A Corruption Impunity Model Considering Anticorruption Policies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Mathematical Model for the CPI
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Model
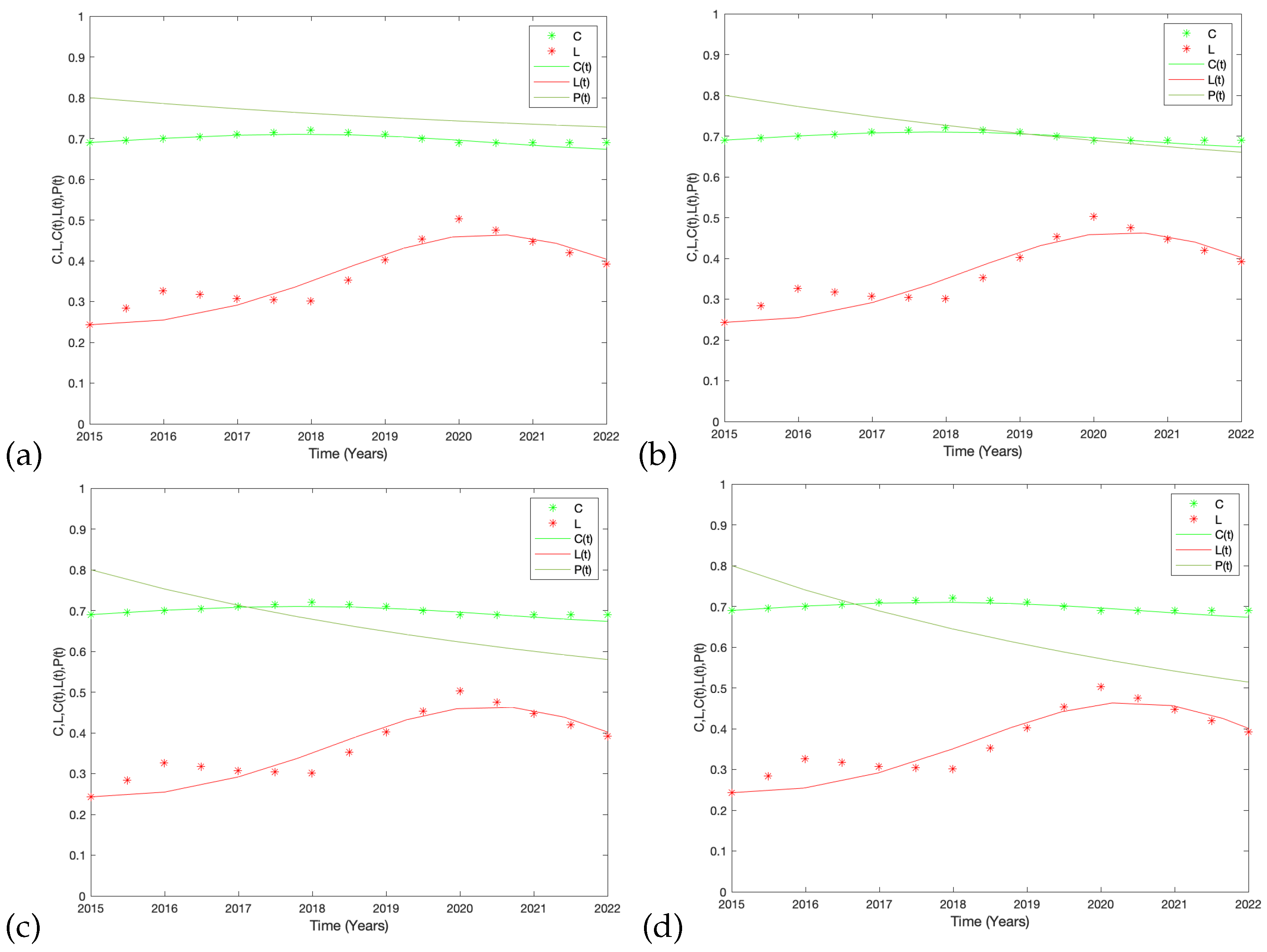
3.2. Data Fitting
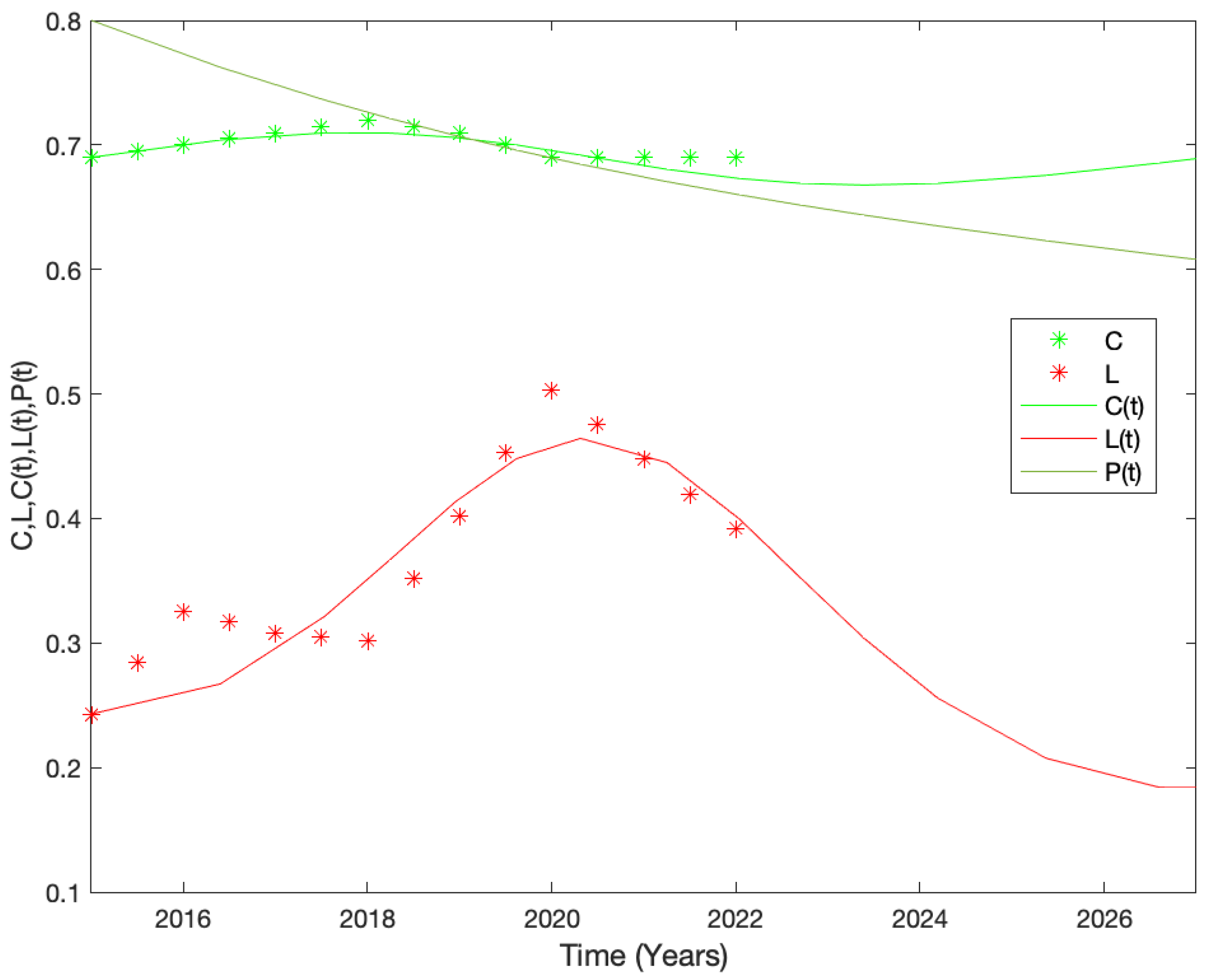
3.3. Numerical Simulations
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- d’Agostino, G.; Dunne, J.; Pieroni, L. Corruption and growth in Africa. Eur. J. Political Econ. 2016, 43, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serritzlew, S.; Sønderskov, K.M.; Svendsen, G.T. Do corruption and social trust affect economic growth? A review. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2014, 16, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründler, K.; Potrafke, N. Corruption and economic growth: New empirical evidence. Eur. J. Political Econ. 2019, 60, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.J.; Fender, J. Corruption and transparency in a growth model. Int. Tax Public Financ. 2006, 13, 115–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transparency-International. What Is Corruption? 2022. Available online: https://www.transparency.org/en/what-is-corruption (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Khan, A.; Krishnan, S. Conceptualizing the impact of corruption in national institutions and national stakeholder service systems on e-government maturity. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 46, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaldi, M.; Del Sarto, S.; Falcone, M.; Troìa, M. Measuring corruption. In Understanding and Fighting Corruption in Europe: From Repression to Prevention; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 43–71. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, A.; Matipira, L.; Saruchera, F.; Musti, K.S. Revisiting corruption mathematical models in the fourth industrial revolution. In Advanced Perspectives on Global Industry Transitions and Business Opportunities; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 270–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rose-Ackerman, S. Corruption: A Study in Political Economy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carloni, E.; Gnaldi, M. Understanding and Fighting Corruption in Europe: From Repression to Prevention; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Accinelli, E.; Martins, F.; Pinto, A.A.; Afsar, A.; Oliveira, B.M. The power of voting and corruption cycles. J. Math. Sociol. 2022, 46, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokoltsov, V.N.; Malafeyev, O.A. Mean-field-game model of corruption. Dyn. Games Appl. 2017, 7, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemecha, L. Modelling corruption dynamics and its analysis. Ethiop. J. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 5, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Alemneh, H.T. Mathematical modeling, analysis, and optimal control of corruption dynamics. J. Appl. Math. 2020, 2020, 5109841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantaye, A.K.; Birhanu, Z.K. Mathematical Model and Analysis of Corruption Dynamics with Optimal Control. J. Appl. Math. 2022, 2022, 8073877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, I.; Abdulrahman, S.; Musa, B.; Adamu, G. Controlling the spread of corruption through social media; a mathematical modelling approach. IOSR J. Math. 2016, 12, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Elnawawy M., S.; Okasha, A.E.; Hosny, H.A. Agent-based models of administrative corruption: An overview. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2022, 42, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Poza, E.; Jódar, L.; Merello, P. Modeling Political Corruption in Spain. Mathematics 2021, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orentlicher, D. Report of Commission on Human Rights of United Nations, 2005; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; Available online: https://www.ohchr.org/sites/default/files/Documents/AboutUs/annualreport2005.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- contra la corrupción y la impunidad, M. Tercera Encuesta Sobre la Corrupción y la Impunidad; REFORMA: Mexico city, Mexico, 2021; Available online: https://contralacorrupcion.mx/tercera-encuesta-nacional-sobre-corrupcion-e-impunidad/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Le Clercq, J.A.; Rodríguez Sánchez Lara, G.R. Global Impunity Index 2020 (GII 2020). Impunity Levels in the World (April 30, 2021). Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3837642 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Yap, J.B.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Rose, T.; Skitmore, M. Corruption in the Malaysian construction industry: Investigating effects, causes, and preventive measures. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJesus, E.X.; Kaufman, C. Routh-Hurwitz criterion in the examination of eigenvalues of a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 35, 5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transparency-International. 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index. 2022. Available online: https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2022 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
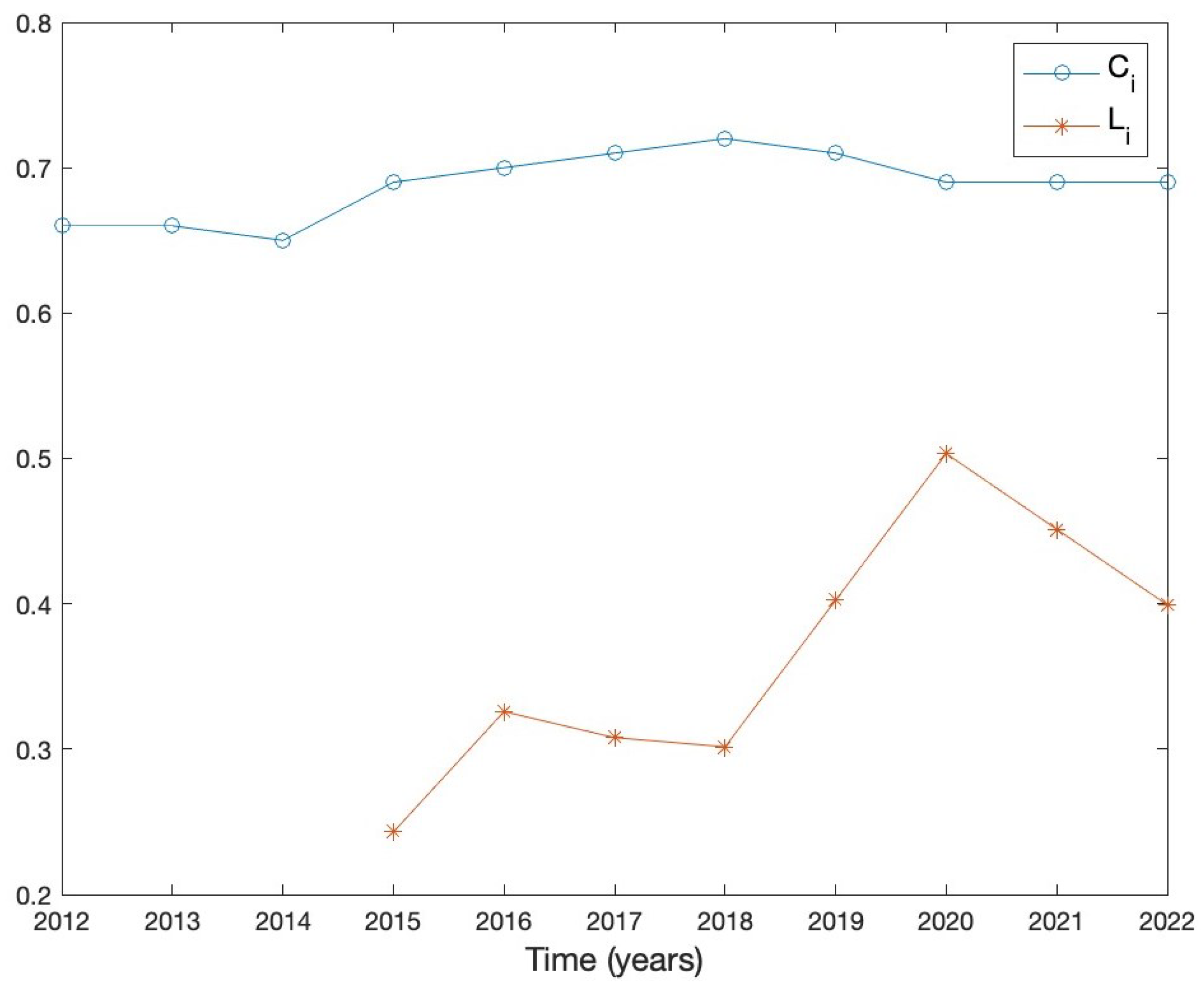
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPI | 34 | 34 | 35 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 29 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGI | 75.7 | 67.42 | 69.21 | 69.84 | — | 49.67 | — | 60.8 |
| 0.2430 | 0.3258 | 0.3079 | 0.3016 | 0.4024 | 0.5033 | 0.4512 | 0.3992 |
| Case P./S. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Flexible/Low | 0.115074042 | 6.37054655 | 0.17792823 | 9.23109606 | 0.0156558527 |
| (b) Flexible/High | 0.10164548 | 6.55250723 | 0.14631298 | 9.49134849 | 0.0156262753 |
| (c) Strict/Low | 0.09616741 | 6.61861840 | 0.13279561 | 9.58577449 | 0.0156320420 |
| (d) Strict/High | 0.03880213 | 7.84229485 | 0.01269290 | 11.35865077 | 0.0156322746 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgadillo-Alemán, S.E.; Kú-Carrillo, R.A.; Torres-Nájera, A. A Corruption Impunity Model Considering Anticorruption Policies. Math. Comput. Appl. 2024, 29, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050081
Delgadillo-Alemán SE, Kú-Carrillo RA, Torres-Nájera A. A Corruption Impunity Model Considering Anticorruption Policies. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2024; 29(5):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050081
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgadillo-Alemán, Sandra E., Roberto A. Kú-Carrillo, and Alejandra Torres-Nájera. 2024. "A Corruption Impunity Model Considering Anticorruption Policies" Mathematical and Computational Applications 29, no. 5: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050081
APA StyleDelgadillo-Alemán, S. E., Kú-Carrillo, R. A., & Torres-Nájera, A. (2024). A Corruption Impunity Model Considering Anticorruption Policies. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 29(5), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050081








