Adsorption of Orange G in Liquid Solution by the Amino Functionalized GO
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of AS-GO
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Data Analysis
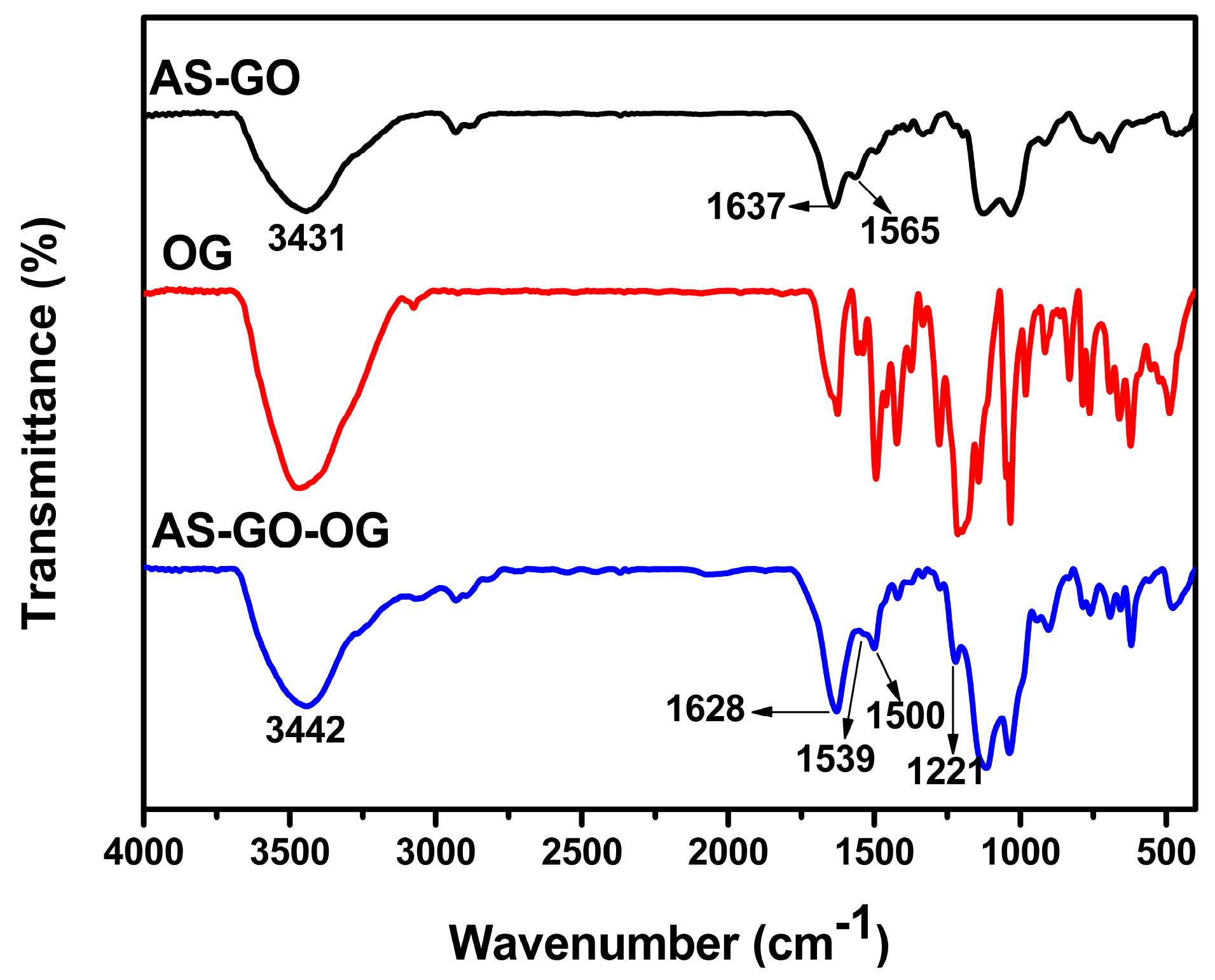
2.5. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal Experiments
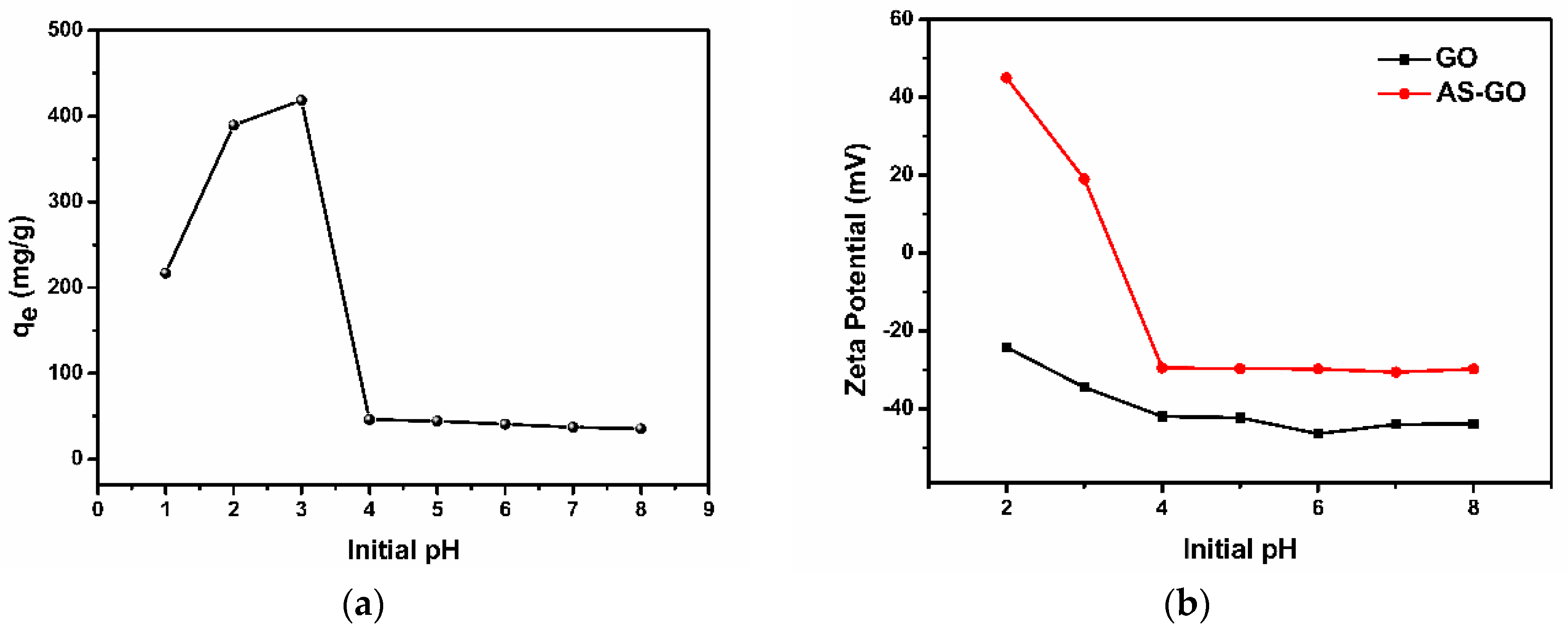
3.1.1. Effect of Initial pH
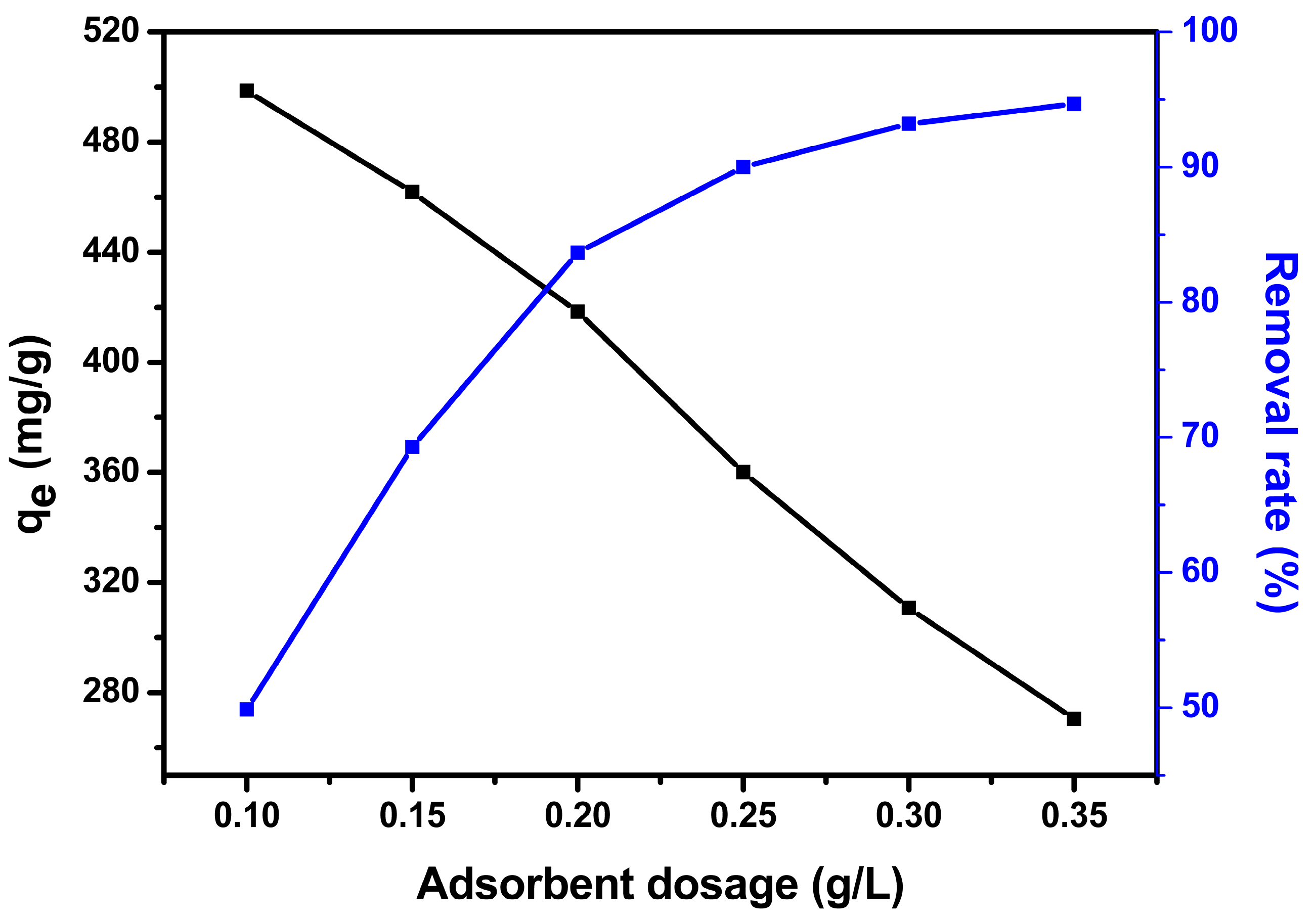
3.1.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
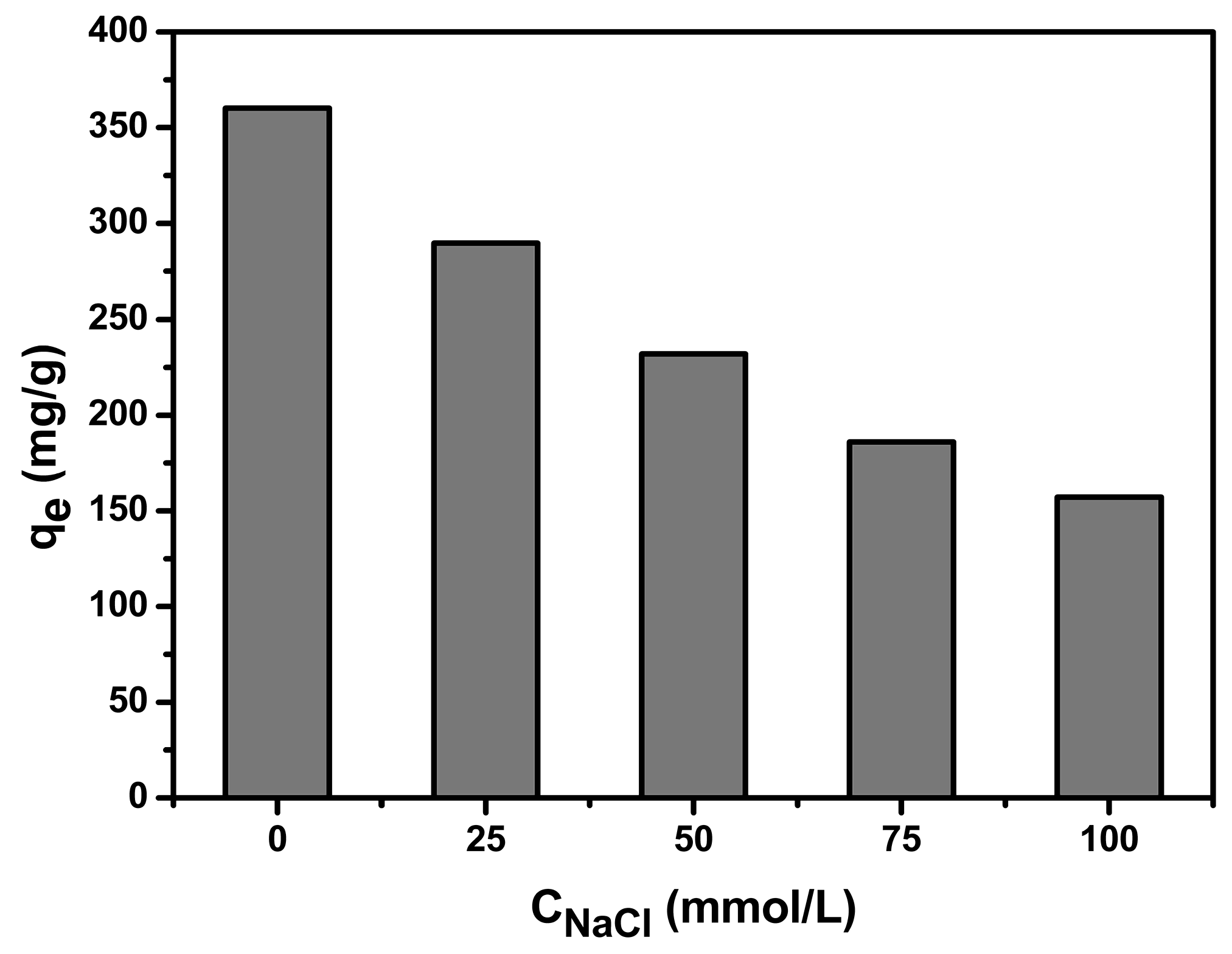
3.1.3. Effect of Chloride Ionic Strength
3.2. Adsorption Isotherm
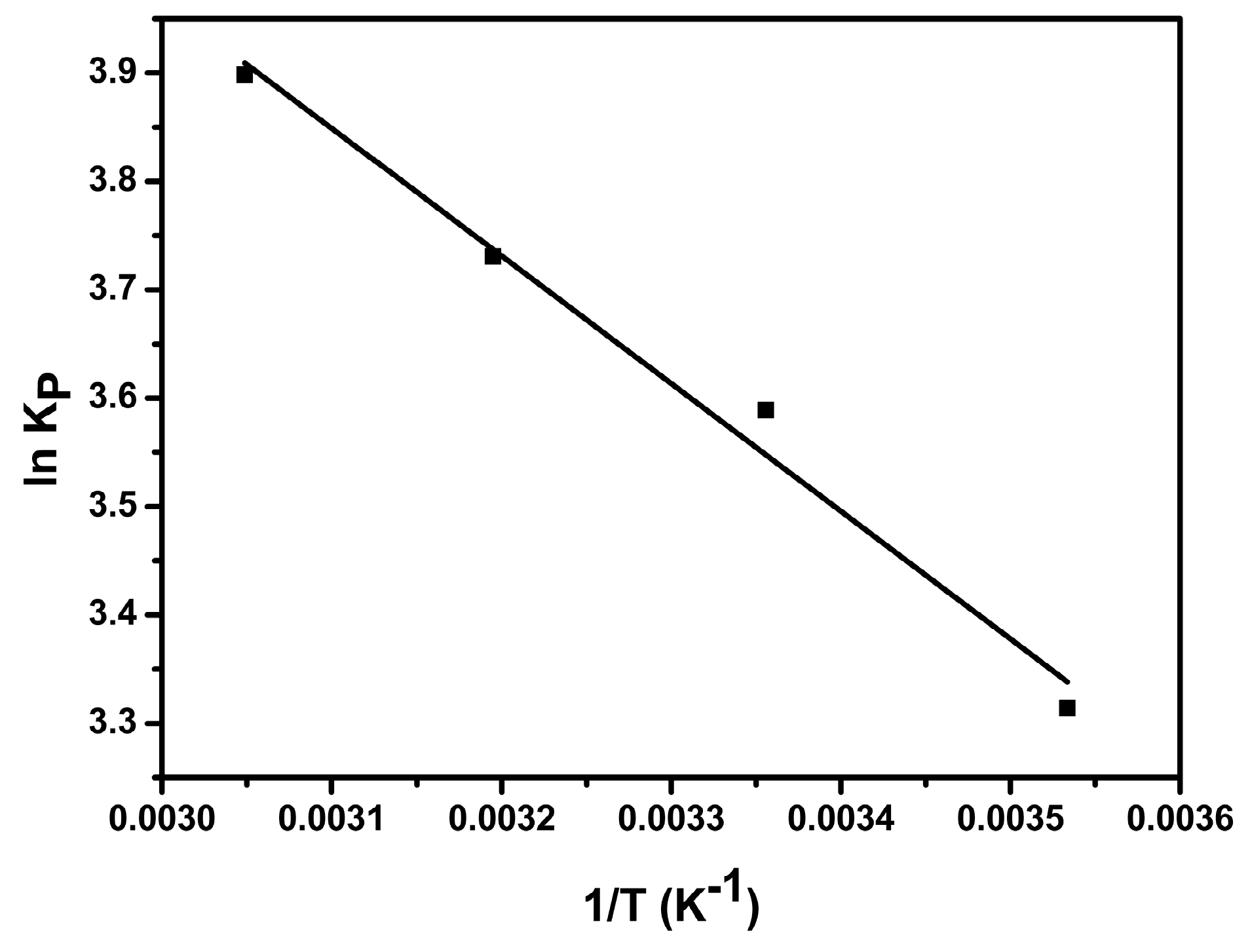
3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
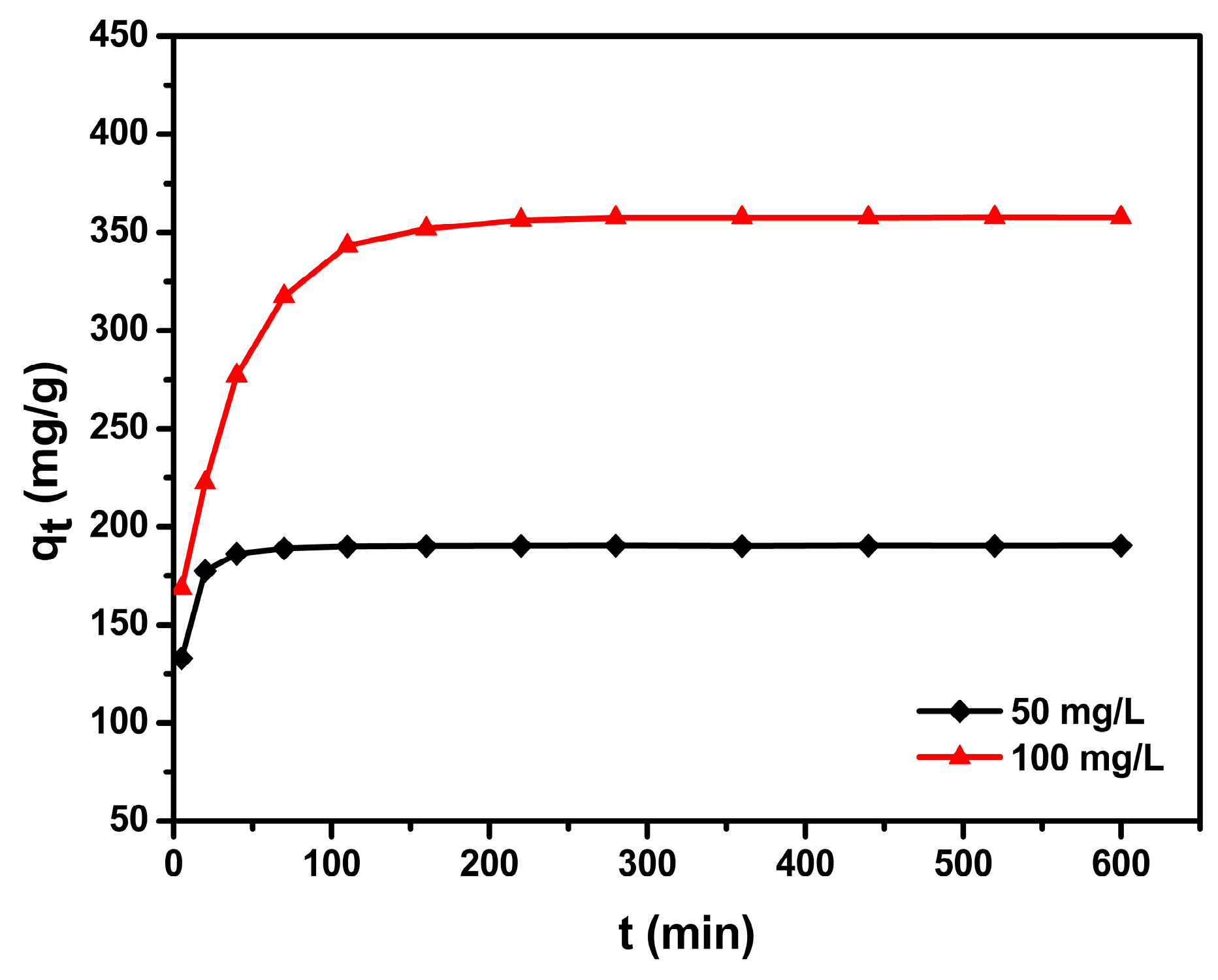
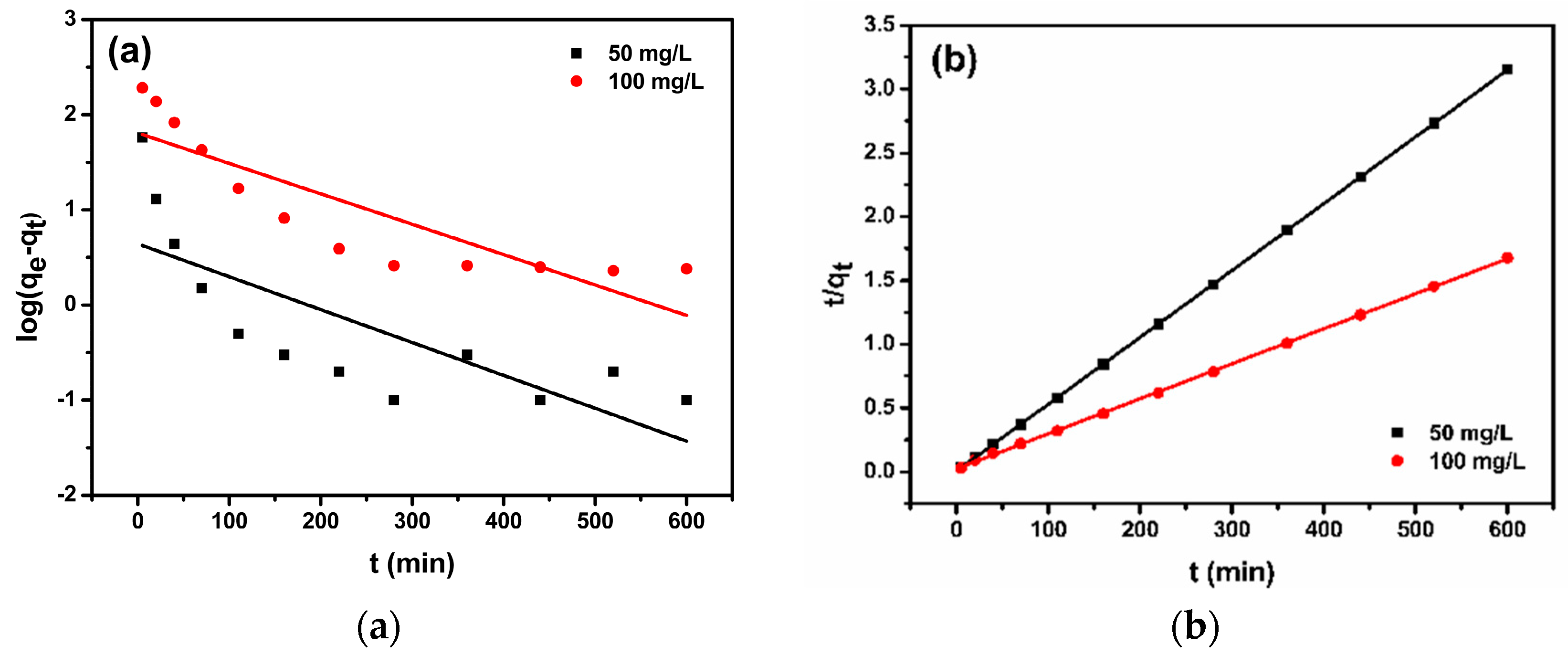
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
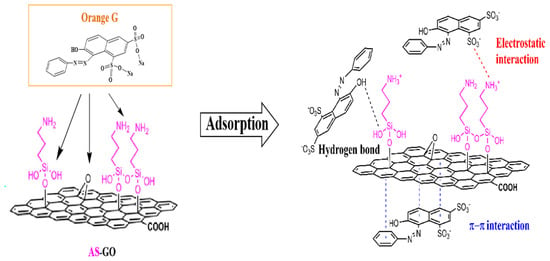
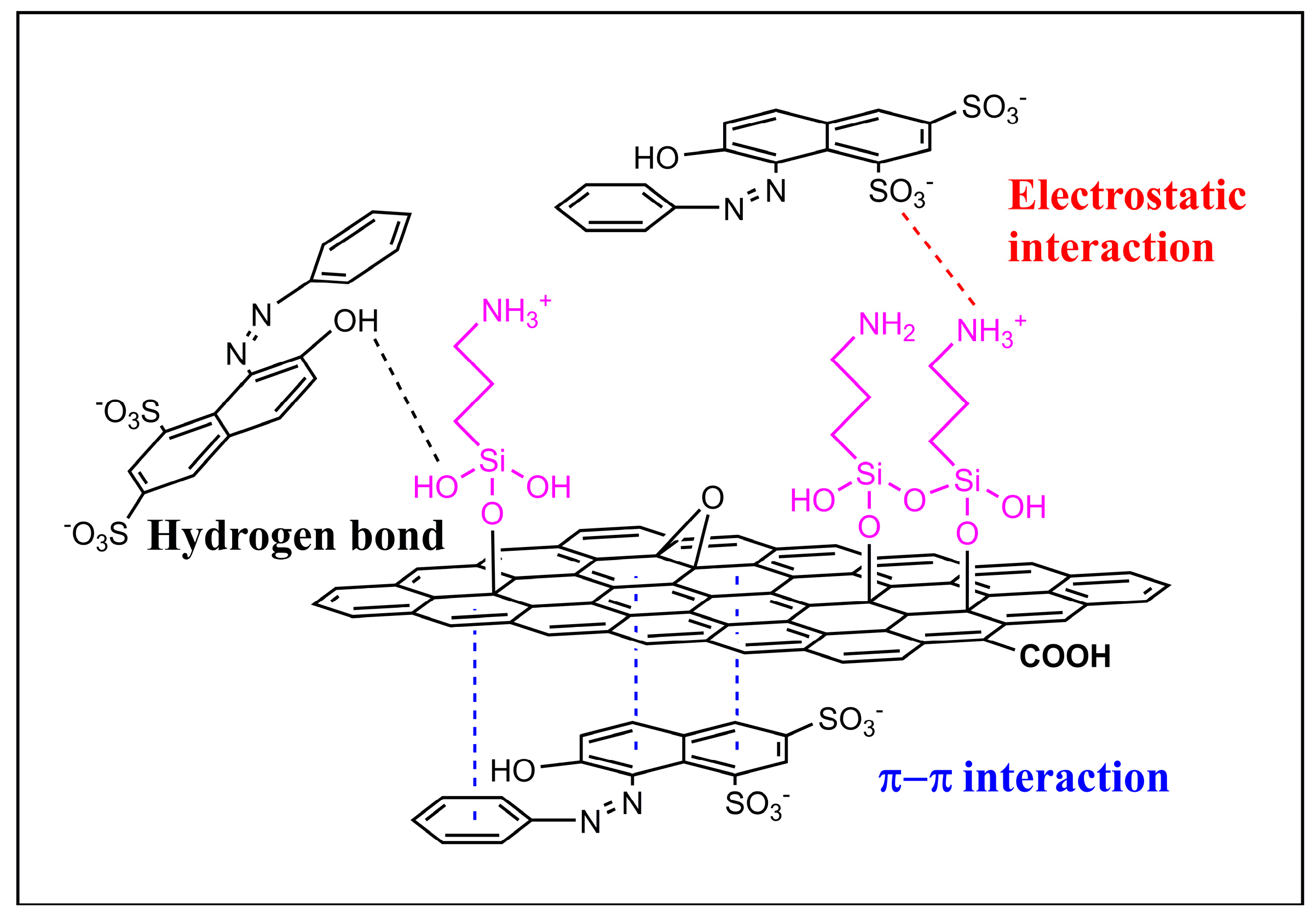
3.5. Probable Mechanisms
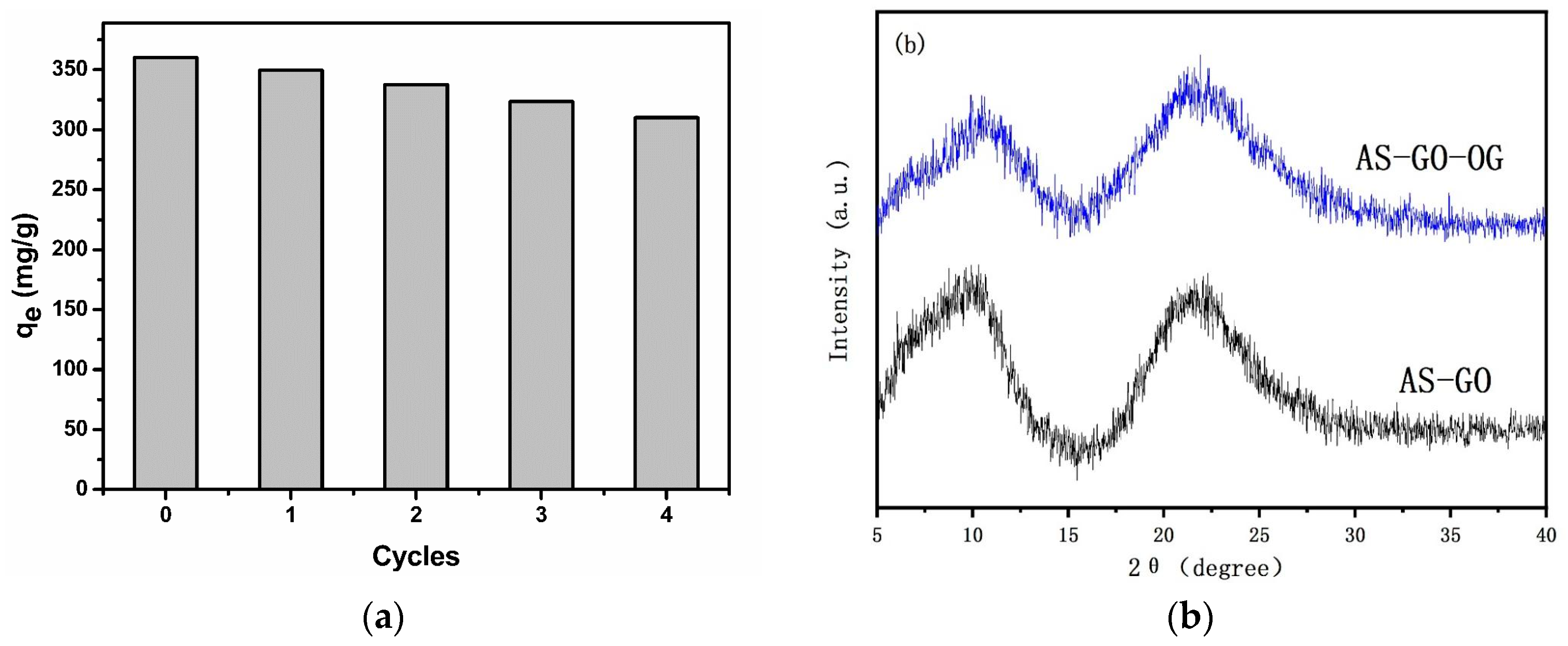
3.6. Adsorbent Regeneration and Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuksel, A.; Sasaki, M.; Goto, M. Complete degradation of Orange G by electrolysis in sub-critical water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, W.; Xie, Z.; Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes via pi-pi interactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12126–12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, D.; Kiziltas, H.; Ungan, H. Kinetic evaluation of ZnO/TiO2 thin film photocatalyst in photocatalytic degradation of Orange G. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddas, S.M.T.H.; Elahi, B.; Javanbakht, V. Biosynthesis of pure zinc oxide nanoparticles using Quince seed mucilage for photocatalytic dye degradation. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xu, J.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W.; Yu, J. Synthesis and adsorption performance of Mg(OH)(2) hexagonal nanosheet-graphene oxide composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. Preparation and utilization of sludge-based activated carbon for the adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, N.B.; Bentouami, A.; Derriche, Z.; Bettahar, N.; de Menorval, L.C. Synthesis and characterization of Mg-Fe layer double hydroxides and its application on adsorption of Orange G from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Shuang, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Effect of polymeric matrix on the adsorption of reactive dye by anion-exchange resins. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2016, 62, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Ma, J.; Shao, L. Highly regenerable alkali-resistant magnetic nanoparticles inspired by mussels for rapid selective dye removal offer high-efficiency environmental remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19960–19968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawagon, C.P.; Amon, R.E.C. Magnetic rice husk ash ‘cleanser’ as efficient methylene blue adsorbent. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, C.; Velmurugan, V.; Jacob, G.; Jeong, S.K.; Grace, A.N.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1116–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dubey, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption characteristics of alumina nanoparticles for the removal of hazardous dye, Orange G from aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5339–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumar, M.; Sathishkumar, P.; Palvannan, T. Optimization of Orange G dye adsorption by activated carbon of Thespesia populnea pods using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, X. Selective and Competitive Adsorption of Azo Dyes on the Metal-Organic Framework ZIF-67. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Yang, S.; Tian, Z.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W. NiFe-LDH nanosheet/carbon fiber nanocomposite with enhanced anionic dye adsorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jiang, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; He, F. Highly efficient selective adsorption of anionic dyes by modified beta-cyclodextrin polymers. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2020, 108, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ni, F.; Cui, A.; Chen, X.; Deng, S.; Shen, F.; Huang, C.; Yang, G.; Song, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. New insight into adsorption and co-adsorption of arsenic and tetracycline using a Y-immobilized graphene oxide-alginate hydrogel: Adsorption behaviours and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene oxide composites as an efficient and recoverable adsorbent for Cd(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhan, X.; Fang, P.; Xia, M.; Yu, J.; Chi, R. A Facile One-Pot Strategy to Functionalize Graphene Oxide with Poly(amino-phosphonic Acid) Derived from Wasted Acrylic Fibers for Effective Gd(III) Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19857–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadrang, C.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, N.; Zhu, J.; Feng, H.; Gorring, M.; Kasner, M.L.; Hou, S. Adsorption Behavior of EDTA-Graphene Oxide for Pb (II) Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Li, X.; Ning, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Efficient adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene oxide modified persimmon tannins. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 108, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, A.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, P. Effective NH2-grafting on attapulgite surfaces for adsorption of reactive dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, V.V.C.; Nora, F.B.D.; Peres, E.C.; Reis, G.S.; Lima, E.C.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Dotto, G.L. Synthesis and characterization of biopolymers functionalized with APTES (3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane) for the adsorption of sunset yellow dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, L.J.; Kim, F.; Huang, J. Langmuir-Blodgett Assembly of Graphite Oxide Single Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Yang, Z.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, Y. Effective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-functionalized graphene oxide. Colloid Surf. A 2017, 520, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, N.; Niu, X. Perchlorate removal from aqueous solution with a novel cationic metal–organic frameworks based on amino sulfonic acid ligand linking with Cu-4,4′-bipyridyl chains. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, A.A.; Donia, A.M.; Al-Amrani, W.A. Adsorption/desorption behavior of acid orange 10 on magnetic silica modified with amine groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, F.; Wu, W.; Bu, R.; Li, W.; Yang, F. Reactive orange 5 removal from aqueous solution using hydroxyl ammonium ionic liquids/layered double hydroxides intercalation composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, C.; Shao, D.; Wang, X. Mutual Effects of Pb(II) and Humic Acid Adsorption on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Polyacrylamide Composites from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3621–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, V.; Botelho, C.; Boaventura, R. Influence of pH, ionic strength and temperature on lead biosorption by Gelidium and agar extraction algal waste. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Hierarchically structured, well-dispersed Ti4+ cross-linked chitosan as an efficient and recyclable sponge-like adsorbent for anionic azo-dye removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 106260–106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, R. Process optimization, kinetics and equilibrium of orange G and acid orange 7 adsorptions onto chitosan/surfactant. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 197, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zeng, G.; Wu, Y. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by rhamnolipid-functionalized graphene oxide from wastewater. Water Res. 2014, 67, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
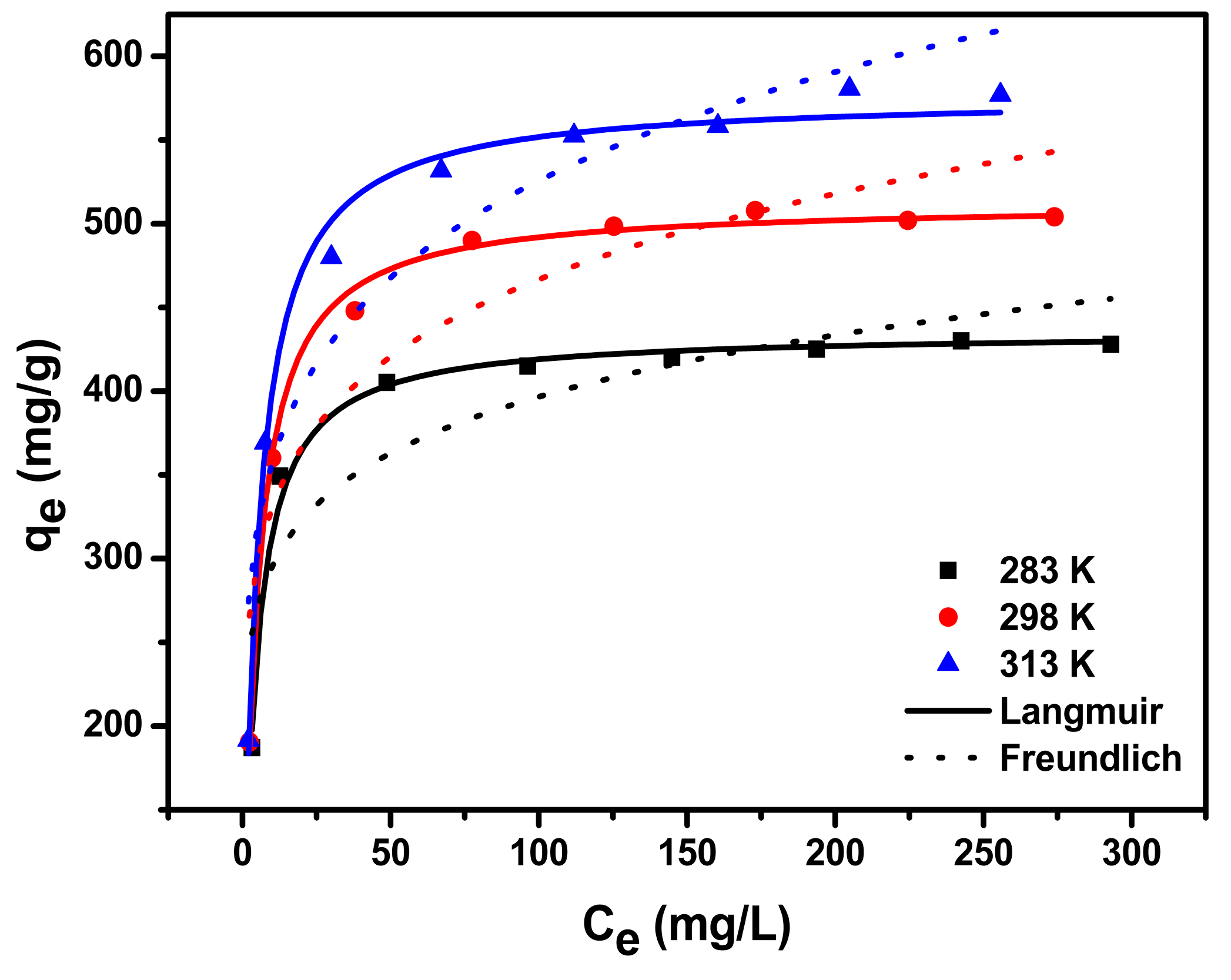
| Temperature (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| 283 | 435.8 | 0.259 | 0.991 | 7.81 | 219.96 | 0.760 |
| 298 | 512.9 | 0.240 | 0.996 | 6.67 | 233.59 | 0.831 |
| 313 | 576.6 | 0.225 | 0.991 | 5.95 | 242.50 | 0.875 |
| Adsorbents | pH | qmax (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| graphene–melamine-sponge | - | 80.51 | [1] |
| activated carbon | 2.0 | 64.93 | [2] |
| MAMPS | 3.0 | 48.98 | [3] |
| Modified P. coccinea | 4.0 | 57.90 | [4] |
| Fe3O4 @catechol/PEI | 4.0 | 192.3 | [5] |
| Fe3O4/MIL-101(Cr) | 3.0 | 200.0 | [6] |
| rGO | 2.0 | 5.98 | [7] |
| Calcined MgAl layered double hydroxides | 4.0 | 665 | [8] |
| magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite | 6.0 | 20.85 | [9] |
| CLDH | - | 378.8 | [10] |
| AS-GO | 3.0 | 576.6 | this work |
| Adsorbent | T (K) | ΔG (KJ mol−1) | ΔH (KJ mol−1) | ΔS (J mol−1 K−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS-GO | 283 | −7.80 | 9.79 | 62.36 | 0.980 |
| 298 | −8.89 | ||||
| 313 | −9.71 | ||||
| 328 | −10.63 |
| C0 (mg/L) | qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | k2 | qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| 50 | 190.5 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 4.4 | 0.568 | 5.09 × 10−3 | 190.8 | 0.999 |
| 100 | 360.1 | 7.37 × 10−3 | 64.3 | 0.732 | 0.33 × 10−3 | 364.9 | 0.999 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; He, C.; Liao, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Zou, B. Adsorption of Orange G in Liquid Solution by the Amino Functionalized GO. Separations 2022, 9, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120391
Yang Z, He C, Liao W, Zhang X, Liu W, Zou B. Adsorption of Orange G in Liquid Solution by the Amino Functionalized GO. Separations. 2022; 9(12):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120391
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhiquan, Chong He, Wenning Liao, Xinyi Zhang, Wanhui Liu, and Baosheng Zou. 2022. "Adsorption of Orange G in Liquid Solution by the Amino Functionalized GO" Separations 9, no. 12: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120391
APA StyleYang, Z., He, C., Liao, W., Zhang, X., Liu, W., & Zou, B. (2022). Adsorption of Orange G in Liquid Solution by the Amino Functionalized GO. Separations, 9(12), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120391