Training a Dataset Simulated Using RGB Images for an End-to-End Event-Based DoLP Recovery Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Work
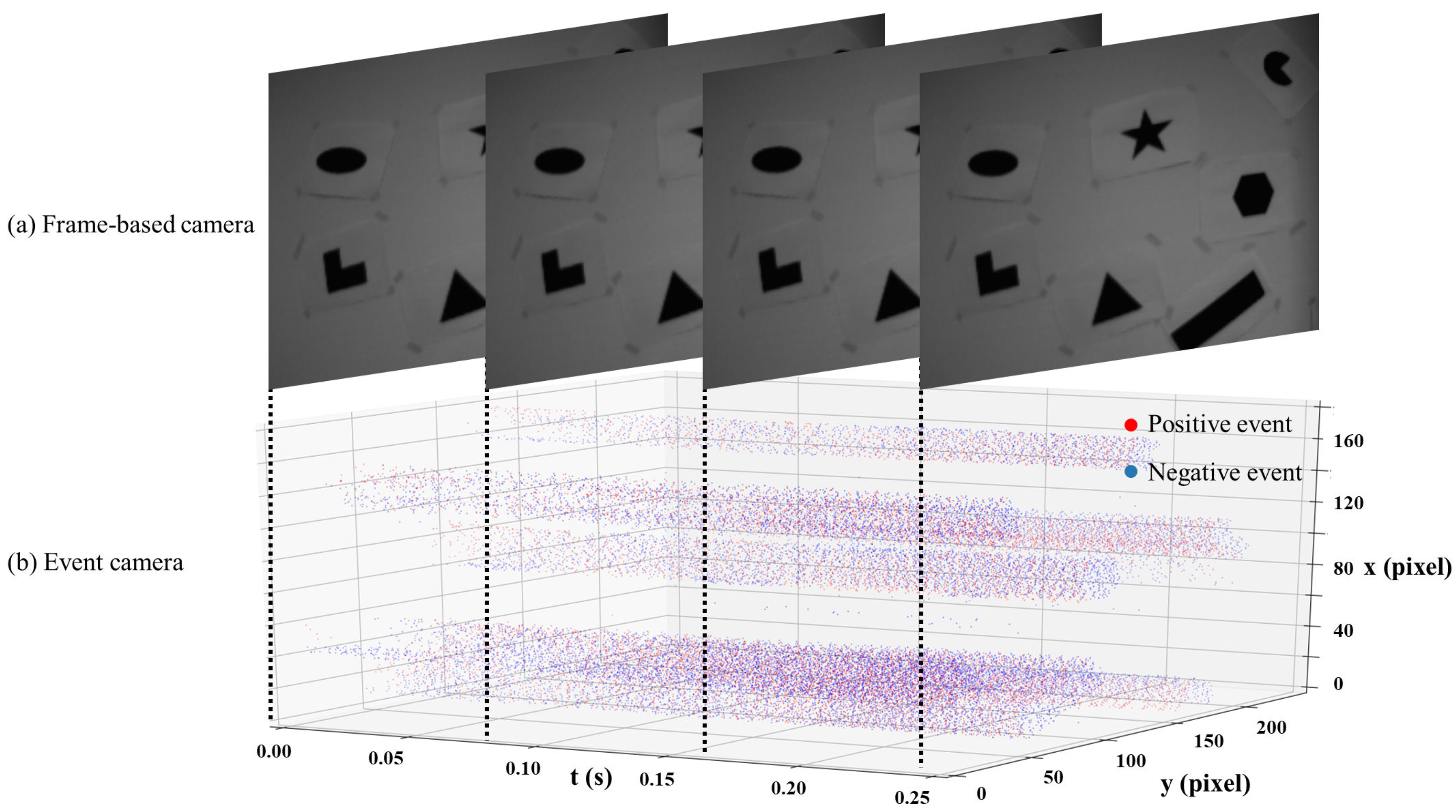
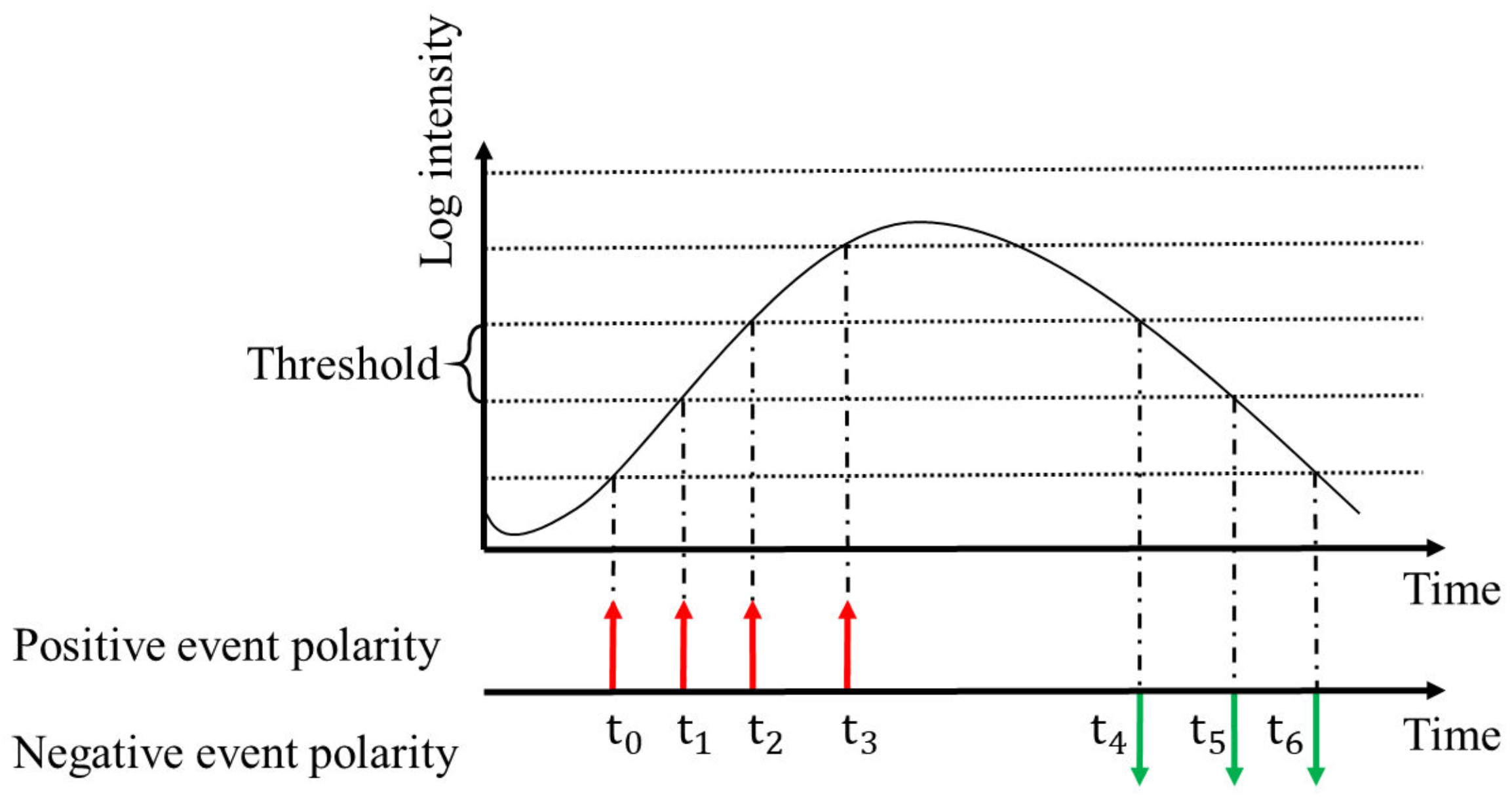
2.1. Event Camera
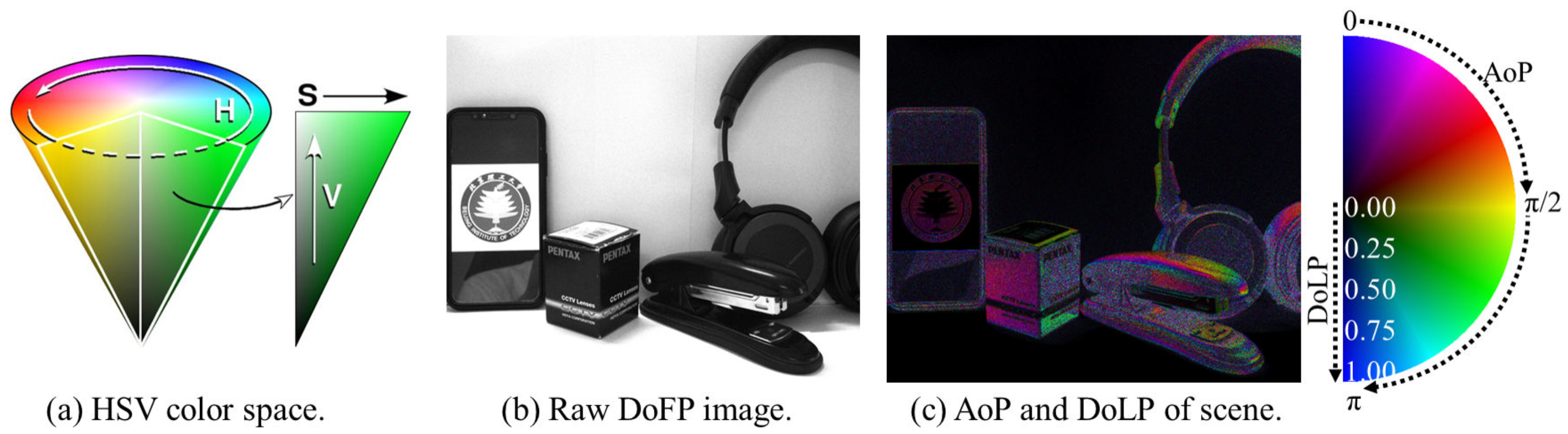
2.2. Polarization
2.3. Polarization Events
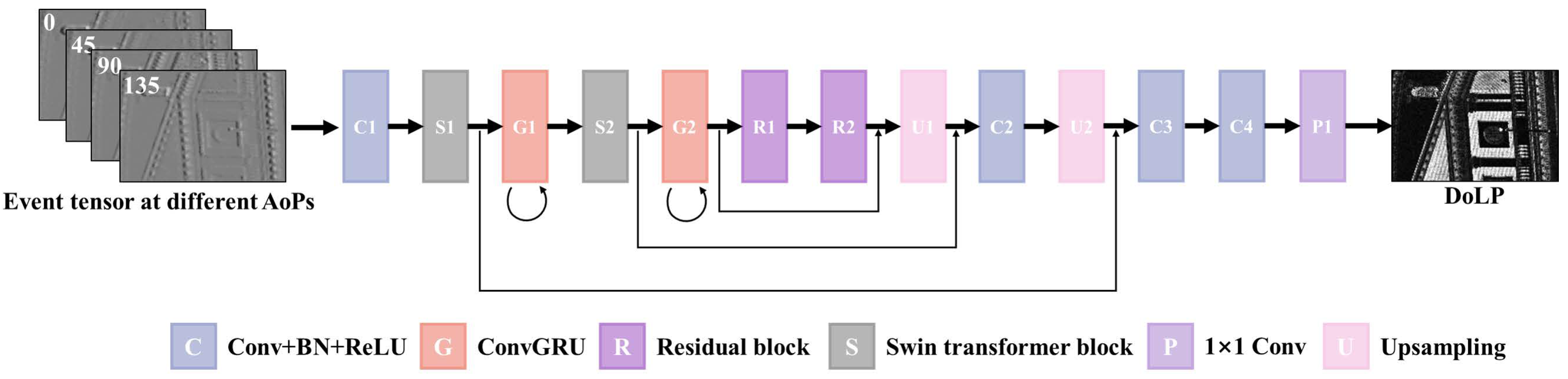
3. Method
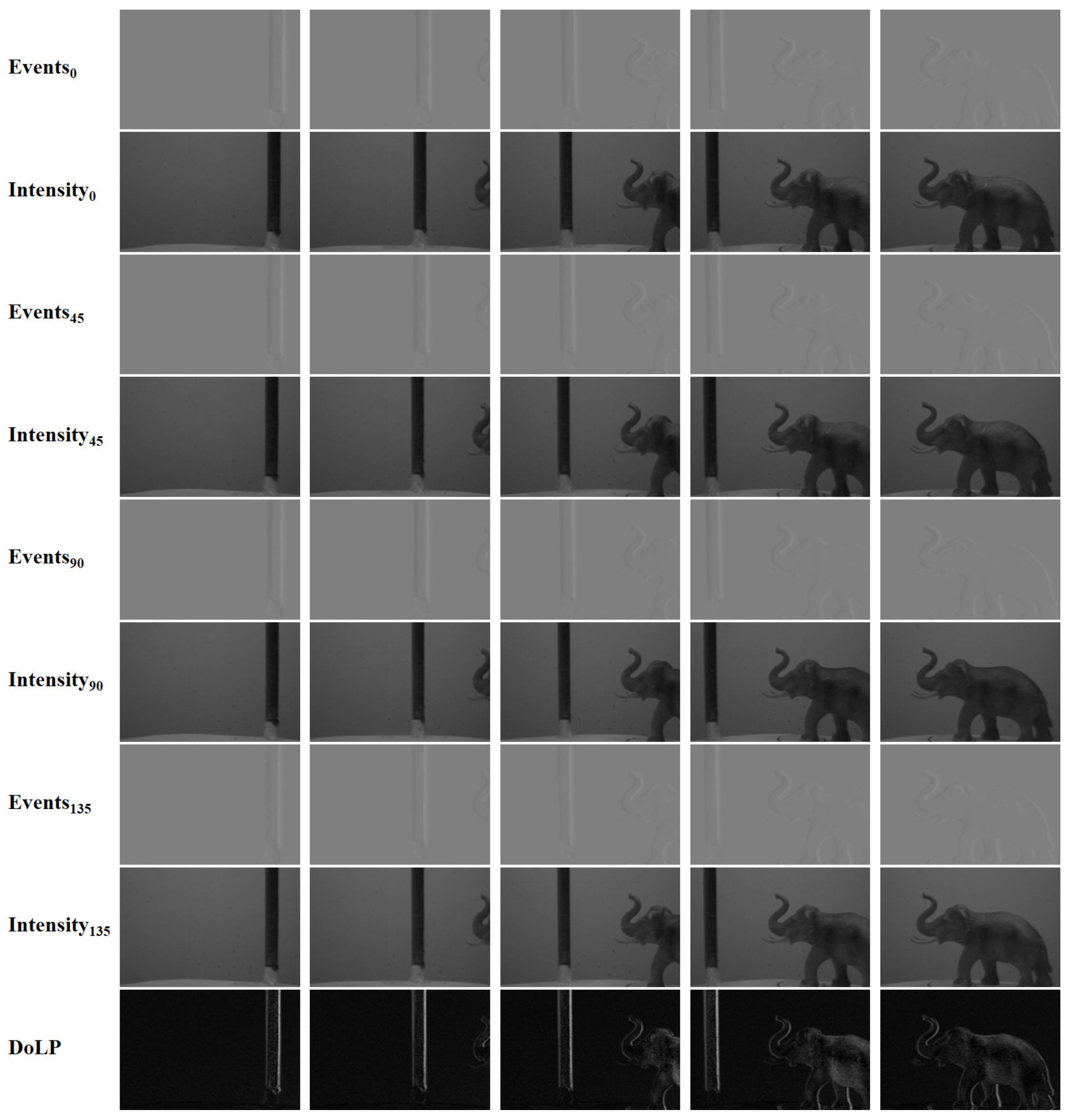
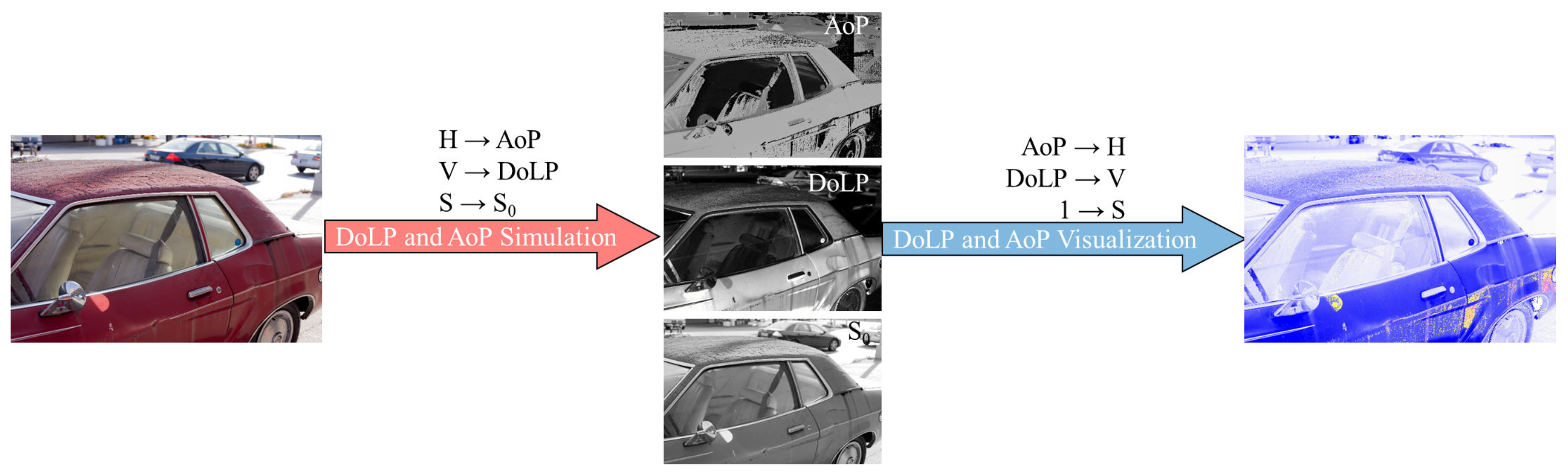
3.1. Simulated Dataset
3.2. Input and Output of the Network
3.3. Network Architecture
3.4. Loss
3.5. Training
4. Experiment Setup
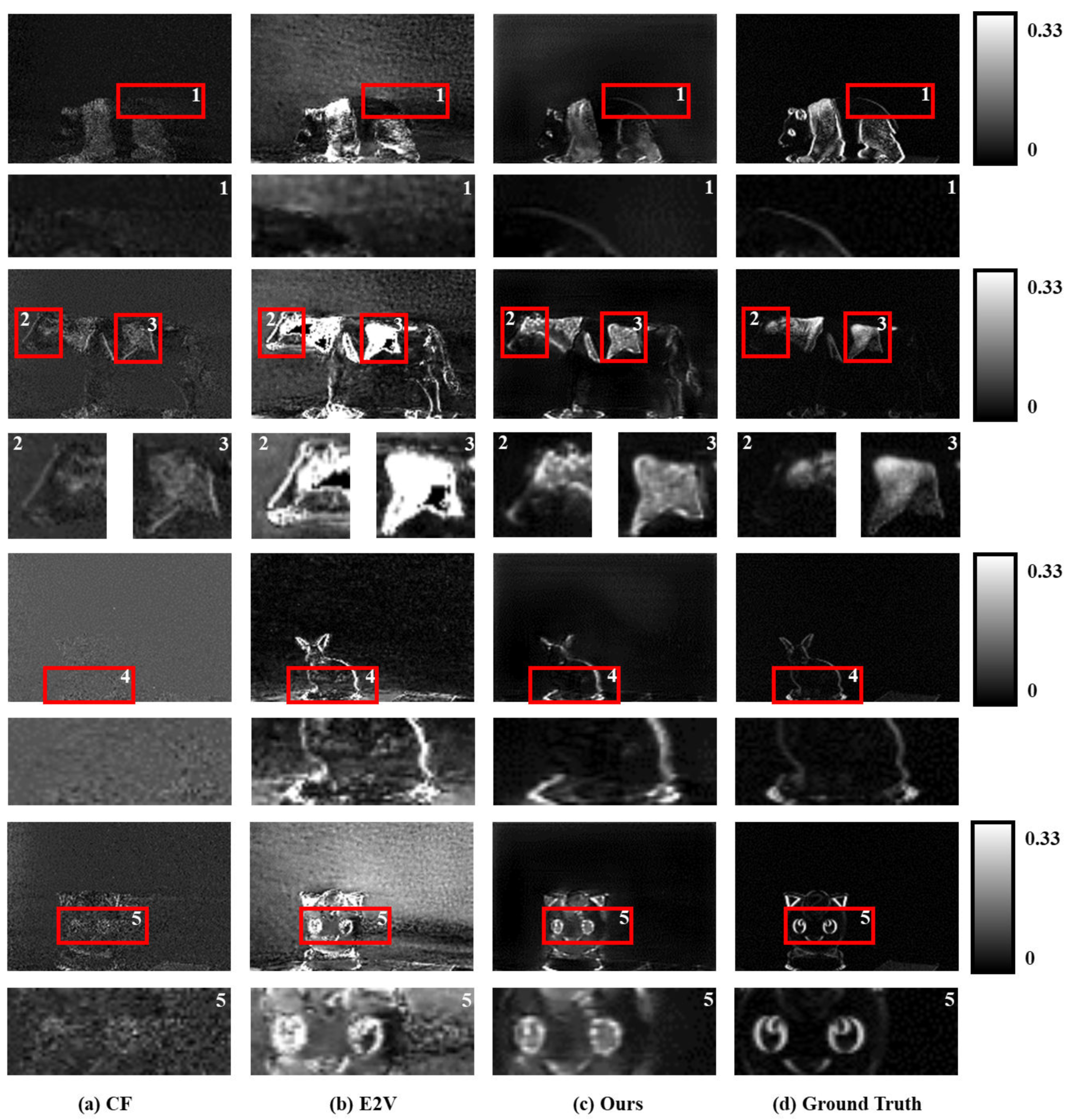
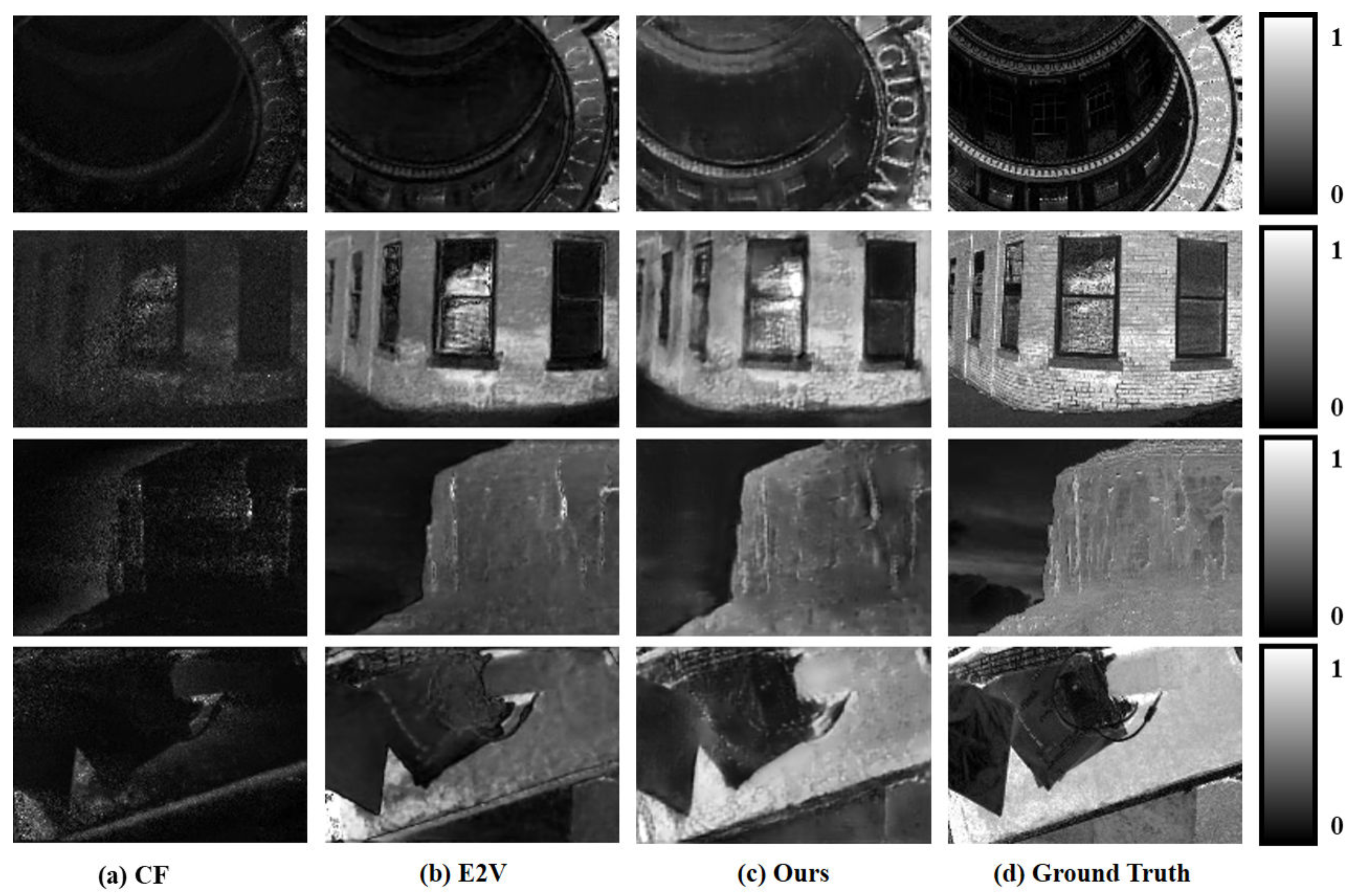
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallego, G.; Delbrück, T.; Orchard, G.; Bartolozzi, C.; Taba, B.; Censi, A.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A.J.; Conradt, J.; Daniilidis, K.; et al. Event-based vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, G.; Lund, J.E.; Mueggler, E.; Rebecq, H.; Delbruck, T.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-based, 6-DOF camera tracking from photometric depth maps. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.R.; Rebecq, H.; Horstschaefer, T.; Scaramuzza, D. Ultimate SLAM? Combining events, images, and IMU for robust visual SLAM in HDR and high-speed scenarios. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Carrió, J.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-aided direct sparse odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5781–5790. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerlinck, C.; Barnes, N.; Mahony, R. Continuous-time intensity estimation using event cameras. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2018: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Revised Selected Papers, Part V. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 308–324. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Ranftl, R.; Koltun, V.; Scaramuzza, D. High speed and high dynamic range video with an event camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1964–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Takatani, T.; Fu, Y. Learning to reconstruct high speed and high dynamic range videos from events. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2024–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Tian, Y. Event-based video reconstruction via potential-assisted spiking neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3594–3604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.Z.; Yuan, L.; Chaney, K.; Daniilidis, K. Unsupervised event-based learning of optical flow, depth, and egomotion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 989–997. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, T. Spike-Based Motion Estimation for Object Tracking Through Bio-Inspired Unsupervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Delbruck, T. EDFLOW: Event driven optical flow camera with keypoint detection and adaptive block matching. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 5776–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Meng, N.; Song, L.; Lam, E.Y. Dynamic laser speckle analysis using the event sensor. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Y.; So, H.K.H.; Lam, E.Y. Lens-free motion analysis via neuromorphic laser speckle imaging. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 2206–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, C.; Pruss, C.; Faulhaber, A.; Herkommer, A. Event based coherence scanning interferometry. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4332–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Gui, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Lang, L.; Cheng, Y. Metal target detection method using passive millimeter-wave polarimetric imagery. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13336–13351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Kerekes, J.P. Adaptive target detection with a polarization-sensitive optical system. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, W.; Sun, Z.; Wu, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, L. Mid-wave infrared polarization imaging system for detecting moving scene. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 5884–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambi, A.; Taamazyan, V.; Shi, B.; Raskar, R. Polarized 3d: High-quality depth sensing with polarization cues. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3370–3378. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Bai, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X. Target enhanced 3D reconstruction based on polarization-coded structured light. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Su, B. Polarization-based approach for multipath interference mitigation in time-of-flight imaging. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 7206–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, T.; Hu, H.; Han, J.; Yu, M. Underwater image recovery considering polarization effects of objects. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 9826–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, M.; Delrot, P.; Leonard, I.; Alfalou, A.; Brosseau, C.; Dogariu, A. Exploring underwater target detection by imaging polarimetry and correlation techniques. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, J.S.; Goldstein, D.L.; Chenault, D.B.; Shaw, J.A. Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5453–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Z. Polarization Patterns of Transmitted Celestial Light under Wavy Water Surfaces. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, T.; Peltoniemi, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Global Skylight Polarization Vector Field. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J. Study on the Polarization Pattern Induced by Wavy Water Surfaces. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawks, M.; Dexter, M. Event-based imaging polarimeter. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 053101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, F.; Xiao, B.; Yang, X.; Xin, L.; Liu, Z. Polarization imaging detection method based on dynamic vision sensor. In Proceedings of the Seventh Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications, Kunming, China, 5–7 November 2020; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11763, pp. 242–251. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Li, F.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, J. Rotary polarization detection imaging system based on dynamic vision sensor. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2021, 29, 2754–2762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haessig, G.; Joubert, D.; Haque, J.; Chen, Y.; Milde, M.; Delbruck, T.; Gruev, V. Bio-inspired polarization event camera. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01933. [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, M. VLSI Analogs of Neuronal Visual Processing: A Synthesis of Form and Function. Ph.D. Dissertation, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner, P.; Posch, C.; Delbruck, T. A 128 × 128 120 dB 15 µs latency asynchronous temporal contrast vision sensor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Delbruck, T. Neuromorphic sensory systems. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbrück, T.; Linares-Barranco, B.; Culurciello, E.; Posch, C. Activity-driven, event-based vision sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, France, 30 May–2 June 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 2426–2429. [Google Scholar]
- Posch, C.; Matolin, D.; Wohlgenannt, R. A QVGA 143 dB dynamic range frame-free PWM image sensor with lossless pixel-level video compression and time-domain CDS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 46, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, C.; Matolin, D.; Wohlgenannt, R. A QVGA 143dB dynamic range asynchronous address-event PWM dynamic image sensor with lossless pixel-level video compression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 February 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, R.; Brandli, C.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Delbruck, T. A 240 × 180 130 dB 3 s latency global shutter spatiotemporal vision sensor. IEEE J. Solid-State 2013, 49, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, R.; Brandli, C.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.C.; Delbruck, T. A 240 × 180 10 mw 12 us latency sparse-output vision sensor for mobile applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 12–14 June 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. C186–C187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Guo, M. Live demonstration: CeleX-V: A 1M pixel multi-mode event-based sensor. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1682–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Finateu, T.; Niwa, A.; Matolin, D.; Tsuchimoto, K.; Mascheroni, A.; Reynaud, E.; Mostafalu, P.; Brady, F.; Chotard, L.; LeGoff, F.; et al. 5.10 a 1280 × 720 back-illuminated stacked temporal contrast event-based vision sensor with 4.86 µm pixels, 1.066 GEPS readout, programmable event-rate controller and compressive data-formatting pipeline. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, Y.; Choi, S.; Ito, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Seo, J.; Jung, H.; Yeo, D.H.; Namgung, S.; Bong, J.; et al. A 1280 × 960 dynamic vision sensor with a 4.95-µm pixel pitch and motion artifact minimization. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Virtual, 10–21 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Ranftl, R.; Koltun, V.; Scaramuzza, D. Events-to-video: Bringing modern computer vision to event cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 5–20 June 2019; pp. 3857–3866. [Google Scholar]
- Walraven, R. Polarization imagery. Opt. Eng. 1981, 20, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendre, L.; Foulonneau, A.; Bigué, L. Stokes imaging polarimetry using a single ferroelectric liquid crystal modulator. In Proceedings of the Polarization: Measurement, Analysis, and Remote Sensing IX, Orlando, FL, USA, 7–8 April 2010; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7672, pp. 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Azzam, R. Arrangement of four photodetectors for measuring the state of polarization of light. Opt. Lett. 1985, 10, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzaniti, J.L.; Chenault, D.; Roche, M.; Reinhardt, J.; Schultz, H. Wave slope measurement using imaging polarimetry. In Proceedings of the Ocean Sensing and Monitoring, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–14 April 2009; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7317, pp. 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzaniti, J.L.; Chenault, D.B. A division of aperture MWIR imaging polarimeter. In Proceedings of the Polarization Science and Remote Sensing II, San Diego, CA, USA, 18 August 2005; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5888, pp. 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Design of Simultaneous Imaging Polarimetry with double separate Wollaston prism. Acta Opt. Sin. 2015, 35, 511001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruev, V.; Perkins, R.; York, T. CCD polarization imaging sensor with aluminum nanowire optical filters. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 19087–19094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kang, G.; Vartiainen, I.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X. Investigation of achromatic micro polarizer array for polarization imaging in visible-infrared band. Optik 2018, 158, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, J.R. Fundamentals of Polarimetric Remote Sensing; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Muglikar, M.; Bauersfeld, L.; Moeys, D.P.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-based shape from polarization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1547–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Gehrig, D.; Scaramuzza, D. ESIM: An open event camera simulator. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Zürich, Switzerland, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 969–982. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, S.C.; Delbruck, T. v2e: From video frames to realistic DVS events. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1312–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Joubert, D.; Marcireau, A.; Ralph, N.; Jolley, A.; van Schaik, A.; Cohen, G. Event camera simulator improvements via characterized parameters. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 702765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K.; Woo, W.c. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Bychkovsky, V.; Paris, S.; Chan, E.; Durand, F. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Washington, DC, USA, 20–25 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Lin, Z.; Desmaison, A.; Antiga, L.; Lerer, A. Automatic differentiation in pytorch. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2017 Workshop, Long Beach, CA, USA, 7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]





| Type | DoLP | AoP | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| DoT | ✓ | ✓ | Static scene in standard dynamic range (SDR) |
| Non-DoT | ✓ | ✓ | Static scene and slow motion in SDR |
| Event-based DoT | ✓ | ✓ | Static scene in high dynamic range (HDR) |
| Event-based non-DoT | ✗ | ✓ | Fast and slow motion in HDR |
| Method | Real Experiment | Simulated Experiment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | MSE ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | |
| CF | 0.0087 | 23.17 | 0.4116 | 0.3342 | 0.1371 | 10.60 | 0.1667 | 0.5890 |
| E2V | 0.0134 | 20.02 | 0.3819 | 0.3350 | 0.0778 | 12.74 | 0.3068 | 0.4140 |
| Ours | 0.0026 | 27.48 | 0.5189 | 0.1369 | 0.0355 | 15.56 | 0.3947 | 0.3295 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Zuo, Y. Training a Dataset Simulated Using RGB Images for an End-to-End Event-Based DoLP Recovery Network. Photonics 2024, 11, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050481
Yan C, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang C, Sun Q, Zuo Y. Training a Dataset Simulated Using RGB Images for an End-to-End Event-Based DoLP Recovery Network. Photonics. 2024; 11(5):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050481
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Changda, Xia Wang, Xin Zhang, Conghe Wang, Qiyang Sun, and Yifan Zuo. 2024. "Training a Dataset Simulated Using RGB Images for an End-to-End Event-Based DoLP Recovery Network" Photonics 11, no. 5: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050481
APA StyleYan, C., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, C., Sun, Q., & Zuo, Y. (2024). Training a Dataset Simulated Using RGB Images for an End-to-End Event-Based DoLP Recovery Network. Photonics, 11(5), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050481





