Self-Adjusting Optical Systems Based on Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
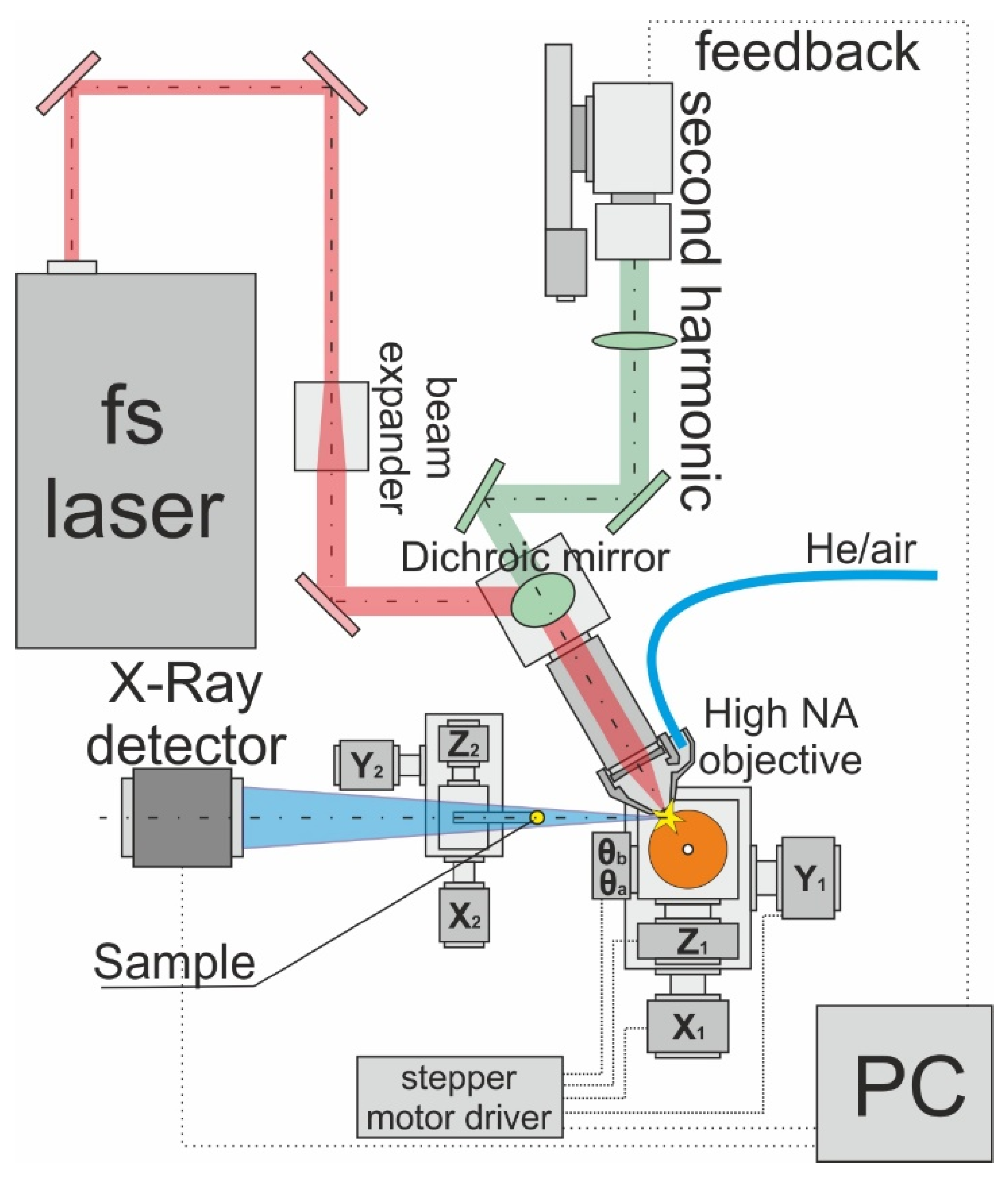
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Neural Network Architecture
2.3. Construction of the Reward Function
- −3 if the neural network suggests leaving the movement area (no movement occurs in this case).
- −1 × (It−1 − It) + (It − Imax)/Imax, where It is the signal amplitude at the current step, It−1 is the signal amplitude at the previous step, and Imax is the maximum amplitude over all previous steps, if the feedback amplitude decreases during the current step.
- (It−1 −It) + (It − Imax)/Imax, if the feedback amplitude increases during the current step.
- 0.5 if the pause occurs within the range of 0.9 Imax–Imax (due to fluctuations in the feedback signal).
- −(It − Imax)/Imax if the pause occurs within the range of 0.9 Imax–Imax (to avoid stopping outside the optimum).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Feedback Signal Selection
3.2. Checking the Operation and Stability of the Neural Network in the Sandbox
3.3. Coupling the Laser Pulse into a Fiber Using Reinforcement Machine Learning
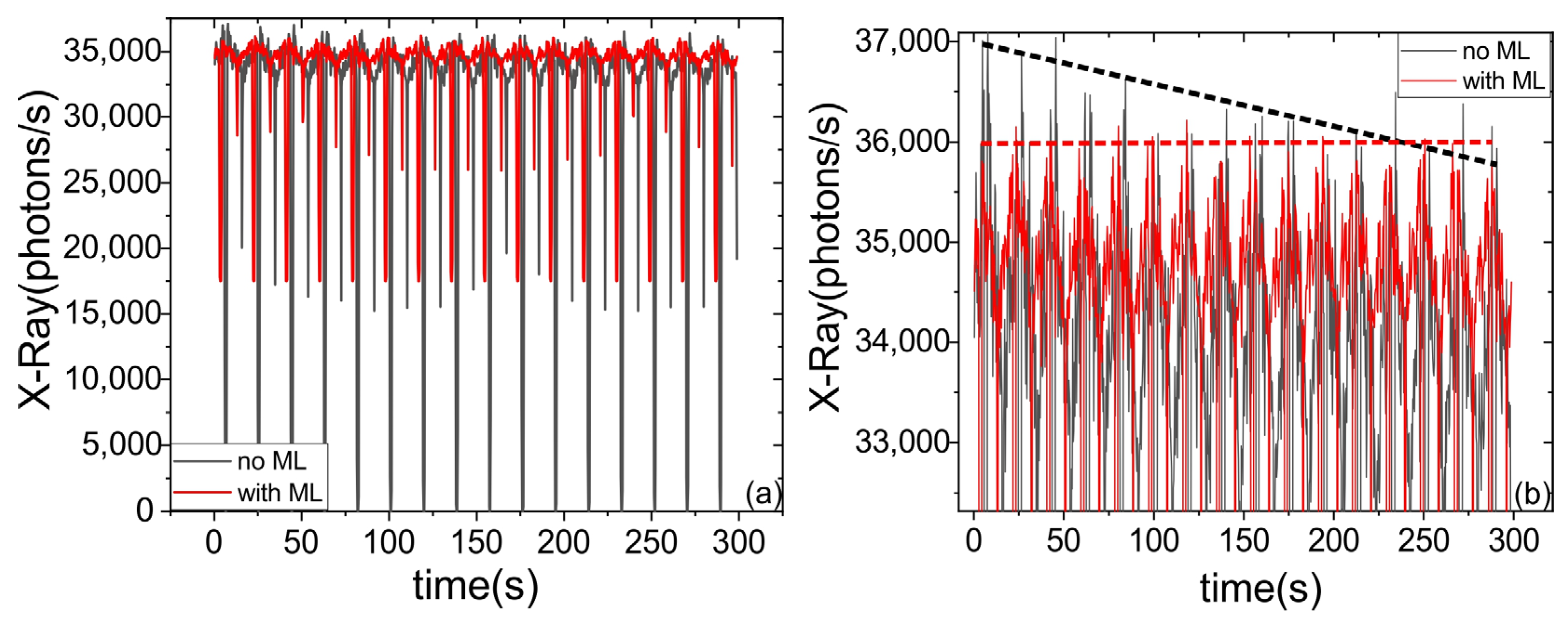
3.4. Stabilising the Intencity of the X-ray Source
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, S.; Rivory, J.; Schoenauer, M. Synthesis of Optical Multilayer Systems Using Genetic Algorithms. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, B.; Yan, Z.; Bünzli, J.C.G. Emerging Role of Machine Learning in Light-Matter Interaction. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, G.; Salmela, L.; Dudley, J.M.; Brunner, D.; Kokhanovskiy, A.; Kobtsev, S.; Turitsyn, S.K. Machine Learning and Applications in Ultrafast Photonics. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.S. Deep Learning: A New Tool for Photonic Nanostructure Design. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Mahjoubfar, A.; Tai, L.C.; Blaby, I.K.; Huang, A.; Niazi, K.R.; Jalali, B. Deep Learning in Label-Free Cell Classification. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, A.; Wiesner, T.; Gardner, M.A.; Robitaille, L.É.; Bilodeau, A.; Gagné, C.; De Koninck, P.; Lavoie-Cardinal, F. A Machine Learning Approach for Online Automated Optimization of Super-Resolution Optical Microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, A.M.; Kovlakov, E.; Bianchi, F.; Yudin, D.; Straupe, S.; Biamonte, J.D.; Kulik, S. Experimental Neural Network Enhanced Quantum Tomography. npj Quantum Inf. 2020, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugnan, A.; Katumba, A.; Laporte, F.; Freiberger, M.; Sackesyn, S.; Ma, C.; Gooskens, E.; Dambre, J.; Bienstman, P. Photonic Neuromorphic Information Processing and Reservoir Computing. APL Photonics 2020, 5, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kaiser, E.; Brunton, S.L.; Nathan Kutz, J. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Optical Systems: A Case Study of Mode-Locked Lasers. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, K.; Li, T.; Wu, D.; Jiang, T. Low-Latency Deep-Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Ultrafast Fiber Lasers. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchon, N.; Fenu, G.; Gaio, G.; Lonza, M.; O’shea, F.H.; Pellegrino, F.A.; Salvato, E. Basic Reinforcement Learning Techniques to Control the Intensity of a Seeded Free-Electron Laser. Electronics 2020, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprikov, E.; Kokhanovskiy, A.; Serebrennikov, K.; Turitsyn, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Self-Tuning Laser Source of Dissipative Solitons. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwami, R.; Mihana, T.; Kanno, K.; Sunada, S.; Naruse, M.; Uchida, A. Controlling Chaotic Itinerancy in Laser Dynamics for Reinforcement Learning. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masinelli, G.; Le-Quang, T.; Zanoli, S.; Wasmer, K.; Shevchik, S.A. Adaptive Laser Welding Control: A Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 103803–103814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmatina, A.A.; Asadchikov, V.E.; Buzmakov, A.V.; Dyachkova, I.G.; Dymshits, Y.M.; Baranov, A.I.; Myasnikov, D.V.; Minaev, N.V.; Gordienko, V.M. Microfocus Source of Characteristic X-rays for Phase-Contrast Imaging Based on a Femtosecond Fiber Laser. Crystallogr. Rep. 2022, 67, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousse, A.; Audebert, P.; Geindre, J.P.; Falliès, F.; Gauthier, J.C.; Mysyrowicz, A.; Grillon, G.; Antonetti, A. Efficient K X-ray Source from Femtosecond Laser-Produced Plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 50, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmatina, A.A.; Shubnyi, A.G.; Asadchikov, V.E.; Nuzdin, A.D.; Baranov, A.I.; Myasnikov, D.V.; Minaev, N.V.; Gordienko, V.M. X-ray Generation under Interaction of a Femtosecond Fiber Laser with a Target and a Prospective for Laser-Plasma X-ray Microscopy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2036, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mareev, E.; Garmatina, A.; Semenov, T.; Asharchuk, N.; Rovenko, V.; Dyachkova, I. Self-Adjusting Optical Systems Based on Reinforcement Learning. Photonics 2023, 10, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101097
Mareev E, Garmatina A, Semenov T, Asharchuk N, Rovenko V, Dyachkova I. Self-Adjusting Optical Systems Based on Reinforcement Learning. Photonics. 2023; 10(10):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101097
Chicago/Turabian StyleMareev, Evgenii, Alena Garmatina, Timur Semenov, Nika Asharchuk, Vladimir Rovenko, and Irina Dyachkova. 2023. "Self-Adjusting Optical Systems Based on Reinforcement Learning" Photonics 10, no. 10: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101097
APA StyleMareev, E., Garmatina, A., Semenov, T., Asharchuk, N., Rovenko, V., & Dyachkova, I. (2023). Self-Adjusting Optical Systems Based on Reinforcement Learning. Photonics, 10(10), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101097




