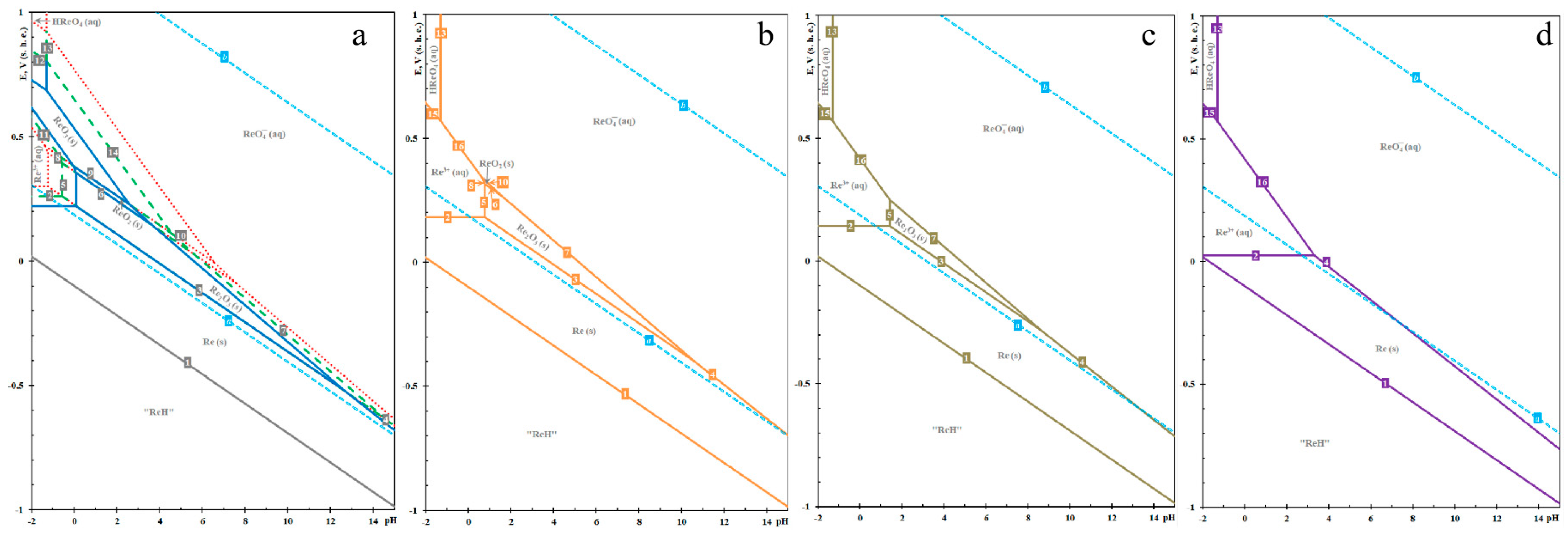
The hydrochemistry of rhenium is crucial for hydrometallurgical processes, particularly for the leaching of rhenium from rhenium-bearing ores and its subsequent purification. Nikolaychuk [13] presents the chemical equilibrium of the Re-H2O system through a Pourbaix diagram. Figure 1 illustrates the E-pH diagram of rhenium at 25 °C, 1 bar air pressure, and varying activities of the rhenium aqueous solution. The lines a and b in the diagram border the domain of electro-chemical stability of water. The thermodynamic stability of rhenium oxides is contingent upon the activity of the rhenium species in aqueous solutions. When α[Re] > 10−5 M, distinct thermodynamic stability regions existed for all rhenium oxides (Re2O3, ReO2, and ReO3). Conversely, when α[Re] < 10−5 M, these stability regions gradually diminished. Specifically, ReO3 remains stable only when α[Re] > 10−6 M, ReO2 is stable when α[Re] > 10−8 M, and Re2O3 is stable when α[Re] > 10−14 M.
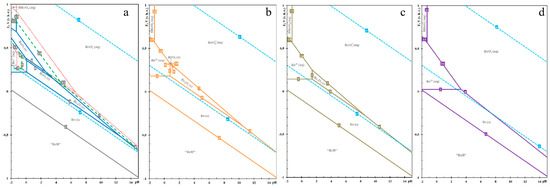
Figure 1.
E-pH diagrams of Re-H2O system at 298 K, under an atmospheric pressure of 1 bar, and varying activities of rhenium species in solution, (a) 10−2 and 10−4 M; (b) 10−6 M; (c) 10−8 M; (d) 10−14 M.
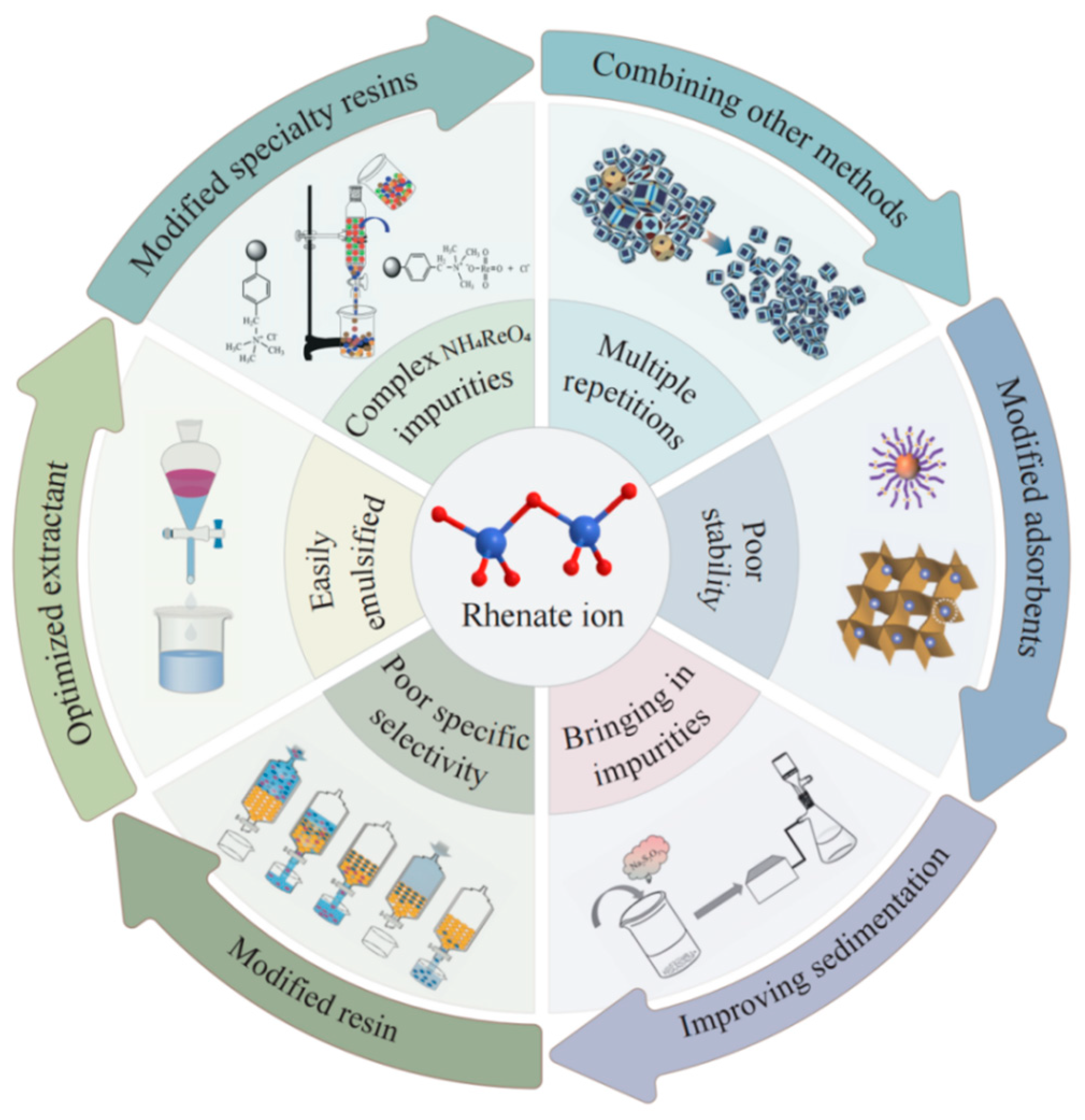
The extraction of ammonium perrhenate from copper-contaminated and molybdenum-contaminated acids primarily necessitates addressing the challenges of low solution rhenium content, high acidity of the system, multiple types of impurities, and high impurity content. The current ammonium perrhenate refining technology system exhibits a low Re and trace impurity metal separation coefficient, and the selective separation capacity requires improvement. Consequently, it is of particular importance to select a separation and purification method with high selectivity and a broad application range. This paper reviews the research progress of several enrichment and purification methods for ammonium perrhenate (chemical precipitation, adsorption, extraction, ion exchange, extraction chromatography, and recrystallisation), and summarizes their advantages and disadvantages. Figure 2 presents the logical framework diagram of this paper, wherein the circular diagram, from the inner to the outer sections, illustrates the various methods of ammonium perrhenate preparation, the challenges associated with each method, an overview of the methodologies, and the future prospects for each approach. The circular diagram depicts the issues related to various methods of preparing ammonium perrhenate, the overview of each method, and the future directions for each approach.

Figure 2.
Logical framework diagram for this paper.
2. Enrichment Methods of Ammonium Perrhenate
2.1. Extraction
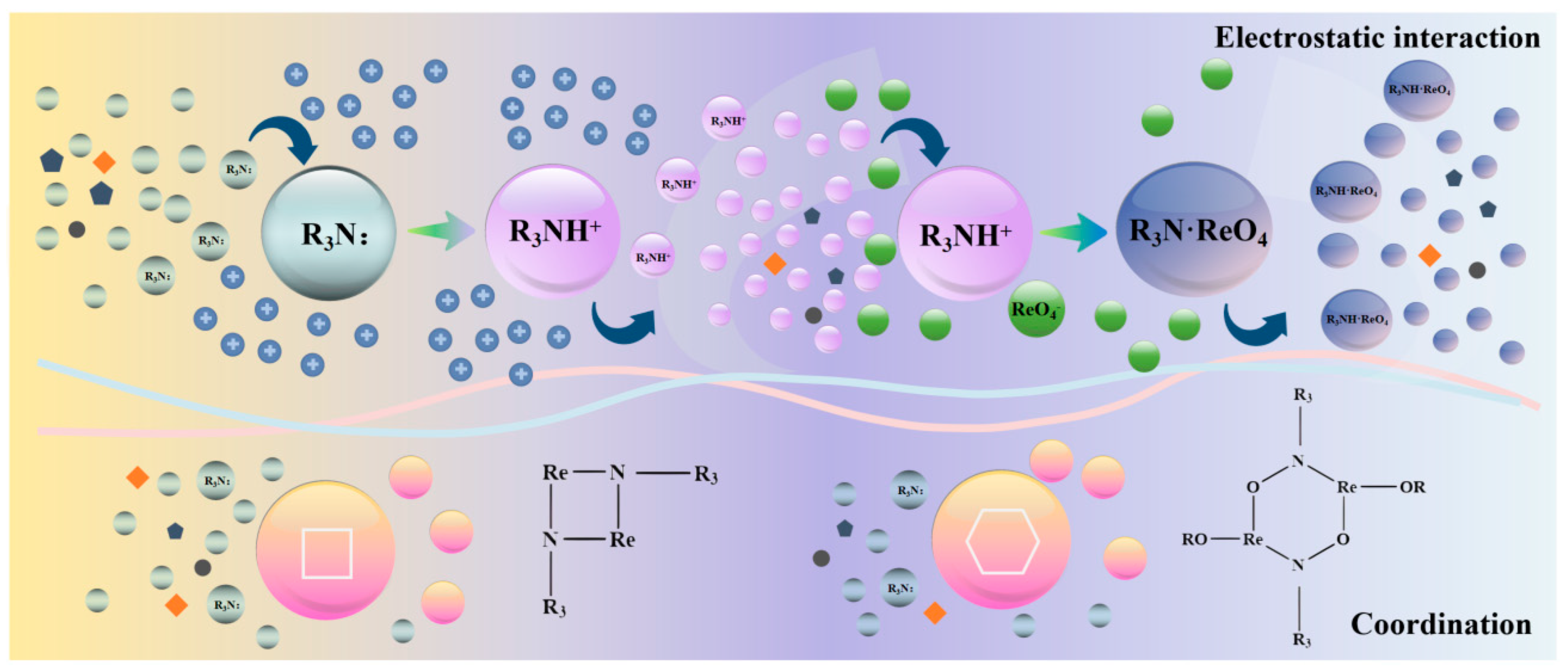
Solvent extraction involves the utilisation of solutes in two immiscible solvents with different solubility and partition coefficients, such that the solute is transferred from one solvent to another to achieve the separation purpose of the method [14]. The rhenium extraction mechanism primarily comprises ion exchange (electrostatic effect) and chelation (ligand effects). Organic amine extractants, such as those containing N atoms with a lone pair of electrons, readily interact with H+ in water under acidic conditions, resulting in a positive charge. Rhenium is predominantly present in solution in the form of perrhenate (ReO4−), and the anionic and cationic electrostatic attraction facilitates the extraction of rhenium as R3NH·ReO4 into the organic phase. According to the principle of electrostatic attraction, the greater the number of alkyl substitutions of organic amines, the stronger the electronegativity of N, and consequently, the more readily it reacts with H+ in water to form a positive charge. The lone pair of electrons on the N atom can directly coordinate with such ions to form a six- or four-membered ring, as illustrated in Figure 3 [15]. These two effects occur simultaneously in the extraction process, with varying contributions to the extraction depending on factors such as the type of extractant, structure, reaction conditions, and other parameters.

Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of extraction mechanism of rhenium [15].
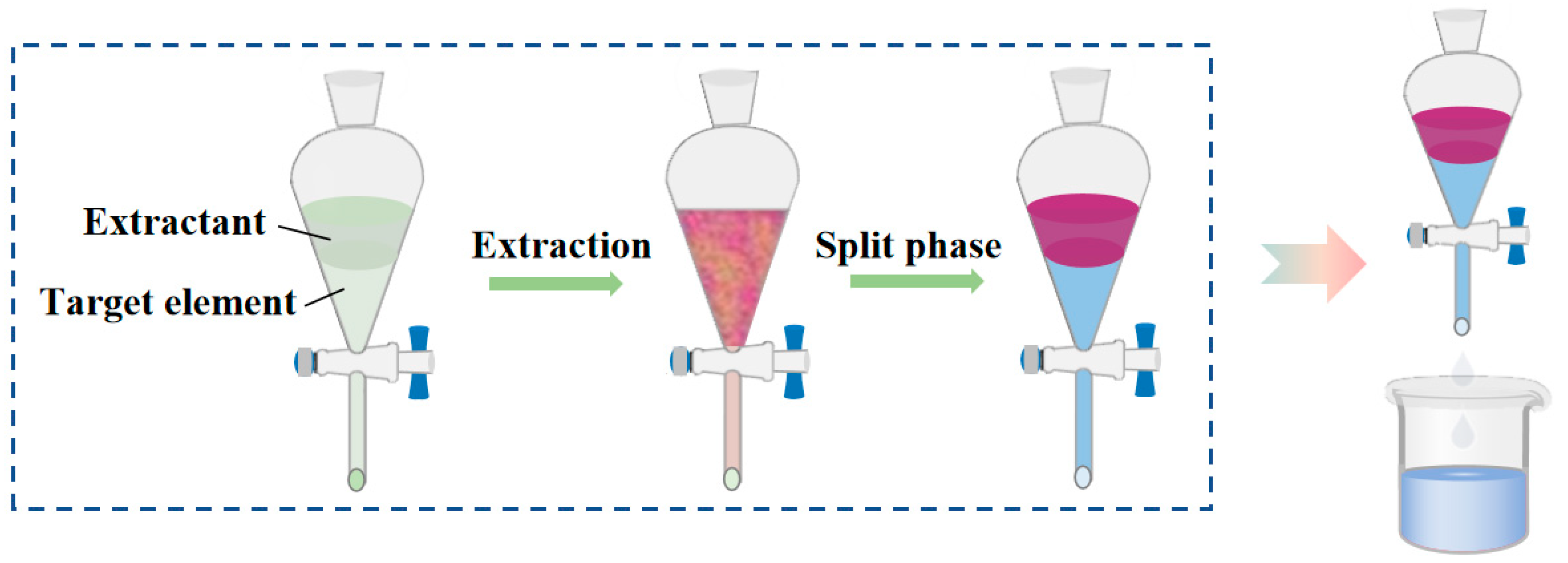
The extraction of ammonium perrhenate comprises two processes: extraction and back extraction. Initially, the extractant and ReO4− form complexes or chelates through electrostatic and ligand interactions, which are subsequently dissolved in the organic phase (e.g., kerosene, benzene, etc.), while the impurity metals (for example, Mo, Cu, and Fe, etc.) with weak binding capacities to the extractant remain in the aqueous phase. The organic phase is then separated, and the pH is adjusted utilising an alkaline solution, which disrupts the structure of the complexes or chelates, enabling ReO4− to re-enter the aqueous phase [16]. The process of solvent extraction and separation is illustrated in Figure 4. The extractant typically comprises an organic solvent with medium and long chain alkyl groups. In industrial applications, organic amine extractants are predominantly utilised for extracting ammonium perrhenate, with tributyl phosphate (TBP) and N235 (trialkyl tertiary amine) being the most commonly employed reagents.

Figure 4.
Reaction flow of extraction process [16].
Salehi et al. [17] recovered molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenum concentrate roasting soot scrubber through a two-stage solvent extraction process utilising a mixture of TBP and phosphoric acid (D2EHPA). Molybdenum was extracted with an efficiency of up to 99.8% at pH 1, whereas rhenium was co-extracted at less than 7.5%. Subsequently, the molybdenum extraction residue underwent solvent extraction, followed by the extraction of up to 99.6% rhenium in a single-stage extraction using TOA. The organic phase was then subjected to vapour stripping with 32 vol% ammonia, and further evaporation of the resulting liquid to obtain an enriched purified solution. Rhenium enrichment was achieved by adjusting the pH to 6.5–7 and precipitating ammonium perrhenate from the enriched solution, yielding a liquid containing 9.955 g·L−1 rhenium. Cao et al. [18] selectively extracted rhenium from an alkaline rhenium and molybdenum mixed solution utilising a mixture of TBP, N235, and kerosene as the extractant. Their results demonstrated that the extraction rate of rhenium was 96.8%, while that of molybdenum was only 1.7%, with the separation coefficient, βRe/Mo, reaching 1.7 × 103. Hong et al. [19] extracted rhenium from copper smelting fouling acid using a synergistic extraction system of Alamine 336 and TBP. In this process, Alamine 336 served as the primary compound binding with the anions in the leach solution, while TBP enhanced the bonding of the neutral complexes. The extraction rate achieved was 98.78%, and the loaded organic phase was subsequently back-extracted with 4 mol·L−1 ammonia. Bismuth and arsenic present in the leachate formed the insoluble compounds (BiO)2SO4 and arsenic acid, respectively.
N235 is primarily utilised for the extraction of acidic or weakly alkaline liquids. Zou et al. [20] employed N235 as an extractant, with the organic phase comprising 30 vol% N235 and 40 vol% sec-octanol-kerosene. The organic phase and water were compared to the O/A at a ratio of 1:2, and the material concentration of sulphuric acid ranged from 0.5-4.0 mo1·L−1. The extraction rates of Mo and Re were 98.5% and 97.5%, respectively, subsequent to back-extraction of Mo and Re by ion exchange resin. Following back extraction, molybdenum and rhenium were separated utilising an ion-exchange resin. Wang et al. [21] utilised N235 extractant to selectively extract rhenium from rhenium-containing molybdenum concentrate roasting flue gas drenches. The principle involves N235 combining with hydrogen ions in the solution to form complex cations, and with anions in the solution to pair, forming a stable extract in the organic phase. Impurities in the solution, such as copper and lead, remain as cations in the solution and cannot be extracted by N235, thus achieving selective separation. The reaction equation is shown in Equation (2). Experimental results indicate that the optimal extraction conditions are as follows: sulphuric acid concentration in the solution is 2.5 mol·L−1, the volume ratio of the organic phase to the aqueous phase is 1:4, and the organic phase composition is 3 vol% N235, 30 vol% sec-octanol, and 65 vol% kerosene. The extraction rate of rhenium in the single-stage countercurrent extraction is 90.64%, and the comprehensive recovery of rhenium in the extraction section is approximately 96%.
Table 1 presents the applications of rhenium extractants and their comparisons in the relevant references. As one of the primary industrial techniques for the preparation of ammonium perrhenate, the extraction method offers several advantages, including high selectivity, process simplicity, a high degree of automation, and the capability to concentrate rhenium directly from contaminated acid solutions. However, the current industrial applications of the extraction method face certain challenges. The impurity composition in contaminated acid systems is complex, and the extraction process is susceptible to emulsification and the formation of a third phase. The practical production of rhenium from contaminated acid containing rhenium necessitates a very low rhenium concentration compared to the large quantities of organic reagents consumed, which also increases, resulting in environmental pollution. The solvent extraction process imposes strict pH requirements on the solution, necessitating significant pH adjustment of the contaminated acid in actual production, which requires substantial quantities of acids and bases.

Table 1.
Separation and purification of ammonium perrhenate by extraction method.
2.2. Ion Exchange
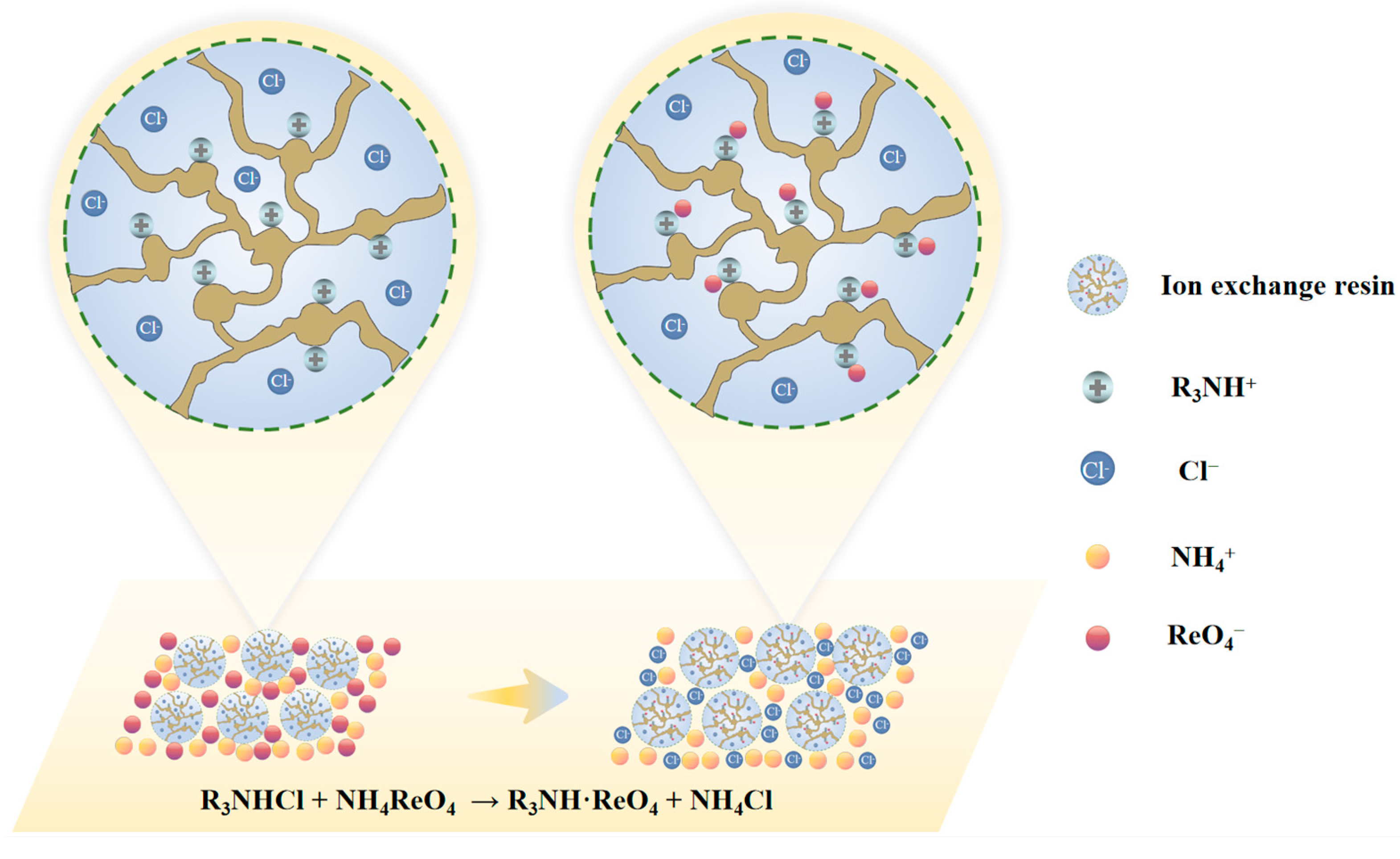
Ion exchange resins are polymeric compounds with functional groups that are insoluble in various organic solvents, such as acids and bases, and are structurally porous solid polymeric substances that neither dissolve nor melt [22,23]. Each resin particle comprises a crosslinked three-dimensional structural network skeleton to which numerous movable functional groups are attached. These functional groups can dissociate the exchange ions with charges opposite to those of the surrounding foreign ions, thereby enabling selective adsorption of ReO4− on the resin. The reaction mechanism is illustrated in Figure 5 [24]. Subsequently, a solution containing ReO4− was obtained by eluting the resin with a desorbent to achieve the selective separation of rhenium.

Figure 5.
Ion exchange reaction mechanism of rhenium enrichment [24].
Wu et al. [25] investigated the adsorption of D301 resin on rhenium (VII)-containing simulated solutions, and the findings indicated that the static saturated adsorption capacity in acetic acid-sodium acetate (HAc-NaAc) buffer solution at T = 25 °C, pH = 2.7, was 715 mg·g−1. Jiang et al. [26] utilised D302-II resin to concentrate rhenium in the ground-leach mining uranium leach solution. The results demonstrated that the adsorption rate of the D302-II resin was rapid, with an adsorption reaction rate constant k = 1.6 × 10−3 s−1. The adsorption rate of rhenium attained more than 95% in the dynamic experiments, with the pH ranging from 2.0 to 5.0, and the flow rate from 1 to 2 mL·min−1. The rhenium adsorption capacity of the resin was determined to be 162 mg·g−1. Zhang et al. [27] utilised D990 resin to recover rhenium from copper smelting fouling acid and investigated the effects of sulphuric acid concentration, adsorption flow rate, and adsorption time on the adsorption rate of Re and As. The findings indicated that the D990 resin exhibited strong adsorption of rhenium, with its saturated adsorption amount of rhenium being 0.1 g·g−1 dry resin, and the adsorption rate of D990 resin was 90.4% under conditions of flow rate of 4 cm·min−1 and adsorption time of 8 h. The adsorption rate of the D990 resin was 0.4% at a flow rate of 6 vol% ammonia. Desorption with 6 vol% ammonia at a flow rate of 4 cm·min−1 resulted in 97.3% desorption. Chen et al. [28] employed D296 resin from acid-containing solution, and the effects of material pH, adsorption flow rate, and material to resin volume ratio on the adsorption rate were examined through dynamic tests. The results demonstrated that the adsorption rate reached 97.91% at a reaction temperature of 25 °C, feed solution pH of 1.5, and adsorption flow rate of 7.2 BV·h−1, and the saturated adsorption capacity of the D296 resin pair was 114 mg·g−1 dry resin.
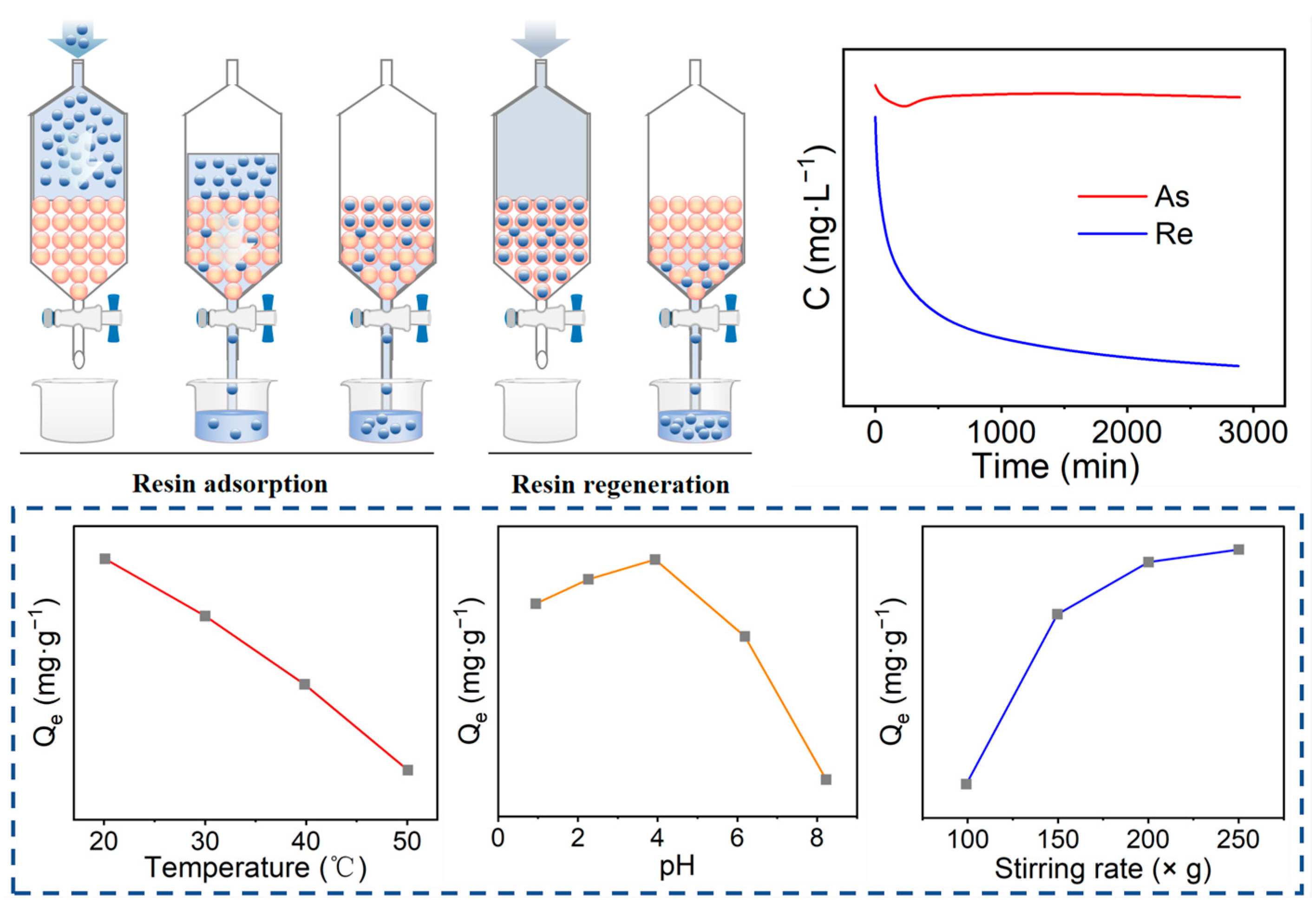
In addition to the aforementioned traditional anionic resins, macroporous anionic resins have also been utilised for the enrichment of ammonium perrhenate. Wang et al. [29] employed the macroporous anion exchange resin RCX-5143 to adsorb rhenium from copper smelting fouling acid, achieving an adsorption rate exceeding 99% at an acid concentration of 5 vol% and a flow rate of 2 BV·h−1. Zhang et al. [30] utilised a macroporous polystyrene weakly basic anion resin containing complex amine functional groups for the highly efficient extraction of rhenium from copper concentrate roasting leachate. The effects of temperature, pH, and stirring speed on the adsorption of rhenium were investigated using dynamic adsorption experiments for rhenium adsorption as illustrated in Figure 6. It is evident that the resin adsorbed rhenium most efficiently at a temperature of 20 °C, pH of 3.92, and stirring speed of 200× g, with rhenium recovered at a rate of 97.13%. Elution of the loaded resin using 2.5 vol% concentration of ammonia yielded a rhenium-enriched solution containing 1995 mg·L−1, in which the rhenium concentration was enriched by a factor of 309 compared with the original leaching solution. Furthermore, a substantial quantity of AsO43− impurity anions was present in the leaching solution, and the amount of arsenic adsorbed remained essentially constant throughout the reaction, with as demonstrating negligible adsorption onto the resin, while Re exhibited excellent kinetic properties during the adsorption process.

Figure 6.
Enrichment of rhenium by ion exchange and related parameters [30].
In addition, novel resins have been utilised for the enrichment of ammonium perrhenate. Zu et al. [31] employed γ-irradiation to initiate the grafting of 4-vinylpyridine onto polystyrene (PS) microspheres, and a novel strongly basic anion exchanger (PS-G-4 VP-IE) was synthesised by a quaternisation reaction. The maximum adsorption capacity of this resin for perrhenate (ReO4−) was 252 mg·g−1 over a wide pH range of 1.5–6. Dong et al. [32] synthesised two ionic liquid-functionalised cellulose microspheres (ILFC-NO3 and ILFC-Cl) using a radiation method. The resins exhibited optimal adsorption of Re (VII) at pH 2.37. The resins demonstrated high adsorption capacity for Re (VII) at elevated concentrations, 581 mg·g−1 for ILFC-NO3 and 552 mg·g−1 for ILFC-Cl, and rapid adsorption kinetics with an equilibrium time of 1.5 h. The adsorption-desorption experiments demonstrated that ILFC-NO3 and ILFC-Cl possessed good reusability and could be recycled four times with negligible loss of capacity. Nebeker et al. [33] investigated the dynamic adsorption of rhenium on two weakly basic ion exchange resins, Tulsion® CR-75 and Purolite® A170. The bed volume (BV) of the Tulsion® CR-75 resin column was 113.3 L, and the flow rate of the material solution into the exchange column was 9.4 L·min−1, equivalent to 5 BV·h−1. The concentration of rhenium in the material was 0.5–0.7 mg·L−1, and the residual concentration of rhenium in the solution obtained after resin adsorption was approximately 0.05 mg·L−1. The initial concentration of rhenium in the material solution was 0.5–0.7 mg·L−1, the residual concentration of rhenium in the solution obtained after resin adsorption was approximately 0.05 mg·L−1, and the recovery rate of rhenium in the solution was approximately 89.6%. The Purolite® A170 resin was loaded onto the column for 28.3 L, and the flow rate of the material solution into the exchange column was 3 L·min−1, corresponding to 6.4 BV·h−1. The recovery rate was approximately 91.7%. The aforementioned resins were subsequently desorbed using NaOH alkaline solution to obtain a concentration-enriched rhenium solution of approximately 1400 mg·L−1. In comparison to the initial solution, the concentration was enriched by a factor of approximately 2400.
The ion exchange method exhibits a broad spectrum of applications in rhenium research and production. Table 2 delineates the process conditions and adsorption efficiency of rhenium recovery utilising the ion exchange method as reported in relevant literature. The principal advantages of the ion-exchange method include its procedural simplicity, absence of organic solvents and organic waste liquids, and the capacity for resin regeneration and recycling. However, due to the limited number of resin regeneration cycles and adsorption capacity, its application to large-scale industrial production remains challenging.

Table 2.
Separation and purification of ammonium perrhenate by ion exchange method.
2.3. Chemical Precipitation
Chemical precipitation is a reliable method for the efficient separation of lower concentrations of metal ions [34]. The precipitation methods can be categorised into alkali precipitation [35,36], sulphide precipitation [37], and iron oxide precipitation [38]. The current chemical precipitation method employed in industry utilises sulphide precipitation to achieve rhenium enrichment, with sodium thiosulfate being the commonly used precipitating agent [39,40]. Sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) is a colourless and transparent monoclinic crystal that serves as an inexpensive and low-toxicity reducing agent. ReO4− reacts with S2O32− under acidic or neutral conditions, wherein S2O32− functions as a reductant to reduce Re (VII) to Re (IV), producing insoluble ReO2 or ReS2 precipitates. The reduction–precipitation process can be represented by Equations (3)–(5) [41].
Hong et al. [42] utilised sodium thiosulfate as a precipitating agent to recover rhenium from the acidic washing solution of copper smelting. The effects of reaction time, reaction temperature, and flocculant addition on rhenium precipitation were investigated. Particle flocculation was found to be conducive to the precipitation of metal sulphides in acidic washing solutions. Employing 0.01 wt% PAM flocculant at a temperature of 70 °C and a reaction time of approximately 30 min resulted in a rhenium recovery of 98.89%, with subsequent coagulation into flocs that were readily filtered from the solution. Wang et al. [41] employed sodium thiosulfate to precipitate rhenium and examined the effect of precipitant addition, reaction time, reaction temperature, and waste acid content on the precipitation rate. The results demonstrated that with 7.5 g·L−1 of Na2S2O3·5H2O, 0.1 mg·L−1 of PAM flocculant, a reaction temperature of 65–75 °C, and a reaction time of 15 min, followed by a period of settling, the rhenium content in the rich slag mud reached 98.89%. The precipitate subsequently coagulated into flocs that were easily filtered from the solution. The rhenium content in the rich sludge attained 1.66 wt%, with a rhenium recovery rate of 99.8%. Lu et al. [43] utilised sodium thiosulfate to precipitate rhenium and investigated the effects of sodium thiosulfate dosage, reaction time, and temperature on the precipitation rate of copper. A rhenium precipitation rate exceeding 99% was achieved under conditions of 1.15 wt% sodium thiosulfate dosage, 140 min reaction time, and 70 °C temperature. Additionally, it was observed that 0.01 wt% of alkaline precipitation promoter significantly reduced the precipitation reaction and particle aging time during the process. This addressed the challenges of rhenium nucleation and growth during precipitation, as well as the issue of re-solubilisation, thereby enhancing the overall process efficiency.
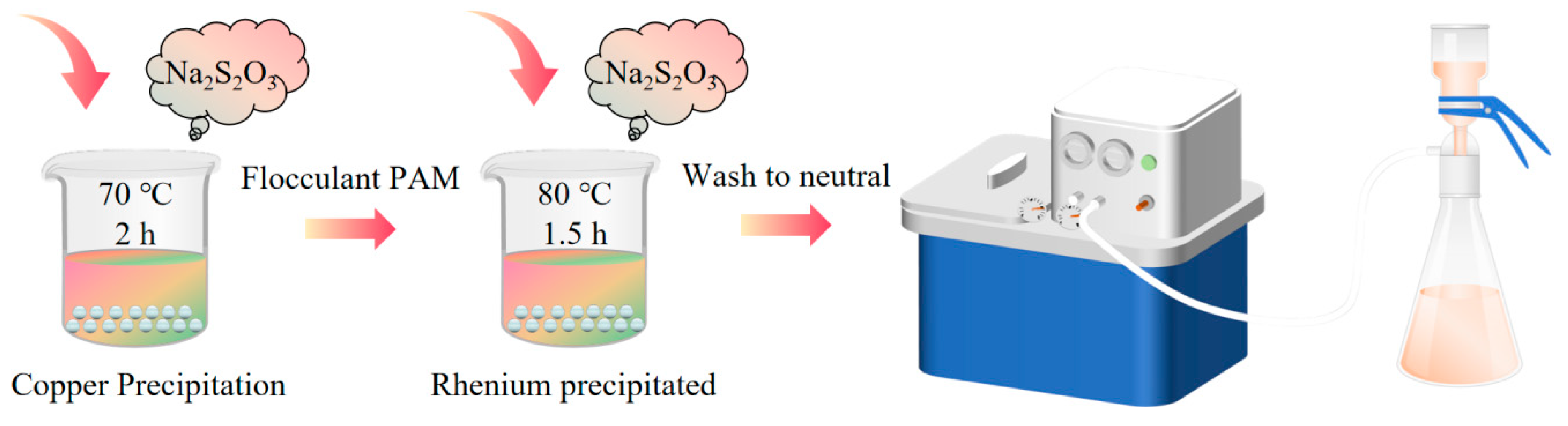
The chemical precipitation method can be more effective for the initial enrichment of rhenium from copper and molybdenum-contaminated acid solutions. However, the contaminated acid contains a wide variety of impurity elements with fluctuating concentrations of impurity ions. Consequently, the one-step sulphide precipitation of rhenium yields concentrates of low grade, which affects the subsequent separation of rhenium. To obtain higher-grade rhenium-rich slag, the process has been industrially improved with a two-step sulfidation precipitation method. Li et al. [44] utilised a two-step sulfidation precipitation method to precipitate copper and rhenium from contaminated acid. The precipitation conditions were controlled by regulating the amount of sodium thiosulfate added, giving priority to the precipitation of copper. Subsequently, additional sodium thiosulfate was introduced to precipitate the majority of rhenium in the solution, thus enriching rhenium, as illustrated in Figure 7. The experimental results demonstrate that in a water bath at 70 °C, with a reaction time of 2 h and sodium thiosulfate addition of 15.7 g·L−1, the copper precipitation rate in the system can reach 99.7%. The copper content in the decopperisation slag is 45 wt–65 wt%, and rhenium is not precipitated in this process. Subsequently, an equal amount of sodium thiosulfate was added to the post-copper removal solution, and the rhenium precipitation rate approached 100% after a 1.5 h reaction in a water bath at 80 °C.

Figure 7.
Rhenium removal by two-step sulfidation precipitation method [44].
In addition to the sulphide precipitant, other precipitants can be utilised for ammonium perrhenate precipitation. Zhang et al. [45] employed KCl to prepare potassium perrhenate by precipitating rhenium from copper smelting waste acid. The precipitation rate of rhenium in the waste acid exceeded 99% when the amount of precipitant added was 10 g·L−1, the reaction time was 1 h, and the temperature of the reaction was 60 °C.
Table 3 presents the reaction conditions and recovery rate of the ammonium perrhenate recovery process utilising the precipitation method. Chemical precipitation is a straightforward process characterised by high efficiency, stable reaction, and minimal equipment requirements, enabling rapid enrichment of rhenium from substantial quantities of contaminated acid. However, the precipitation method exhibits limited selectivity and demonstrates difficulty in mitigating the interference of other impurities (such as copper and arsenic) during the treatment of contaminated acid; the majority of the precipitant is utilised for the precipitation of impurities in the production process, resulting in a complex subsequent separation and purification process [46]. Consequently, the chemical precipitation method is limited to providing preliminary enrichment of rhenium, and for the purification of high-purity ammonium perrhenate, further purification is challenging due to the introduction of additional impurities through the chemical precipitation method.

Table 3.
Precipitation effect of each element in some literature.
2.4. Adsorption
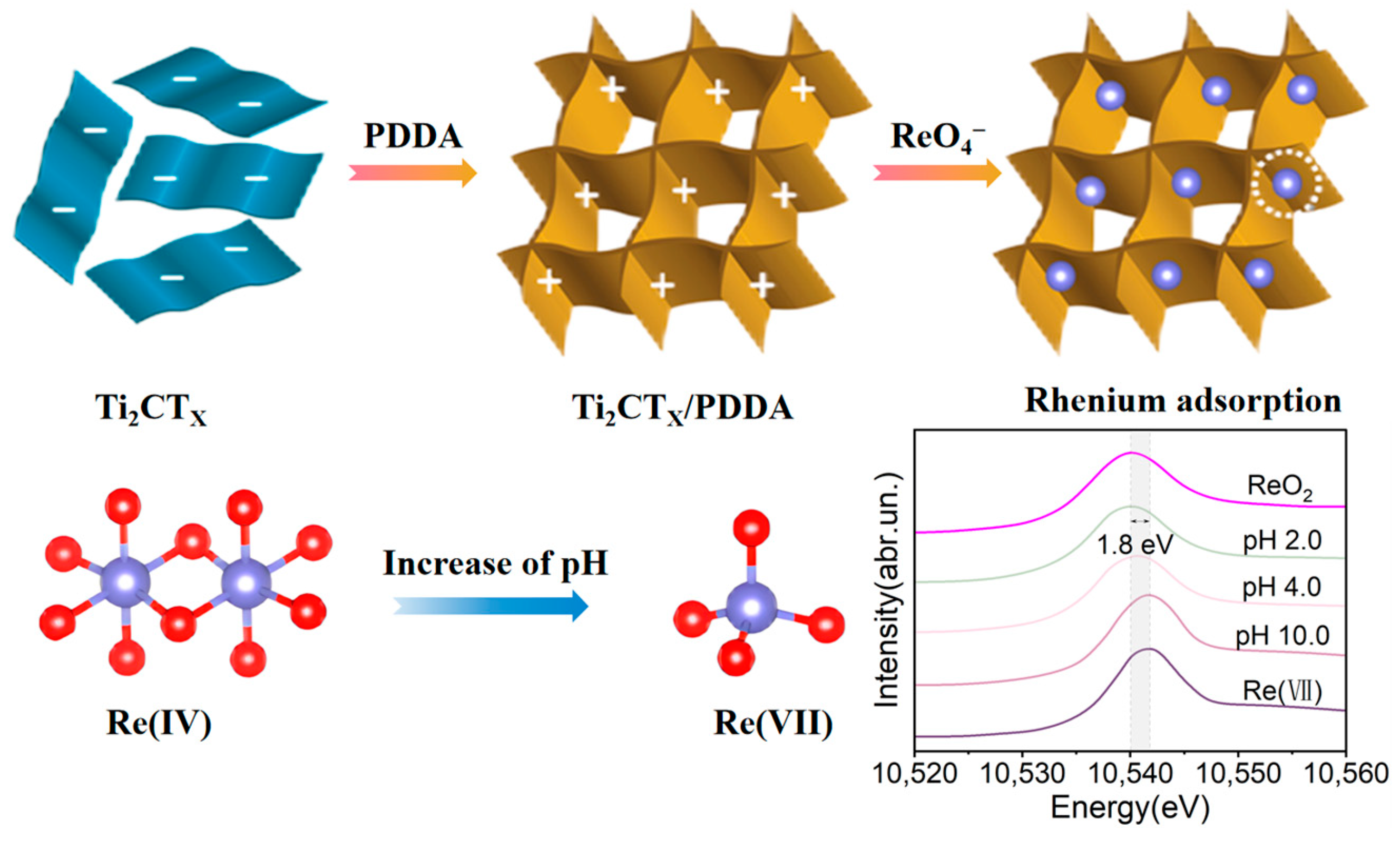
Adsorption is predominantly utilized for the removal of heavy metal ions and trace pollutants from aqueous solutions, offering advantages such as rapid adsorption rates, broad temperature ranges, and efficacy in treating dilute solutions. The adsorbent’s effectiveness is attributed to its porous structure and large specific surface area, which can be chemically modified to achieve selective adsorption of specific elements [47]. Wang et al. [48] reported a Ti2CTx/PDDA nanocomposite with a maximum adsorption capacity of 363 mg·g−1 for ReO4−, reaching reaction equilibrium within 1 h. The composite demonstrated excellent selectivity. XANES spectral analysis revealed an energy shift of 1.8 eV with increasing pH, indicating a change in the nature of the substance and the local environment gradually changes from octahedral coordinated Re (IV) to tetrahedral-coordinated Re (VII). The adsorption of rhenium on this titanium matrix composite and the associated changes with increasing pH are illustrated in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
Adsorption of rhenium on Ti2CTx/PDDA composites [48].
Zhang et al. [49] utilized NH4HCO3− modified nanoalumina to synthesize novel aminated nanosorbents for the separation and enrichment of Re (VII) ions in wastewater. The results demonstrated that the adsorption rate of Re (VII) on modified nano-Al2O3 could attain more than 94% in the pH range of 2.0–3.0, whereas the adsorption rate of unmodified nano-Al2O3 was merely 8.3%. Furthermore, they modified the nanosilica material through amination [50], which enhanced the material’s stability against acid and alkali, and employed it for the simultaneous separation and enrichment of rhenium and molybdenum, two metallic elements with similar atomic structures, in industrial wastewater. In the pH range of 1–3, ReO4− could be quantitatively adsorbed in this material up to more than 92%, while MoO42− was almost not adsorbed. In the pH range of 6–8, the adsorption rate of MoO42− was approximately 94%, whereas the adsorption rate of ReO4− was less than 10%. Consequently, the adsorbent material can be adjusted to achieve simultaneous separation of rhenium and molybdenum by modifying the pH. Shan et al. [51] successfully introduced a high density of active centres (C = N groups) on the surface of silica via a crosslinking reaction and synthesized a novel adsorbent that can be utilized for rhenium adsorption. The adsorption process of this adsorbent adhered to the Langmuir adsorption model, and the maximum adsorption of rhenium was 270.13 mg·g−1 at pH 3.0. Alfarol et al. [52] synthesized a superparamagnetic core-shell adsorbent material consisting of magnetite nanoparticles coated with a layer of silica, which can be applied for the recovery of rhenium acidic ions from acidic aqueous solutions. The produced nanoparticles were predominantly spherical with an average diameter of 14.3 ± 1.7 nm. The adsorbent nanomaterials could adsorb perrhenate with a maximum loading capacity of 19 mg·g−1 of Re. The utilization of a silica coating (MNP@SiO2) allowed the magnetite nanoparticles (MNPs) to exhibit higher resistance to highly acidic aqueous media to prevent oxidation and dissolution. The adsorption mechanism of the adsorbent on the surface of functionalized nanoparticles may be a combination of chemisorption (surface monolayer) and physisorption (diffusion or multilayer), as analysed by the adsorption kinetics of rhenium [53,54].
Activated carbon possesses a high number of fine pores and its extensive surface area can be utilized for the adsorption of rhenium. Seo et al. [55] employed an activated carbon adsorption method for a pilot adsorption test in pyromolybdenum ore leach solution. The adsorption was conducted at 20 °C, pH = 6–8 for 8 h, resulting in 14.4 mg·g−1 rhenium and 4.2 mg·g−1 molybdenum loaded charcoal. Subsequently, the loaded charcoal underwent elution, with NaOH and NH3·H2O solutions selected as eluents. The results indicated that NH3·H2O solution exhibited superior elution compared to NaOH solution, yielding 2.8–3.2 g·L−1 rhenium when eluted with 1 mol·L−1 NH3·H2O at 95 °C for 4 h. Kolczyk et al. [56] investigated carbon adsorbents for the recovery of rhenium and molybdenum from highly diluted selenium (VI) containing electrolytes for the recovery of rhenium (VII). Activated carbon is considered a suitable adsorbent for rhenium recovery due to its high chemical and osmotic shock resistance compared to ion exchange resins. The reaction process primarily involves physical adsorption, accompanied by the reduction of Re (VII) to Re (VI). Post-adsorption, Re (VII) in the solution remained in a stable state. Hu et al. [57] synthesized a novel copper-coated biochar composite using bamboo shoot shells for the adsorption of rhenium in acidic solutions. The bamboo shoot shells, obtained from the market, were dried, ground, and thermally decomposed at 500 °C to produce the original charcoal material. This material was then immersed in Cu(C2H3O2)2·H2O for 12 h, dried, and heated in a tube furnace under a nitrogen atmosphere for 4 h. After cooling, the material was repeatedly washed with deionized water and dried to obtain Cu-impregnated biochar (Cu-ASBC). Adsorption experiments revealed that the rhenium adsorption capacity of the copper-based biochar was 3–12 times higher than that of the original biochar at pH 3–6. The adsorption process aligned with the Redlich-Peterson isotherm model. The proposed adsorption mechanism involves electrostatic attraction and surface complexation. Xiong et al. [58] developed a rhenium adsorbent using diisobutylamine and diethanolamine-modified graphene oxide (GO-DEA-DIBA). Experimental results demonstrated that the saturated adsorption capacity of GO-DEA-DIBA for Re (VII) reached 140.82 mg·g−1. The adsorption mechanism is attributed to the electrostatic attraction between R3NH+ in GO-DEA-DIBA and Re (VII).
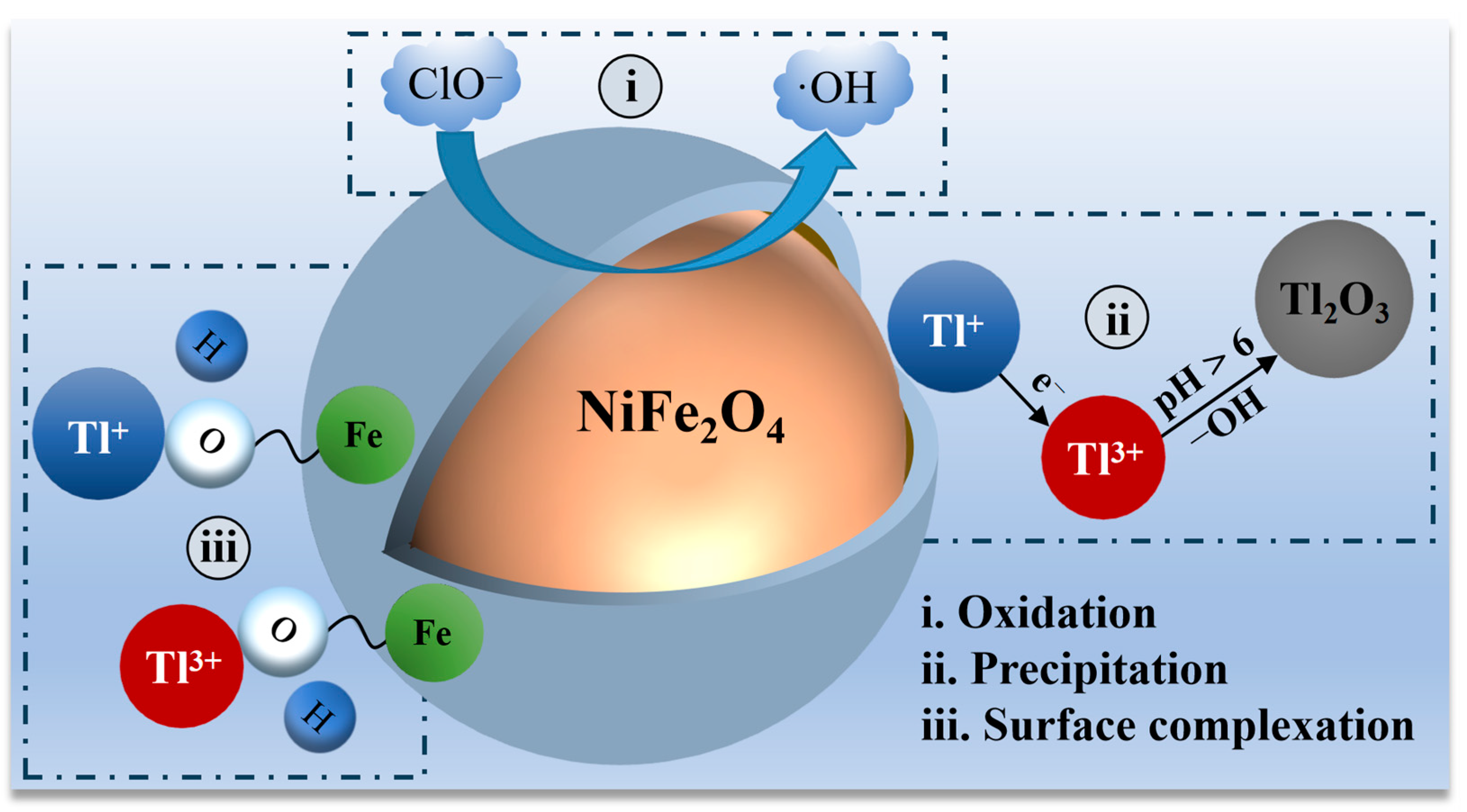
In addition to the adsorption of the anion ReO4−, as described above, adsorbents also exhibit a wide range of applications in the adsorptive removal of cations, which is pertinent to the future removal of impurity cations from ammonium perrhenate. Li et al. [59] synthesized a magnetic carbon-coated nickel ferrite composite (NiFe2O4@C) in conjunction with hypochlorite for the adsorption of thallium from wastewater utilizing a hydrothermal method. The maximum removal of Tl(I) was 1699 mg·g−1 at pH 10. The removal of Tl by the NiFe2O4@C/NaClO system was a complex process involving oxidation, precipitation, and adsorption. Initially, the NiFe2O4@C composite catalysed the decomposition of ClO− and the formation of free radicals, which enhanced the oxidizability of the NiFe2O4@C/NaClO system. Subsequently, Tl (I) was oxidized to Tl (III) and converted to Tl(OH)3 precipitate, which was dehydrated and then transformed to Tl2O3 precipitate, as shown in Equations (6) and (7). Finally, the remaining Tl (I)/Tl (III) cations were adsorbed on the surface of the NiFe2O4@C composite, replacing the H+ of the surface −OH. Figure 9 illustrates the modelling of Tl removal by NiFe2O4@C/NaClO, as described above.

Figure 9.
Schematic representation of Tl(I) removal by NiFe2O4@C/NaClO system [59].
Table 4 delineates the applicable conditions and adsorption effects of various adsorbents utilized for ammonium perrhenate. The extraction of ammonium perrhenate through adsorption is characterized by its simplicity, brevity, and robust adsorption capacity for large perrhenate molecules. However, the process is hindered by several factors: the complexity of adsorbent preparation, high associated costs, substantial adsorbent consumption, challenges in adsorbent cycle regeneration, and poor stability. These limitations impede the reusability of the adsorbents, consequently restricting their widespread adoption in the rhenium industry.

Table 4.
Adsorbents and their effects on rhenium adsorption in selected literature.
3. Purification Methods of Ammonium Perrhenate
The low purity of ammonium perrhenate obtained from molybdenum, copper concentrates, and other enrichment sources presents challenges in the subsequent production of rhenium metal, making it difficult to meet the requirements of high-precision industries. Traditional methods of extracting rhenium from copper, molybdenum, tungsten, and other impurities through enrichment processes are characterized by simplicity, high efficiency, and low equipment requirements. These methods enable rapid enrichment of rhenium from large quantities of contaminated acid. However, the selectivity of these enrichment methods is limited during the extraction of rhenium, resulting in the co-extraction of arsenic anions and metal cations such as thallium, potassium, and sodium. This leads to difficulties in the purification of rhenium. Consequently, to obtain high-purity ammonium perrhenate, further purification of the enriched ammonium perrhenate is necessary. The primary methods applied for the purification of ammonium perrhenate include extraction, ion exchange, extraction chromatography, and recrystallization.
3.1. Extraction
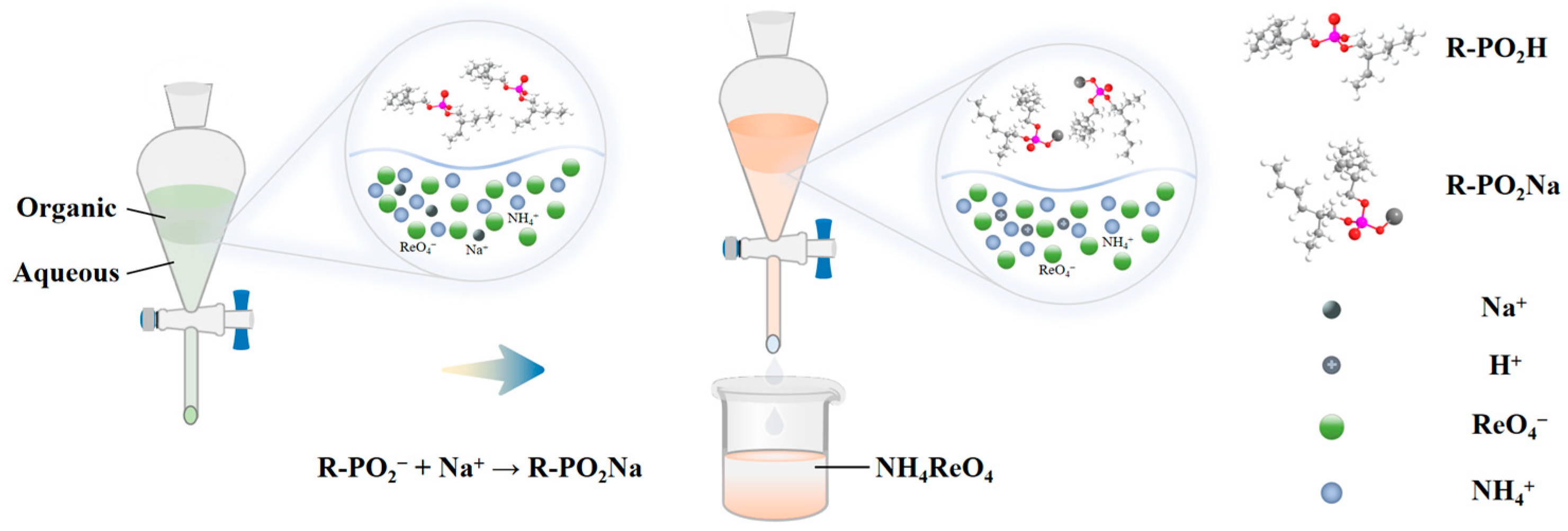
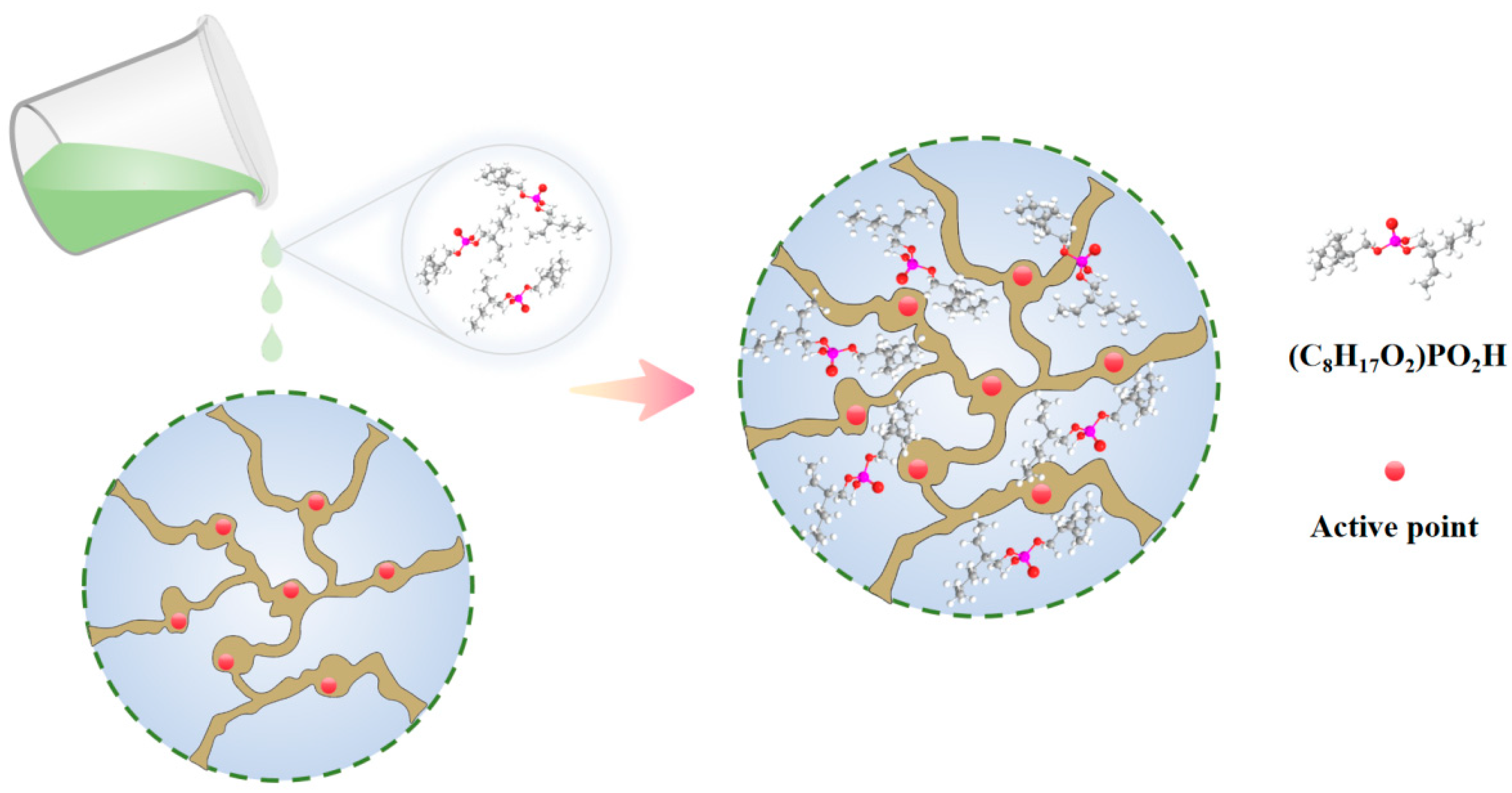
Ammonium perrhenate purification extraction is primarily categorised into two methods: the first involves the extraction agent solely extracting ammonium perrhenate from the aqueous phase to the organic phase, followed by back-extraction, the mechanism of which has been summarised in the previous content on enrichment; the second method entails the extracting agent exclusively extracting impurity ions into the organic phase, while the ammonium perrhenate remains in the original aqueous phase. Compared to the first method of extracting rhenium, the second method of extracting impurity elements results in an increased concentration of the target element. Although the content of impurity elements in the enriched solution of ammonium perrhenate is minimal, which necessitates a smaller quantity of extractant, this method demonstrates significant potential for industrial applications [60,61,62,63,64]. Utilising bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate containing phosphate groups as an extractant for the adsorption of sodium exemplifies this process, with the reaction mechanism illustrated in Figure 10.

Figure 10.
Purification mechanism of ammonium perrhenate extraction [64].
Fang et al. [65] utilised N235 extractant to extract rhenium from hydrochloric acid medium. The organic phase was prepared by dissolving N235 in (C5mim)(PF6) at room temperature. Lower temperature and ionic strength favoured the extraction, which achieved 97.07% at 25 °C. Furthermore, Fang et al. [66] investigated the extraction thermodynamics of ammonium perrhenate in a sulfuric acid system with N235 extractant, and determined that the Gibbs free energy of the rhenium extraction reaction process ΔGM0 < 0, indicating spontaneity at constant temperature and pressure. Under excess extractant N235, the extraction reaction is represented by Equation (8), where (aq) and (org) denote the aqueous and organic phases, respectively, NR3 represents the extractant N235, and H+·NR3·ReO4− signifies the extraction complex. The standard equilibrium constant K0 is expressed by Equation (9), where m denotes the molar concentration, and γ represents the activity coefficient.
Lou et al. [67] investigated the extraction kinetics of ammonium perrhenate extracted by a mixed extractant of N235 and TBP, and examined the effects of stirring rate, temperature, interfacial area, extractant concentration, and chloride concentration on the extraction rate. Their findings confirmed that the extraction of Re (VII) occurs at the liquid-liquid interface, which is governed by the kinetics of the chemical reaction. The reaction equilibrium equations for the extraction of Re and Mo using N235 are provided in Equations (10) and (11). Rhenium and molybdenum can have different partition coefficients owing to different N235 concentrations during the extraction process, causing the metal ions to form different complexes with N235 in heptane. The mass transfer process can be considered a reversible reaction [68] with respect to the metal cations, as shown in Equation (12). The kinetic process is expressed as shown in Equation (13), where kao represents the forward pseudo-primary rate constant, koa denotes the inverse pseudo-primary constant, kd signifies the distribution constant of the metal ions, Q represents the interfacial area, V denotes the volume of the aqueous phase or the organic phase, (a) indicates the aqueous phase, (o) indicates the organic phase, and (e) indicates the extraction equilibrium. Furthermore, the addition of TBP was found to decrease the activation energy and increase the Re (VII) extraction rate.
Rhenium exists in solution in the form of ReO4−. In addition to the aforementioned primary method of purifying ammonium perrhenate, the cations in ammonium perrhenate solution can be extracted utilising extractants such as P204 (di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid) or P507 (2-ethylhexylphosphoric acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester), whilst the ReO4− remains in the mother liquor, thus achieving the purification of ammonium perrhenate [69]. Yi et al. [70] proposed the thallium extraction of ammonium perrhenate in solution without P204, employing additive II to extract thallium from ammonium perrhenate solution. For thallium in ammonium perrhenate solution, P204 demonstrated efficacy in thallium removal when the solution environment (pH, ligand, and temperature) was not constrained. Under experimental conditions of P204 0.6 mol·L−1, Tl 3.27 mg·L−1, and O/A 1:1, the removal of Tl attained 96% within 3 min. Furthermore, Yi et al. [71] successfully extracted a 99.0% ammonium perrhenate solution containing 44 ppm of potassium using a mixture of 5 vol% P507 and 95 vol% 260# kerosene. The volume ratio of the organic phase to the ammonium perrhenate solution (O/A) was maintained at 2:1, and the extraction process was conducted over a duration of 3 min. Following the removal of potassium through phase separation, an ammonium peroxide extract was obtained. Activated carbon powder was subsequently added, and the adsorption and degreasing treatment were thoroughly agitated to produce 99.99% ammonium perchlorate. The potassium ion content was reduced to the ppb level, with a potassium removal rate exceeding 99%.
The process of purification of ammonium perrhenate by extraction is highly selective for specific ions, but the extraction process requires two steps of extraction and back-extraction, and due to the complexity of the impurity composition, it is easy to cause the formation of the third phase of emulsification, which makes the extraction process unstable, and its application to actual production requires further research.
3.2. Ion Exchange
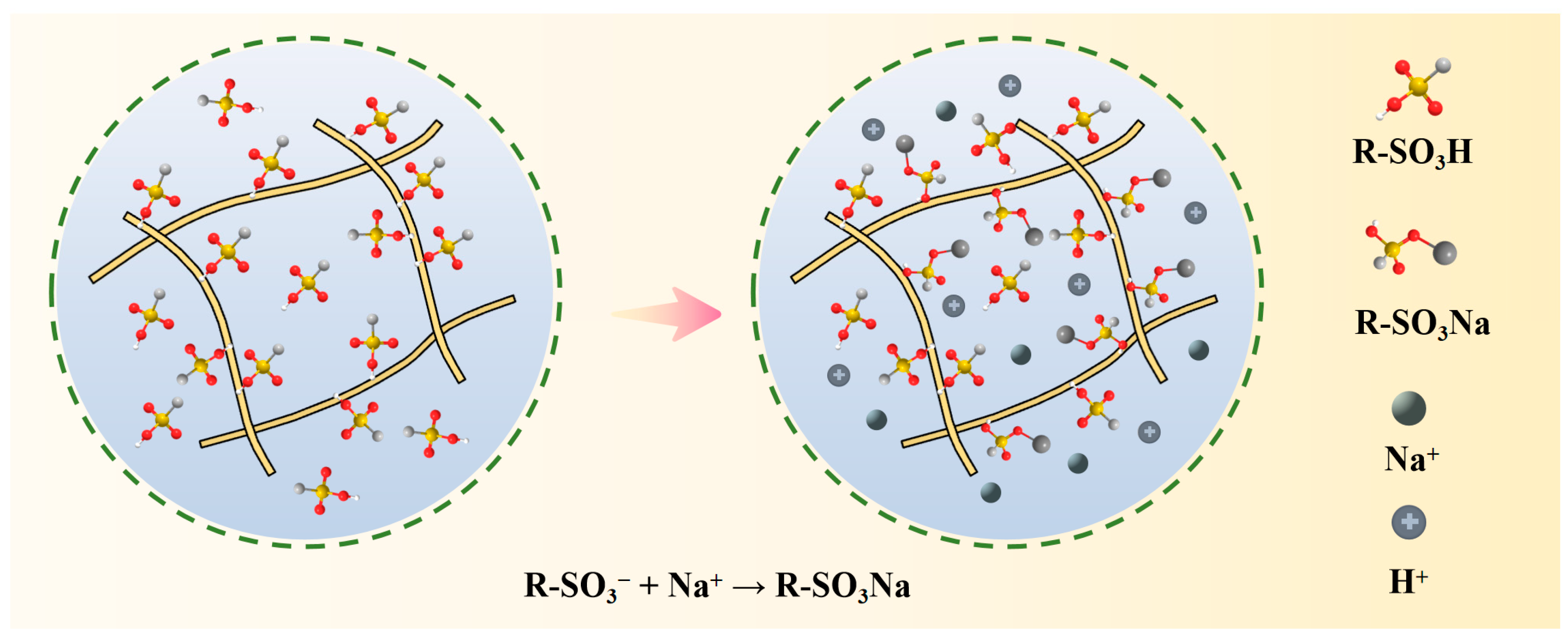
Ion exchange purification of ammonium perrhenate is primarily categorised into two methods: one involves the adsorption of ReO4− through anionic resin, followed by elution to obtain the mechanism, which has been summarised in the content of the previous enrichment; the other utilises cationic resin to adsorb impurity cations from the ammonium perrhenate solution, allowing ReO4− to remain in the original solution, and subsequently removes the adsorbed impurity ions individually to obtain high-purity ammonium perrhenate [72,73,74,75]. As an illustrative example, the reaction mechanism of sodium adsorption by an ion-exchange resin containing a sulfonic acid group is depicted in Figure 11.
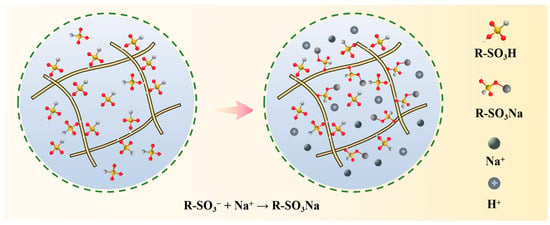
Figure 11.
Purification mechanism of ammonium perrhenate ion exchange [75].
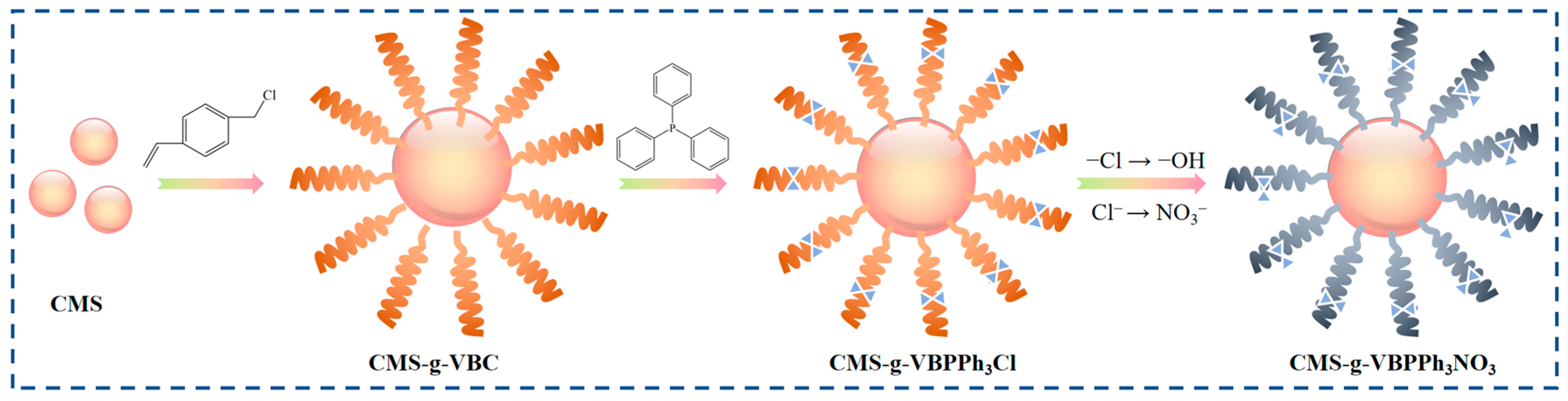
Kirillov et al. [76] conducted dynamic column experiments to isolate and purify rhenium from uranium ore leachate utilising a phosphate-containing modified anion exchange resin. The modification enabled the resin to form more complex bonds with N, which concentrated rhenium as a halide, and the exchange capacity of the novel resin was 33.2 mg·g−1. Yu et al. [77] synthesised a novel quaternary phosphorus (PPh3) modified by halogenation reaction resin for the efficient extraction of rhenium from molybdenum and uranium ores. The adsorption performance remained stable over a wide pH range, and the resin also demonstrated excellent adsorption efficiency for Re (VII) in the presence of multiple coexisting anions (NO3−, SO42− and PO43−). The synthesis pathway of the novel resin is illustrated in Figure 12. Mo (VI) and Re (VII) possess similar chemical properties and are challenging to separate due to their identical anionic form in solution and similar ionic radii. However, in the Mo/Re binary system, the resin adsorbs the least amount of Mo (VI) while effectively adsorbing Re (VII) simultaneously under highly acidic pH conditions. The resin exhibits high selective adsorption of Re and negligible adsorption of molybdenum. Furthermore, the novel resin demonstrates excellent specific selectivity for rhenium in molybdenum and uranium ore simulated leaching solutions, indicating significant potential in the rhenium purification industry.

Figure 12.
Reaction flow for extraction [77].
In the aforementioned study on the separation of ammonium perrhenate, alkaline anion resin was utilised to directly adsorb ReO4− from the target solution and subsequently desorb to obtain ammonium perrhenate. However, the ammonium perrhenate obtained through this method necessitates further desorption after adsorption is complete, and the predominant ReO4− in the ammonium perrhenate solution results in accelerated saturation of the resin. An alternative purification method involves cation exchange resin adsorption of cations from the ammonium perrhenate solution, wherein the rhenium remaining in the adsorption liquid is crystallised as ammonium perrhenate, and decontamination is performed to obtain high-purity ammonium perrhenate, which can reduce processing time and enhance the purity of ammonium perrhenate [78,79,80]. Jadbabaei et al. [81] investigated the adsorption mechanism of cationic organic compounds on cation exchange resin (CXR). The adsorption of these compounds involved polarisation, H+ acidic interaction, induced dipoles, and electrostatic interactions. Zagorodnyaya et al. [82] removed potassium from crude ammonium perrhenate solution using KU-2 cation exchange resin. The optimal flow rate for the ion exchange process was determined to be 1–2 BV·h−1, with higher flow rates resulting in increased potassium concentration in the effluent. The initial solution contained 24.6 mg·L−1 of potassium and 1.5 mg·L−1 of sodium. Following ion exchange adsorption, the concentrations were reduced to 0.307 mg·L−1 for potassium and 0.143 mg·L−1 for sodium. XRD analysis of the purified ammonium perrhenate crystals revealed single-phase NH4ReO4, with a potassium concentration in the salt of less than 0.001 wt% and no detectable sodium, meeting the standard for high-purity ammonium perrhenate. Parizi et al. [83] examined the adsorption of potassium by a strongly acidic cation exchange resin, Purolite®C100, and investigated the effects of adsorption parameters such as contact time, initial potassium concentration, and temperature on the adsorption process. The Purolite®C100 resin demonstrated high efficacy in K+ adsorption. The removal of potassium ions from the ammonium perrhenate solution increased with contact time until saturation was achieved. Furthermore, in the presence of sodium ions, their competition for adsorption sites resulted in a slight decrease in potassium adsorption capacity.
The process of purifying ammonium perrhenate via ion exchange is characterised by its simplicity and efficiency. However, the resin exhibits a limited adsorption capacity, and a high concentration of ions in the solution may result in complete resin failure, rendering regeneration unfeasible. Furthermore, the selectivity of ion exchange resin for specific ions is suboptimal, necessitating the utilisation of complementary methods to achieve comprehensive rhenium purification.
3.3. Extractive Chromatography
Extractive chromatography is a general term for copolymers with a backbone of ion-exchange resins possessing a macroporous structure and containing a selective extractant [84]. The resin utilised in the extractive chromatography method is termed extractant impregnated resin (SIR), which is produced by impregnating the extractant onto the porous material via dry or wet methods, or through the addition of modifiers. This process combines ion exchange and solvent extraction techniques. Extractive chromatography was initially applied in the field of rare earth metals, which present greater separation challenges [85,86,87,88]. The extractant-impregnated resin combines the characteristics of both liquid-phase extraction and ion-exchange separation methods and exhibits a morphology similar to that of a circular ion-exchange resin. The liquid extractant is incorporated into the skeleton of a porous polymer material, and its properties are predominantly determined by the liquid extractant contained therein [89,90,91]. A schematic representation of the synthesis of the extractant-impregnated resin using bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate as the extractant is illustrated in Figure 13.

Figure 13.
Schematic diagram of extractant impregnated resin synthesis [91].
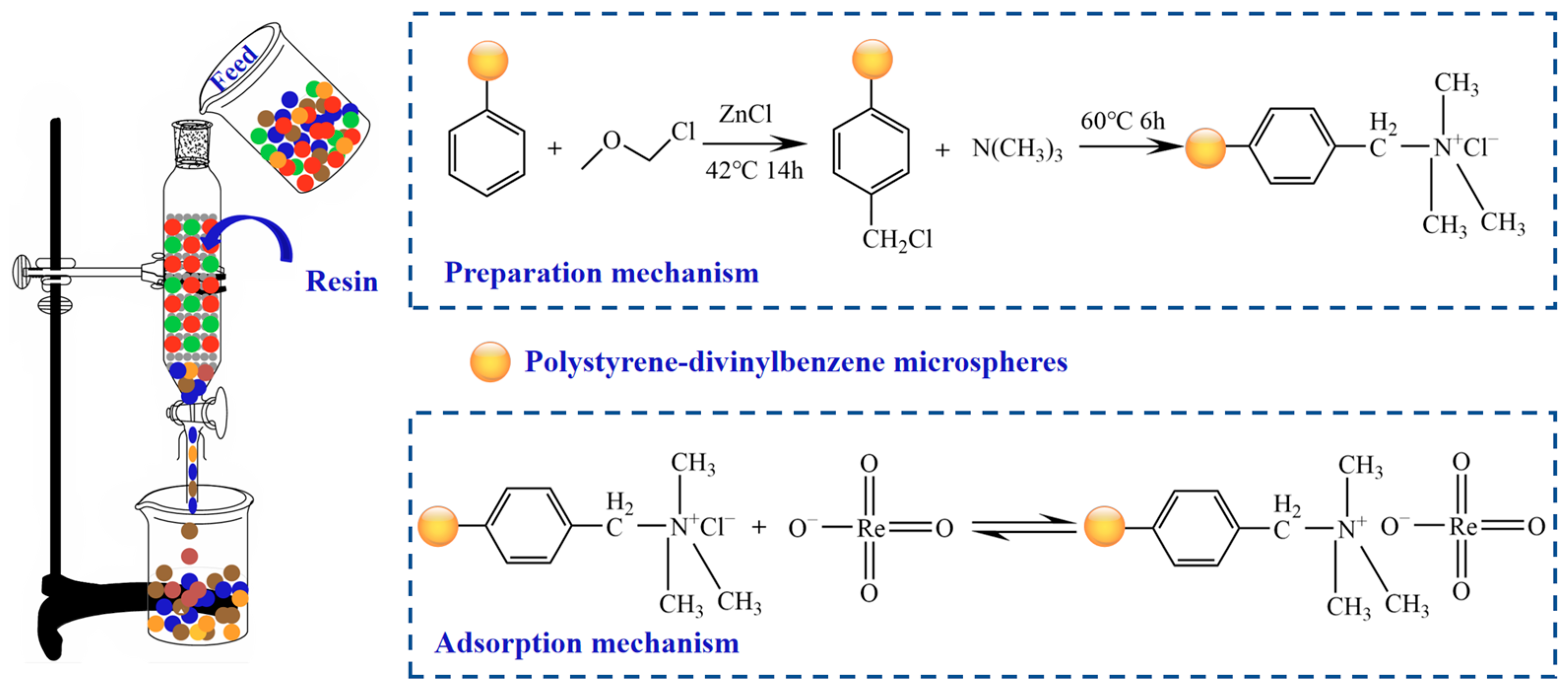
Lučanikova et al. [92] synthesised Aliquat 336-PAN (polyacrylonitrile) impregnated resin utilising the impregnation method and determined that the PAN-A336 prepared via this technique exhibited the most efficacious separation of rhenium. Moon et al. [93] impregnated Aliquat 336 (methyl tri-octylammonium chloride) into XAD-4 commercial resin to produce an extractant impregnated resin for the separation of rhenium and rhodium in nitric acid solution. The optimal loading quantity for 1 g of XAD-4 resin was approximately 0.4 g of Aliquat 336 resin. The synthesised impregnated resin demonstrated effective adsorption performance for rhenium in both single-component and multi-component systems, with the maximum adsorption capacities measured in single-component and multi-component systems being 374 mg·g−1 and 366.8 mg·g−1, respectively. Jiang et al. [94] successfully designed and synthesised a novel trialkylamine impregnation resin (L-N235) by utilising porous SiO2 powder combined with extractant N235 and subsequently condensed with cyclic resin. This resin was applied to the separation of Re and Mo. Both Mo and Re were effectively adsorbed at low acidity, precluding separation; however, the extraction rate of Re attained 70% at pH 6–8, while Mo remained unadsorbed. Liu et al. [95] synthesised an innovative strongly alkaline anion-exchange resin (LSL-1) by grafting a trimethylamine group onto polystyrene-divinylbenzene microspheres, as illustrated in Figure 14. This resin was employed for the selective recovery of ReO4− from uranium-containing wastewater. The maximum adsorption capacity of ReO4− by LSL-1 was determined to be 154.13 mg·g−1, and the adsorption process was characterised as a monolayer adsorption, predominantly governed by chemical adsorption. The adsorption mechanism was driven by anion-exchange, facilitated by the binding of ReO4− to quaternary amine groups via N-O bonds.

Figure 14.
Preparation and adsorption mechanism of LSL-1 resin on ReO4− [95,96].
In addition, extraction chromatography is widely utilised in the separation of rare earths. Saha et al. [97] employed an impregnated resin synthesised with the extractant Aliquat336 and Amberlite XAD-7 resin to separate Cr(VI) from solution, and Cr(VI) was effectively adsorbed at pH 6. Lee et al. [98] investigated the separation of La and impurities such as Ce, Pr, and Zn in a hydrochloric acid medium using P204 impregnated resin. By optimising conditions such as the desorption rate and bed height, 0.15 mol·L−1 hydrochloric acid completely separated La from other impurities. Furthermore, Lee et al. [99] prepared La2O3 with a purity exceeding 99.9998% from a high-concentration La solution using P204 impregnated resin.
Extractive chromatography possesses distinct advantages over alternative separation techniques, not only in terms of multistage and high efficiency but also with regard to high selectivity, effective mass transfer, and extended service life. However, the extractant-impregnated resin exhibits the issue of extractant loss during utilisation. The mitigation of extractant loss and enhancement of resin substrate strength during the operational process remain challenges to be addressed. Extraction chromatography bears operational similarities to the ion exchange method, with its mechanism of action aligning with that of the solvent extraction method. It not only offers the advantages of effective selective separation of extractants but also incorporates the operational characteristics of ion exchange resin, rendering it more straightforward in application. This technique can be employed in the purification of ammonium perrhenate and demonstrates significant industrial potential.
3.4. Recrystallization
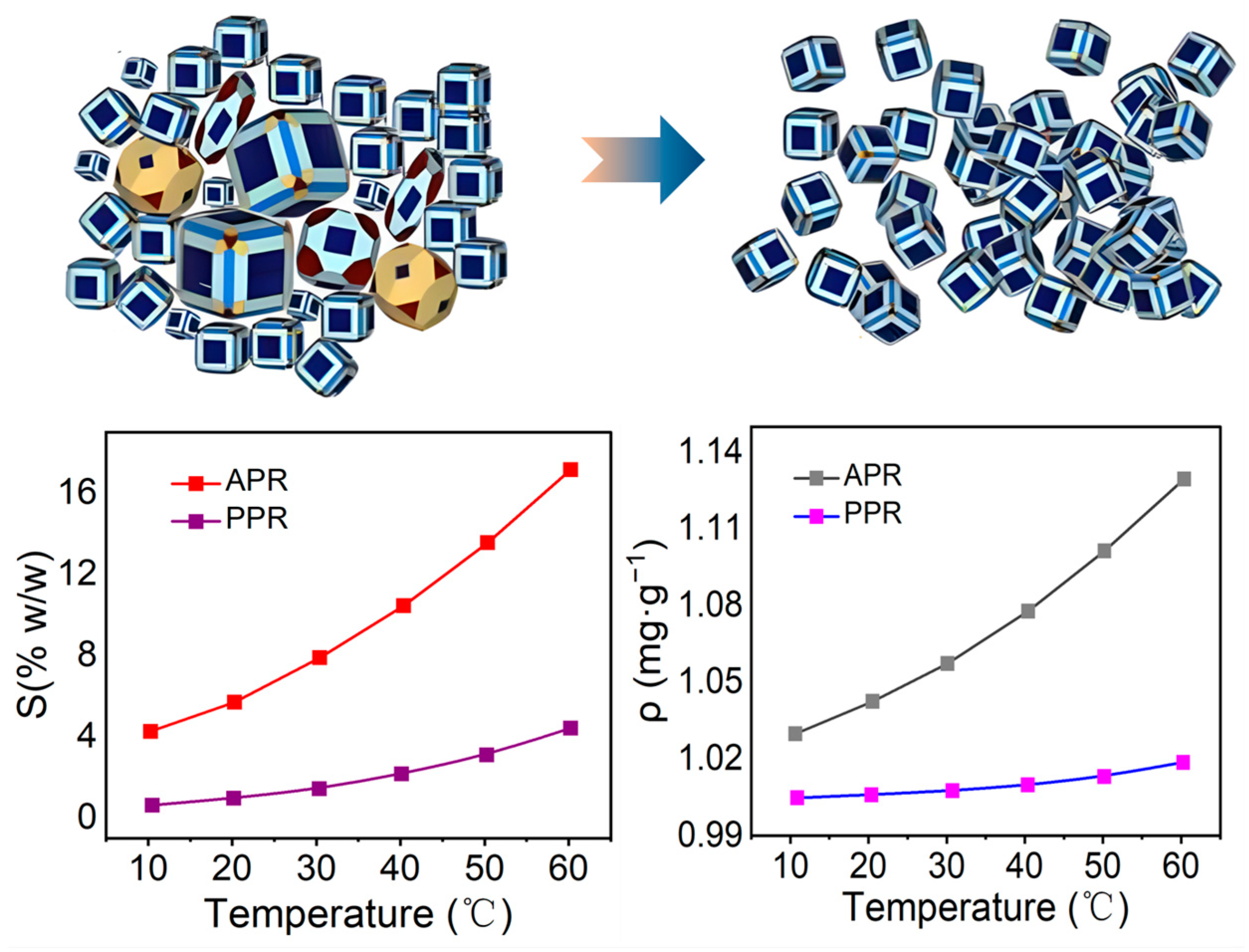
Recrystallisation is a method of precipitating ammonium perrhenate from an ammonium perrhenate solution in the form of crystals by reducing the temperature and subsequently obtaining higher-purity ammonium perrhenate products through multiple cycles of cooling and crystallisation. The recrystallisation process comprises three stages: solution supersaturation, nucleation, and crystal growth. In industrial applications, the concentration point of the ammonium perrhenate solution is typically shifted to the lower half of the metastable region by modifying the cooling rate, evaporation rate, or the quantity of reactants added, thus yielding crystals with large and uniform particles and preventing the formation of numerous new nuclei [100,101,102]. Orda et al. [103] investigated the effects of the concentration point of ammonium perrhenate in solution. The density and solubility of ammonium perrhenate (APR) NH4ReO4 and potassium perrhenate (PPR) KReO4 were examined. The solubility of this salt is significantly lower compared to that of ammonium perrhenate. Only at 60 °C was the solubility of KReO4 comparable to that of NH4ReO4 at 10 °C. Furthermore, when the saturation temperature was decreased, the change in density with temperature was minimal. A schematic diagram of the substance changes in crystallisation and the relationship between solubility, density, and temperature for APR and PPR are illustrated in Figure 15.
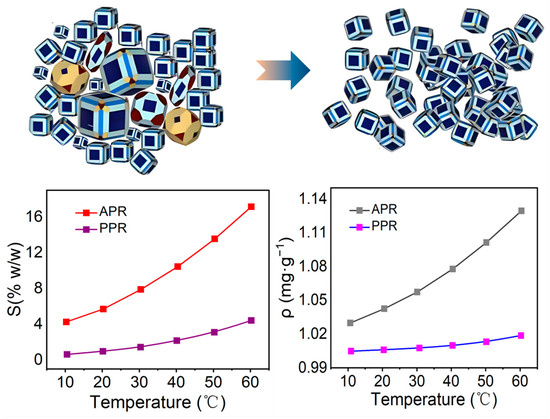
Figure 15.
Solubility and density of NH4ReO4 and KReO4 [103,104].
Liu et al. [105] developed a methodology for the preparation of ultrafine high-purity ammonium perrhenate. The rhenium content in the raw material was 68.1%, and the pH was adjusted to 8.5 through the addition of ammonia, which was subsequently adsorbed by a cation exchange resin. The process involved steam jacket heating negative pressure concentration, with a negative pressure of 0.07 MPa and a stirring speed of 100 r·min−1. The reactor jacket was cooled with cooling water to a temperature of 3 °C for discharge. High-purity ammonia was introduced into the double-layer reactor, and the ammonia was cooled to 20 °C utilising a refrigerant. The concentrated solution of high-purity rhenic acid was discharged via high-speed injection into the double-layer reactor containing high-purity ammonia at 20 °C to neutralise the reaction. High-speed centrifugation was then employed to separate the mother liquor, which was washed with ultrapure water at 3 °C, followed by constant temperature drying with hot air to obtain 4 N-grade ultrafine high-purity ammonium perrhenate.
Tang et al. [106] investigated the influence of stirring intensity on ammonium perrhenate during homogeneous recrystallisation. The recrystallisation of ammonium perrhenate is accompanied by agglomeration, and an appropriate increase in stirring intensity mitigates the effect of agglomeration and facilitates the growth rate of ammonium perrhenate crystals. However, excessive stirring intensity disrupts the equilibrium of the nucleation process, resulting in the fragmentation of generated nuclei through collision, leading to a decrease in the number of nuclei and an increase in crystal grain size, which consequently impedes optimal crystal development. At a stirring intensity of 200× g, the crystal characteristic peaks corresponding to the (101) and (112) crystal faces exhibit accelerated growth. Conversely, at a stirring intensity of 250× g, the system’s agglomeration is excessively reduced, inhibiting the growth rate of the crystal characteristic peaks corresponding to the (101) and (112) crystal faces, resulting in slow and incomplete crystal development.
Fan et al. [107] employed the square rhenium method of homogeneous recrystallisation to purify ammonium perrhenate, and investigated the effects of temperature, pH, and cooling regime on the crystallisation process. The average solubility of ammonium perrhenate was 25.3 g·(100 g)−1 at 100 °C and 4.0 g·(100 g)−1 at 0 °C. The precipitation of ammonium perrhenate crystals from the saturated rhenic acid solution was achieved through cooling. As the pH of the ammonium perrhenate solution increased, the NH4+ content in the solution also increased. When the pH reached 10, the dissolution equilibrium of ammonium perrhenate was reversed, which shortened the induction period of ammonium perrhenate crystallisation and nucleation, and resulted in the formation of ammonium perrhenate nuclei and crystal growth to attain the ideal equilibrium state. When the initial temperature of the ammonium perrhenate solution was 50 °C, the solution pH was 10, the cooling system was 50-20-10-5 °C, and the number of recrystallizations was four, ammonium perrhenate crystals with a purity of 99.99% or higher, complete grain growth, and uniform morphology were obtained.
The recrystallisation method can enhance the purity of ammonium perrhenate; however, it necessitates high-purity raw materials, requires an extended purification period, demands multiple iterations, and presents an indistinct separation boundary. Industrial applications of this method in isolation are more challenging and are frequently integrated with extraction and ion-exchange techniques as subsequent processing methods.
In summary, ammonium perrhenate enrichment in the purification method presents challenges. The chemical precipitation method exhibits poor selectivity, introducing additional impurity elements during the purification process of ammonium perrhenate. The adsorption method is characterised by high consumption, and the adsorbent demonstrates poor cyclical regeneration and stability. Consequently, chemical precipitation and adsorption methods are predominantly employed in the enrichment of ammonium perrhenate. Alternative methods that can contribute to the enrichment process of ammonium perrhenate may also be applied to its purification. The extraction method demonstrates high selectivity for ions; however, the extraction process may result in emulsification due to the complexity of impurity composition, and the procedure is intricate. Although the ion exchange method can purify ammonium perrhenate, the adsorption capacity of the ion exchange resin is limited, and it exhibits poor selectivity for specific ions. Recrystallisation in the purification of ammonium perrhenate generally requires multiple crystallisation cycles, resulting in a prolonged extraction process. The extraction chromatography method operates similarly to the ion exchange method, with a mechanism of action consistent with the solvent extraction method. This approach not only possesses the advantages of good selective separation of extractants but also features simpler operational characteristics compared to ion exchange resin. Consequently, extraction chromatography holds significant potential in the purification of ammonium perrhenate. Table 5 shows the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of ammonium perrhenate enrichment and purification techniques.

Table 5.
Advantages and disadvantages of enrichment and purification techniques for ammonium perrhenate.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the enrichment and purification of ammonium perrhenate, chemical precipitation and adsorption methods, due to their limited regeneration capacity and selectivity, introduce additional impurity elements during the purification process. These methods are commonly employed in the enrichment of ammonium perrhenate. Consequently, enhancing the selective precipitation of rhenium to obtain higher-grade rhenium-rich slag and developing low-cost adsorbent materials with strong specific adsorption of rhenium will be the primary focus of future research on precipitation and adsorption techniques.
- (2)
- Extraction and ion exchange methods demonstrate superior efficacy for the separation and purification of ammonium perrhenate. In addition to their application in rhenium enrichment, these methods are frequently employed in rhenium purification. However, the extraction process is susceptible to emulsification due to the complex composition of impurities, while ion exchange resins exhibit limited adsorption capacity and poor selectivity for specific ions. Consequently, future research directions for extraction and ion exchange methods may focus on enhancing extractant properties, improving extraction efficiency, and developing resins with higher saturation adsorption capacity.
- (3)
- Extractive chromatography possesses the advantages of both extraction and ion exchange, demonstrating significant potential for the purification of ammonium perrhenate; however, the complex impurity composition of ammonium perrhenate presents a considerable challenge in the selection and preparation of specific resins for various ammonium perrhenates. Recrystallization can enhance the purity of ammonium perrhenate; nevertheless, its efficacy as a standalone method is limited. Future research endeavours may explore the synergistic combination of extraction chromatography and recrystallization techniques applied to the purification and preparation of high-purity ammonium perrhenate, potentially yielding a more efficient process for obtaining high-purity ammonium perrhenate.
Author Contributions
H.J. (Hailong Jing): Writing—original draft, visualization, investigation. Q.Z.: Writing—review and editing, validation. H.J. (Honlin Jiang): Supervision, funding acquisition, formal analysis. Z.H.: Writing—review and editing, supervision, formal analysis. B.G.: Writing—review and editing, visualization, formal analysis. T.Z.: Supervision, funding acquisition, formal analysis, conceptualization. Y.Y.: Supervision, funding acquisition, formal analysis, conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2023YFC2907905).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Liu, E.Z.; Guan, X.R.; Zheng, Z. Effect of rhenium on solidification and segregation of nickel-based superalloy. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamei, A.F.; Anton, D.L. Rhenium additions to a Ni-base superalloy: Effects on microstructure. Metall. Trans. A 1985, 16, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Lu, F.; Cao, K.L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Su, H.J.; Liu, L. The effect of rhenium on the microstructure stability and γ/γ′ interfacial characteristics of Ni-based single crystal superalloys during long-term aging. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160114. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Lv, C. Recovery of rhenium, a strategic metal, from copper smelting effluent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulou, D. Technetium-99m radiochemistry for pharmaceutical applications. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Hao, W.; Zou, H.; Xue, W.J.; Mei, D.H.; Song, Y.H.; Yan, W.F. Highly selective removal of Technetium-99 using imidazolium-based macroporous anion exchange resins. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142951. [Google Scholar]
- Feruza, B.; Abdurassul, Z.; Alma, T.; Alimgazy, S.; Akmaral, S. Extraction of rhenium and osmium from lead technogenic raw materials of copper production. Materials 2022, 15, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Jiang, L.; Duan, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sun, X.L.; Jin, H. The sulfurization precipitation and competition mechanisms of Cu(II) and As(V) in electrolyte towards efficient recovery of copper. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 473, 143526. [Google Scholar]
- Barakan, S.; Aghazadeh, V. Rhenium extraction from pressure oxidative leaching solution of molybdenite concentrate using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121481. [Google Scholar]
- Entezari, A.; Karamoozian, M.; Eskandari Nasab, M. Investigation on selective rhenium leaching from molybdenite roasting flue dusts. J. Min. Environ. 2013, 4, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Entezari-Zarandi, A.; Azizi, D.; Nikolaychuk, P.A.; Larachi, F.; Pasquier, L.C. Selective recovery of molybdenum over rhenium from molybdenite flue dust leaching solution using PC88A extractant. Metals 2020, 10, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.Y. Recent advances of rhenium separation and enrichment in China: Industrial processes and laboratory trials. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaychuk, P.A. The potential-pH diagram for rhenium. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2022, 7, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Khopkar, S.M.; Chalmers, R.A. Solvent Extraction of Metals; Van Nostrand Reinhold: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, C.F.; Brown, K.B.; Moore, J.G.; Crouse, D.J. Solvent extraction with alkyl amines. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1958, 50, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, D.P.; Chiarizia, R.; Coleman, C.F. The kinetics of metal solvent extraction. C R C Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1980, 10, 1–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; Tavakoli, H.; Aboutalebi, M.R.; Samim, H.R. Recovery of molybdenum and rhenium in scrub liquors of fumes and dusts from roasting molybdenite concentrates. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.F.; Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.H. Solvent extraction of rhenium from molybdenum in alkaline solution. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Yang, G.; Li, L.B.; Mumford, K.A.; Stevens, G.W. Selective recovery of rhenium from industrial leach solutions by synergistic solvent extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.Q.; Zhou, Q.J. Recovery of Molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenite concentratein dexing copper ore by lime roasting-Ns extraction method. Min. Metall. Eng. 2002, 22, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.D.; Wang, S.R.; Gan, M.; Fan, X.H.; Deng, Q.; Guo, H. Selective extraction Re by N235 in eluent of flue gas. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2017, 27, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Levan, M.D.; Carta, G.; Yon, C.M. Adsorption and ion exchange. Energy 1997, 16, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Jain, S. History, introduction, and kinetics of ion exchange materials. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 957647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, S.; Kołodyńska, D. Arsenate removal on the iron oxide ion exchanger modified with neodymium (III) ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114551. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.M.; Shu, Z.N. Adsorption of rhenium (VII) with D301 resin. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 25, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.H.; Lou, M.B.; Hua, R.; Li, H.N.; Jiang, Q.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Tang, R.J.; Xu, B.; Guo, R.H.; Su, X.B.; et al. Application and Characteristics of Adsorption Rhenium with D302-II Resin. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2012, 36, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.L.; Li, W.; Ning, R.; An, L.C. Experimental study of rhenium recovery by adsorbed it from thewaste acid using D990 ion exchange. China Nonferrous Metall. 2017, 1, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.K.; Meng, H.Q.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.S.; Cao, Q.G. Study on preparation of perrhenic acid. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2017, 7, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Guo, X.Y.; Shi, X.S.; Hou, M.W. A Method of Extracting Rhenium from Fouling Acid in Copper Refining; Zhengzhou Datong Patent and Trademark Agency Co., Ltd.: Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z.G.; Cao, Y.H. Recovery of rhenium from copper leach solutions using ion exchange with weak base resins. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 173, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, J.H.; Ye, M.S.; Wang, P.Y.; Tang, F.D.; He, L.F. Design of a strong-base anion exchanger and its adsorption and elution behavior of rhenium (VII). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18868–18873. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wen, D.; Zhang, M.M.; Xie, K.J.; Hua, R.; Zhao, L. Recovery of rhenium (VII) from synthetic leaching solutions of uranium ore using ionic liquid modified cellulose microsphere adsorbents. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebeker, N.; Hiskey, J.B. Recovery of rhenium from copper leach solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 125, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, Y.J.; Chien, S.K.; Jhang, S.R.; Lin, Y.C. Chemical leaching, precipitation and solvent extraction for sequential separation of valuable metals in cathode material of spent lithium ion batteries. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Feng, X.Y.; Jin, B.J. An effective separation process of arsenic, lead, and zinc from high arsenic-containing copper smelting ashes by alkali leaching followed by sulfide precipitation. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chang, J.; Wei, Y.X.; Qiao, J.X.; Yue, X.L.; Fan, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.Y. Green and efficient recovery of tungsten from spent SCR denitration catalyst by Na2S alkali leaching and calcium precipitation. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, 2400895. [Google Scholar]
- Estay, H.; Barros, L.; Troncoso, E. Metal sulfide precipitation: Recent breakthroughs and future outlooks. Minerals 2021, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.T.; Zhang, S.J.; Ge, J.; Wei, J.S.; Christodoulatos, C.; Korfiatis, G.P.; Meng, X.G. Lead immobilization by phosphate in the presence of iron oxides: Adsorption versus precipitation. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115853. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhong, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.W. Separating lithium and magnesium in brine by aluminum-based materials. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Abisheva, Z.S.; Zagorodnyaya, A.N.; Bekturganov, N.S. Review of technologies for rhenium recovery from mineral raw materials in Kazakhstan. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Huang, J.F.; Li, W.; Liang, F.M. An experimental study of the enrichment of rhenium from copper smeltingwaste acid by the sodium thiosulfate precipitation method. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2015, 34, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.; Zheng, T.; Liu, M.B.; Mumford, K.A.; Stevens, G.W. Investigation on the recovery of rhenium in the high arsenite wash acid solution from the copper smelting process using reducing sulfide precipitation method. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105402. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.W.; Li, S.R.; Zhang, E.Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.L.; Niu, Y.S. Study on enrichment technology of rhenium in wasteacid from copper smelting. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2020, 4, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Separation of copper and rhenium from copper smelting waste acid by chemical precipitation. Hydrometall. China 2016, 35, 440–443. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhong, S.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, J.E. Study on potassium perrhenate preparation by rhenium extraction from copper smelting waste-acid. China Acad. J. Electron. Publ. House 2018, 1, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, H.; Yonezato, Y.; Ito, K. Recovery of platinum and rhenium using selective precipitation induced by two-stage photochemical treatment. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 211, 105883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Kinetics of adsorption of metal ions on inorganic materials: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 162, 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Song, H.; Yuan, L.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, P.; Gibson, J.K.; Zheng, L.R.; Wang, H.Q.; Chai, Z.F.; Shi, W.Q. Effective removal of anionic Re (VII) by surface-modified Ti2CTx MXene nanocomposites: Implications for Tc (VII) sequestration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3739–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.Q.; Xu, T.C.; Yang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Jin, H.J. Sorption characteristics and separation of rhenium ions from aqueous solutions using modified nano-Al2O3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5577–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.Y. Simultaneous speciation of inorganic rhenium and molybdenum in the industrial wastewater by aminofunctionalized nano-SiO2. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 55, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.J.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, Z.T.; Lou, Z.N.; Xiong, Y.; Fan, Y. Synthesis of Schiff base-functionalized silica for effective adsorption of Re (VII) from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 100, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, I.; Molina, L.; González, P.; Gaete, J.; Valenzuela, F.; Marco, J.F.; Sáez, C.; Basualto, C. Silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with betaine and their use as an adsorbent for Mo (VI) and Re (VII) species from acidic aqueous solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 271–283. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.Y.; Choi, W.S.; Yang, T.J.; Kim, M.J.; Tran, T. Recovery of rhenium and molybdenum from a roaster fume scrubbing liquor by adsorption using activated carbon. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 129, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołczyk, S.K.; Socha, R.P.; Yang, X.G.; Eckert, K.; Wojnicki, M. Study on kinetics and mechanism of Re (VII) ion adsorption and desorption using commercially available activated carbon and solutions containing Se (VI) as an impurity. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 215, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Sun, L.; Jiang, B.; Wu, H.X.; Huang, Q.M.; Chen, X.H. Low concentration Re (VII) recovery from acidic solution by Cu-biochar composite prepared from bamboo (Acidosasa longiligula) shoot shell. Miner. Eng. 2018, 124, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.J.; Lou, Z.N.; Shan, W.J. Improving Re (VII) adsorption on diisobutylamine-functionalized graphene oxide. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Lin, M.; Xiao, T.F.; Long, J.Y.; Liu, F.L.; Li, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Liao, D.D.; Chen, Z.X.; Zhang, P.; et al. Highly efficient removal of thallium (I) from wastewater via hypochlorite catalytic oxidation coupled with adsorption by hydrochar coated nickel ferrite composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tesfaye, F.; Li, X.; Lindberg, D.; Taskinen, P. Review of rhenium extraction and recycling technologies from primary and secondary resources. Miner. Eng. 2021, 161, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Guo, C.; Feng, X.; Zhang, S.Q.; Xing, Z.Q.; Shan, W.J.; Xiong, Y. Selective extraction and separation of Re (VII) from Mo (VI) by TritonX-100/N235/iso-amyl alcohol/n-heptane/NaCl microemulsion system. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, H.A.; Ilyas, S.; Masud, S.; Muhsan, M.A.; Mahmood, I.; Lee, J.C. Selective recovery of rhenium from molybdenite flue-dust leach liquor using solvent extraction with TBP. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Allain, A.; Pérez, B.; Merlet, G.; Cabezas, R.; Tapia, R.; Romero, J. Selective liquid-liquid extraction of molybdenum (VI) and rhenium (VII) from a synthetic pregnant leach solution: Comparison between extractants and diluents. Miner. Eng. 2020, 145, 106060. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Shu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, W.; Ru, H.Q.; Xiong, Y. The recovery of molybdenum (VI) from rhenium (VII) on amino-functionalized mesoporous materials. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.W.; Song, Z.R.; Zhou, Z.K.; Shan, W.J.; Li, J. Solvent extraction of rhenium in ionic liquid with N235. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 2423–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.W.; Shan, W.J.; Yan, Q.; Li, D.; Xia, L.X.; Zang, S.L. Extraction of rhenium from sulphuric acid solution with used amine N235. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 383, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.N.; Xiong, Y.; Song, J.J.; Shan, W.J.; Han, G.X.; Xing, Z.Q.; Kong, Y.X. Kinetics and mechanism of Re (VII) extraction and separation from Mo (VI) with trialkyl amine. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s10–s14. [Google Scholar]
- Danesi, P.R.; Vandergrift, G.F. Kinetics and mechanism of the interfacial mass transfer of Eu3+ and Am3+ in the System bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate-n-dodecane-NaCl-HCl-water. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 3646–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of molybdenum (VI), rhenium (VII), tungsten (VI), and vanadium (V) by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, A.F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.W.; Chen, S.; Jiang, H.L.; Shao, C.B.; Yuan, X.T.; Yin, Y.X. New approach for thallium removal by P204 extraction and its effect on the ammonium rhenate refining. Separations 2022, 9, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, A.F.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.H.; Wang, C.Z.; Lu, X.W.; Jin, M.H.; LI, Y.L.; Shao, C.B. A Method of Purifying and Removing Potassium from Ammonium Perrhenate; Research Resources and Environmental Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.H.; Kim, Y.U.; Kang, J.G.; Kumar, J.R.; Yoon, H.s.; Parhi, P.K.; Shin, S.M. Recovery of rhenium and molybdenum from molybdenite roasting dust leaching solution by ion exchange resins. Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.A.; Meloche, V.W. Ion exchange separation of rhenium from molybdenum. Anal. Chem. 1952, 24, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, H.; Kawabuchi, K.; Kuroda, R. Anion exchange separation of rhenium from molybdenum and technetium in thiocyanate-chloride media. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazy, P.; Jdid, E.A.; Floreancig, A.; Mottet, B. Selective recovery of rhenium from gas-scrubbing solutions of molybdenite roasting using direct precipitation and separation on resins. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 2073–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, E.; Bochkareva, Z.; Semenishchev, V.; Kirillov, S.; Bunkov, G.; Rychkov, V. Anion exchange recovery of rhenium from industrial liquors followed by direct synthesis of a rhenium halide salt. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 230, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Zhai, M.L.; Hua, R.; Yan, J.T.; Li, X.F.; Que, X.Y.; Zhao, L. Highly efficient recovery of Re (VII) from uranium and molybdenum ores leaching solution by quaternary phosphonium modified cellulose microspheres. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 168, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusuya, B.; Murty, V.S.; Rao, K.V.S.R. New rhenium centers in ammonium and potassium perrhenates. J. Mol. Struct. 1995, 344, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.S.; Rudskikh, V.V. Mechanism and sorption parameters of alkali metal ions on strongly acidic cation exchange resins. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholsaipant, P.; George, J.L.; Kim, D.; Kruger, A.A. Volatility of sodium, potassium, and cesium perrhenates determined by thermogravimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 9291–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadbabaei, N.; Zhang, H. Sorption mechanism and predictive models for removal of cationic organic contaminants by cation exchange resins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14572–14581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorodnyaya, A.N.; Abisheva, Z.S.; Sadykanova, S.E.; Sharipova, A.S.; Akcil, A. Purification of ammonium perrhenate solutions from potassium by ion exchange. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2017, 38, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi, M.T.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T. Potassium adsorption from ammonium perrhenate solutions via ion exchange resin: Characterization and kinetic study. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, Y.; Moritake, I.; Kurihara, S.; Nonaka, T. Preparation of resins having various phosphonium groups and their adsorption and elution behavior for anionic surfactants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 72, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, H.; Ismail, A.A.; Wakui, Y.; Yokoyama, T. Extraction of rare earth elements with 2-ethylhexyl hydrogen 2-ethylhexyl phosphonate impregnated resins having different morphology and reagent content. React. Funct. Polym. 2001, 49, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Ikawa, T.; Nishihama, S.; Yoshizuka, K. Selective recovery of indium from acid sulfate media with solvent impregnated resin of bis (4-cyclohexylcyclohexyl) phosphoric acid as an extractant. Ion Exch. Lett. 2009, 2, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.F.; Jiao, Y.F.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, P.G.; Nie, H.P. Adsorption-extraction mechanism of heavy rare earth by Cyanex272-P507 impregnated resin. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Helaly, O.S.; El-Ghany, M.S.A.; Moustafa, M.I.; Abuzaid, A.H.; El-Monem, N.M.A.; Ismail, I.M. Extraction of cerium (IV) using tributyl phosphate impregnated resin from nitric acid medium. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, E.P.; Dietz, M.L.; Rhoads, S.; Felinto, C.; Gale, N.H.; Houghton, J. A lead-selective extraction chromatographic resin and its application to the isolation of lead from geological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 292, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.F.; Li, J. Extraction-macroporous resin combined technology. Technol. Water Treat. 2010, 36, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gujar, R.B.; Ansari, S.A.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Egberink, R.J.M.; Huskens, J.; Verboom, W. Highly efficient extraction chromatography resin containing hexa-n-octyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) for selective recovery of plutonium from acidic feeds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 5954–5961. [Google Scholar]
- Lučaníková, M.; Kučera, J.; Šebesta, F. New extraction chromatographic material for rhenium separation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2008, 277, 479–485. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.K.; Han, Y.J.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, B.C. Adsorption of rhenium and rhodium in nitric acid solution by Amberlite XAD-4 impregnated with Aliquat 336. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.X.; Zhai, Y.C.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.F. Study on the extraction and separation of rhenium and molybdenum by levextrel resins containing trialkyl amine. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2010, 2, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Hua, R.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.P.; Liu, H.S.; Xu, B. Adsorption and separation of Re (VII) using trimethylamine-functionalized strong base anion exchange resin. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 326, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Ansari, S.A.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Egberink, R.J.M.; Huskens, J.; Valsala, T.P.; Sathe, D.B.; Bhatt, R.B.; Verboom, W. Sequestration of actinides by an extraction chromatography resin containing a triaza-9-crown-3 functionalized diglycolamide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 13966–13973. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.; Gill, R.J.; Bailey, D.G.; Kabay, N.; Arda, M. Sorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by amberlite XAD-7 resin impregnated with aliquat 336. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 60, 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.S.; Uchikoshi, M.; Mimura, K.; Isshiki, M. Separation of major impurities Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Al, Ca, Fe, and Zn from La using bis (2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (D2EHPA)- impregnated resin in a hydrochloric acid medium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.S.; Uchikoshi, M.; Mimura, K.; Isshiki, M. Preparation and evaluation of high-purity La2O3. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logé, R.E. Nanotwinning-assisted recrystallization. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinand Knipschildt, E.F. Nucleation of recrystallization. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 38, 765–779. [Google Scholar]
- Tiamiyu, A.A.; Pang, E.L.; Chen, X.; Lebeau, J.M.; Nelson, K.A.; Schuh, C.A. Nanotwinning-assisted dynamic recrystallization at high strains and strain rates. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 786–794. [Google Scholar]
- Orda, S.; Drzazga, M.; Leszczyńska-Sejda, K.; Ciszewski, M.; Kocur, A.; Branecka, P.; Gall, K.; Słaboń, M.; Lemanowicz, M. Investigations of the density and solubility of ammonium perrhenate and potassium perrhenate aqueous solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, J.; Maier, B.; Rosenberg, R.; Sturm, S.; Cölfen, H.; Sturm, E.V. Nonclassical recrystallization. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 15242–15248. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Li, R.D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Tong, P.Y. A Preparation Method of High Purity Rhenium Powder. Pilot Film Materials (Guangdong) Co., Ltd.: Qingyuan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Fang, D.W.; Liu, Y. The influences of stirring on the recrystallization of ammonium perrhenate. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tang, J.J.; Pei, X.Y.; Cao, N.; Liu, Y. Research and process of 4 N grade high purity ammonium rhenate prepared by homogeneous recrystallization. Mod. Chem. Res. 2023, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).