Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. General Procedure for Solubility Testing, Solvent Optimization, and Thin-Layer Chromatography
2.2.1. Dissolution Testing of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
2.2.2. Procedures for Optimization of Solvent Blends
2.2.3. Thin-Layer Chromatography
3. Results
3.1. Dissolution Testing of Analytes
3.2. Thin-Layer Chromatography
3.3. Addition of Caffeine as a Second Analyte
3.4. Chemical Hazard Classification of the Potential Alternative Solvents
3.5. Optimization of Safer Solvents Blends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bryan, M.C.; Dunn, P.J.; Entwistle, D.; Gallou, F.; Koenig, S.G.; Hayler, J.D.; Hickey, M.R.; Hughes, S.; Kopach, M.E.; Moine, G.; et al. Key Green Chemistry research areas from a pharmaceutical manufacturers’ perspective revisited. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5082–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, J.D. Toxicological Profile for Methylene Chloride; United States Department of Health and Human Services, Ed.; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2000.
- U.S. Government. Toxicological Review of Dichloromethane (Methylene Chloride); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Ed.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Pietsch, A. Decaffeination—Process and Quality. In The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 225–243. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.O.; Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Ultrafine porous fibers electrospun from cellulose triacetate. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2998–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulishankar, A.; Ganesan, P.; Elumalai, M.; Lakshmanan, K. Significance of TLC and HPTLC in Phytochemical Screening of Herbal Drugs. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2020, 13, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Jessop, P.G.; Jessop, D.A.; Fu, D.; Phan, L. Solvatochromic parameters for solvents of interest in green chemistry. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ferlin, F.; Bai, R.; Li, M.; Vaccaro, L.; Gu, Y. Replacing halogenated solvents by a butyl acetate solution of bisphenol S in the transformations of indoles. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3588–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taygerly, J.P.; Miller, L.M.; Yee, A.; Peterson, E.A. A convenient guide to help select replacement solvents for dichloromethane in chromatography. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3020–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Reimonn, G.; Morose, G.; Yu, E.; Chen, W.-T. Removing Acrylic Conformal Coating with Safer Solvents for Re-Manufacturing Electronics. Polymers 2021, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Sarker, Z.I.; Uddin, A.H.; Bin Yunus, K.; Prasad, R.; Mia, A.R.; Ferdosh, S. Kamlet Taft Parameters: A Tool to Alternate the Usage of Hazardous Solvent in Pharmaceutical and Chemical Manufacturing/Synthesis—A Gateway towards Green Technology. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2020, 10, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallar, M.; Tenaglia, N.; Morose, G.; Wong, H.-W. Safer Solvent Blends for Food, Dye, and Environmental Analyses Using Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, P.A.; Seoud, O.A.E.; Machado, V.G.; de Jesus, J.C.; de Melo, C.E.; Buske, J.L.; Cardozo, A.P. Understanding Solvation: Comparison of Reichardt’s Solvatochromic Probe and Related Molecular “Core” Structures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic dyes as solvent polarity indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, E.R.; Khabade, S.S.; Sutar, T.B.; Bhat, M.R.; Payghan, S.A. Three-dimensional hansen solubility parameters as predictors of miscibility in cocrystal formation. Asian J. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 11, 302–318. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Le, H.M.; Kaale, E.; Long, K.D.; Layloff, T.; Lumetta, S.S.; Cunningham, B.T. Characterization of drug authenticity using thin-layer chromatography imaging with a mobile phone. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivai, H.; Kardela, W.; Kartanti, A. Development and validation of analysis method for tablet ibuprofen by thin layer chromatography-densitometry. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Komsta, Ł.; Kobyłka, M. Chemometric Approach to Selectivity in TLC with Densitometric Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 51, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferenczi-Fodor, K.; Végh, Z.; Renger, B. Thin-layer chromatography in testing the purity of pharmaceuticals. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, S.; Tsakiridou, G.; Ditzinger, F.; Koehl, N.; Price, D.J.; Ilie, A.-R.; Kalantzi, L.; Kimpe, K.; Holm, R.; Nair, A.; et al. Application of the solubility parameter concept to assist with oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs—A PEARRL review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, S.; Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters in Practice; Hansen-Solubility.com: Online, 2008; Volume 110. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.M. The Three Dimensional Solubility Parameter; Danish Technical: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1967; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, S. Solubility Science: Principles and Practice; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2017; pp. 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- MIT OpenCourse. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Guide. 2012. Available online: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/chemistry/5-301-chemistry-laboratory-techniques-january-iap-2012/labs/MIT5_301IAP12_TLC_Handout.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Santiago, M.; Strobel, S. Thin layer chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 533, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peter, E.W. Thin-Layer Chromatography: A Modern Practical Approach; RSC Chromatography Monographs; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2005; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim, F.A.; Landesberg, J.M. Experiments for Introduction to Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale Approach; Saunders College Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, K.M.; Williamson, K.L. Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 161–162. [Google Scholar]
- De los Ríos, M.D.; Ramos, E.H. Determination of the Hansen solubility parameters and the Hansen sphere radius with the aid of the solver add-in of Microsoft Excel. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Condon, G. In World of over-the-Counter Pain Relief, the Venerable Aspirin Gets: Hartford Courant. 2018. Available online: www.courant.com/news/connecticut/hc-xpm-1993-02-05-0000106290-story.html (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Chen, D.; Sun, Q.; Huang, W.; Yang, B.-S. Diverse Solvent Selection for Polymorph Landscape Investigation Based on Specific API–Solvent Interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 2251–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, A.; Budzisz, M.; Dołowy, M. Validation Thin Layer Chromatography for the Determination of Acetaminophen in Tablets and Comparison with a Pharmacopeial Method. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavallali, H.; Zareiyan, J.S.F.; Naghian, M. An Efficient and Simultaneous Analysis of Caffeine and Paracetamol in Pharmaceutical Formulations Using TLC with a Fluorescence Plate Reader. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northern Arizona University, Thin Layer Chromatography of Analgesics and Amino Acids. Available online: https://jan.ucc.nau.edu/~jkn/235L7-TLC%20Analgesics.htm (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Alder, C.M.; Hayler, J.D.; Henderson, R.K.; Redman, A.M.; Shukla, L.; Shuster, L.E.; Sneddon, H.F. Updating and further expanding GSK’s solvent sustainability guide. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3879–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxics Use Reduction Institute, Pollution Prevention Options Analysis System: P2OASys. 2021. Available online: https://p2oasys.turi.org/ (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- Chemicals, G.F.S. GreenScreen Chemicals. 2021. Available online: https://www.greenscreenchemicals.org/ (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- Gauthier, A.M.; Fung, M.; Panko, J.; Kingsbury, T.; Perez, A.L.; Hitchcock, K.; Ferracini, T.; Sahmel, J.; Banducci, A.; Jacobsen, M.; et al. Chemical assessment state of the science: Evaluation of 32 decision-support tools used to screen and prioritize chemicals. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 11, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, Y. Are solubility parameters relevant to supercritical fluids? J. Supercrit. Fluids 2006, 38, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MilliporeSigma. 2021. Available online: https://www.emdmillipore.com/US/en (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Gandhi, N.; Farfaras, N.; Wang, N.-H.L.; Chen, W.-T. Life Cycle Assessment of Recycling High-Density Polyethylene Plastic Waste. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1463–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

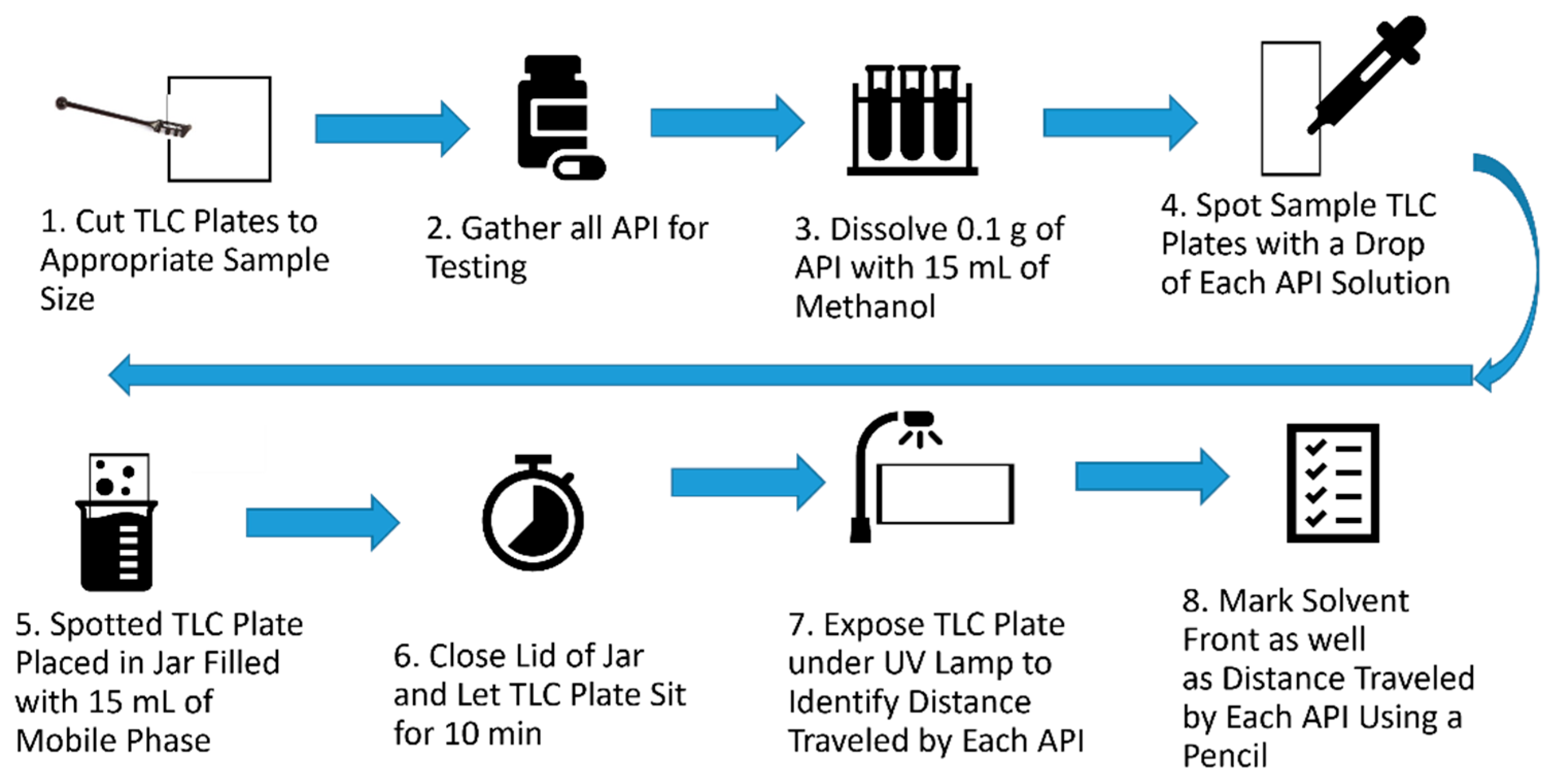
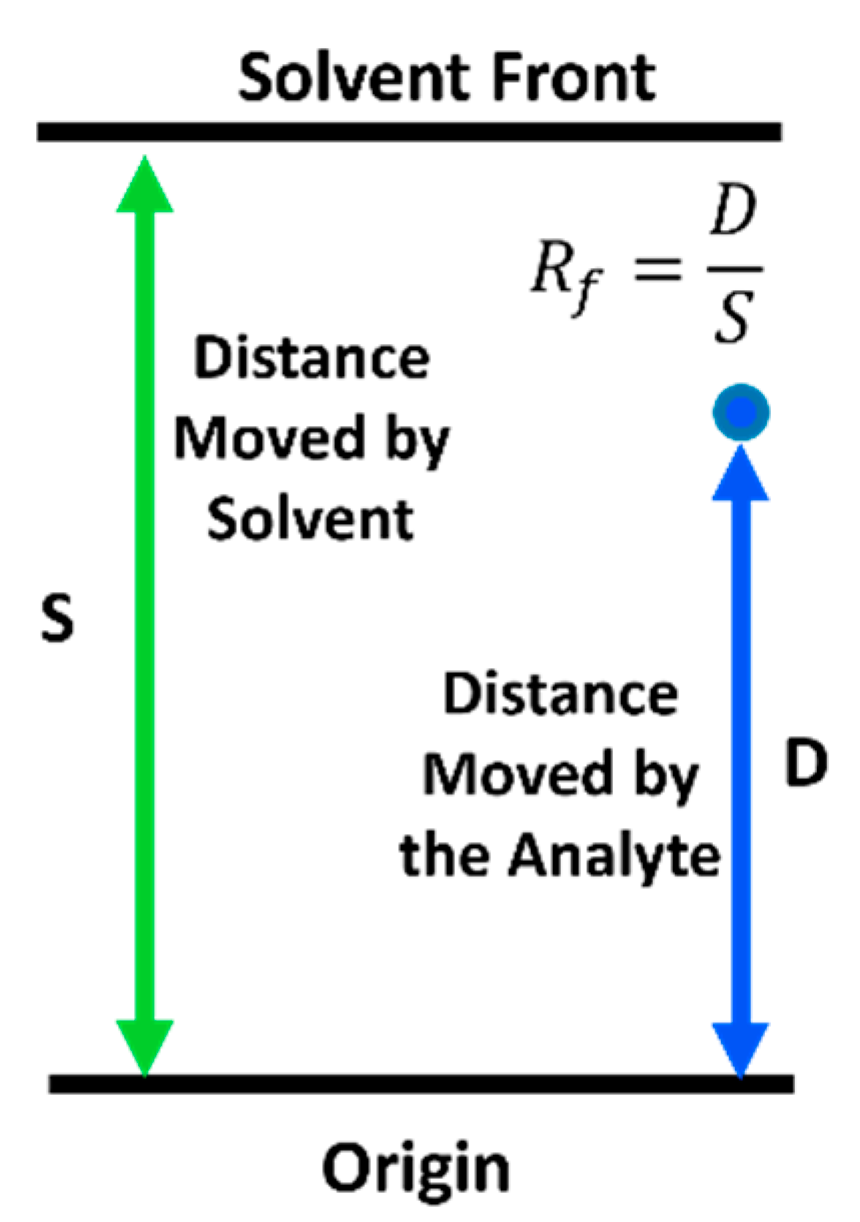
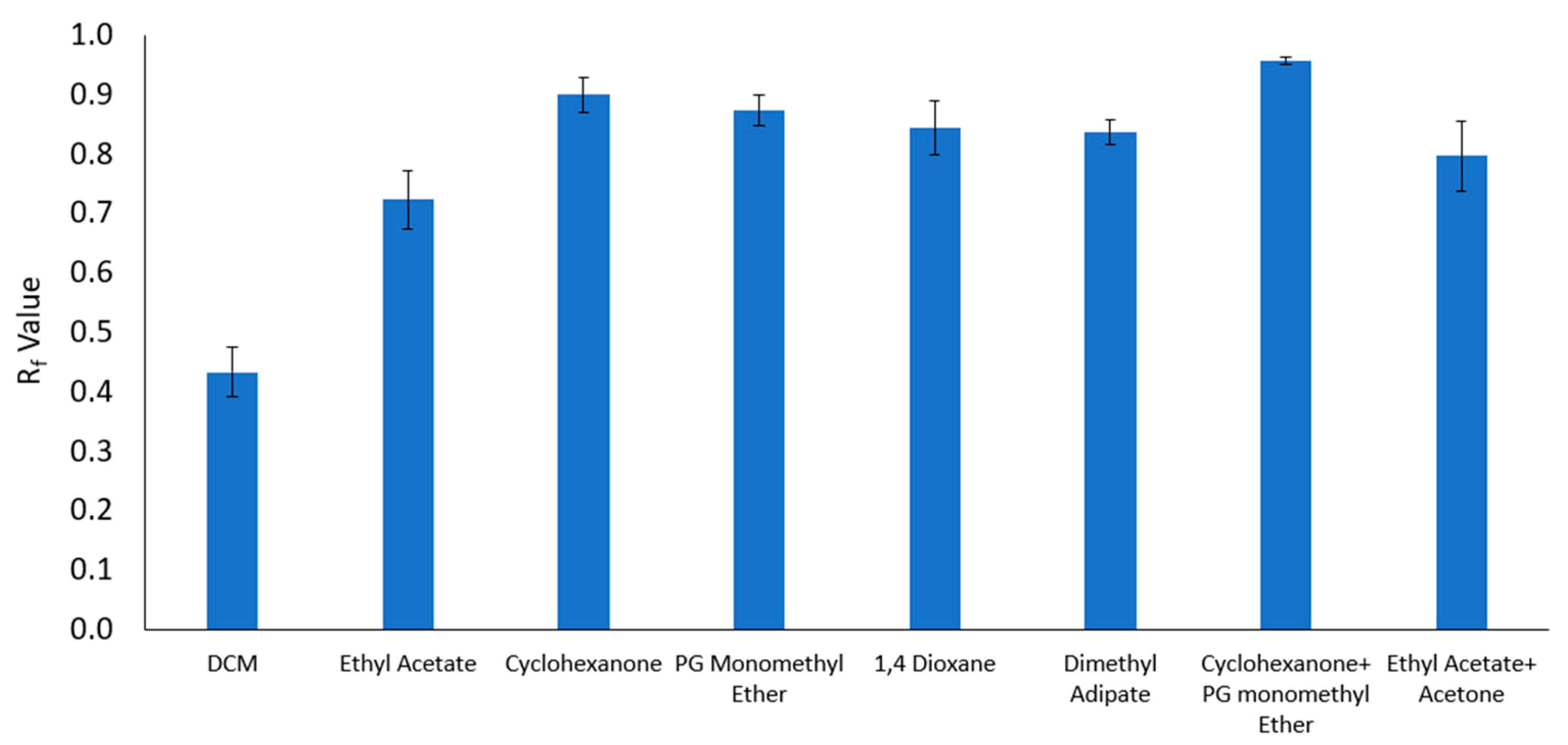

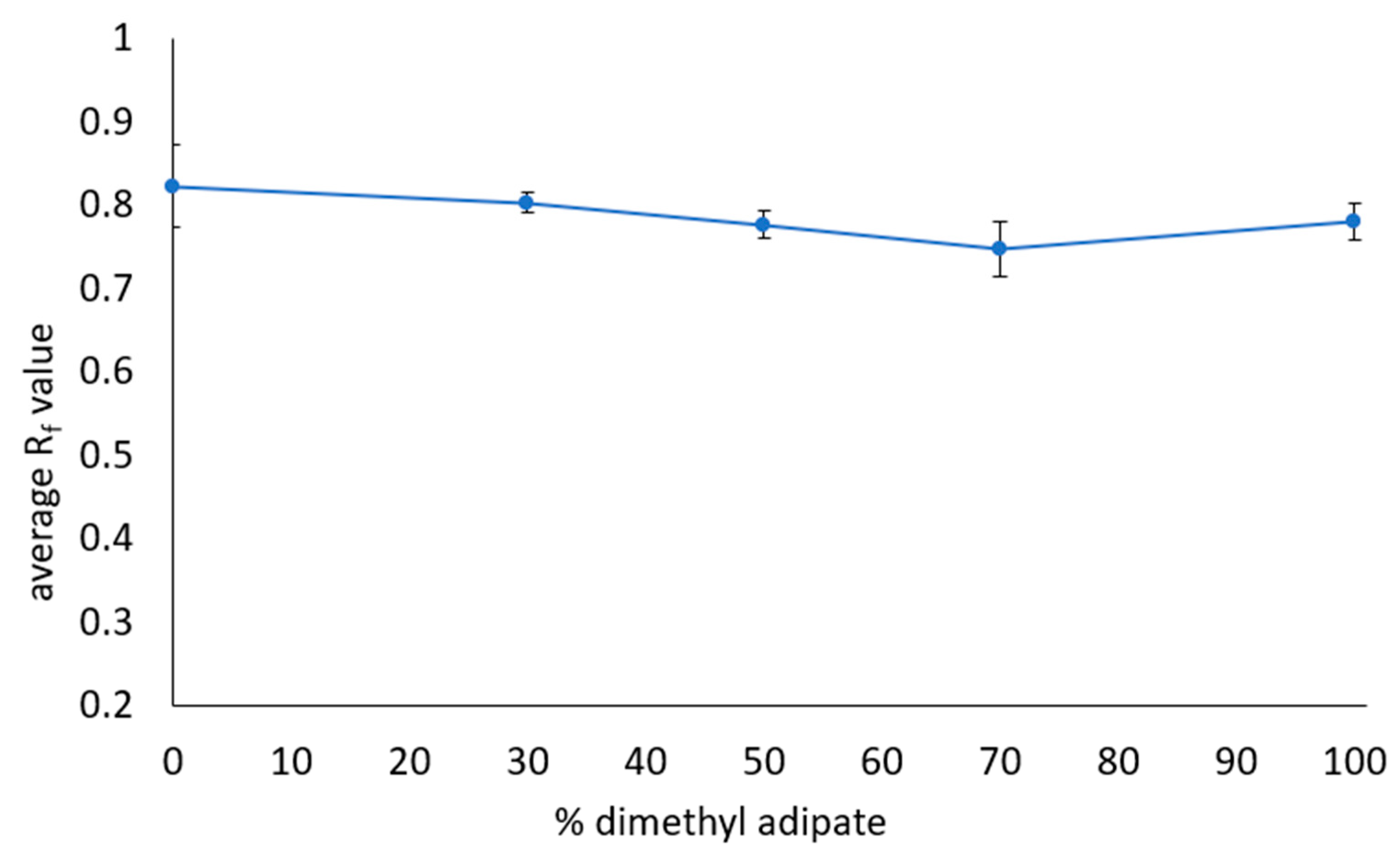

| Solvent and Solvent Blends | Hansen Solubility Parameters | Scores with 2 min Dissolution Time 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δD | δP | δH | Ace | Asp | Ibu | |
| acetic acid | 14.5 | 8 | 13.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| acetone | 15.5 | 10.4 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| acetonitrile | 15.3 | 18 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| acetophenone | 18.8 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| amyl acetate | 15.8 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| anisole | 17.8 | 4.4 | 6.9 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| cyclohexanone | 17.8 | 8.4 | 5.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| cyclopentyl methyl ether | 16.7 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| cyrene | 18.9 | 12.4 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| diacetone alcohol | 15.8 | 8.2 | 10.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| dichloromethane | 17 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| diethyl ether | 14.5 | 2.9 | 4.6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| dimethyl adipate | 16.3 | 6.8 | 8.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| DI Water | 15.5 | 16 | 42.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DMF | 17.4 | 13.7 | 11.3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DMSO | 18.4 | 16.4 | 10.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ethanol | 15.8 | 8.8 | 19.4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ethyl acetate | 15.8 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ethylene glycol | 17 | 11 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| formic acid | 14.6 | 10 | 14 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| glycerol | 17.4 | 11.3 | 27.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Isophorone | 17 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| methanol | 14.7 | 12.3 | 22.3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| n-butyl benzoate | 18.3 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| n-heptane | 15.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| sulfolane | 17.8 | 17.4 | 8.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| tetrahydrofuran | 16.8 | 5.7 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| toluene | 18 | 1.4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| xylene | 17.8 | 1 | 3.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 bromonaphthalene | 20.6 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 chlorobutane | 16.2 | 5.5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 methoxy 2 propanol (propylene glycol monomethyl ether) | 15.6 | 6.3 | 11.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 2 propanediol monomethyl ether acetate | 15.6 | 5.6 | 9.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1,4 dioxane | 17.1 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 2 3 4 tetrahydronaphthalene | 19.6 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 butanol | 15.8 | 5.7 | 14.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2-picoline | 18.4 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| cyclohexanone (65%) + PG monomethyl ether (35%) 2 | 17 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ethanol (80%) + toluene (20%) 2 | 16.2 | 7.3 | 15.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ethyl acetate (60%) + acetone (40%) 2 | 15.7 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ethyl acetate (75%) + ethanol (25%) 2 | 15.8 | 6.2 | 10.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| tetrahydrofuran (55%) + cyclohexanone (45%) 2 | 17.3 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| tetrahydrofuran (85%) + toluene (15%) 2 | 17 | 5.1 | 7.1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| water (50%) + acetonitrile (50%) 2 | 15.4 | 17 | 24.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Solvent/Solvent Blend | Distance Traveled by Spot 1 (cm) | Distance Traveled by Spot 2 (cm) | Distance between the Spots |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCM | 2.6 | 2.4 | 0.2 |
| 1,4 dioxane | 3.4 | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| dimethyl adipate | 2.5 | 1.9 | 0.6 |
| cyclohexanone | 2.6 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| cylohexanone (65%) + PG monomethyl ether (35%) | 3.0 | 1.8 | 1.2 |
| PG monomethyl ether | 3.3 | 2.0 | 1.3 |
| ethyl acetate (75%) + ethanol (25%) | 4.3 | 2.8 | 1.5 |
| ethyl acetate (60%) + acetone (40%) | 4.5 | 2.9 | 1.6 |
| ethyl acetate | 3.9 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| Solvent | TURI P2OAsys 10: High Hazard 2: Low Hazard | GSK Scores 1: High Hazard 10: Low Hazard | Green Screen Score BM-1: High Hazard; BM-4: Low Hazard | Reasons for Selection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCM | 7.8 | 4 | BM-1 | Baseline, chemical to be replaced |
| 1,4 dioxane | 7.9 | 4 | BM-LT1 | HSP similar to DCM to evaluate |
| cyclohexanone | 7.8 | 6 | No evaluation | HSP similar to DCM to evaluate |
| 1,3 dioxolane | 6.5 | No evaluation | BM-2 | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| acetone | 5.4 | 8 | BM-2 | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| PG monomethyl ether | 5.0 | No evaluation | No evaluation | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| ethyl acetate | 4.2 | 8.0 | No evaluation | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| methyl acetate | 4.1 | No evaluation | BM-2 | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| dimethyl adipate | 3.5 | No evaluation | No evaluation | Safer alternative to evaluate |
| Blend Combination | Blend Ratio (Solvent 1/Solvent 2) | Blend Price (USD) | Max Boiling Point (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| dimethyl adipate/1,3 dioxolane | 72/28 | $115 | 215.2 |
| ethyl acetate/1,3 dioxolane | 51/49 | $118 | 78 |
| methyl acetate/ethyl acetate | 56/44 | $98 | 77 |
| dimethyl adipate/ethyl acetate | 50/50 | $90 | 215.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, A.; Yu, E.; Morose, G.; Nguyen, D.T.; Chen, W.-T. Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool. Separations 2021, 8, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8100172
Sharma A, Yu E, Morose G, Nguyen DT, Chen W-T. Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool. Separations. 2021; 8(10):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8100172
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Apekshya, Evan Yu, Gregory Morose, David Trung Nguyen, and Wan-Ting Chen. 2021. "Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool" Separations 8, no. 10: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8100172
APA StyleSharma, A., Yu, E., Morose, G., Nguyen, D. T., & Chen, W.-T. (2021). Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool. Separations, 8(10), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8100172






