Effect of a Novel Handheld Photobiomodulation Therapy Device in the Management of Chemoradiation Therapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Case Series Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. The New Handheld PBMT Device
2.3. Treatment Protocol
2.4. Clinical Efficacy and Patients’ Quality of Life
2.5. Metagenomics Analysis Based on 16S rRNA Gene for the Salivary Microbiome
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy of PBMT in the Study Population
3.2. Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) by EORTC QLQ-C30 Questionnaires
3.3. Safety and Patient Compliance
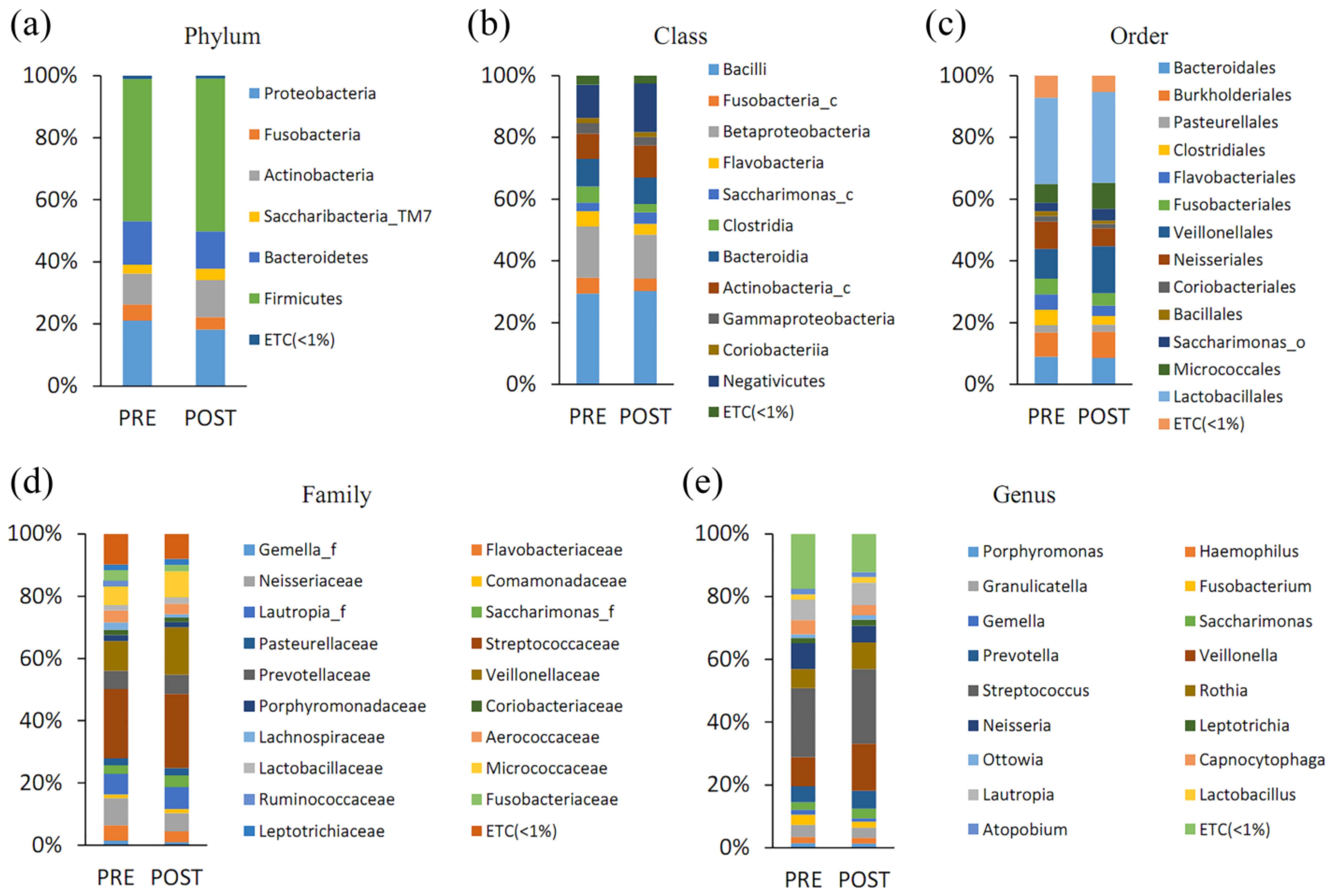
3.4. Effects of PBMT Device on the Microbiome Composition in the Saliva of Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Legouté, F.; Bensadoun, R.-J.; Seegers, V.; Pointreau, Y.; Caron, D.; Lang, P.; Prévost, A.; Martin, L.; Schick, U.; Morvant, B. Low-level laser therapy in treatment of chemoradiotherapy-induced mucositis in head and neck cancer: Results of a randomised, triple blind, multicentre phase III trial. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, L. Managing Oral Mucositis in Patients with Cancer. Wounds 2021, 33, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronshaw, M.; Parker, S.; Anagnostaki, E.; Mylona, V.; Lynch, E.; Grootveld, M. Photobiomodulation and oral mucositis: A systematic review. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.M.; Lee, C.M.; Saunders, D.P.; Curtis, A.; Dunlap, N.; Nangia, C.; Lee, A.S.; Gordon, S.M.; Kovoor, P.; Arevalo-Araujo, R.; et al. Phase IIb, Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of GC4419 Versus Placebo to Reduce Severe Oral Mucositis Due to Concurrent Radiotherapy and Cisplatin for Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, M.; Alfonsi, M.; Foa, P.; Giralt, J.; Bardet, E.; Cerezo, L.; Salzwimmer, M.; Lizambri, R.; Emmerson, L.; Chen, M.G.; et al. Palifermin decreases severe oral mucositis of patients undergoing postoperative radiochemotherapy for head and neck cancer: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, P.; Glenny, A.M.; Worthington, H.V.; Littlewood, A.; Mauleffinch, L.M.F.; Clarkson, J.E.; McCabe, M.G. Interventions for preventing oral mucositis in patients with cancer receiving treatment: Cytokines and growth factors. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD011990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oton-Leite, A.F.; Silva, G.B.L.; Morais, M.O.; Silva, T.A.; Leles, C.R.; Valadares, M.C.; Pinezi, J.C.D.; Batista, A.C.; Mendonça, E.F. Effect of low-level laser therapy on chemoradiotherapy-induced oral mucositis and salivary inflammatory mediators in head and neck cancer patients. Lasers Surg. Med. 2015, 47, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.; Al-Dasooqi, N.; Bossi, P.; Wardill, H.; Van Sebille, Y.; Al-Azri, A.; Bateman, E.; Correa, M.E.; Raber-Durlacher, J.; Kandwal, A.; et al. The pathogenesis of mucositis: Updated perspectives and emerging targets. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 4023–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.; Cronshaw, M.; Grootveld, M. Photobiomodulation Delivery Parameters in Dentistry: An Evidence-Based Approach. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser. Surg. 2022, 40, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillot, E.; Denis, F. Radio-induced oral and pharyngeal mucositis: Management updates. Cancer Radiother. 2012, 16, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.R.; Ambrad, A.A.; Arshoun, Y.; Carmel, R.J.; Ciuba, D.F.; Feldman, E.; Finkelstein, S.E.; Gandhavadi, R.; Heron, D.E.; Lane, S.C.; et al. Multi-institutional, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the efficacy of a mucoadhesive hydrogel (MuGard) in mitigating oral mucositis symptoms in patients being treated with chemoradiation therapy for cancers of the head and neck. Cancer 2014, 120, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.; Powell, R.; Ellis, A.; Hewett, J. Comparing pain control and ability to eat and drink with standard therapy vs Gelclair: A preliminary, double centre, randomised controlled trial on patients with radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Support Care Cancer 2007, 15, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenstra, J.L.; Miller, R.C.; Qin, R.; Martenson, J.A.; Dornfeld, K.J.; Bearden, J.D.; Puri, D.R.; Stella, P.J.; Mazurczak, M.A.; Klish, M.D.; et al. Doxepin rinse versus placebo in the treatment of acute oral mucositis pain in patients receiving head and neck radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy: A phase III, randomized, double-blind trial (NCCTG-N09C6 [Alliance]). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.G.; Trotti, A.; Kim, J.; Schell, M.J.; Zhao, X.; Amdur, R.J.; Brizel, D.M.; Chambers, M.S.; Caudell, J.J.; Miyamoto, C.; et al. Phase II multicenter trial of Caphosol for the reduction of mucositis in patients receiving radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvizadeh, M.; Hemati, S.; Meidani, M.; Ashouri, M.; Roayaei, M.; Shahsanai, A. Morphine mouthwash for the management of oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2015, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.H.; Kuciejewska, A.; Sharabiani, M.T.A.; Ng-Cheng-Hin, B.; Hoy, S.; Hurley, T.; Rydon, J.; Grove, L.; Santos, A.; Ryugenji, M.; et al. A randomised controlled trial of Caphosol mouthwash in management of radiation-induced mucositis in head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sio, T.T.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Leenstra, J.L.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Rine, G.; Curtis, A.; Singh, A.K.; Martenson, J.A., Jr.; Novotny, P.J.; Tan, A.D.; et al. Effect of Doxepin Mouthwash or Diphenhydramine-Lidocaine-Antacid Mouthwash vs Placebo on Radiotherapy-Related Oral Mucositis Pain: The Alliance A221304 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damani, A.; Salins, N.; Ghoshal, A.; Muckaden, M. Specialist Pediatric Palliative Care Prescribing Practices: A Large 5-year Retrospective Audit. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2016, 22, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Hua, X.; Cai, Y.; Fan, Y. Standardized nursing and therapeutic effect of oxycontin on oral mucosal pain in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W. Clinical Trial of Nonthermal 633 nm Omnilux LED Array for Renewal of Photoaging: Clinical Surface Profilometric Results. J. Korean Soc. Laser Med. 2005, 9, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Nestor, M.; Andriessen, A.; Berman, B.; Katz, B.E.; Gilbert, D.; Goldberg, D.J.; Gold, M.H.; Kirsner, R.S.; Lorenc, P.Z. Photobiomodulation with non-thermal lasers: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses in dermatology and aesthetic medicine. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2017, 19, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.M.; Eduardo, F.P.; Guthrie, K.A.; Franquin, J.-C.; Bensadoun, R.-J.J.; Migliorati, C.A.; Lloid, C.M.E.; Eduardo, C.P.; Walter Filho, N.; Marques, M.M. A phase III randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial to determine the efficacy of low level laser therapy for the prevention of oral mucositis in patients undergoing hematopoietic cell transplantation. Support Care Cancer 2007, 15, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, L.F.; Hamblin, M.R. Proposed Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation or Low-Level Light Therapy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017, 4, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rola, P.; Włodarczak, S.; Lesiak, M.; Doroszko, A.; Włodarczak, A. Changes in Cell Biology under the Influence of Low-Level Laser Therapy. Photonics 2022, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, B.B.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.P.; Liu, X.; Tang, L.L.; Mao, Y.P.; Li, W.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, A.H.; et al. A network meta-analysis in comparing prophylactic treatments of radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis for patients with head and neck cancers receiving radiotherapy. Oral Oncol. 2017, 75, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalla, R.V.; Brennan, M.T.; Gordon, S.M.; Sonis, S.T.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Keefe, D.M. Oral Mucositis Due to High-Dose Chemotherapy and/or Head and Neck Radiation Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2019, 2019(53), lgz011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardo, A.V.N.; Andrade, M.F.; Figueiredo, A.; Rosin, F.C.P.; Corrêa, L.; Zezell, D.M. Does Photobiomodulation Affects CK10 and CK14 in Oral Mucositis Radioinduced Repair? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.F.; Sardo, A.V.N.; Benetti, C.; Sicchieri, L.B.; Corrêa, L.; Zezell, D.M. Comparison of Two Light Wavelengths (λ = 660 nm and λ = 780 nm) in the Repair Process of Oral Mucositis Induced by Ionizing Radiation: Clinical and Microscopic Evaluations in Rats. Photonics 2023, 10, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Avci, P.; Gupta, A.; Sadasivam, M.; Vecchio, D.; Pam, Z.; Pam, N.; Hamblin, M.R. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: Stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2013, 32, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zanin, T.; Zanin, F.; Carvalhosa, A.A.; de Souza Castro, P.H.; Pacheco, M.T.; Zanin, I.C.J.; Brugnera, A. Use of 660-nm diode laser in the prevention and treatment of human oral mucositis induced by radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2010, 28, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, E.B.; Peterson, D.E.; Schubert, M.; Keefe, D.; McGuire, D.; Epstein, J.; Elting, L.S.; Fox, P.C.; Cooksley, C.; Sonis, S.T. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of cancer therapy-induced oral and gastrointestinal mucositis. Cancer 2004, 100, 2026–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadik, Y.; Arany, P.R.; Fregnani, E.R.; Bossi, P.; Antunes, H.S.; Bensadoun, R.-J.; Gueiros, L.A.; Majorana, A.; Nair, R.G.; Ranna, V. Systematic review of photobiomodulation for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients and clinical practice guidelines. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3969–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elad, S.; Cheng, K.K.F.; Lalla, R.V.; Yarom, N.; Hong, C.; Logan, R.M.; Bowen, J.; Gibson, R.; Saunders, D.P.; Zadik, Y. MASCC/ISOO clinical practice guidelines for the management of mucositis secondary to cancer therapy. Cancer 2020, 126, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.W. Efficacy of Red or Infrared Light-Emitting Diodes in a Mouse Model of Propionibacterium acnes-Induced Inflammation. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.R.; Paiva, J.L.; Gomes, J.; Boer, N.P.; Godoy, J.M.P.; Batigalia, F. Photodynamic action of the red laser on Propionibacterium acnes. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, M.; Verzegnassi, F.; Ronfani, L.; Zanon, D.; Melchionda, F.; Bagattoni, S.; Majorana, A.; Bardellini, E.; Mura, R.; Piras, A. Multicenter randomized, double-blind controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of laser therapy for the treatment of severe oral mucositis induced by chemotherapy in children: laMPO RCT. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, G.; Gobbo, M.; Sturnega, M.; Martinelli, V.; Mano, M.; Zanconati, F.; Bussani, R.; Perinetti, G.; Long, C.S.; Di Lenarda, R. Effect of class IV laser therapy on chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis: A clinical and experimental study. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dose, A.M. The symptom experience of mucositis, stomatitis, and xerostomia. In Seminars in Oncology Nursing; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Khouri, V.Y.; Stracieri, A.B.P.L.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Moraes, D.A.d.; Pieroni, F.; Simões, B.P.; Voltarelli, J.C. Use of therapeutic laser for prevention and treatment of oral mucositis. Braz. Dent. J. 2009, 20, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmink, B.A.; Khan, M.A.W.; Hermann, A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Wargo, J.A. The microbiome, cancer, and cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheflin, A.M.; Whitney, A.K.; Weir, T.L. Cancer-promoting effects of microbial dysbiosis. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, G.R.M.; Gattuso, G.; Pedullà, E.; Rapisarda, E.; Nicolosi, D.; Salmeri, M. Association of oral dysbiosis with oral cancer development. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.Y.; Sobue, T.; Choquette, L.; Dupuy, A.K.; Thompson, A.; Burleson, J.A.; Salner, A.L.; Schauer, P.K.; Joshi, P.; Fox, E.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis is associated with detrimental bacterial dysbiosis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perales-Puchalt, A.; Perez-Sanz, J.; Payne, K.K.; Svoronos, N.; Allegrezza, M.J.; Chaurio, R.A.; Anadon, C.; Calmette, J.; Biswas, S.; Mine, J.A.; et al. Frontline Science: Microbiota reconstitution restores intestinal integrity after cisplatin therapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagury-Orly, I.; Khaouam, N.; Noujaim, J.; Desrosiers, M.Y.; Maniakas, A. The Effect of Radiation and Chemoradiation Therapy on the Head and Neck Mucosal Microbiome: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 784457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotta, N.; Ottaviani, G.; Campisciano, G.; Poropat, A.; Bovenzi, M.; Rupel, K.; Gobbo, M.; Comar, M.; Di Lenarda, R.; Biasotto, M.; et al. Photobiomodulation modulates inflammation and oral microbiome: A pilot study. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Kaser, A. Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; Johnstone, D.; Kiat, H. Photobiomodulation of the microbiome: Implications for metabolic and inflammatory diseases. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.H.; Sensing, W.; Biron, J.A. Clinical efficacy of home-use blue-light therapy for mild-to moderate acne. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2011, 13, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, C.; Harrison, A.; Drew, S.; Whittall, R. A randomized controlled study for the treatment of acne vulgaris using high-intensity 414 nm solid state diode arrays. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2015, 17, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.P.; Fernandes, D.J.; Vidyasagar, M.S.; Maiya, A.G.; Guddattu, V. Low level laser therapy against radiation induced oral mucositis in elderly head and neck cancer patients-a randomized placebo controlled trial. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2015, 144, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Seo, H.; Rahim, M.A.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, H.Y. Changes in the Microbiome of Vaginal Fluid after Menopause in Korean Women. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul-Haq, A.; Lee, K.A.; Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Jo, S.; Ko, K.M.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, J.R.; Song, H.Y.; et al. Characteristic alterations of gut microbiota in uncontrolled gout. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, S.; Yarom, N.; Zadik, Y.; Kuten-Shorrer, M.; Sonis, S.T. The broadening scope of oral mucositis and oral ulcerative mucosal toxicities of anticancer therapies. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.G.; Antequera, R.; Peres, M.P.; Snitcosky, I.M.; Federico, M.H.; Villar, R.C. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy and aluminum hydroxide in patients with chemotherapy and radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Braz. Dent. J. 2010, 21, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elting, L.S.; Cooksley, C.D.; Chambers, M.S.; Garden, A.S. Risk, outcomes, and costs of radiation-induced oral mucositis among patients with head-and-neck malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, H.S.; Herchenhorn, D.; Small, I.A.; Araújo, C.M.; Viégas, C.M.; Cabral, E.; Rampini, M.P.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Silva, T.G.; Ferreira, E.M.; et al. Phase III trial of low-level laser therapy to prevent oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 109, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pauli Paglioni, M.; Araújo, A.L.D.; Arboleda, L.P.A.; Palmier, N.R.; Fonsêca, J.M.; Gomes-Silva, W.; Madrid-Troconis, C.C.; Silveira, F.M.; Martins, M.D.; Faria, K.M.; et al. Tumor safety and side effects of photobiomodulation therapy used for prevention and management of cancer treatment toxicities. A systematic review. Oral Oncol. 2019, 93, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecha, J.A.; Raber-Durlacher, J.E.; Nair, R.G.; Epstein, J.B.; Sonis, S.T.; Elad, S.; Hamblin, M.R.; Barasch, A.; Migliorati, C.A.; Milstein, D.M.; et al. Low level laser therapy/photobiomodulation in the management of side effects of chemoradiation therapy in head and neck cancer: Part 1: Mechanisms of action, dosimetric, and safety considerations. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 2781–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, M.; Ottaviani, G.; Perinetti, G.; Ciriello, F.; Beorchia, A.; Giacca, M.; Di Lenarda, R.; Rupel, K.; Tirelli, G.; Zacchigna, S.; et al. Evaluation of nutritional status in head and neck radio-treated patients affected by oral mucositis: Efficacy of class IV laser therapy. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires Oliveira, D.A.; de Oliveira, R.F.; Zangaro, R.A.; Soares, C.P. Evaluation of low-level laser therapy of osteoblastic cells. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2008, 26, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karu, T.I. Multiple roles of cytochrome c oxidase in mammalian cells under action of red and IR-A radiation. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.P. Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase is not the primary acceptor for near infrared light-it is mitochondrial bound water: The principles of low-level light therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.Y.; Tam, V.C.W.; Ramkumar, S.; Khaw, M.L.; Law, H.K.W.; Lee, S.W.Y. Review on the Cellular Mechanisms of Low-Level Laser Therapy Use in Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.-P.; Tan, R.K.; Lee, H.-W.; Han, S.-K. Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy on Proliferation and Collagen Synthesis of Human Fibroblasts in Vitro. J. Wound Manag. Res. 2018, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupel, K.; Zupin, L.; Colliva, A.; Kamada, A.; Poropat, A.; Ottaviani, G.; Gobbo, M.; Fanfoni, L.; Gratton, R.; Santoro, M.; et al. Photobiomodulation at Multiple Wavelengths Differentially Modulates Oxidative Stress In Vitro and In Vivo. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 6510159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaroli, A.; Ravera, S.; Zekiy, A.; Benedicenti, S.; Pasquale, C. A Narrative Review on Oral and Periodontal Bacteria Microbiota Photobiomodulation, through Visible and Near-Infrared Light: From the Origins to Modern Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, F.G.; Oliveira, C.F.; Fontana, A.; Kurachi, C.; Bagnato, V.S.; Spolidório, D.M.; Hebling, J.; de Souza Costa, C.A. In Vitro effect of low-level laser therapy on typical oral microbial biofilms. Braz Dent. J. 2011, 22, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.K.; Molassiotis, A.; Chang, A.M.; Wai, W.C.; Cheung, S.S. Evaluation of an oral care protocol intervention in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis in paediatric cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, R.V.; Sonis, S.T.; Peterson, D.E. Management of oral mucositis in patients who have cancer. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 52, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, D.B.; Correa, M.E.; Johnson, J.; Wienandts, P. The role of basic oral care and good clinical practice principles in the management of oral mucositis. Support. Care Cancer 2006, 14, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, S.; Zamperlini-Netto, G.; Beyene, J.; Treister, N.S.; Sung, L. Effect of prophylactic low level laser therapy on oral mucositis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



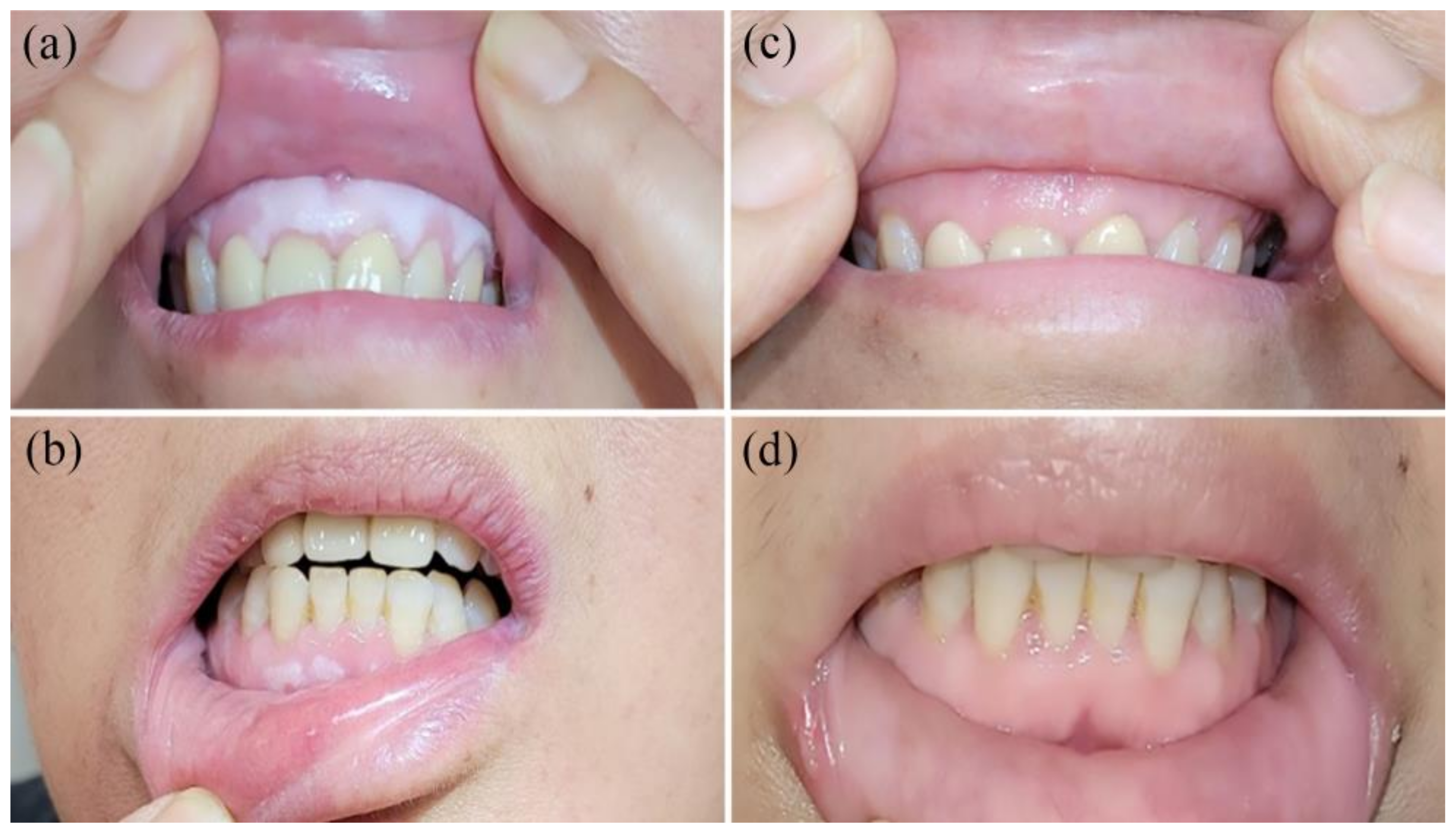


| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | None |
| 1 | Mild severity; oral soreness, erythema |
| 2 | Moderate severity; greater than Grade 1; oral erythema, ulcers, solid diet tolerated |
| 3 | Severe severity; greater than Grade 2; oral ulcers, liquid diet only |
| 4 | Life-threatening; greater than Grade 3; oral alimentation impossible |
| Laser Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Ptech Co., Ltd. |
| Model Name | PetalB |
| Wavelengths | 670 nm, 780 nm, 830 nm, 910 nm |
| Pulse mode | 625 Hz pulse mode (200 μs-on, 1400 μs-off in 1600 μs cycle) |
| Spectral Half Width | 670 nm:18 nm |
| 780 nm:20 nm | |
| 830 nm:34 nm | |
| 910 nm:40 nm | |
| Power (average) | 670 nm:8.0 mW |
| 780 nm:1.2 mW | |
| 830 nm:17.0 mW | |
| 910 nm:4.0 mW | |
| Power density | 670 nm:20.7 mW/cm2 |
| 780 nm:3.1 2 mW/cm2 | |
| 830 nm:44.0 mW/cm2 | |
| 910 nm:10.3 mW/cm2 | |
| Energy | 670 nm:4.8 J |
| 780 nm:0.72 J | |
| 830 nm:10.2 J | |
| 910 nm:2.4 J | |
| Energy density | 670 nm:12.44 J/cm2 |
| 780 nm:1.87 J/cm2 | |
| 830 nm:26.44 J/cm2 | |
| 910 nm:6.22 J/cm2 | |
| Exposure duration | 18 min |
| Beam diameter | 7 mm |
| Variable | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 14 | 66.7% |
| Female | 7 | 33.3% |
| Age (y, median (range)) | 63.9 (47–83) | |
| Smoking (before cancer) | ||
| Yes | 14 | 66.7% |
| No | 7 | 33.3% |
| Primary cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal cancer | 10 | 47.62% |
| Oral cavity cancer | 6 | 28.57% |
| Laryngeal cancer | 3 | 14.29% |
| Nasopharyngeal cancer | 1 | 4.76% |
| Esophageal cancer | 1 | 4.76% |
| Pre-treatment OM grade (WHO) | ||
| Grade 4 (life-threatening) | 0 | |
| Grade 3 (severe) | 12 | 57.1% |
| Grade 2 (moderate) | 9 | 42.9% |
| Grade 1 (mild) | 0 | |
| Grade 0 (clear) | 0 | |
| Mean of WHO scale pre-treatment | 2.57 |
| Grade | Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | p-Value | 2 wks Follow-Up | p-Value | 4 wks Follow-Up | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | % | No. | % | No. of Patients | % | No. of Patients | % | ||||
| Grade 3 (severe) | 10 | 62.5 | 7 | 43.8 | 0.041 | - | <0.001 | - | <0.001 | ||
| Grade 2 (moderate) | 6 | 37.5 | 4 | 25.0 | 6 | 28.6 | 1 | 4.8 | |||
| Grade 1 (mild) | - | 5 | 31.3 | 9 | 42.9 | 10 | 47.6 | ||||
| Grade 0 (clear) | - | - | 1 | 4.8 | 5 | 23.8 | |||||
| Parameter | Baseline | after PBMT | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Global health status (QL2) | 26.0 | 19.7 | 66.2 | 13.1 | <0.001 |
| Physical functioning (PF2) | 67.1 | 16.1 | 89.2 | 11.1 | <0.001 |
| Role functioning (RF) | 49.0 | 26.9 | 83.3 | 23.6 | <0.001 |
| Emotional functioning (EF) | 59.4 | 19.2 | 88.0 | 9.1 | <0.001 |
| Cognitive functioning (CF) | 70.8 | 20.6 | 84.4 | 11.3 | 0.005 |
| Social functioning (SF) | 52.1 | 31.0 | 86.5 | 15.2 | <0.001 |
| Fatigue (FA) | 62.5 | 16.7 | 25.7 | 15.0 | <0.001 |
| Nausea and vomiting (NV) | 35.4 | 24.3 | 14.6 | 19.1 | <0.001 |
| Pain (PA) | 64.6 | 22.7 | 19.8 | 19.5 | <0.001 |
| Dyspnea (DY) | 31.3 | 25.7 | 8.3 | 14.9 | <0.001 |
| Insomnia (SL) | 47.9 | 32.1 | 20.8 | 16.7 | 0.001 |
| Appetite loss (AP) | 72.9 | 30.4 | 29.2 | 29.5 | <0.001 |
| Constipation (CO) | 29.2 | 29.5 | 31.3 | 37.5 | 0.806 |
| Diarrhea (DI) | 12.5 | 24.0 | 6.3 | 18.1 | 0.270 |
| Financial difficulties (FI) | 29.2 | 26.9 | 18.8 | 17.1 | 0.136 |
| PRE-POST | ||
|---|---|---|
| Jenson–Shannon | species | N.S. (p = 0.869) |
| genus | N.S. (p = 0.528) | |
| Bray–Curtis | species | N.S. (p = 0.820) |
| genus | N.S. (p = 0.579) | |
| Generalized UniFrac | species | N.S. (p = 0.634) |
| genus | N.S. (p = 0.534) | |
| UniFrac | species | N.S. (p = 0.680) |
| genus | N.S. (p = 0.632) |
| Rank | Taxa | PRE | POST |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Proteobacteria | 21.2 | 18.3 |
| Fusobacteria | 5.2 | 3.9 | |
| Actinobacteria | 10.0 | 11.9 | |
| Saccharibacteria_TM7 | 2.8 | 3.7 | |
| Bacteroidetes | 13.9 | 12.1 | |
| Firmicutes | 45.8 | 49.1 | |
| ETC (<1%) | 1.1 | 1.0 | |
| Class | Bacilli | 29.4 | 30.3 |
| Fusobacteria_c | 5.2 | 3.9 | |
| Betaproteobacteria | 16.6 | 14.3 | |
| Flavobacteria | 4.9 | 3.5 | |
| Saccharimonas_c | 2.8 | 3.7 | |
| Clostridia | 5.2 | 2.7 | |
| Bacteroidia | 9.0 | 8.6 | |
| Actinobacteria_c | 8.2 | 10.4 | |
| Gammaproteobacteria | 3.3 | 2.8 | |
| Coriobacteriia | 1.8 | 1.5 | |
| Negativicutes | 10.7 | 15.7 | |
| ETC (<1%) | 3.0 | 2.6 | |
| Order | Bacteroidales | 9.0 | 8.6 |
| Burkholderiales | 7.8 | 8.5 | |
| Pasteurellales | 2.3 | 2.4 | |
| Clostridiales | 5.2 | 2.7 | |
| Flavobacteriales | 4.9 | 3.5 | |
| Fusobacteriales | 5.2 | 3.9 | |
| Veillonellales | 9.6 | 15.3 | |
| Neisseriales | 8.8 | 5.8 | |
| Coriobacteriales | 1.8 | 1.5 | |
| Bacillales | 1.6 | 1.1 | |
| Saccharimonas_o | 2.8 | 3.7 | |
| Micrococcales | 6.1 | 8.5 | |
| Lactobacillales | 27.8 | 29.3 | |
| ETC (<1%) | 7.2 | 5.4 | |
| Family | Gemella_f | 1.5 | 1.0 |
| Flavobacteriaceae | 4.9 | 3.5 | |
| Neisseriaceae | 8.8 | 5.8 | |
| Comamonadaceae | 1.2 | 1.4 | |
| Lautropia_f | 6.5 | 7.1 | |
| Saccharimonas_f | 2.8 | 3.7 | |
| Pasteurellaceae | 2.3 | 2.4 | |
| Streptococcaceae | 22.2 | 23.7 | |
| Prevotellaceae | 5.9 | 6.2 | |
| Veillonellaceae | 9.6 | 15.3 | |
| Porphyromonadaceae | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| Coriobacteriaceae | 1.8 | 1.5 | |
| Lachnospiraceae | 2.3 | 1.1 | |
| Aerococcaceae | 3.9 | 3.4 | |
| Lactobacillaceae | 1.7 | 2.0 | |
| Micrococcaceae | 6.1 | 8.5 | |
| Ruminococcaceae | 1.8 | 0 | |
| Fusobacteriaceae | 3.4 | 2.0 | |
| Leptotrichiaceae | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| ETC (<1%) | 9.8 | 8.0 | |
| Genus | Porphyromonas | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Haemophilus | 2.1 | 1.9 | |
| Granulicatella | 3.8 | 3.1 | |
| Fusobacterium | 3.4 | 2.0 | |
| Gemella | 1.5 | 1.0 | |
| Saccharimonas | 2.4 | 3.1 | |
| Prevotella | 5.1 | 5.7 | |
| Veillonella | 9.3 | 15.0 | |
| Streptococcus | 22.0 | 23.7 | |
| Rothia | 6.1 | 8.5 | |
| Neisseria | 8.2 | 5.3 | |
| Leptotrichia | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| Ottowia | 1.2 | 1.4 | |
| Capnocytophaga | 4.6 | 3.3 | |
| Lautropia | 6.5 | 7.1 | |
| Lactobacillus | 1.7 | 1.9 | |
| Atopobium | 1.7 | 1.5 | |
| ETC (<1%) | 17.5 | 12.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, I.-Y.; Byeon, H.-K.; Ban, M.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Won, Y.K.; Eun, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yang, N.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Effect of a Novel Handheld Photobiomodulation Therapy Device in the Management of Chemoradiation Therapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Case Series Study. Photonics 2023, 10, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030241
Jo I-Y, Byeon H-K, Ban M-J, Park J-H, Lee S-C, Won YK, Eun Y-S, Kim J-Y, Yang N-G, Lee S-H, et al. Effect of a Novel Handheld Photobiomodulation Therapy Device in the Management of Chemoradiation Therapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Case Series Study. Photonics. 2023; 10(3):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030241
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, In-Young, Hyung-Kwon Byeon, Myung-Jin Ban, Jae-Hong Park, Sang-Cheol Lee, Yong Kyun Won, Yun-Su Eun, Jae-Yun Kim, Na-Gyeong Yang, Sul-Hee Lee, and et al. 2023. "Effect of a Novel Handheld Photobiomodulation Therapy Device in the Management of Chemoradiation Therapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Case Series Study" Photonics 10, no. 3: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030241
APA StyleJo, I.-Y., Byeon, H.-K., Ban, M.-J., Park, J.-H., Lee, S.-C., Won, Y. K., Eun, Y.-S., Kim, J.-Y., Yang, N.-G., Lee, S.-H., Lee, P., Heo, N.-H., Jo, S., Seo, H., Kim, S., Song, H.-Y., & Kim, J.-E. (2023). Effect of a Novel Handheld Photobiomodulation Therapy Device in the Management of Chemoradiation Therapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Case Series Study. Photonics, 10(3), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030241






