Experimental Study on Evolution of Chemical Structure Defects and Secondary Contaminative Deposition during HF-Based Etching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
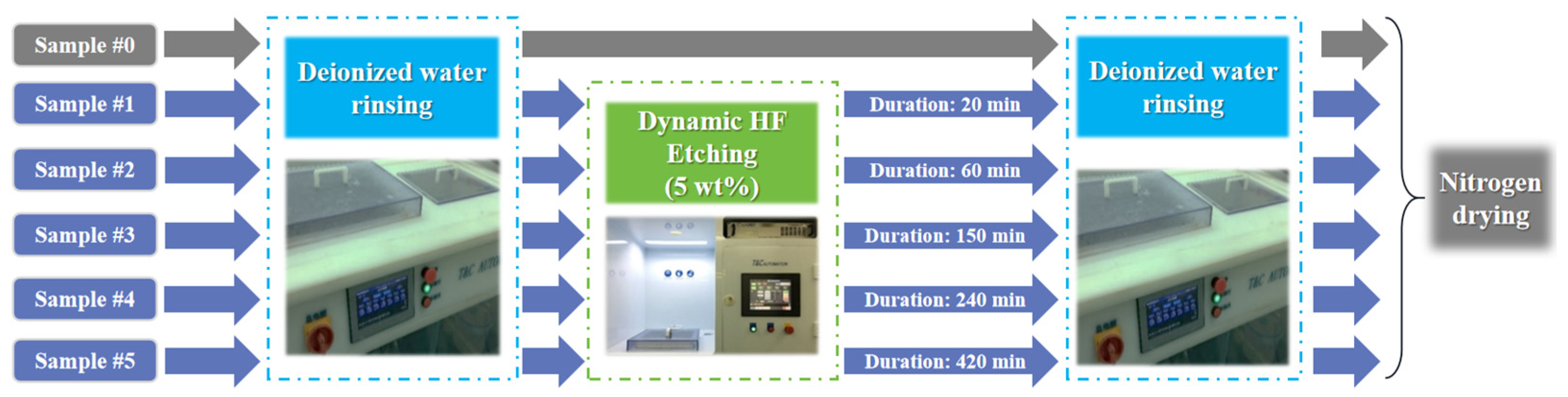
2.1. Sample Preparation
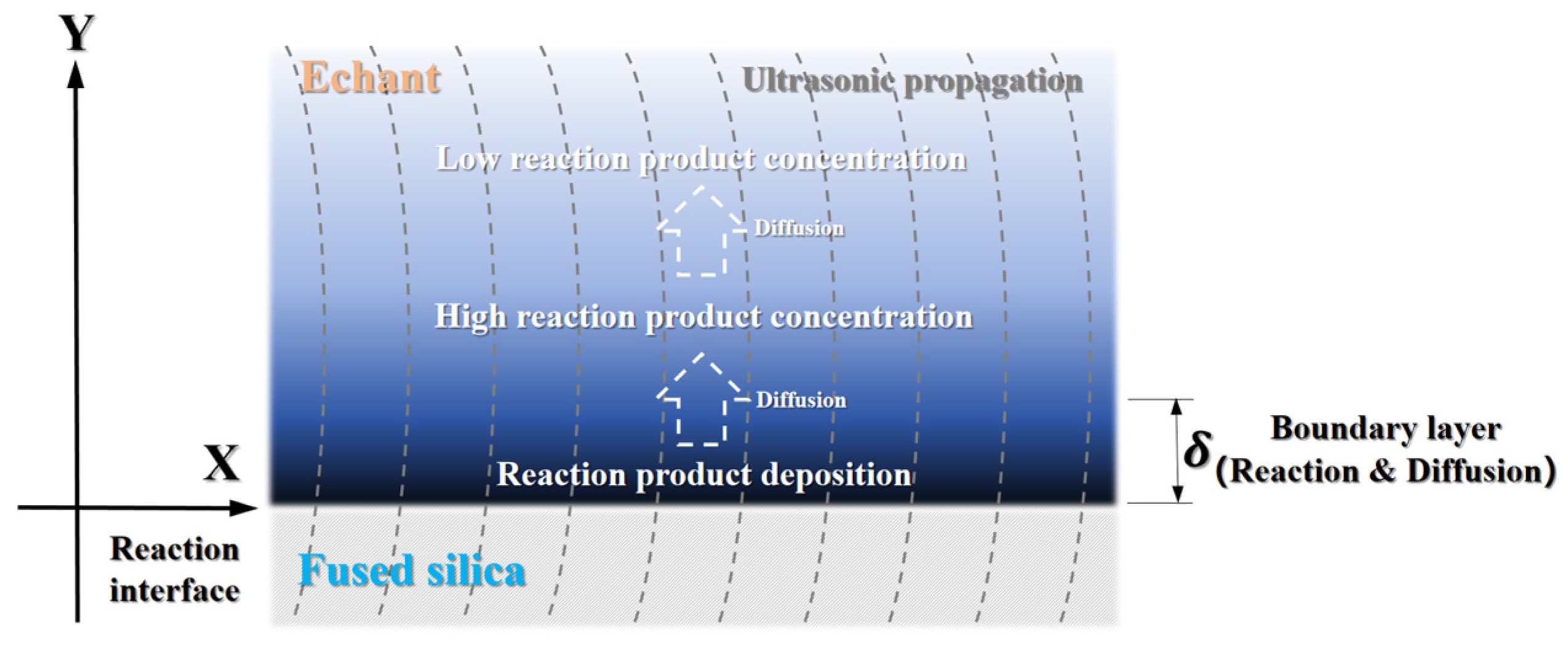
2.2. Megasonic-Aided Etching Configuration
2.3. Laser-Induced Damage Threshold Test Configuration
3. Results
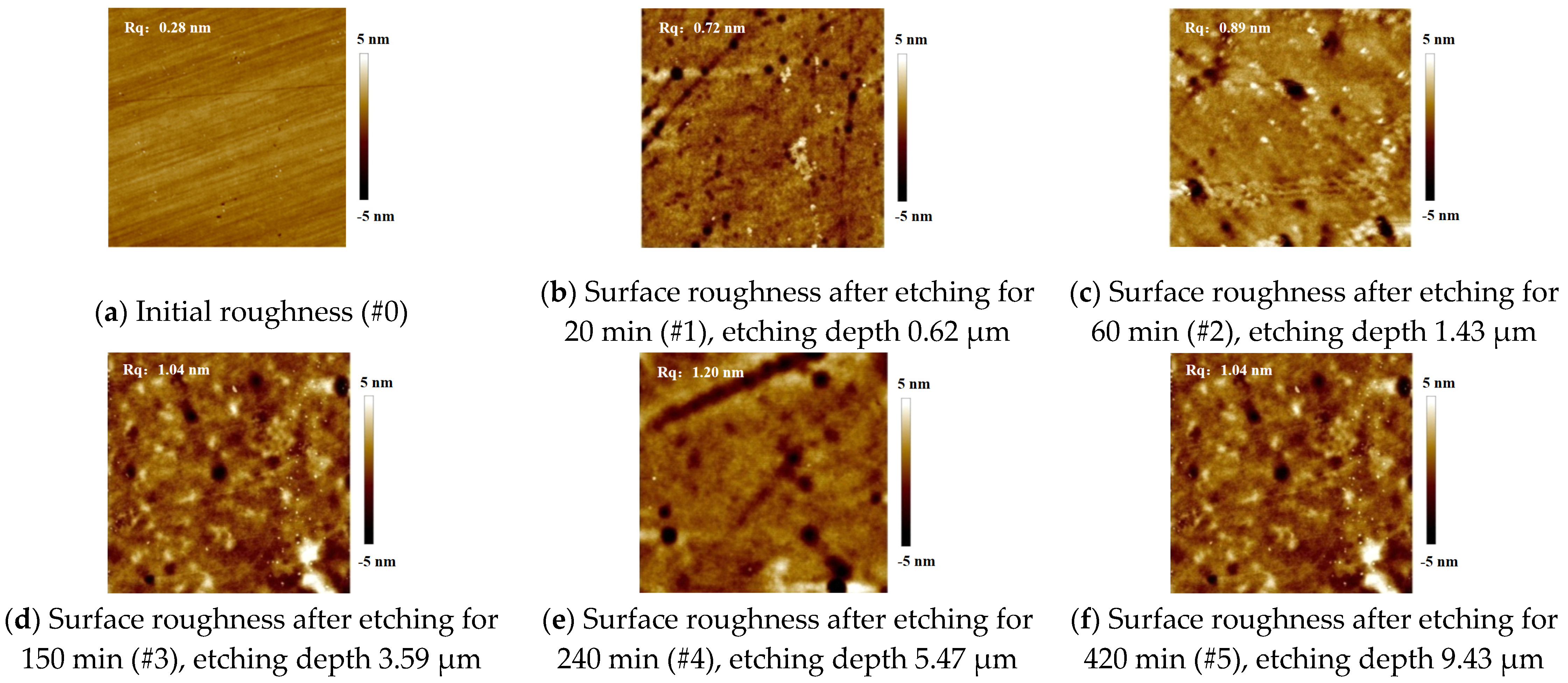
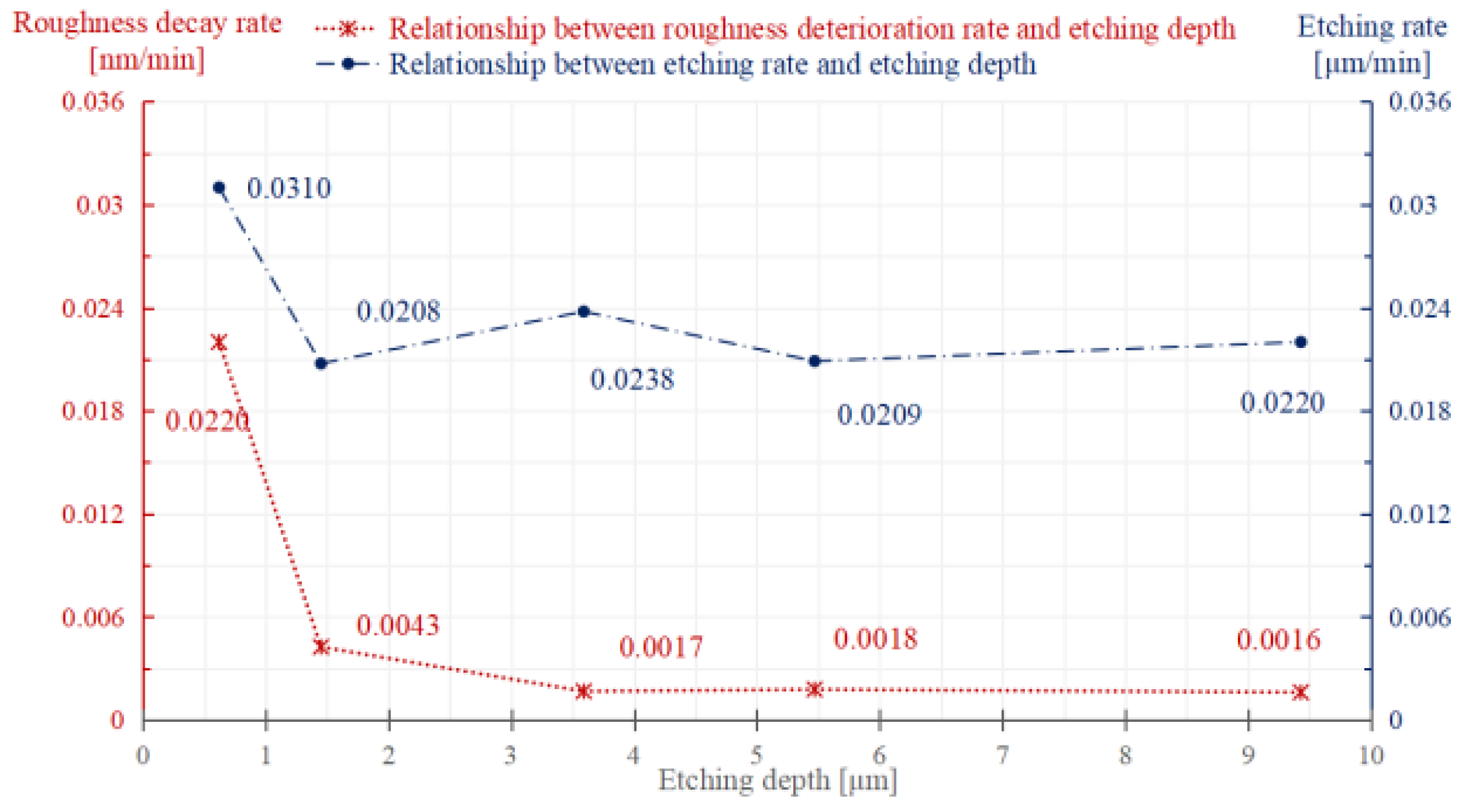
3.1. Evolution of Surface Micro Morphology
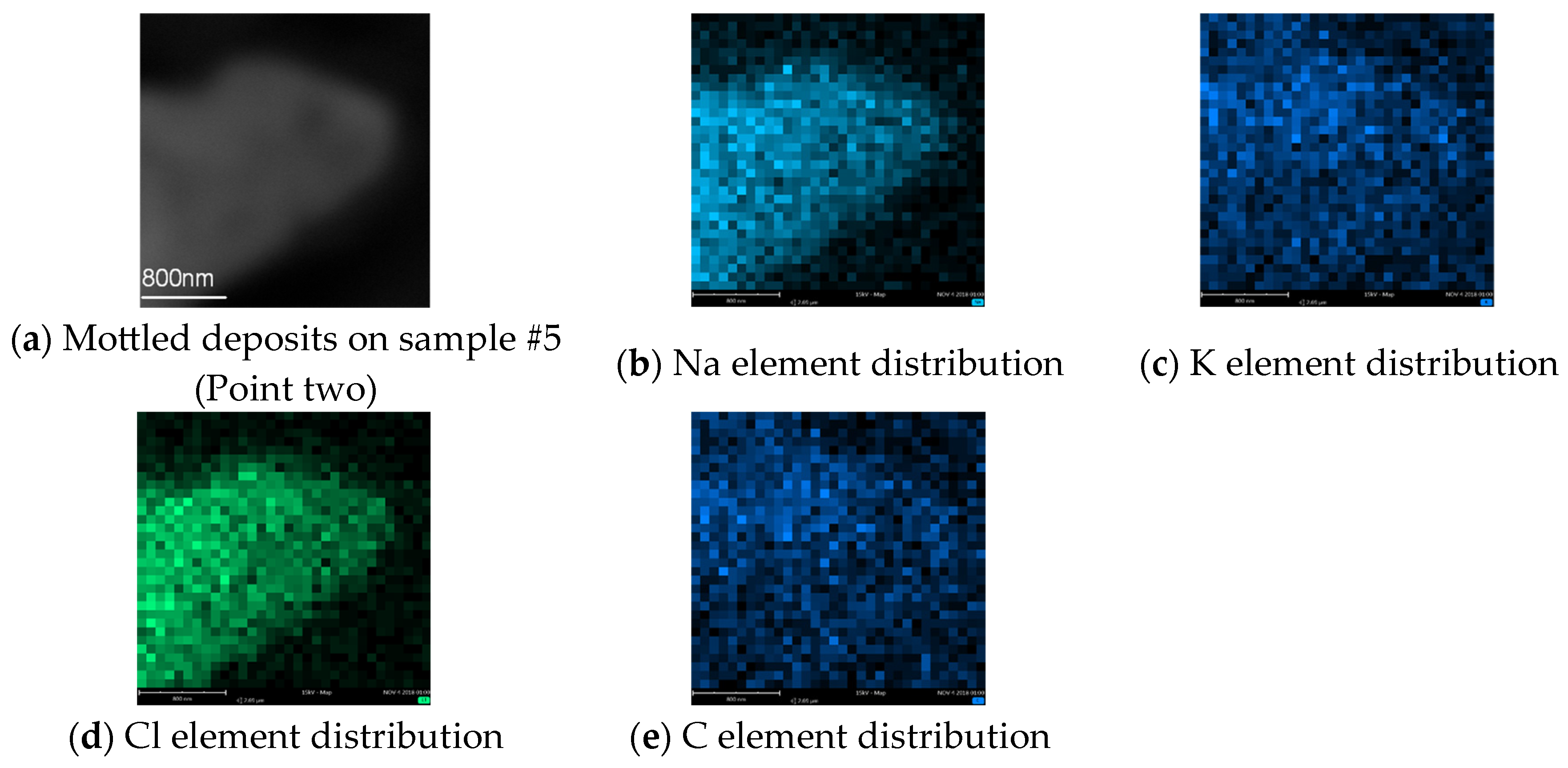
3.2. Composition Identification of Micro Depositions
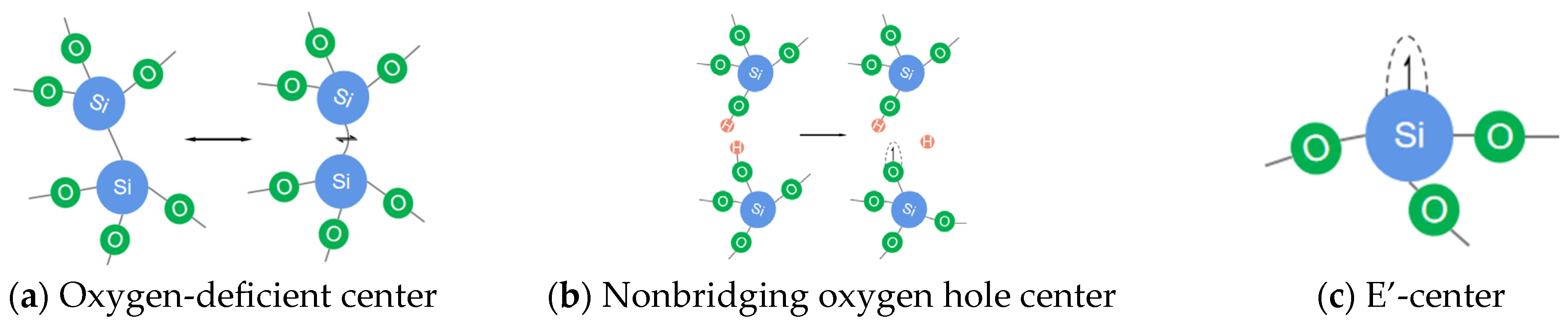
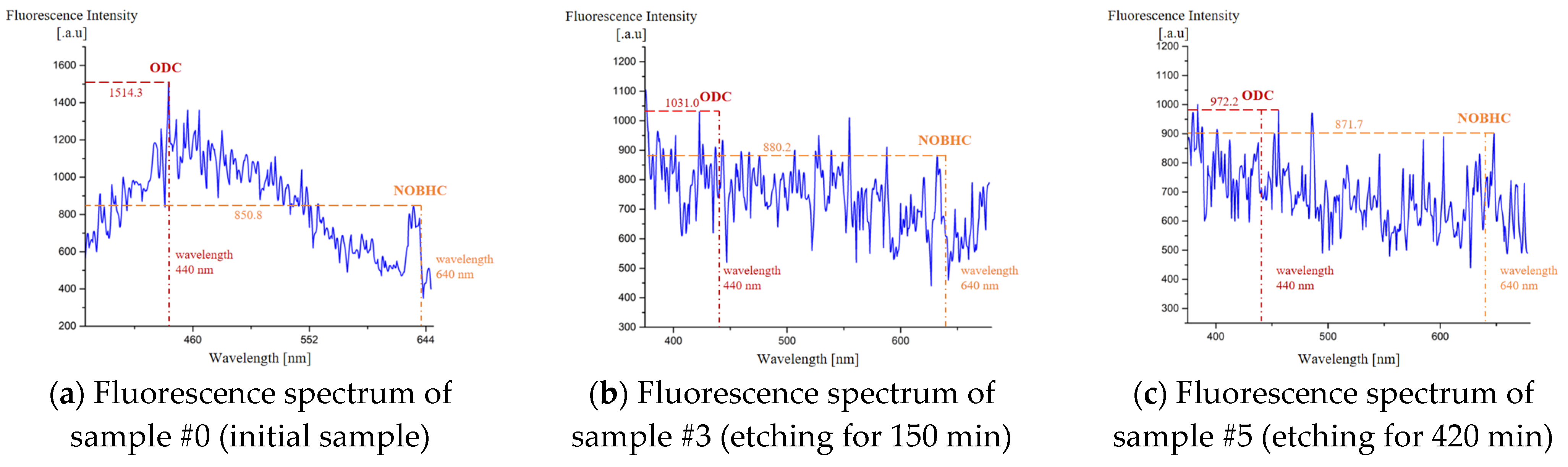
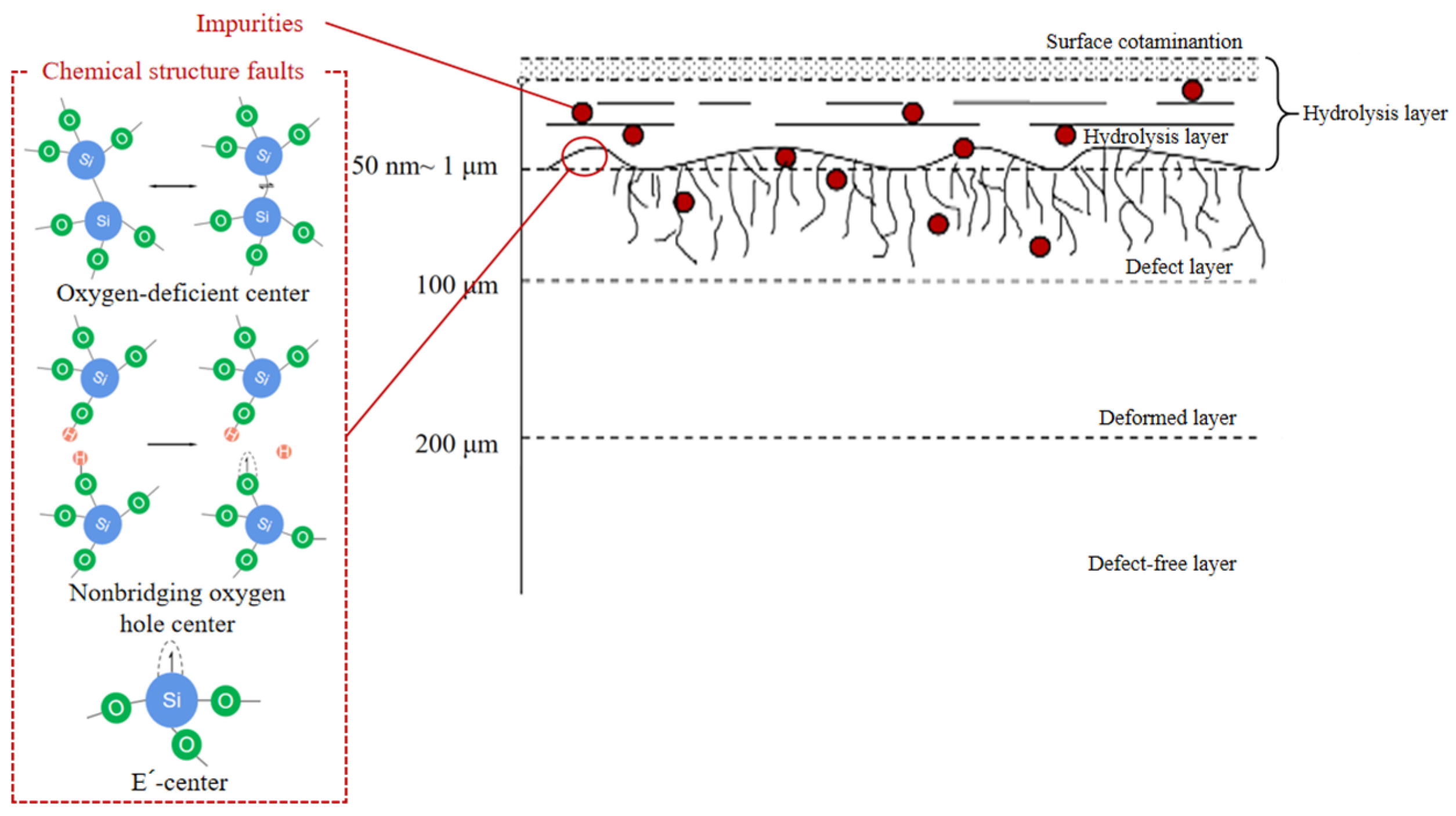
3.3. Evolution of Chemical Structural Defects
3.4. LIDT Testing Results
4. Discussion
- (1)
- From fused silica samples: in HF etching, the chemical network structure of silicane will be disassembled, causing the dissolution of the alkalis initially embedded in fused silica. For example, the contents of calcium, potassium and sodium elements in suprasil 300 produced by Heraeus that are used in this paper are 0.05 ppm, 0.01 ppm and 0.05 ppm, respectively [31];
- (2)
- From deionized water: the alkali elements may also stem from deionized water in HF solution, as deionized water often contains trace amount of dissolved ionic impurities.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- During etching, the surface roughness deteriorates steadily; as the etching continues, white mottled gel-like depositions emerge. The roughness deterioration rate illustrates that the concentration of the hydrolysis layer diminishes with the increase in layer depth, and the depositions also add to further surface roughness deterioration;
- (2)
- For chemical structure defects elimination, HF exhibits a significant suppressive effect on ODC defects for fused silica-based optical elements;
- (3)
- The white mottled depositions consist of Na, K, Ca, Cl and C elements originating from either substrate or deionized water. The precisely shared shape between deposition and impure elements distributions illustrate that during etching, the impure ions are absorbed and deposited with the reaction product. For the thorough removal of impure elements, additional processes are suggested.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spaeth, M.L.; Manes, K.R.; Kalantar, D.H.; Miller, P.E.; Heebner, J.E.; Bliss, E.S.; Spec, D.R.; Parham, T.G.; Whitman, P.K.; Wegner, P.J.; et al. Description of the NIF laser. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 25–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, E.I.; Campbell, H.; Stolz, C.; Wuest, C.R. The national ignition facility: The world’s largest optics and laser system, High-Power Lasers and Applications. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2003, 5001, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Besnard, D. Fusion with the mega joule laser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2008, 112, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, L.D.; Koumvakalis, N.; Bass, M. Laser-induced bulk damage in SiO2 at 1.064, 0.532, and 0.355 μm. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Yuan, X.; Zu, X. Research Progress on Subsurface Defects in Fused Silica. Mater. Rep. 2009, 22, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.E.; Suratwala, T.I.; Bude, D. Laser damage precursors in fused silica. Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2009, 7504, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, E.; Hou, J.; Chen, X. Investigation of subsurface damage density and morphology impact on the laser-induced damage threshold of fused silica. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 9839–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Cai, C.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Xie, L.; Huang, Y.; Yan, D.; Ma, P. Effect of pad elastic modulus on polishing-induced subsurface damages distribution and laser-induced damage performance of fused silica optics. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suratwala, T.I.; Miller, P.E.; Ehrmann, P.R.; Steele, R.A. Polishing slurry induced surface haze on phosphate laser glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 351, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suratwala, T.; Steele, W.; Wong, L.; Feit, M.D.; Miller, P.E.; Dylla-Spears, R.; Shen, N.; Desjardin, R. Chemistry and Formation of the Beilby Layer During Polishing of Fused Silica Glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffer, M.; Longuet, J.L.; Labrugère, C.; Fargin, E.; Bousquet, B.; Dussauze, M.; Lambert, S.; Cormont, P.; Néauport, J. Characterization of the Polishing-Induced Contamination of Fused Silica Optics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bude, J.; Miller, P.E.; Shen, N.; Suratwala, T.; Laurence, T.; Steele, W.; Baxamusa, S.; Wong, L.; Carr, W.; Cross, D.; et al. Silica laser damage mechanisms, precursors and their mitigation. Proc. Laser-Induc. Damage Opt. Mater. 2014, 9237, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bude, J.; Miller, P.; Baxamusa, S.; Shen, N.; Laurence, T.; Steele, W.; Suratwala, T.; Wong, L.; Carr, W.; Cross, D.; et al. High fluence laser damage precursors and their mitigation in fused silica. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5839–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q. Post-processing of fused silica and its effects on damage resistance to nanosecond pulsed UV lasers. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 3017–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suratwala, T.I.; Miller, P.E.; Bude, J.D.; Steele, W.A.; Shen, N.; Monticelli, M.V.; Feit, M.D.; Laurence, T.A.; Norton, M.A.; Carr, C.W.; et al. HF-Based Etching Processes for Improving Laser Damage Resistance of Fused Silica Optical Surfaces. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.; Suratwala, T.; Feit, M.D.; Miller, P.E.; Steele, R. The effect of HF/NH4F etching on the morphology of surface fractures on fused silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Geng, F.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, W.; Qiao, L.; Zu, X.; Zheng, W. Advanced Mitigation Process (AMP) for Improving Laser Damage Threshold of Fused Silica Optics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bude, J.; Carr, C.W.; Miller, P.E.; Parham, T.; Whitman, P.; Monticelli, M.; Raman, R.; Cross, D.; Welday, B.; Ravizza, F.; et al. Particle damage sources for fused silica optics and their mitigation on high energy laser systems. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 11414–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zu, X.; Jiang, X.; Xiang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, L. Effect of HF etching on the surface quality and laser-induced damage of fused silica. Opt. Laser Technol. 2012, 44, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotter, D.M. Etching mechanism of vitreous silicon dioxide in HFBased solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 122, 4345–4351. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y. The Key Technology Research of High Precision and Low-Defect Fabrication for Silicon Reflectors. Doctor’s Thesis, University of National Defense, Changsha, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, S. A Study of the Dissolution of SiO2 in Acidic Fluoride Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1971, 118, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grieken, R.; Markowicz, A. Handbook of X-ray Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Neauport, J.; Lamaignere, L.; Bercegol, H.; Pilon, F.; Birolleau, J.C. Polishing-induced contamination of fused silica optics and laser induced damage density at 351 nm. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 10163–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, R.; Mittal, K.L. Methods for Removal of Particle Contaminants, in Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chmel, A.; Eronko, S.B. Optical strength of glasses implanted with argon ions. Glass Technol. 1998, 39, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Feit, M.D.; Rubenchik, A.M. Influence of subsurface cracks on laser-induced surface damage. In Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Salh, R. Silicon Nanocluster in Silicon Dioxide: Cathodoluminescence, Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis, Infrared Spectroscopy Studies. In Crystalline Silicon Properties and Uses; InTech: Atyrau, Republic of Kazakhstan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y. Study on etching process of fused silica with concentrated HF. Optik 2018, 178, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Jinghe, W.; Peiyue, Z.; Lei, Z. Experimental study on HF etching of fused silica optical elements. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2017, 29, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Quarzglas, H. Quartz Glass for Optics Data and Properties; Heraeus Quarzglas GmbH & Co. KG: Hanau, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Shi, F.; Tian, Y.; Dai, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Z. Detailed near-surface nanoscale damage precursor measurement and characterization of fused silica optics assisted by ion beam etching. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 10826–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Dai, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shi, F. Effect on nanoscale damage precursors of fused silica with wet etching in KOH solutions. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Polishing abrasive | CeO2 |
| Abrasive diameter | 1.5 μm |
| Rotating rate | 150 r/min |
| Feeding rate | 300 mm/min |
| Smoothing pressure | 0.02 Mpa |
| Smoothing duration | 180 min |
| Step | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency [kHz] | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| Duration [min] | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Temperature [°C] | 22 | ||||||
| Element | Si | O | Na | C | Cl | Ca | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition ratio | 50.48% | 18.42% | 1.13% | 27.87% | 0.51% | 0.11% | 1.48% |
| Element | Si | O | Na | C | Cl | K | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition ratio | 15.62% | 39.33% | 3.76% | 35.48% | 2.10% | 0.24% | 3.47% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Shi, F.; Qiao, S.; Peng, X.; Xiong, Y. Experimental Study on Evolution of Chemical Structure Defects and Secondary Contaminative Deposition during HF-Based Etching. Photonics 2024, 11, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050479
Shen X, Shi F, Qiao S, Peng X, Xiong Y. Experimental Study on Evolution of Chemical Structure Defects and Secondary Contaminative Deposition during HF-Based Etching. Photonics. 2024; 11(5):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050479
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiao, Feng Shi, Shuo Qiao, Xing Peng, and Ying Xiong. 2024. "Experimental Study on Evolution of Chemical Structure Defects and Secondary Contaminative Deposition during HF-Based Etching" Photonics 11, no. 5: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050479
APA StyleShen, X., Shi, F., Qiao, S., Peng, X., & Xiong, Y. (2024). Experimental Study on Evolution of Chemical Structure Defects and Secondary Contaminative Deposition during HF-Based Etching. Photonics, 11(5), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050479






