Adaptive Image-Defogging Algorithm Based on Bright-Field Region Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
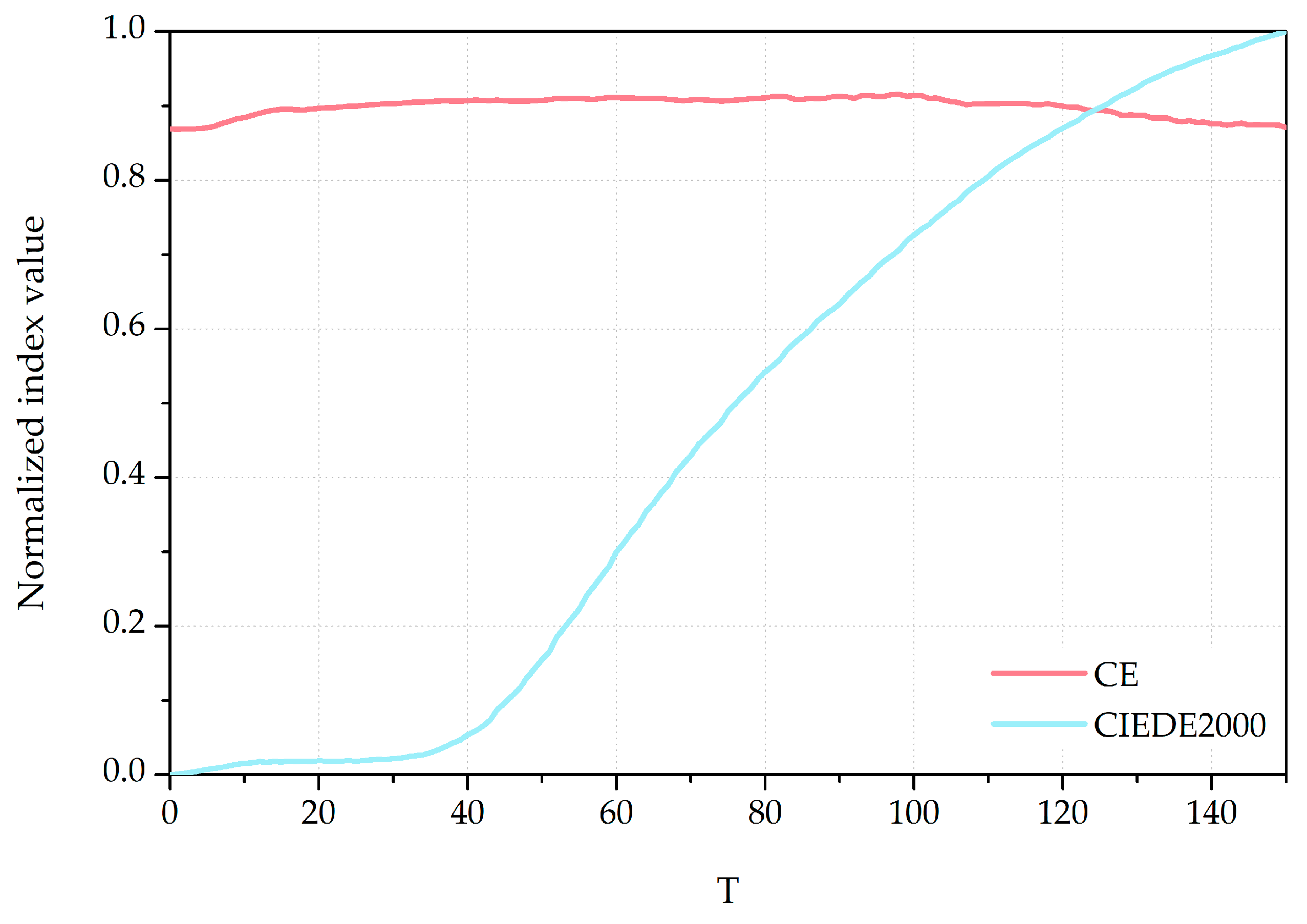
- By leveraging the correlation between the lowest value among the R, G, and B color channels of the obscured initial image and the dark-channel prior, the compensation threshold is established through the application of the contrast energy (CE) and CIEDE2000 metrics. This process enhances the dark-channel image and effectively mitigates the halo effect present in the resulting image.
- 2.
- A novel bright-field region-segmentation algorithm is proposed that initially segments the bright-field region based on three prior conditions to determine the baseline of the target area. Subsequently, region growing is employed to further refine the bright-field region.
- 3.
- Introducing an adaptive adjustment factor to optimize the transmittance mapping effectively addresses the potential color distortion issues that may arise in the process of dehazing bright-field regions.
2. DCP Defogging Algorithm and Background
2.1. Atmospheric Scattering Model
2.2. Dark-Channel Prior Defogging
2.3. Guided Filter
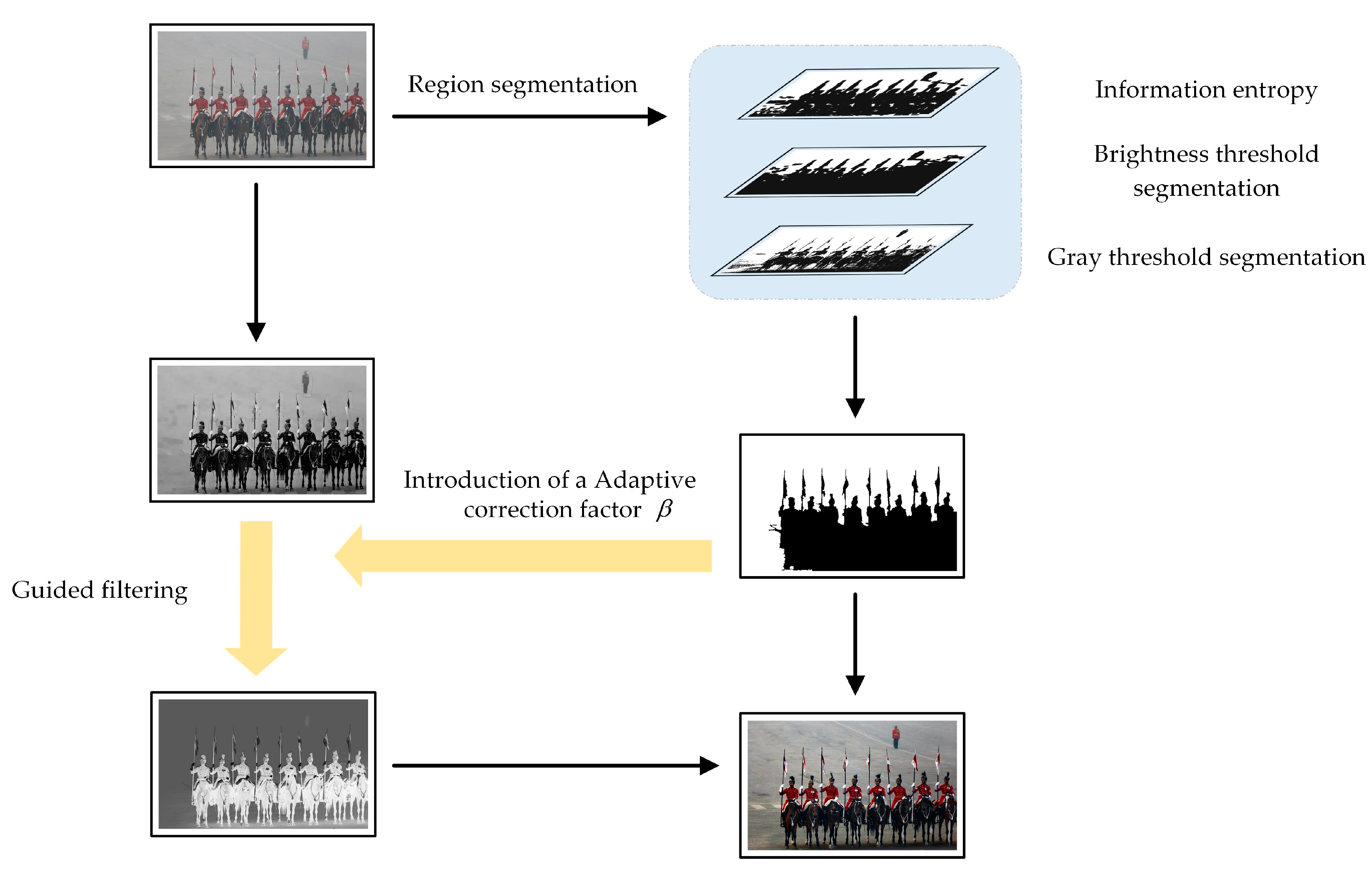
3. Proposed Algorithm
3.1. Improved Dark-Channel Image
- 4.
- According to the dark-channel prior theory, the size of is pixels, and the initial dark-channel image is obtained:
- 5.
- Obtain the MC:
- 6.
- Calculate the absolute value of the difference between the two:
- 7.
- Screening: When the difference is greater than , it is considered that the central pixel and its neighborhood are in different depth-of-field ranges. The MC is used to replace and correct pixels of image , reducing the impact of changes in the depth of field at the edges.
- 8.
- Introduce tolerance : = 5. In the dark-channel image obtained in the first step, if the gray value of a pixel falls within the tolerance range of , that pixel and the pixels to its left and right are adjusted by the central pixel’s MC.
3.2. Determination of Threshold
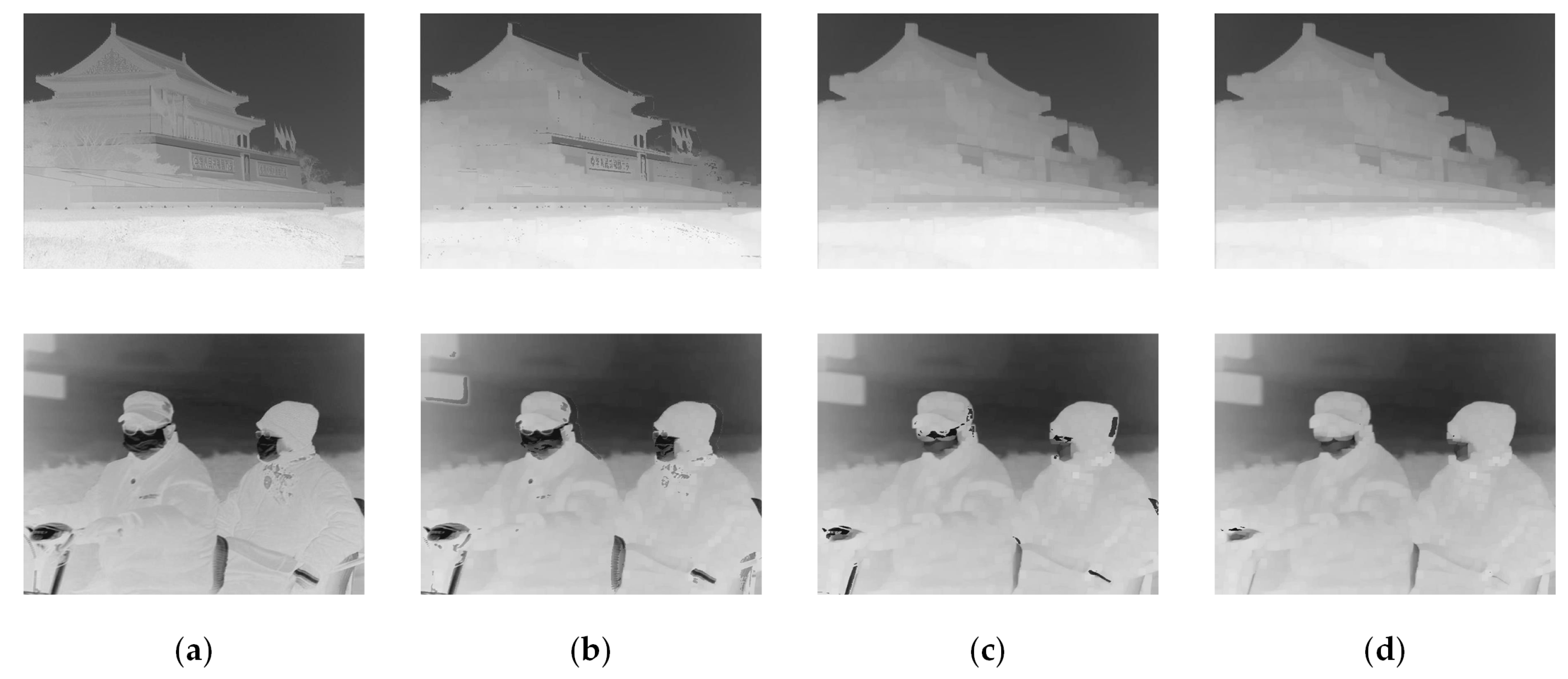
3.3. Bright-Field Region Segmentation
3.4. Transmission-Adaptive Optimization
4. Experiment and Discussion
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Image Quality Evaluation Method
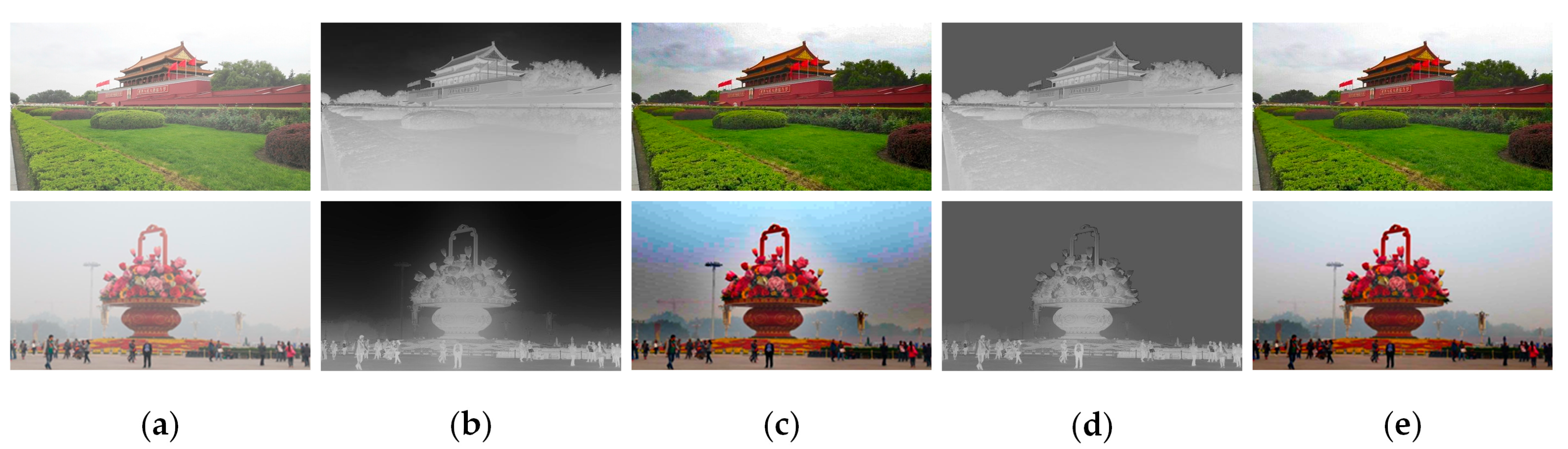
4.3. Result Analysis
4.3.1. Comparison with DCP Algorithm
4.3.2. Comparison with Other Methods
5. Conclusions
- Developing defogging algorithms with lower time complexity and higher robustness while maintaining image resolution;
- How traditional algorithms and neural networks can learn from each other to propose new defogging models for the better realization of the defogging task.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse Gradient Regularized Deep Retinex Network for Robust Low-Light Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Song, M. Single Image Dehazing Algorithm Based on Sky Segmentation and Optimal Transmission Maps. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Gupta, R.; Son, L.H.; Kumar, R.; Jha, S. Fog Removal in Images Using Improved Dark Channel Prior and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 23281–23307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.A. Adaptive Image Contrast Enhancement Using Generalizations of Histogram Equalization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, J.; Hao, Y.; Zou, F.; Lin, F.; Han, S. Advanced RetinexNet: A Fully Convolutional Network for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2023, 112, 116916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamini, S.; Kumar, S.S. Homomorphic Filtering for the Image Enhancement Based on Fractional-Order Derivative and Genetic Algorithm. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 106, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhi, S.; Liu, W.; Deng, J.; Ren, J. An Improved Dark Channel Defogging Algorithm Based on the HSI Colour Space. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.T. Visibility in Bad Weather from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Efficient Image Dehazing with Boundary Constraint and Contextual Regularization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, D.; Treibitz, T.; Avidan, S. Non-Local Image Dehazing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1674–1682. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single Image Haze Removal Using Dark Channel Prior. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1956–1963. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided Image Filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Mai, J.; Shao, L. A Fast Single Image Haze Removal Algorithm Using Color Attenuation Prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Ou, B.; Tian, Q. An Improved Dark Channel Prior Image Defogging Algorithm Based on Wavelength Compensation. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, L.; Fang, L.; Dong, H. Improved Color Image Defogging Algorithm Based on Dark Channel Prior. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 8187–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Xu, X.; Jia, K.; Qing, C.; Tao, D. DehazeNet: An End-to-End System for Single Image Haze Removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, D. AOD-Net: All-in-One Dehazing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4780–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Pan, J.; Xiang, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, M.-H. Multi-Scale Boosted Dehazing Network with Dense Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2154–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Yan, Q.; Anwar, S.; Cong, R.; Ren, W.; Li, C. Image Dehazing Transformer with Transmission-Aware 3D Position Embedding. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5810. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Tao, D. Self-Augmented Unpaired Image Dehazing via Density and Depth Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2027–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Ren, W.; Pan, J.; Gao, C.; Sang, N.; Yang, M.-H. Semi-Supervised Image Dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 2766–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.-Q.; Duan, Z.-P.; Guo, C.-L.; Chai, Z.; Li, C. RIDCP: Revitalizing Real Image Dehazing via High-Quality Codebook Priors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22282–22291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; He, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Dark Channel: The Devil Is in the Details. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and the Atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Carvalho, P.; Côrte-Real, L. Boosting Color Similarity Decisions Using the CIEDE2000_PF Metric. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, I.I.A.; Ghebreab, S.; Prins, H.; Lamme, V.A.F.; Scholte, H.S. From Image Statistics to Scene Gist: Evoked Neural Activity Reveals Transition from Low-Level Natural Image Structure to Scene Category. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18814–18824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Cimr, D.; Fujita, H.; Cimler, R. Image Entropy Equalization: A Novel Preprocessing Technique for Image Recognition Tasks. Inf. Sci. 2023, 647, 119539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, M. Single Image Dehazing via Large Sky Region Segmentation and Multiscale Opening Dark Channel Model. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8890–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ren, W.; Fu, D.; Tao, D.; Feng, D.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z. Benchmarking Single-Image Dehazing and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “Completely Blind” Image Quality Analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautière, N.; Tarel, J.-P.; Aubert, D.; Dumont, É. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges. Image Anal. Ster. 2011, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, L.K.; You, J.; Bovik, A.C. Referenceless Prediction of Perceptual Fog Density and Perceptual Image Defogging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3888–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.; Lee, G.-D.; Kang, B. Improved Color Attenuation Prior for Single-Image Haze Removal. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.; Lee, S.; Kang, B. Robust Single-Image Haze Removal Using Optimal Transmission Map and Adaptive Atmospheric Light. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Bhanu, B.; Long, S.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z. Fast Region-Adaptive Defogging and Enhancement for Outdoor Images Containing Sky. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 8267–8274. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Ding, C.; Ren, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.J. IDE: Image Dehazing and Exposure Using an Enhanced Atmospheric Scattering Model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2180–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D. PSD: Principled Synthetic-to-Real Dehazing Guided by Physical Priors. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 7176–7185. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Wu, H.; Yao, S. Image Defogging Based on Joint Contrast Enhancement and Multi-Scale Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications (ICPECA), Shenyang, China, 29–31 January 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]




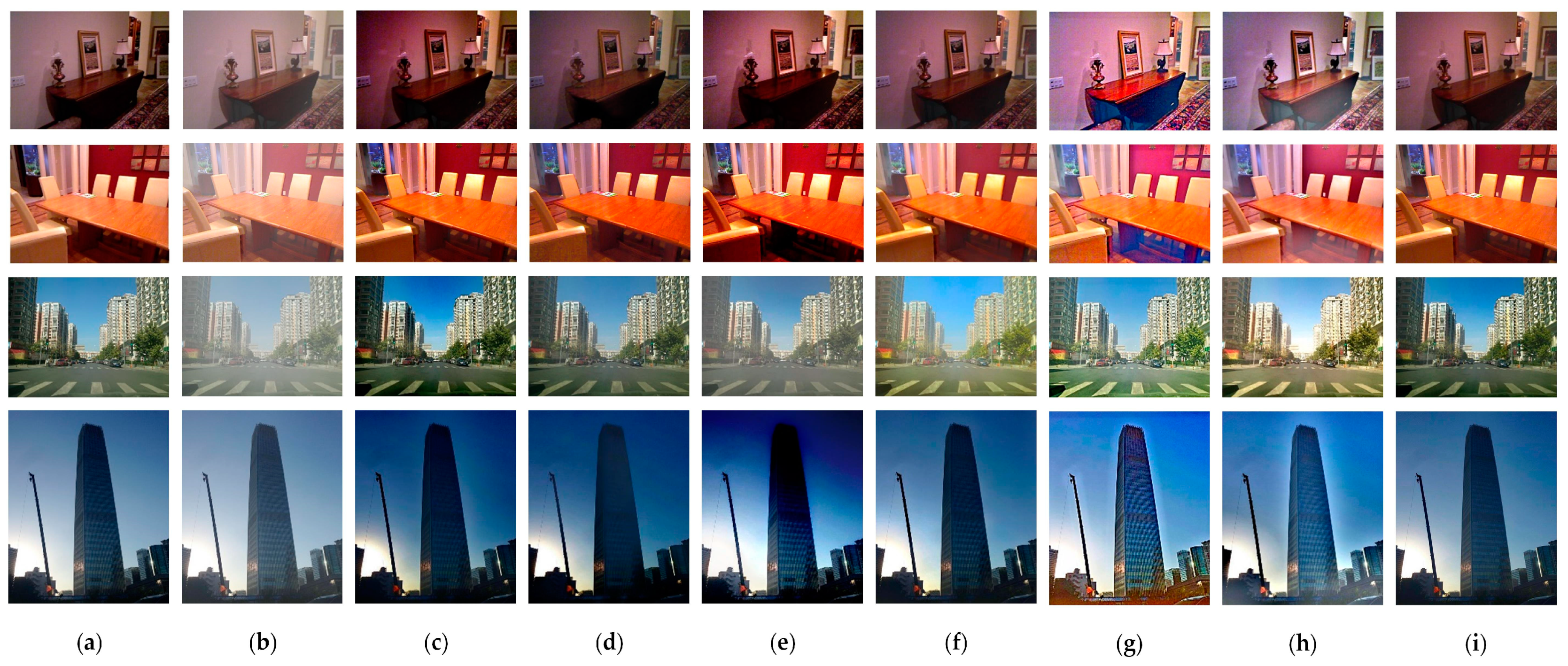
| Foggy Image | DCP | CAP | DEFADE | ICAP | OTM-AAL | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | |
| 1 | 0.79 | 12.01 | 3.19 | 0.81 | 11.86 | 3.00 | 0.91 | 17.35 | 3.10 | 0.84 | 13.49 | 3.03 | 0.88 | 15.00 | 2.66 |
| 2 | 0.95 | 20.07 | 3.64 | 0.85 | 15.53 | 3.29 | 0.78 | 15.77 | 3.72 | 0.90 | 17.79 | 3.73 | 0.89 | 16.21 | 3.12 |
| 3 | 0.77 | 10.97 | 3.68 | 0.88 | 14.62 | 3.85 | 0.66 | 9.25 | 3.74 | 0.87 | 16.17 | 4.05 | 0.85 | 16.28 | 3.80 |
| 4 | 0.93 | 17.76 | 2.62 | 0.72 | 12.59 | 2.81 | 0.77 | 12.93 | 2.55 | 0.83 | 12.70 | 3.52 | 0.85 | 13.66 | 2.47 |
| 5 | 0.75 | 10.92 | 2.59 | 0.82 | 12.49 | 2.71 | 0.83 | 12.59 | 2.74 | 0.88 | 14.23 | 2.97 | 0.90 | 16.37 | 2.76 |
| 6 | 0.75 | 10.08 | 3.36 | 0.84 | 12.05 | 3.49 | 0.81 | 11.24 | 3.60 | 0.88 | 13.42 | 3.56 | 0.91 | 15.93 | 3.39 |
| 7 | 0.71 | 13.57 | 3.19 | 0.82 | 19.47 | 3.38 | 0.83 | 11.86 | 3.35 | 0.91 | 16.15 | 3.95 | 0.93 | 20.23 | 3.95 |
| 8 | 0.64 | 8.55 | 5.07 | 0.81 | 12.16 | 5.38 | 0.87 | 11.78 | 5.02 | 0.87 | 13.74 | 5.01 | 0.93 | 17.61 | 5.08 |
| Foggy Image | RADE | IDE | PSD | CEEF | Proposed Method | ||||||||||
| ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | ssim | psnr | NI QE | |
| 1 | 0.57 | 12.49 | 4.50 | 0.81 | 16.19 | 3.25 | 0.74 | 16.31 | 4.70 | 0.66 | 10.61 | 3.89 | 0.88 | 16.43 | 2.65 |
| 2 | 0.56 | 14.50 | 5.06 | 0.81 | 15.10 | 3.63 | 0.70 | 14.28 | 5.08 | 0.77 | 14.00 | 3.66 | 0.95 | 18.81 | 2.95 |
| 3 | 0.67 | 13.59 | 3.12 | 0.71 | 14.35 | 3.45 | 0.84 | 16.35 | 3.94 | 0.71 | 10.22 | 3.74 | 0.89 | 16.58 | 3.54 |
| 4 | 0.59 | 14.34 | 2.97 | 0.72 | 16.64 | 2.41 | 0.70 | 14.79 | 2.63 | 0.72 | 12.80 | 2.57 | 0.93 | 16.90 | 2.45 |
| 5 | 0.68 | 14.56 | 2.87 | 0.83 | 16.02 | 2.55 | 0.81 | 18.69 | 3.12 | 0.71 | 10.63 | 2.53 | 0.88 | 15.82 | 2.59 |
| 6 | 0.66 | 13.22 | 2.89 | 0.82 | 13.97 | 3.10 | 0.83 | 18.25 | 3.04 | 0.70 | 9.95 | 3.15 | 0.90 | 13.98 | 2.92 |
| 7 | 0.80 | 12.65 | 3.20 | 0.89 | 15.94 | 4.06 | 0.86 | 20.19 | 3.68 | 0.76 | 11.22 | 4.13 | 0.88 | 18.74 | 3.24 |
| 8 | 0.80 | 15.39 | 4.87 | 0.86 | 14.03 | 4.88 | 0.89 | 18.72 | 4.03 | 0.73 | 11.19 | 4.22 | 0.92 | 16.89 | 4.13 |
| Foggy Image | DCP | CAP | DEFADE | ICAP | OTM-AAL | RADE | IDE | PSD | CEEF | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.03 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.63 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 2.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.94 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 1.14 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 3.26 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
| 7 | 1.43 | 4.84 | 4.68 | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.69 | 4.24 | 0.68 |
| 8 | 1.91 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 1.42 | 0.00 |
| Method | Outdoor | Indoor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ssim | psnr | ssim | psnr | |
| DCP | 0.76 | 11.48 | 0.72 | 10.51 |
| CAP | 0.74 | 11.57 | 0.75 | 11.25 |
| DEFADE | 0.80 | 12.24 | 0.77 | 12.82 |
| OTM-AAL | 0.90 | 15.95 | 0.89 | 15.75 |
| IDE | 0.85 | 16.32 | 0.84 | 15.23 |
| PSD | 0.77 | 17.20 | 0.79 | 17.03 |
| Proposed method | 0.88 | 16.29 | 0.86 | 14.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yue, F.; Duan, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Dong, J.; Zeng, J.; Cui, S. Adaptive Image-Defogging Algorithm Based on Bright-Field Region Detection. Photonics 2024, 11, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11080718
Wang Y, Yue F, Duan J, Zhang H, Song X, Dong J, Zeng J, Cui S. Adaptive Image-Defogging Algorithm Based on Bright-Field Region Detection. Photonics. 2024; 11(8):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11080718
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yue, Fengying Yue, Jiaxin Duan, Haifeng Zhang, Xiaodong Song, Jiawei Dong, Jiaxin Zeng, and Sidong Cui. 2024. "Adaptive Image-Defogging Algorithm Based on Bright-Field Region Detection" Photonics 11, no. 8: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11080718
APA StyleWang, Y., Yue, F., Duan, J., Zhang, H., Song, X., Dong, J., Zeng, J., & Cui, S. (2024). Adaptive Image-Defogging Algorithm Based on Bright-Field Region Detection. Photonics, 11(8), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11080718




