The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Biochar Preparation
2.3. Biochar Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Biochars
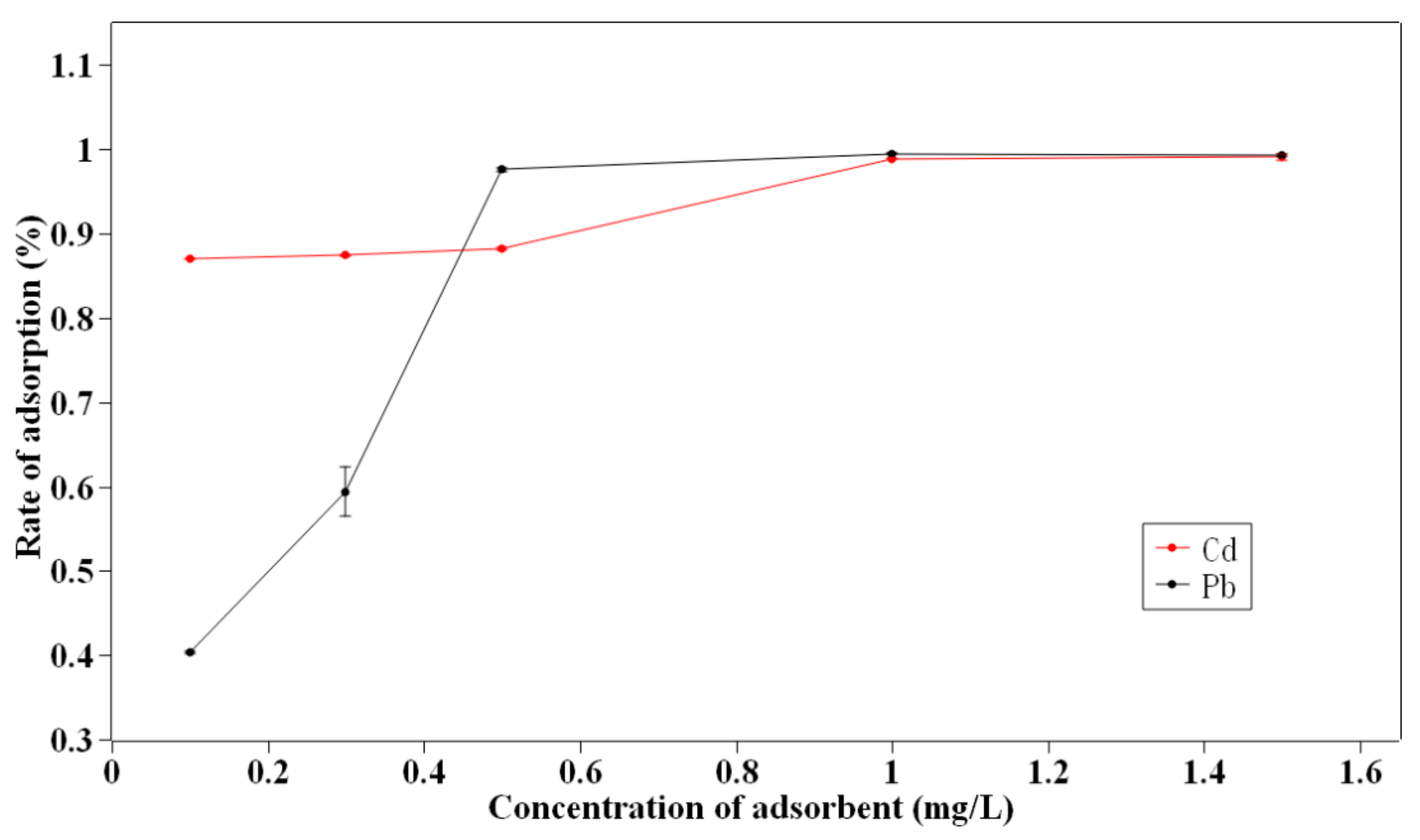
3.2. Adsorbent Dosage Effect
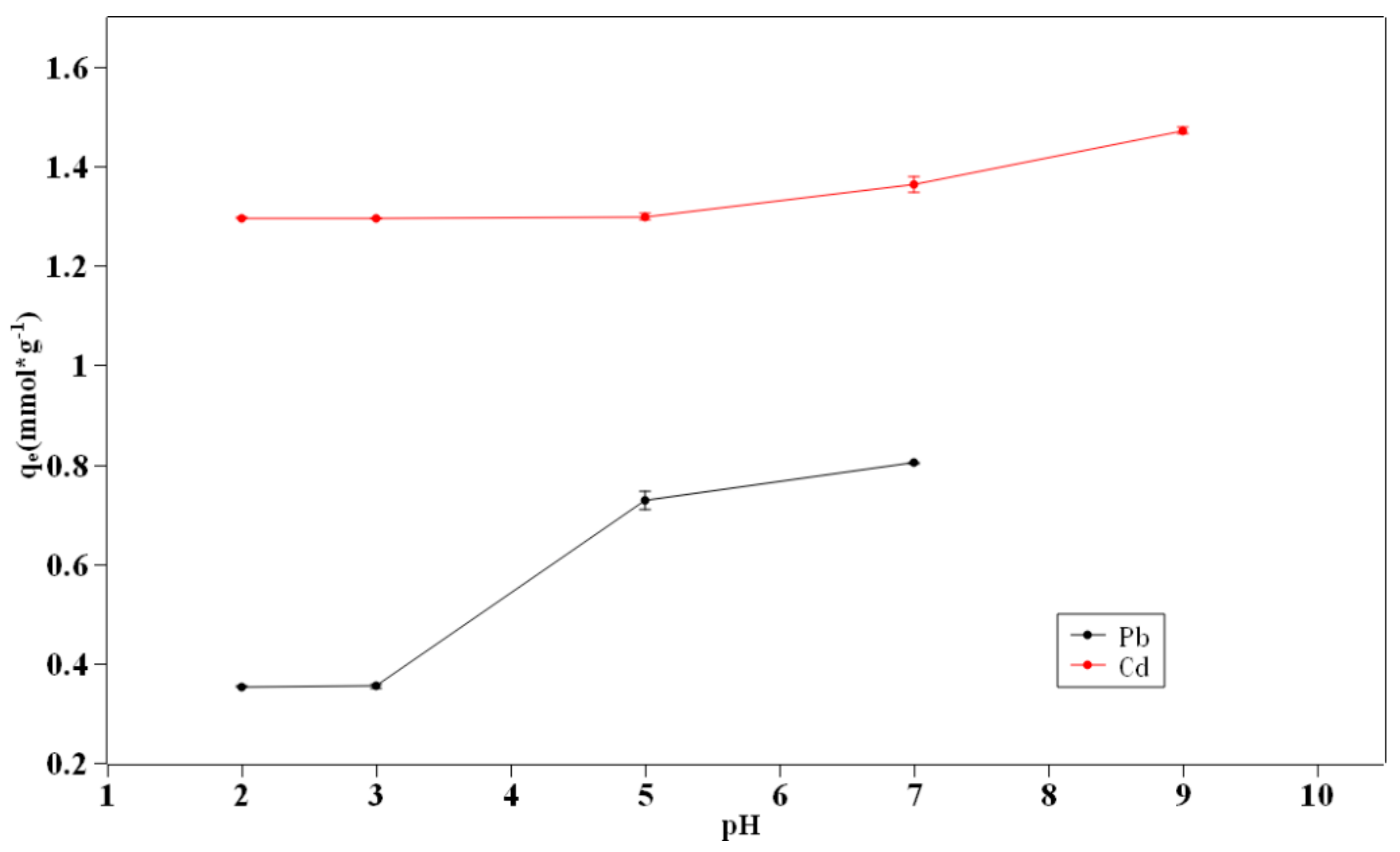
3.3. pH Effect to Biochar Adsorption
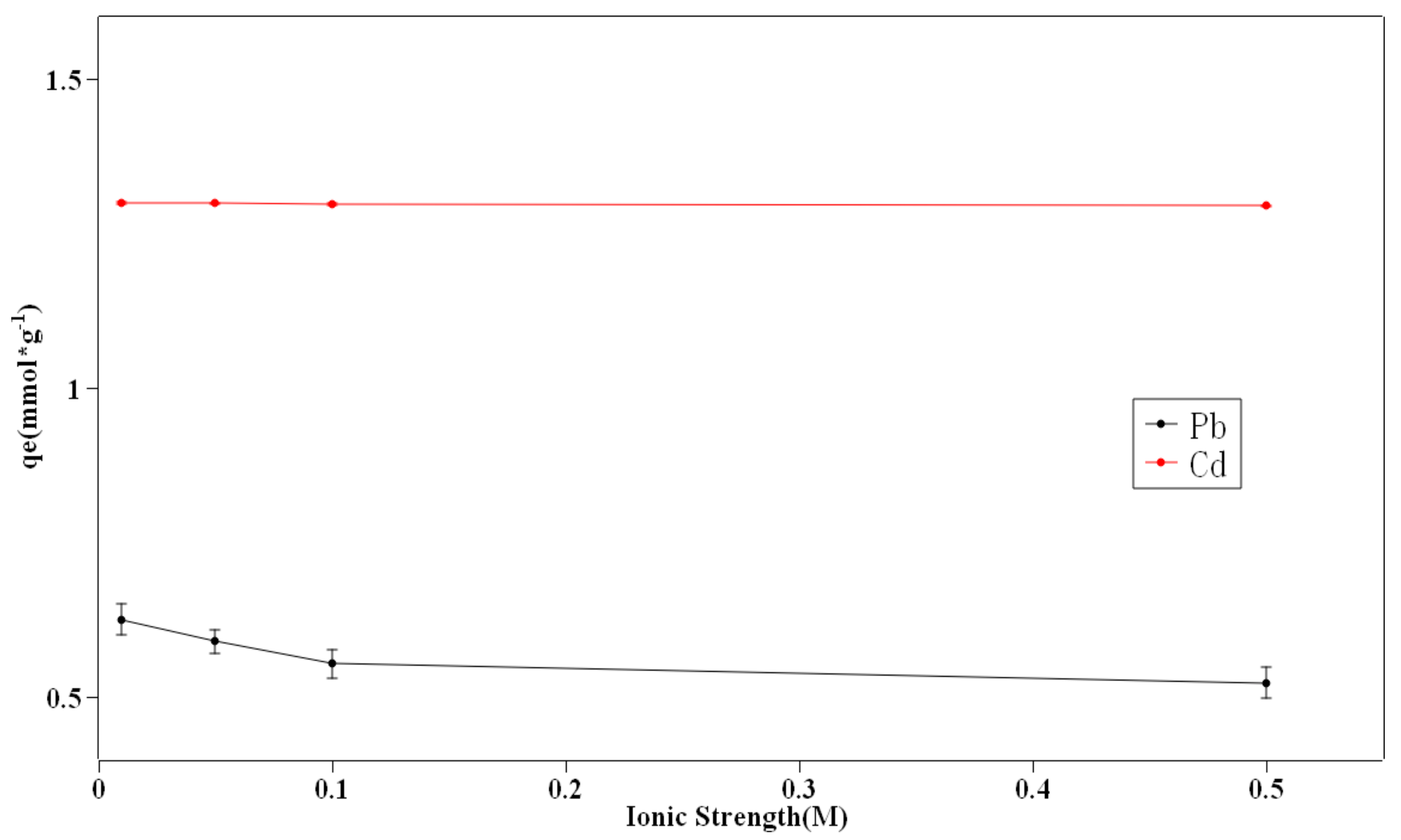
3.4. Ionic Strength and Tempareture Effect
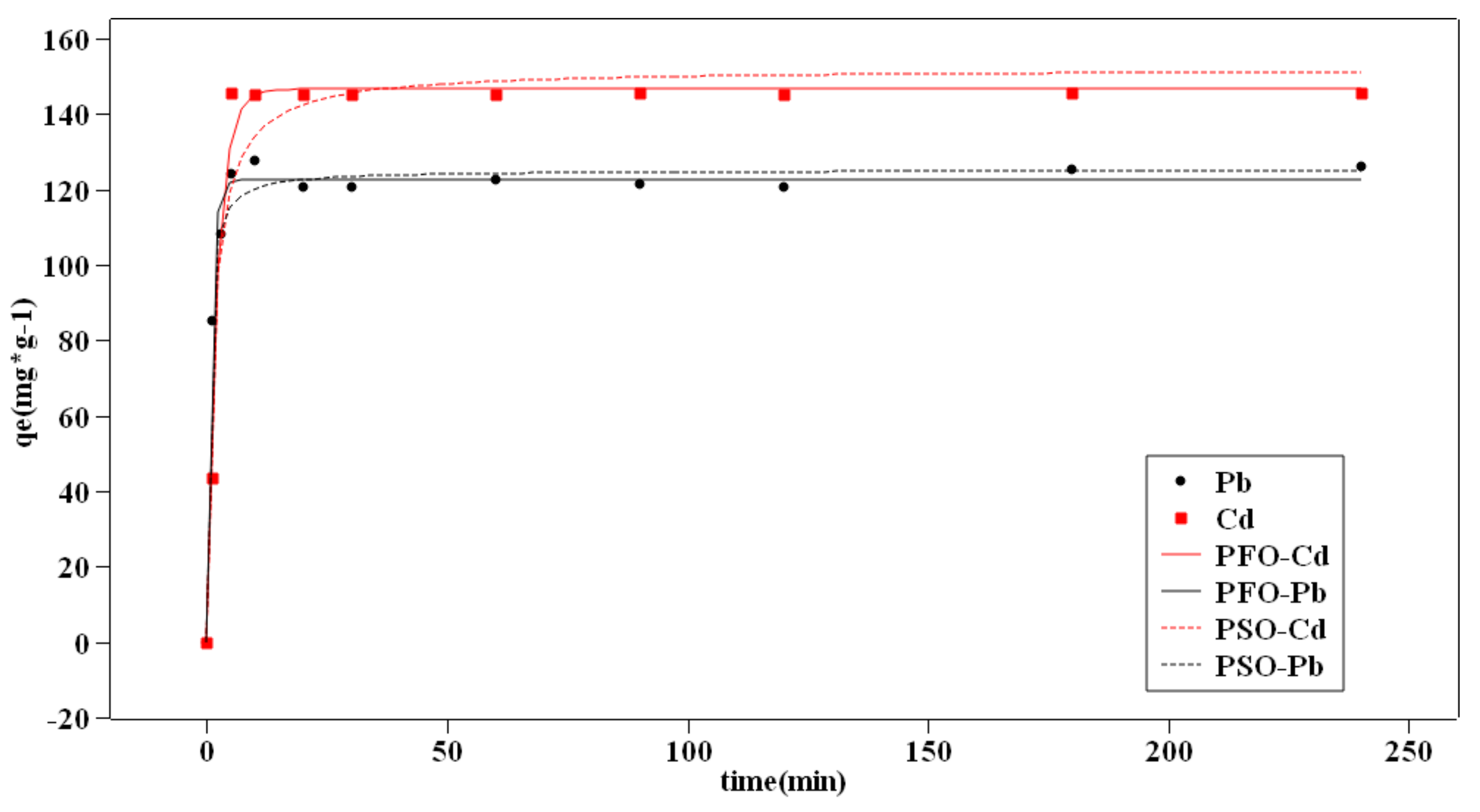
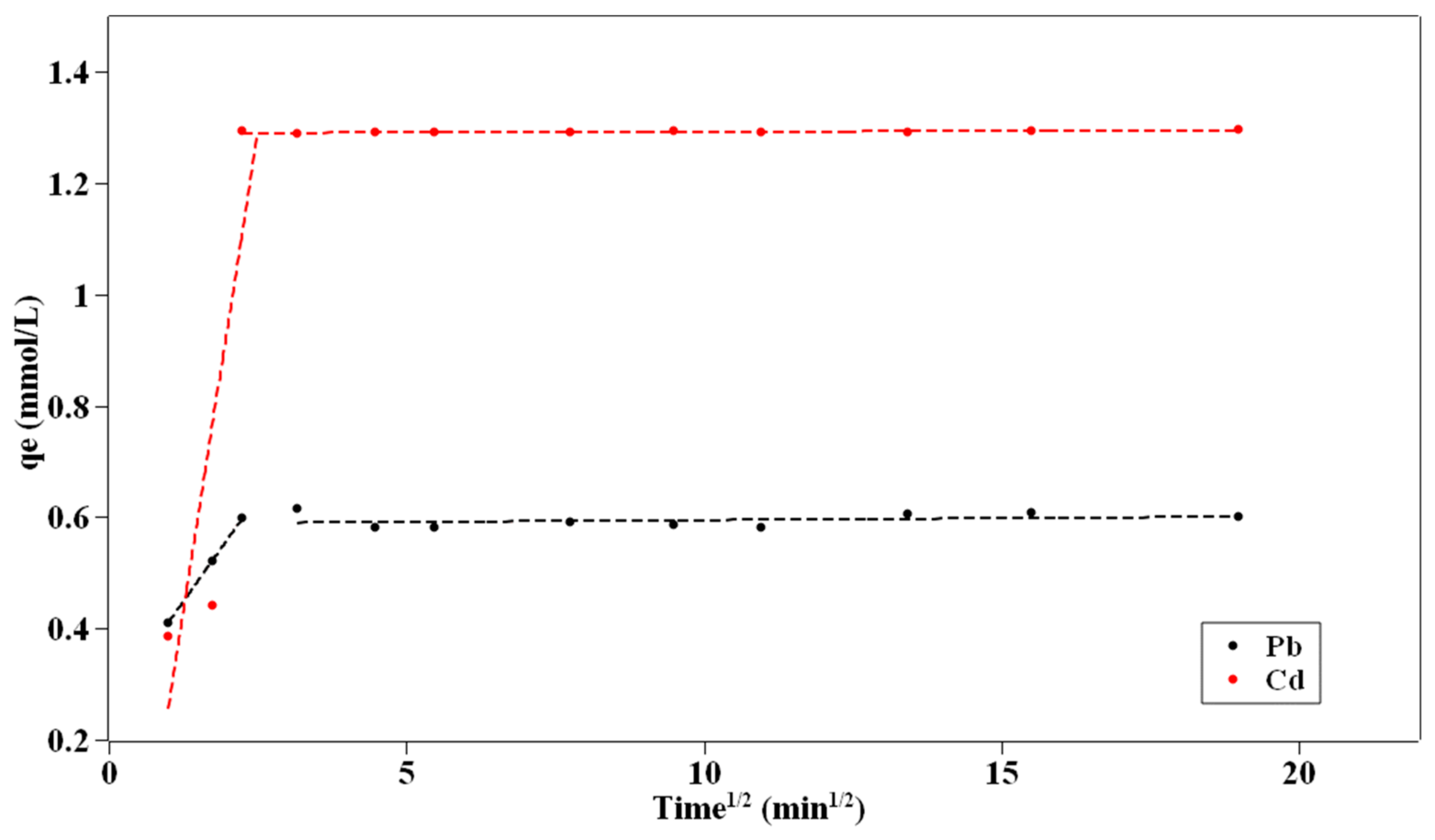
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
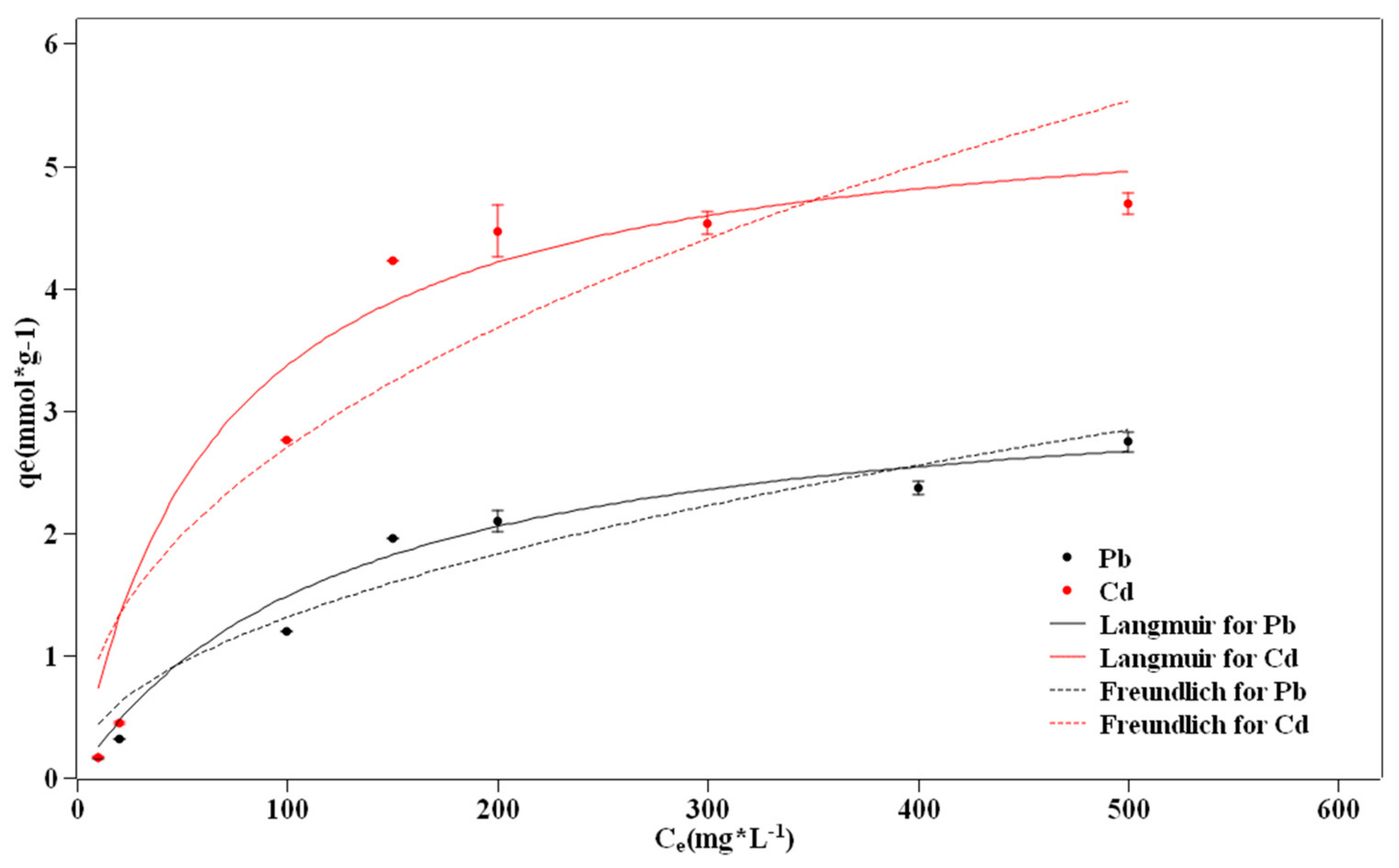
3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3.7. Possible Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
- The adsorption capacity of biochar was high compared to biochar made from other biomasses. According to the adsorbent dosage experiment, the adsorption rate of 0.3 mg/L of biochar reached 60% and 88% for Pb and Cd, respectively, suggesting its good application potential.
- The effects of pH value, ionic strength, and temperature on the removal efficiency were unraveled. Due to the electrostatic attraction, the adsorption capacity improved with the increase of pH value. The background ionic strength caused the adsorption capacity to decrease while the higher temperature could slightly increase the capacity.
- Material characterization revealed possible mechanisms for biochar, and porous structure and functional groups promoted the heavy metals adsorption together. XPS and element ratio analysis indicated that carbon functional group’s reaction was an important adsorption mechanism.
- The kinetic and adsorption isotherm processes were clarified. The PFO model can fit the adsorption data better, and the IPD model showed that more than two steps control the adsorption process. The adsorption process can be described with the Langmuir model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, C.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Ju, M. A water quality management strategy for regionally protected water through health risk assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metal pollution in 3 marine reserves. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Hutchinson, S.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z.; Gao, X. China’s Yangtze Estuary: I. Geomorphic influence on heavy metal accumulation in intertidal sediments. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Fang, P. Analysis of the impact of heavy metal on the Chinese aquaculture and the ecological hazard. AER-Adv. Eng. Res. 2016, 75, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Noerpel, M.R.; Scheckel, K.G.; Ippolito, J.A. Wheat straw biochar reduces environmental cadmium bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Ye, B. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, M.; Wan, X.; Chen, W. Estimation of the accumulation rates and health risks of heavy metals in residential soils of three metropolitan cities in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 115, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Al-Shannag, M. Heavy metal ions removal from wastewater using electrocoagulation processes: A comprehensive review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2649–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: A review of microbial biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.M.; Salem, N.M.; Al-Dujaili, A.H.; Awwad, A.M. Biosorption studies of Cr(VI) ions from electroplating wastewater by walnut shell powder. Am. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.-M.; Flora, J.R.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of heavy metals from water sources in the developing world using low-cost materials: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiyadh, S.S.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Jaafar, W.Z.; AlOmar, M.K.; Fayaed, S.S.; Mohd, N.S.; Hin, L.S.; El-Shafie, A. Review on heavy metal adsorption processes by carbon nanotubes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Lu, H.; Fu, S.; Méndez, A.; Gascó, G. Use of phytoremediation and biochar to remediate heavy metal polluted soils: A review. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.F.; Liu, S.-B.; Liu, Y.-G.; Gu, Y.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Hu, X.-J.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.-H.; Jiang, L.-H. Biochar as potential sustainable precursors for activated carbon production: Multiple applications in environmental protection and energy storage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 227, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam, S.; Arun, J.; Gopinath, K.P.; Ribhu, G.; Ashish, M.; Ajay, S. Biomass as source for hydrochar and biochar production to recover phosphates from wastewater: A review on challenges, commercialization, and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 286, 131490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, O.; Tor, A. In situ preparation of magnetic hydrochar by co-hydrothermal treatment of waste vinasse with red mud and its adsorption property for Pb(II) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by biochar obtained by co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge with tea waste. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 35–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, X. Average Amount and Stability of Available Agro-Climate Resources in the Main Maize Cropping Regions in China during 1981–2010. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, D. Preparation and Application of Porous Biomass Carbon from Corn Stalk. Heilongjiang Sci. 2021, 12, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.; Cai, X. Competitive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by biochars produced from water hyacinths: Performance and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X. Sorption of Sulfamethoxazole on Inorganic Acid Solution-Etched Biochar Derived from Alfalfa. Materials 2021, 14, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yang, G.-D.; Zeng, G.-M.; Cai, Y.; Li, S.-S.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luna, B. Synergistic effect of iron doped ordered mesoporous carbon on adsorption-coupled reduction of hexavalent chromium and the relative mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Askari, M.; Velashjerdi, M.; Arab, B. Phosphoric acid-treated Spent Tea Residue Biochar for Wastewater Decoloring: Batch Adsorption Study and Process Intensification using Multivariate Data-based Optimization. Chem. Eng. Process 2020, 158, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Lehmann, J.; McBride, M.B.; Hay, A.G. Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, J.; Hellwig, P.; Mäntele, A.W.; Michel, H. Redox dependent changes at the heme propionates in cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans: Direct evidence from FTIR difference spectroscopy in combination with heme propionate 13C labeling. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7400–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBeath, A.V.; Smernik, R.J.; Schneider, M.P.; Schmidt, M.W.; Plant, E.L. Determination of the aromaticity and the degree of aromatic condensation of a thermosequence of wood charcoal using NMR. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Lima, I.; Xing, B.; Gaskin, J.W.; Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Ahmedna, M.; Rehrah, D.; Watts, D.W.; Busscher, W.J.; et al. Characterization of designer biochar produced at different temperatures and their effects on a loamy sand. Ann. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, M.; Hugo, T.; Gorgens, J.; Knoetze, H. Comparison of slow and vacuum pyrolysis of sugar cane bagasse. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 90, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Harris, W. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5222–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channa, A.M.; Baytak, S.; Memon, S.Q.; Talpur, M.Y. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of removal of phenol from aqueous solution using surface engineered chemistry. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.Y.; Cao, Y.; Qi, F.F.; Li, X.Q.; Xu, Q. Atrazine adsorption removal with nylon6/ polypyrrole core-shell nanofibers mat: Possible mechanism and characteristics. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.-S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beni, A.A.; Esmaeili, A. Biosorption, an efficient method for removing heavy metals from industrial effluents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Dahiya, S. An experimental and quantum chemical study of removal of utmostly quantified heavy metals in wastewater using coconut husk: A novel approach to mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taqvi, S.; Hasany, S.M. Sorption profile of Cd(II) ions onto beach sand from aqueous solutions. Main Group Met. Chem. 2011, 141, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Min, M.; Shen, L.; Hong, G.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hsiao, B.S. Micro-nano structure poly(ether sulfones)/poly(ethyleneimine) nanofibrous affinity membranes for adsorption of anionic dyes and heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Dai, G.; Wu, J.; Yan, H. Adsorption characteristics of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto a natural biosorbent, fallen Cinnamomum camphora leaves. Desalination 2010, 262, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božić, D.; Stanković, V.; Gorgievski, M.; Bogdanović, G.; Kovačević, R. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sawdust of deciduous trees. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, B.; Das, S.K. Adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural/agricultural wastes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 107, 7–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
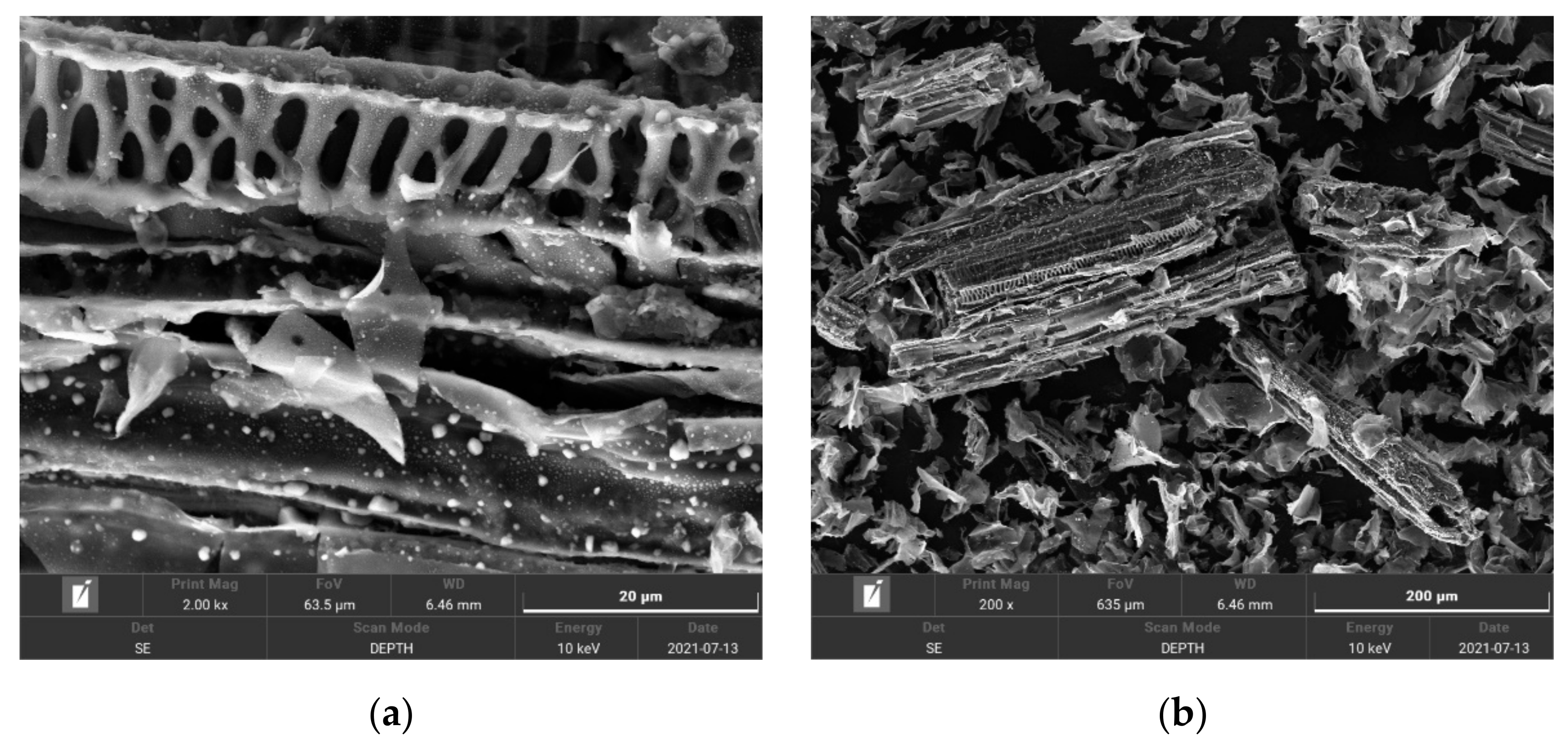
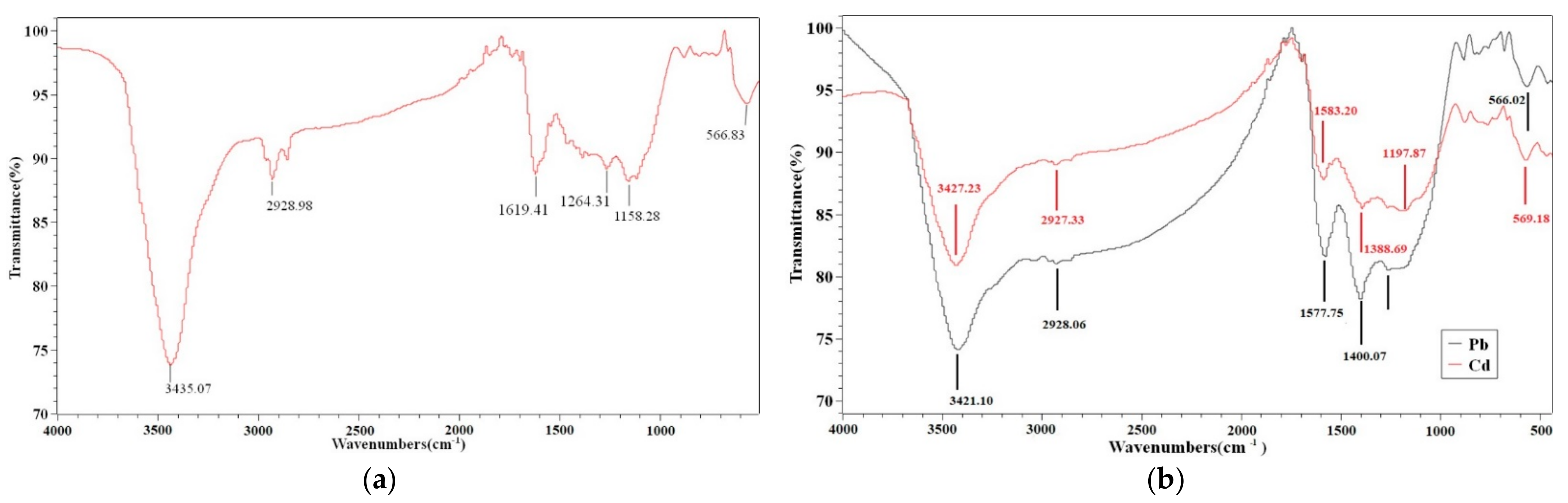


| Biochar | C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC400 | 61.26 | 3.94 | 23.65 | 0.79 |
| BC500 | 68.37 | 3.22 | 19.01 | 0.33 |
| BC600 | 65.49 | 2.24 | 15.97 | 0.69 |
| Name | Peak Binding Energy | Atomic % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Adsorption | Pb Adsorption | Cd Adsorption | ||
| C1s | 284.11 | 75.98 | 84.04 | 81.5 |
| O1s | 531.29 | 22.73 | 11.95 | 10.98 |
| N1s | 400.08 | 1.29 | 0.05 | 6.81 |
| Cd3d | 413.27 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.68 |
| Pb4f | 140.08 | 0.00 | 1.49 | 0.03 |
| Biochar | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC400 | 0.6228 | 0.000386 | 1.239 |
| BC500 | 0.2246 | 0.00145 | 12.873 |
| BC600 | 1.2331 | 0.00305 | 4.947 |
| Metals | PFO | PSO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mmol/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe (mmol/g) | K2 (g ∗ mmol−1 ∗ min−1) | R2 | |
| Pb | 0.592 | 1.104 | 0.988 | 0.603 | 3.597 | 0.987 |
| Cd | 1.306 | 0.293 | 0.987 | 1.356 | 0.353 | 0.985 |
| Metals | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax(mmol/g) | KL(L/mg) | R2 | KF(L/mg) | n | R2 | |
| Pb | 3.334 | 0.008 | 0.986 | 0.143 | 2.079 | 0.933 |
| Cd | 5.613 | 0.015 | 0.962 | 0.347 | 2.245 | 0.841 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Guo, J. The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study. Separations 2022, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020022
Yan S, Yu W, Yang T, Li Q, Guo J. The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study. Separations. 2022; 9(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shiwei, Wei Yu, Ting Yang, Qi Li, and Jiahua Guo. 2022. "The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study" Separations 9, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020022
APA StyleYan, S., Yu, W., Yang, T., Li, Q., & Guo, J. (2022). The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study. Separations, 9(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020022







