Abstract
Mycotoxins are a very diverse group of natural products produced as secondary metabolites by fungi. Patulin is produced by mold species normally related to vegetable-based products and fruit, mainly apple. Its ingestion may result in agitation, convulsions, edema, intestinal ulceration, inflammation, vomiting, and even immune, neurological or gastrointestinal disorders. For this reason, the European Commission Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 established a maximum content for patulin of 10 ppb in infant fruit juice, 50 ppb for fruit juice for adults and 25 ppb in fruit-derived products. In this work, a rapid and selective method based on magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bar (MMISB) extraction has been developed for the isolation of patulin, using 2-oxindole as a dummy template. The final extraction protocol consisted of simply pouring in, stirring and pouring out samples and solvents from a beaker with the MMISB acting inside. The magnetic device provided satisfactory recoveries of patulin (60%–70%) in apple samples. The successful MMISB approach has been combined with high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) to determine patulin.
1. Introduction
Mycotoxins are low-molecular-weight natural products, very diverse in terms of structure and abilities, produced as secondary metabolites by fungi. Patulin (PAT) is an important mycotoxin produced by over 30 genera of mold such as Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Byssochlamys. In particular, Penicillium expansum is recognized as the main source of PAT and it has been commonly associated with apple rot [1]. These molds grow easily in damaged fruit or in derived products such as juices, if storage conditions are deficient. Some of the most serious health effects of PAT ingestion in humans are agitation, convulsions, edema, intestinal ulceration, inflammation and vomiting [2]. The toxicity of these molecules has led to the set-up of strict regulations in many countries for their control in food and feed, and the consequent establishment of official legislation. The establishment of maximum limits in some food products resulted in an increasing demand of sensitive, selective and effective analytical methods. The European Commission Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 established a maximum content for PAT of 10 ppb in infant fruit juices, 50 ppb for fruit juices for adults and 25 ppb in fruit-derived products [3].
For the determination of PAT, thin layer chromatography was firstly used. Nowadays, the official analytical method adopted by the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) for the analysis of PAT in food is high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet (UV) detection, using an extraction with ethyl acetate and clean-up with sodium carbonate [4]. The main drawback of UV detection is the poor resolution between PAT and other co-extracted compounds such as hydroxymethylfurfural. To overcome this interference, liquid chromatography may be combined with mass spectrometric determination [1]. As an additional problem, PAT is vulnerable to the alkaline conditions of the previously mentioned extraction method. Purification by solid-phase extraction (SPE) has been frequently applied as an alternative procedure [5]. In the last years, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) started to be used, and are becoming promising materials for extracting different analytes present in food and beverages [6]. However, mycotoxins are usually too toxic or too expensive to be used as template molecules in MIP preparation. Template bleeding may be an additional problem of these polymers, especially when dealing with very low detection levels. To overcome these limitations, dummy templates can be applied during MIP synthesis [7]. Also, magnetic materials can provide fast and simple methods of extraction and have already demonstrated their effectiveness to extract patulin [8].
In the present work, a rapid and selective method based on an in-house designed magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bar (MMISB) has been developed for the isolation of PAT. For MIP synthesis, a structural analogue of PAT, 2-oxindole, was used as a dummy template (Figure 1) [9]. The molecularly imprinted polymer was grafted on the silanized surface of a glass-covered stir-bar using an adaptation of typical protocols used in grafting techniques. The applicability of this novel stirring bar for the extraction of PAT has been tested in spiked apple samples using HPLC-MS/MS for detection.
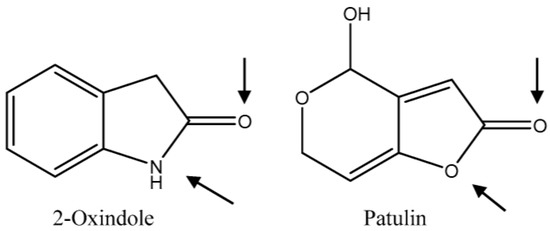
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of patulin and dummy template used for molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) synthesis. The potential sites for intermolecular interactions between template or patulin and the functional monomer methacrylic acid (MAA) are indicated by arrows.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The standard for PAT was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company (Madrid, Spain). The dummy template 2-oxindole, methacrylic acid (MAA), divinylbenzene 80% (DVB-80), ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA), and the initiator 2,2′-azobis-(2-methyl-butyronitril) (AIMN) were from Sigma-Aldrich. The 3-(methacryloxy) propyltrimethoxysilane was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company. HPLC grade solvents were supplied by Merck (Madrid, Spain).
MAA and EGDMA were freed from stabilizers by distillation under reduced pressure and AIMN was recrystallized from methanol prior to use. DVB-80 was freed from stabilizers by passing through a small column packed with neutral alumina (Aldrich).
2.2. Apparatus
The polymerization was carried out into a temperature controllable incubator (Stuart Scientic, Redhill, Surrey, UK). Separation was performed in an 1100 series HPLC system from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA). A Luna 3 µm C18 (150 × 2 mm) column from Phenomenex (Torrance, CA, USA) was used. The mobile phase was water and methanol with 0.1% formic acid, mixed in isocratic mode at 70% and 30%, respectively; the analytical run lasted for 10 min at 250 µL·min−1. A Q-Trap 2000 mass spectrometer with ESI Source from AB Sciex (Toronto, ON, Canada) was used, working in negative mode for PAT and in positive mode for 2-oxindole. For quantification of PAT, the most intense MRM transition was monitored along with a second transition for identity confirmation: 153 > 109 and 153 > 81, respectively.
2.3. Design of Molecularly Imprinted Stir-Bars (MMISB) for Patulin Extraction
To achieve a stir-bar grafted with molecularly imprinted polymer on its surface, a chemical coating protocol adapted from the work of Turiel and Martin-Esteban was used [10]. First, a commercial glass-covered magnetic stir-bar remained in a combination of methanol and hydrochloric acid (1:1, v/v), stirring for 30 min for clean-up of the glass surface. Next, the surface was silanized with 2% 3-(methacryloxy) propyltrimethoxysilane in toluene for 1 h. Finally, the stir-bar was rinsed methanol and let dry under N2 stream.
Once the silanized glass surface was ready, the chemical coating process took place as follows: in a glass tube of 4 mL, the bar was placed and covered with the pre-polymerization mixture. The polymerization mixture was prepared with 2-oxindole, MAA and EGDMA, ratio 1:4:20, dissolved in the porogen solvent toluene/methanol (90:10) at 40 wt % and initiator 2 wt %. The stirring bar immersed in the monomeric recipe was allowed to polymerize at 60 °C for 12 h, or until the appearance of the polymer was completely white.
After (bulk) polymerization, the glass tube was broken to release the polymer-coated stir bar (Figure 2). Then, the bars were placed in a beaker and covered with water and methanol (50/50, v/v) to test the adhesion to the surface and the resistance of the polymer, using a magnetic stirrer. Next, the template molecule was removed by Soxhlet extraction for 12 h with methanol/acetic acid (1/1, v/v) solution. To optimize the conditions of use of this MMISB for the extraction of PAT, different loading, washing and elution solution were tested. A magnetic non-imprinted stir bar (MNISB) was prepared in parallel, without the addition of template.
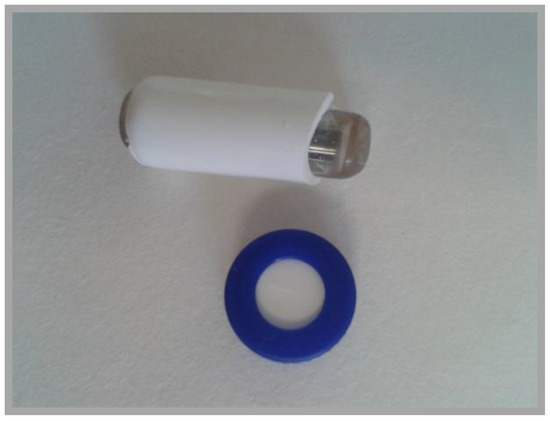

Figure 2.
Magnetic molecularly imprinted stir bar (MMISB) developed for the extraction of patulin; a screw cap was placed below the stir-bar to illustrate its size (Reproduced with permission from [11]. MDPI under , 2015).
2.4. Application to Real Samples
The extraction protocol started adding water to cover 3 g of diced apple in a 50 mL plastic tube. Apple samples were spiked with water containing PAT at 50 ng·g−1 (MRL to for fruit juices in adults) and introduced into an ultrasound bath for 30 min. Samples were shaken for 10 min, centrifuged at 5000 g for 10 min and the supernatant was transferred to a baker with the molecularly imprinted stir-bar (MMISB). A conventional SPE protocol was applied, consisting of loading, washing and elution steps with different solvents.
The analyte was loaded within the pores (active sites) of the MMISB under stirring for 30 min. After this sorptive extraction, water was removed with the aid of external magnet and the stir-bar was washed with water for 5 min. Then, to elute the retained patulin from the MMISB, 5 mL methanol/acetic acid (75/25) were added and the solution was kept stirring in a beaker for 30 min. Finally, the eluate was evaporated under nitrogen stream at 30 °C and re-dissolved in 100 µL of mobile phase. Twenty microliters were immediately injected into the chromatographic system for analysis. Recoveries were calculated using HPLC-MS/MS.
3. Results and Discussion
Nowadays, the official analytical method adopted by AOAC International is HPLC with UV detection, using clean-up with ethyl acetate and sodium carbonate. However, the diverse drawbacks of this method (poor stability of patulin under alkaline extraction, poor resolution between patulin and co-extracted hydroxymethylfurfural) have originated interest in alternative options, such as LC methods coupled to mass spectrometry [1]. In the last years, purification with molecularly imprinted polymers and magnetic materials started to be used and they are becoming promising materials in analytical chemistry and, more specifically, in mycotoxins determination [7,8,12,13]. Imprinted polymers have also showed potential for detoxification purposes in large-scale environmental applications [14].
3.1. Molecularly Imprinted Stir-Bars (MMISB) for Patulin Extraction
In this study, 2-oxindole, a compound structurally related to PAT, was selected as a dummy template for the design of a MIP selective towards PAT. This analogue of patulin has already been used successfully to synthesize a MIP capable of selectively binding PAT molecules [9]. The removal of the template leaves binding sites within the polymeric matrix that are complementary in shape and functionality to the template and to the target molecule of PAT (Figure 1). Dummy templates are usually selected to overcome bleeding problems. Additional advantages of these templates may include lower cost and toxicity. In this context, a dummy-template approach was preferred to avoid the manipulation of patulin during MIP synthesis, as it could be hazardous to the personnel working in the laboratory. Patulin has been classified as having acute toxicity (oral, dermal, inhalation) for humans, while 2-oxindole has not been classified as hazardous (Sigma-Aldrich website). As for the costs, relatively high amounts of template are normally required to synthesize imprinted polymers. In that respect, 2-oxindole is much cheaper than patulin. To provide just one example, 5 mL of PAT correspond to the price of 25 g of 2-oxindole in the Spanish market (Sigma-Aldrich website).
The polymer coated on the surface of the magnetic stir-bars was prepared by a non-covalent approach, based on the formation of the non-covalent interactions of MAA and the dummy template. MAA was selected because of its high capability to act both as a hydrogen bond and a proton donor and as a hydrogen bond acceptor [15]. The selected polymerization technique was bulk polymerization, because it does not require sophisticated instrumentation and the reaction conditions can be easily controlled. Furthermore, it is the most widely used method for the preparation of imprinted polymers [16]. In the design of any pre-polymerization mixture, the selection of the cross-linker and porogen solvent are two key factors, as they would determine the aspect, strength and even the color and porosity of the final polymer. DVB-80 and EGDMA were therefore tested separately and in combination with various solvent mixtures, in order to achieve the best option for MIP synthesis. The tested combinations were methanol and/or acetonitrile with different percentages of toluene, as follows: 0%, 20%, 50%, 70% and 90% toluene in methanol and 0%, 20%, 50%, 70% and 90% toluene in acetonitrile. The different combinations of monomer-solvent were introduced in an injection vial and allowed to polymerize under bulk conditions for 24 h at 60 °C. After polymerization, the glass vials were broken and the resulting material was tested visually and by touching. With the use of DVB-80 as a cross-linker, it was impossible to obtain a strong and tough polymer. The resulting polymer would be a plastic, yellowish, cracked and fragile material, not suitable for resisting the required stirring conditions. Thus, adequate divinylbenzene polymers could not be achieved using the different tested solvents (acetonitrile or methanol), even changing the toluene percentage (from 0% to 90% toluene). As for EGDMA, in every case the polymers were stronger than those obtained with DVB, showing more resistance to compressive strength and even more when using methanol (combined with toluene) instead of acetonitrile. As for the color, EGDMA polymers were white and DVB yellowish. The mixture of methanol and toluene (90:10) with EGDMA proved to be useful, resulting in a hard and white polymer. Consequently, this combination was used to prepare the magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bar (MMISB).
3.2. Analytical Method and Application of MMISB in Apple Samples
The efficiency of the obtained polymer was evaluated with a very simple extraction protocol for the isolation of PAT from apple samples prior to analysis. The protocol consisted simply of pouring in, stirring and pouring out solvents from a beaker. To carry out the extraction process, it was only necessary to have a magnetic stirrer and an external magnet. Satisfactory recoveries of PAT were obtained using this molecularly imprinted glass-covered stir-bar, with 60%–70% of recovery in a minimum loading time of 45 min under stirring. These results were in the range of the recoveries obtained by Wang et al. using a graphene-based magnetic material to extract PAT from apple juice [8]. In this context, Lucci et al. applied commercial MIP-SPE columns for detection of patulin in apple products, obtaining recoveries of >77% [12]. Figure 3 shows a chromatogram of a blank apple sample (a) and a sample spiked with patulin (b) at 50 ng·g−1, both extracted with the MMISB protocol and analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS. The magnetic NIP stir-bar showed a mean recovery difference of 20% less.
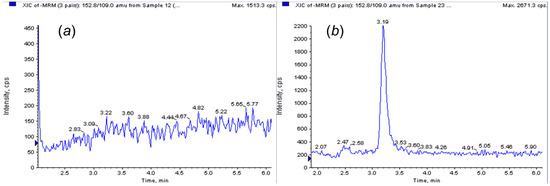
Figure 3.
Reconstructed LC-MS/MS chromatograms of a blank apple sample (a) and the same sample spiked with patulin at 50 ng·g−1 (b), both extracted using the MMIP stir-bar.
On the other hand, the deterioration of the polymeric coat of the stir-bar was imperceptible after several hours of use, resisting the whole set of experiments, thus indicating that the adhesion of the polymer was strong and stable. The glass layer as a cohesion agent between the bar and the polymeric coat can be assumed. Imprinted polymers, especially the ones cross-linked with DVB, are stable over a long time and can be reused [17]. The analytical limits were calculated from the signal-to-noise ratio. Using this method, the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) correspond to the concentrations of the analyte that would yield a signal equal to three and 10 times the noise level, respectively [18]. The calculated LOD (S/N = 3) was 10 ng·g−1 and the LOQ (S/N = 10) was 50 ng·g−1.
4. Conclusions
The proposed magnetic extraction has demonstrated its usefulness for the isolation of PAT in apple. The stir-bars are easy to use and the extraction protocol was reduced to simply add and remove solvents from a beaker, with the aid of a magnetic stirrer and an external magnet. The main drawback of the proposed methodology lies in its limits, which could be improved using more sensitive instruments or further optimizing the whole method. Additionally, the design approach applied to obtain the imprinted stir-bar was easy and fast, readily reproducible in other laboratories and for different analytes.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the project EM 2012/153 from Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Ordenacion Universitaria, Xunta de Galicia.
Author Contributions
P.R. and M.D.-B. conceived and designed the experiments and wrote the paper; R.B. performed the experiments and contributed to the writing; C.F. and A.C. lead the work and revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Desmarchelier, A.; Mujahid, C.; Racault, L.; Perring, L.; Lancova, K. Analysis of Patulin in Pear- and Apple-Based Foodstuffs by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7659–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.J.N.D.; Schuch, P.Z.; Bernardi, C.R.; Vainstein, M.H.; Jablonski, A.; Bender, R.J. Patulin in food: State-of-the-art and analytical trends. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2007, 29, 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- EC Commission Regulation (EC) No. 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 Setting the Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs as Regards Aflatoxins. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 50, 8–11.
- Brause, A.R.; Trucksess, M.W.; Thomas, F.S.; Page, S.W. Determination of patulin in apple juice by liquid chromatography: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 1996, 79, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barreira, M.J.; Alvito, P.C.; Almeida, C.M. Occurrence of patulin in apple-based-foods in Portugal. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regal, P.; Diaz-Bao, M.; Barreiro, R.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in food analysis: Clean-up and chromatographic improvements. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 10, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Bao, M.; Regal, P.; Barreiro, R.; Fente, C.A.; Cepeda, A. A facile method for the fabrication of magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bars: A practical example with aflatoxins in baby foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1471, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Ling, Y. Graphene oxide-based magnetic solid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography for determination of Patulin in Apple Juice. Food Anal. Method 2017, 10, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, A.; Taherkhani, M. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Pre-concentration of Patulin from Apple Juice. Chromatographia 2011, 73, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted stir bars for selective extraction of thiabendazole in citrus samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2962–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Bao, M.; Regal, P.; Barreiro, R.; Miranda, J.; Cepeda, A. Magnetic molecularly imprinted stirring bar for isolation of patulin using grafting technique. Int. Electron. Conf. Synth. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, d002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, P.; Moret, S.; Bettin, S.; Conte, L. Selective solid-phase extraction using a molecularly imprinted polymer for the analysis of patulin in apple-based foods. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Kong, W.; Zhou, S.; Yin, L.; Wan, L.; Yang, M. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based solid phase clean-up for analysis of ochratoxin A in beer, red wine, and grape juice. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, Ü. Comparing determination methods of detection and quantification limits for aflatoxin analysis in hazelnut. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).