Developments of Waveguide Lasers by Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology in Optical Waveguide
3. Development of Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Optical Waveguide Laser
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bae, J.E.; Loiko, P.; Normani, S.; Brasse, G.; Benayad, A.; Braud, A.; Camy, P. Er:LiYF4 planar waveguide laser at 2.8 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 081101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeselmann, S.H.; Rüter, C.E.; Kip, D.; Kränkel, C.; Huber, G. Nd:sapphire channel waveguide laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilchik, S.V.; Prentice, J.J.; Eason, R.W.; Mackenzie, J.I. Characterisation and laser performance of a Yb:LuAG double–clad planar waveguide grown by pulse laser deposition. Appl. Phys. B 2019, 125, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Che, L.; Wang, S.; Meng, H.; Liu, X. Buried Optical Waveguide in Photo–Thermo–Refractive Glass by Ion Exchange Technology. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2023, 35, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Ren, X.; Ruan, S.; Wang, L.; Yan, P.; Han, H.; Wang, M.; Yin, J. Visible to near–infrared supercontinuum generation in yttrium orthosilicate bulk crystal and ion implanted planar waveguide. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.C.; Wang, S.X.; Chen, F. Femtosecond laser direct writing of flexibly configured waveguide geometries in optical crystals: Fabrication and application. Opto–Electron. Adv. 2020, 3, 190042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.M.; Miura, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Hirao, K. Writing waveguides in glass with a femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lu, F.; Chen, F.; Shi, B.-R.; Wang, K.-M.; Shen, D.-Y. Monomode optical waveguide in lithium niobate formed by MeV Si+ ion implantation. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5224–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevnin, M.; Atar, G.; Čampelj, S.; Lenardič, B.; Kaplan, N.; Sherman, V.; Gvishi, R.; Sfez, B.; Eger, D. Low–Loss Waveguides by Planar Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; He, S.; Liu, H. Annular waveguide lasers at 1064 nm in Nd:YAG crystal produced by femtosecond laser inscription. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 5420–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, T.; Nakagome, H. Optical waveguide formed by electrically induced migration of ions in glass plates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 21, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S.; Pintori, G.; Sglavo, V.M. Conventional and electric field–assisted ion exchange on glass–ceramics for dental applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 5341–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, J.F. Ion implantation in semiconductors–Part I: Range distribution theory and experiments. Proc. IEEE 1968, 56, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liao, Y.; Lin, J.; Song, J.; Qiao, L.; Cheng, Y.; Sugioka, K. Femtosecond Laser Fabrication of Monolithically Integrated Microfluidic Sensors in Glass. Sensors 2014, 14, 19402–19440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugioka, K.; Xu, J.; Wu, D.; Hanada, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Midorikawa, K. Femtosecond laser 3D micromachining: A powerful tool for the fabrication of microfluidic, optofluidic, and electrofluidic devices based on glass. Lab. A Chip. 2014, 14, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethfeld, B.; Sokolowski-Tinten, K.; von der Linde, D.; Anisimov, S.I. Timescales in the response of materials to femtosecond laser excitation. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ams, M.; Marshall, G.D.; Dekker, P.; Dubov, M.; Mezentsev, V.K.; Bennion, I.; Withford, M.J. Investigation of Ultrafast Laser–Photonic Material Interactions: Challenges for Directly Written Glass Photonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2008, 14, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.S.; Almeida, J.M.P.; Almeida, G.F.B.; Cardoso, M.R.; De Boni, L.; Mendonça, C.R. Ultrafast Laser Pulses for Structuring Materials at Micro/Nano Scale: From Waveguides to Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Photonics 2017, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.; Dubov, M.; Withford, M.J. On the use of the Type I and II scheme for classifying ultrafast laser direct–write photonics. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 7767–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, F. Femtosecond laser–induced optical waveguides in crystalline garnets: Fabrication and application. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.R.; Campbell, S.; Blewett, I.J.; Kar, A.K.; Reid, D.T. Optical waveguide fabrication in z–cut lithium niobate (LiNbO3) using femtosecond pulses in the low repetition rate regime. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 111109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Thomson, R.R.; Beecher, S.J.; Psaila, N.D.; Bookey, H.T.; Kar, A.K. Ultrafast laser inscription of near–infrared waveguides in polycrystalline ZnSe. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 4036–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, F.; Calmano, T.; Müller, S.; Marzahl, D.T.; Metz, P.W.; Huber, G. Efficient visible laser operation of Pr,Mg:SrAl12O19 channel waveguides. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2698–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R. Near–infrared lasers and self–frequency–doubling in Nd:YCOB cladding waveguides. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 11562–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Nie, W.; Romero, C.; Aldana, J.R.V.d.; Chen, F. Femtosecond–Laser–Written S–Curved Waveguide in Nd:YAP Crystal: Fabrication and Multi–Gigahertz Lasing. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 6845–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, C.; Ismaeel, R.; Corbari, C.; Huang, C.-C.; Hewak, D.W.; Lagoudakis, P.; Brambilla, G. Generation of Multi–Gigahertz Trains of Phase–Coherent Femtosecond Laser Pulses in Ti:Sapphire Waveguides. Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1800167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Mu, W.; Ren, Y.; Jia, Z.; Fu, X.; Sun, X.; Jia, Y. Dual–wavelength self–Q–switched mode–locked waveguide lasers based on Nd:LGGG cladding waveguides. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmano, T.; Kränkel, C.; Huber, G. Laser oscillation in Yb:YAG waveguide beam–splitters with variable splitting ratio. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1753–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Aldana, J.R.V.d.; Hong, M.; Chen, F. Femtosecond Laser Inscribed Y–Branch Waveguide in Nd:YAG Crystal: Fabrication and Continuous–Wave Lasing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; He, R.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Liu, H.; Chen, F. Femtosecond laser direct writing of few–mode depressed–cladding waveguide lasers. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 30941–30951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-P.; Zou, X.; Bai, Z.; Leng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, L. Mid–infrared laser emission from Cr:ZnS channel waveguide fabricated by femtosecond laser helical writing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Cheng, C.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Castillo, G.R.; Rabes, B.d.R.; Tan, Y.; Jaque, D.; Chen, F. Monolithic crystalline cladding microstructures for efficient light guiding and beam manipulation in passive and active regimes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.E.; Park, T.G.; Kifle, E.; Mateos, X.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F.; Romero, C.; Rodríguez Vázquez de Aldana, J.; Lee, H.; Rotermund, F. Carbon nanotube Q–switched Yb:KLuW surface channel waveguide lasers. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-L.; Ye, Y.-K.; Wang, H.-L. Cladding waveguide lasers in femtosecond laser written Nd:KGW waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2020, 110, 110517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Lau, K.Y.; Wu, Z.; Zou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; et al. 3D Laser Writing of Low–Loss Cross–Section–Variable Type–I Optical Waveguide Passive/Active Integrated Devices in Single Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2404493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccheo, S.; Della Valle, G.; Osellame, R.; Cerullo, G.; Chiodo, N.; Laporta, P.; Svelto, O.; Killi, A.; Morgner, U.; Lederer, M.; et al. Er:Yb–doped waveguide laser fabricated by femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2626–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocco, D.; Lopez-Quintas, I.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Tonelli, M.; Tredicucci, A. High efficiency diode–pumped Pr:LiLuF4 visible lasers in femtosecond–laser–written waveguides. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 9767–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmano, T.; Siebenmorgen, J.; Reichert, F.; Fechner, M.; Paschke, A.-G.; Hansen, N.-O.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G. Crystalline Pr:SrAl12O19 waveguide laser in the visible spectral region. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4620–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, C.; Corbari, C.; Brambilla, G.; Lagoudakis, P.G. Tunable, continuous–wave Ti:sapphire channel waveguide lasers written by femtosecond and picosecond laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 4630–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Calmano, T.; Rotermund, F.; Kränkel, C. 2–GHz carbon nanotube mode–locked Yb:YAG channel waveguide laser. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 5140–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakobyan, S.; Wittwer, V.J.; Hasse, K.; Kränkel, C.; Südmeyer, T.; Calmano, T. Highly efficient Q–switched Yb:YAG channel waveguide laser with 5.6 W of average output power. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4715–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebenmorgen, J.; Calmano, T.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G. Highly efficient Yb:YAG channel waveguide laser written with a femtosecond–laser. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 16035–16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Chen, F. Efficient waveguide lasers in femtosecond laser inscribed double–cladding waveguides of Yb:YAG ceramics. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmano, T.; Siebenmorgen, J.; Hellmig, O.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G. Nd:YAG waveguide laser with 1.3 W output power, fabricated by direct femtosecond laser writing. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 100, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Cheng, C.; Aldana, J.R.V.d.; Chen, F. Three–Dimensional Waveguide Splitters Inscribed in Nd:YAG by Femtosecond Laser Writing: Realization and Laser Emission. J. Light. Technol. 2016, 34, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, N.; Yang, J.; Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Lu, Q. Channel waveguide lasers in Nd:GGG crystals fabricated by femtosecond laser inscription. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 12503–12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jia, Y.; Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R. Continuous wave laser operation in Nd:GGG depressed tubular cladding waveguides produced by inscription of femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Rodenas, A.; Chen, F.; Thomson, R.R.; Kar, A.K.; Jaque, D.; Lu, Q. 70% slope efficiency from an ultrafast laser–written Nd:GdVO4 channel waveguide laser. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24994–24999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, N.; Salamu, G.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M. Diode–laser pumping into the emitting level for efficient lasing of depressed cladding waveguides realized in Nd:YVO4 by the direct femtosecond–laser writing technique. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 23057–23065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Dong, N.; Macdonald, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Kar, A.K. Continuous wave channel waveguide lasers in Nd:LuVO4 fabricated by direct femtosecond laser writing. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; An, Q.; Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; del Rosal Rabes, B. Continuous–wave lasing at 1.06μm in femtosecond laser written Nd:KGW waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2014, 37, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhrimchuk, A.G.; Obraztsov, P.A. 11–GHz waveguide Nd:YAG laser CW mode–locked with single–layer graphene. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Cheng, C.; Jia, Y.; Romero, C.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Chen, F. Dual–wavelength waveguide lasers at 1064 and 1079 nm in Nd:YAP crystal by direct femtosecond laser writing. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 2437–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kifle, E.; Mateos, X.; de Aldana, J.R.V.; Ródenas, A.; Loiko, P.; Choi, S.Y.; Rotermund, F.; Griebner, U.; Petrov, V.; Aguiló, M.; et al. Femtosecond–laser–written Tm:KLu(WO4)2 waveguide lasers. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Jia, Y.; Chen, F. Tm,Ho:YLF waveguide lasers at 2.05 µm. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 1977–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Jia, Y.; Chen, F. Femtosecond laser direct writing of compact Tm:YLF waveguide lasers. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayevi, B.; Morova, Y.; Tonelli, M.; Sennaroglu, A. Er3+:YLiF4 channeled waveguide laser near 2.7–2.8 μm fabricated by femtosecond laser inscription. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiocco, D.; Lopez-Quintas, I.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Tonelli, M.; Tredicucci, A. Comparative Performance Analysis of Femtosecond–Laser–Written Diode–Pumped Pr:LiLuF4 Visible Waveguide Lasers. Photonics 2023, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocco, D.; Lopez-Quintas, I.; de Aldana, J.R.V.; Tonelli, M.; Tredicucci, A. Thermal analysis of diode–pumped femtosecond–laser–written Pr:LiLuF4 waveguide lasers. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 180, 111499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Calmano, T.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Baek, I.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Yeom, D.-I.; Kränkel, C.; Rotermund, F. Monolayer graphene coated Yb:YAG channel waveguides for Q–switched laser operation. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponarina, M.V.; Okhrimchuk, A.G.; Rybin, M.G.; Smayev, M.P.; Obraztsova, E.D.; Smirnov, A.V.; Zhluktova, I.V.; Kamynin, V.A.; Dolmatov, T.V.; Bukin, V.V.; et al. Dual–wavelength generation of picosecond pulses with 9.8 GHz repetition rate in Nd:YAG waveguide laser with graphene. Quantum Electron. 2019, 49, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, X.; Guo, R.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, J. MHz repetition rate femtosecond radially polarized vortex laser direct writing Yb:CaF2 waveguide laser operating in continuous–wave and pulse regimes. Nanophotonics 2024, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.E.; Mateos, X.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Romero, C.; Lee, H.; Rotermund, F. Transition of pulse operation from Q–switching to continuous–wave mode–locking in a Yb:KLuW waveguide laser. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 18027–18034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, F. 6.5 GHz Q–switched mode–locked waveguide lasers based on two–dimensional materials as saturable absorbers. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 11321–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ams, M.; Dekker, P.; Gross, S.; Withford, M.J. Fabricating waveguide Bragg gratings (WBGs) in bulk materials using ultrashort laser pulses. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 743–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Jia, Y.; Chen, F. 1.8–μm laser operation based on femtosecond–laser direct written Tm:YVO4 cladding waveguides. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 16560–16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, F. Compact solid–state waveguide lasers operating in the pulse regime: A review [Invited]. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2019, 17, 012302. [Google Scholar]


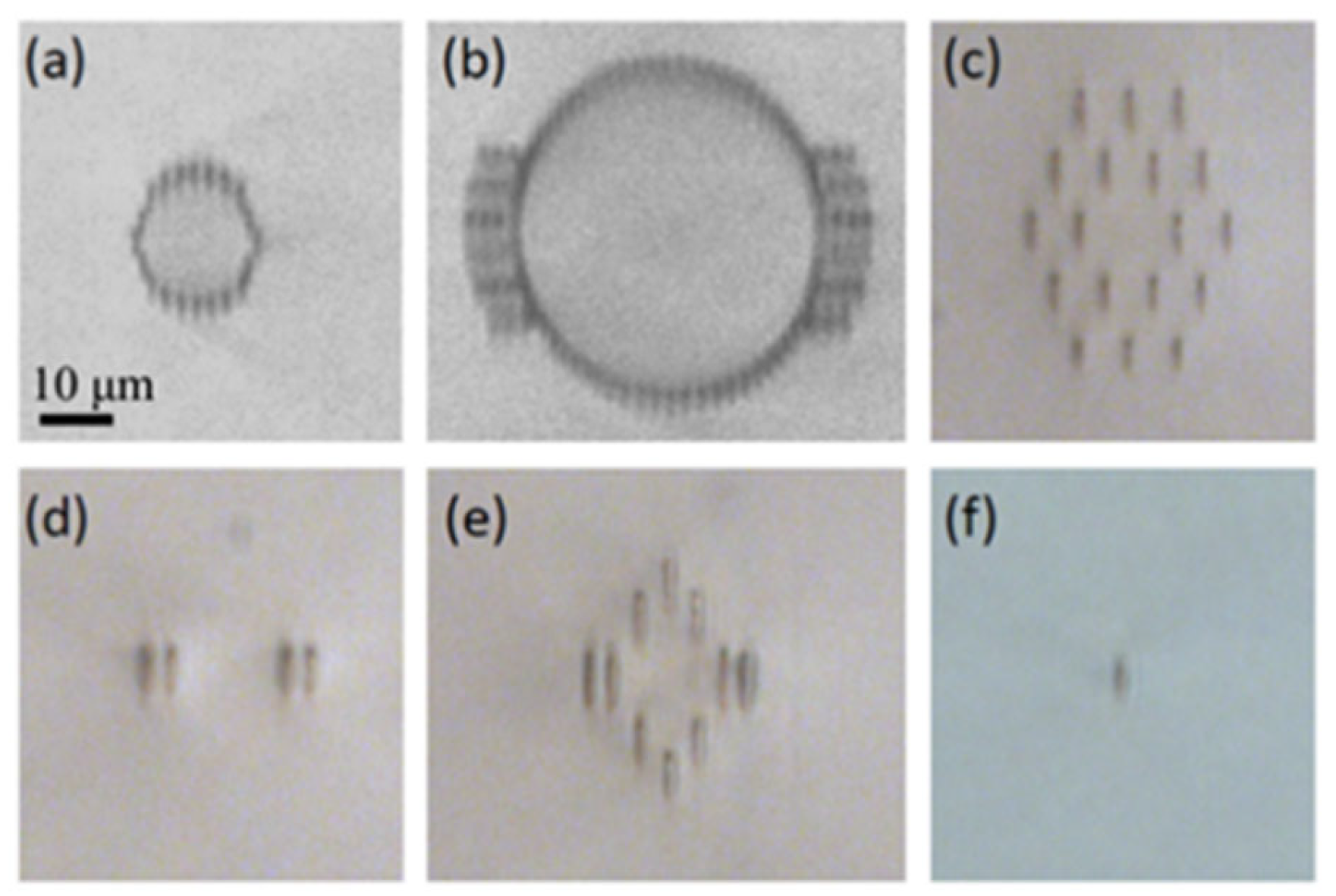


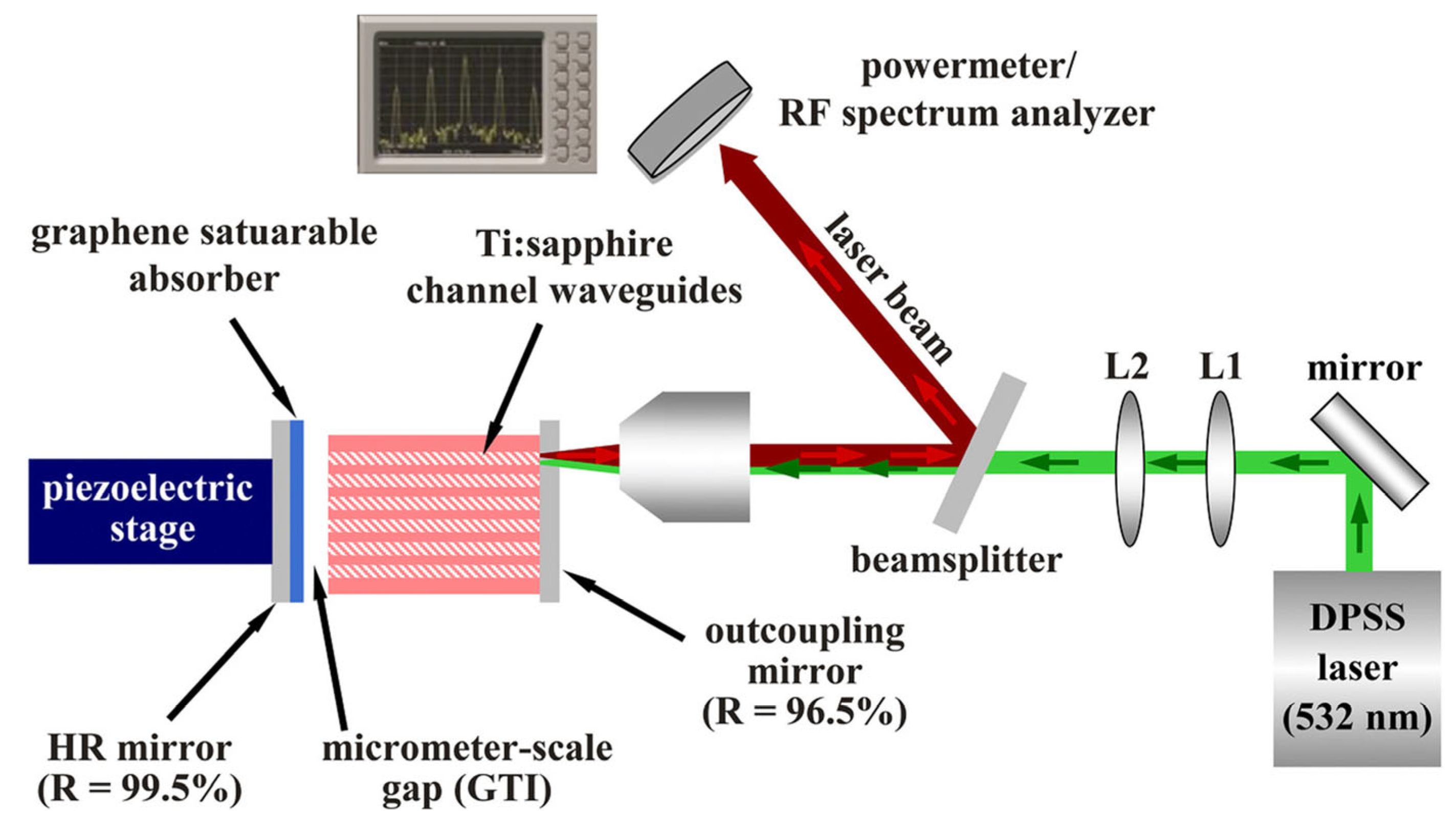
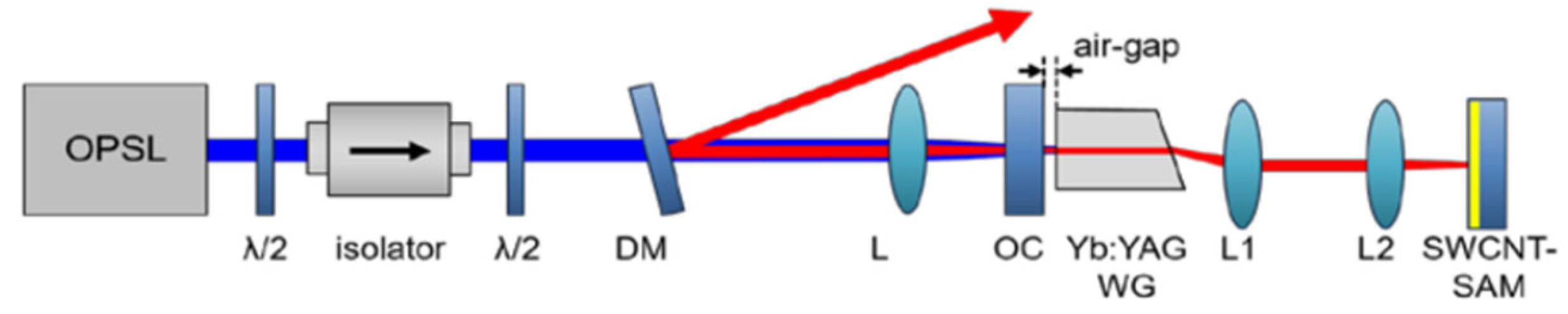
| Gain media | Working Wavelength (nm) | Cavity Configuration | Lasing Threshold (mW) | Maximum Output Power (mW) | Slope Efficiency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr,Mg:SrAl12O19 | 525.3 | dual–line | 1088 | 36 | – | [23] |
| Pr:LiLuF4 | 604 | ear–like cadding | – | 278 | 40 | [37] |
| Pr:SrAl12O19 | 643.9 | dual–line | 190 | 28.1 | 8 | [38] |
| Ti:sapphire | 798.5 | dual–line | 84 | 143 | 23.5 | [39] |
| Yb:YAG | 1030 | cadding | 43 | 410 | 15.2 | [40] |
| dual–line | – | 5.7 W | 78 | [41] | ||
| dual–line | – | 765 | 75 | [42] | ||
| double–cladding | – | 80.2 | 62.9 | [43] | ||
| Y–branch dual–line | 271 | 2.29 W | 52 | [28] | ||
| Nd:YAG | 1064 | Y–branch cladding | – | 231 | 22 | [29] |
| dual–line | 63 | 1.29 | 59 | [44] | ||
| 1 × 4 splitters | 90 | 217 | 22 | [45] | ||
| Nd:GGG | 1061 | dual–line | 29 | 11 | 25 | [46] |
| 1063 | cladding | 270 | 209 | 44.4 | [47] | |
| Nd:GdVO4 | 1063.6 | dual–line | – | 256 | 70 | [48] |
| Nd:YVO4 | 1064 | cladding | – | 1.5 | 28 | [49] |
| 1065 | cladding | 59 | 443 | 57 | [30] | |
| Nd:LuVO4 | 1066.4 | dual–line | 98 | 30 | 14 | [50] |
| Nd:KGW | 1065 | dual–line | 141 | 33 | 52.3 | [51] |
| 1067 | cladding | 140 | 198.5 | 39.4 | [52] | |
| Nd:YAP | 1064 and 1079 | cladding | 243 | 199.8 | 33.4 | [53] |
| Er–Yb co–doped phosphate glass | 1533.5 | Type–I | 335 | 1.7 | 2 | [36] |
| Tm:Klu(WO4)2 | 1912 | cladding | 21 | 46 | 15.2 | [54] |
| Tm,Ho:YLF | 2050 | cladding | 181 | 47.5 | 20.1 | [55] |
| Ho:YLF | 1877 | cladding | 107.1 | – | 19 | [56] |
| Cr:ZnS | 2244 | spiral cladding | 29.17 | 78 | 8.6 | [31] |
| Er:YliF4 | 2808 | cladding | – | 66 | 19.6 | [57] |
| Material | Working Wavelength (nm) | SA | Cavity Configuration | Operation Regime | Repetition Rate | Pulse Duration | Slope Efficiency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti:sapphire | 798.5 | graphene | Dual line | CWML | 21.25 GHz | 41.4 fs | – | [26] |
| Yb:YAG | 1030 | SWCNT–SAM | Dual line | CWML | 2.08 GHz | 1.89 ps | 11.3 | [40] |
| SESAM | Dual line | Q–switched | 5.4 MHz | 11 ns | 74 | [41] | ||
| Yb:KLuW | 1040 | SWCNTs | Surface cladding | Q–switched | 1.16 MHz | 88.5 ns | 61 | [33] |
| Yb:KLuW | 1042.3 | SWCNTs | Cladding | CWML | 0.5 GHz | 2.05 ps | 30.8 | [63] |
| Yb:CaF2 | 1045.2 | ReS0.2Se1.2 | Cladding | Q–switched | 125~692.5 kHz | 513 ns | 9.4 | [62] |
| Nd:YVO4 | 1064 | Bi2Se3 | Cladding | QSML | 6.436 GHz | 52 ps | 46 | [64] |
| MoS2 | 6.48 GHz | 43 ps | 56 | |||||
| Bi2Se3 | 6.556 GHz | 26 ps | 33 | |||||
| Nd:LGGG | 1061 and 1063 | – | Cladding | SQSML | 8.03 GHz | 30 ps | 25.38 | [27] |
| Nd:YAG | 1061 and 1064 | graphene | Cladding | CWML | 9.8 GHz | 102 ps | – | [61] |
| Nd:YAP | 1079 and 1064 | MoS2 | S–curved cladding waveguide | QSML | 7.9 GHz | 64 ps | 14.10 | [25] |
| 31.68 GHz | 16 ps | 14.1 | ||||||
| Er:YLiF4 | 2717 | – | Cladding | SQS | 368 kHz | 240 ns | 15.2 | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, X.; Wang, J. Developments of Waveguide Lasers by Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology. Photonics 2024, 11, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11090803
Zhang Y, Yu B, Zhang Z, Duan X, Wang J. Developments of Waveguide Lasers by Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology. Photonics. 2024; 11(9):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11090803
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Boyan Yu, Zihao Zhang, Xinghao Duan, and Junli Wang. 2024. "Developments of Waveguide Lasers by Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology" Photonics 11, no. 9: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11090803
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yu, B., Zhang, Z., Duan, X., & Wang, J. (2024). Developments of Waveguide Lasers by Femtosecond Laser Direct–Writing Technology. Photonics, 11(9), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11090803






