Research on Sugar Concentration Sensing Based on Real-Time Polarization and Interaction Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
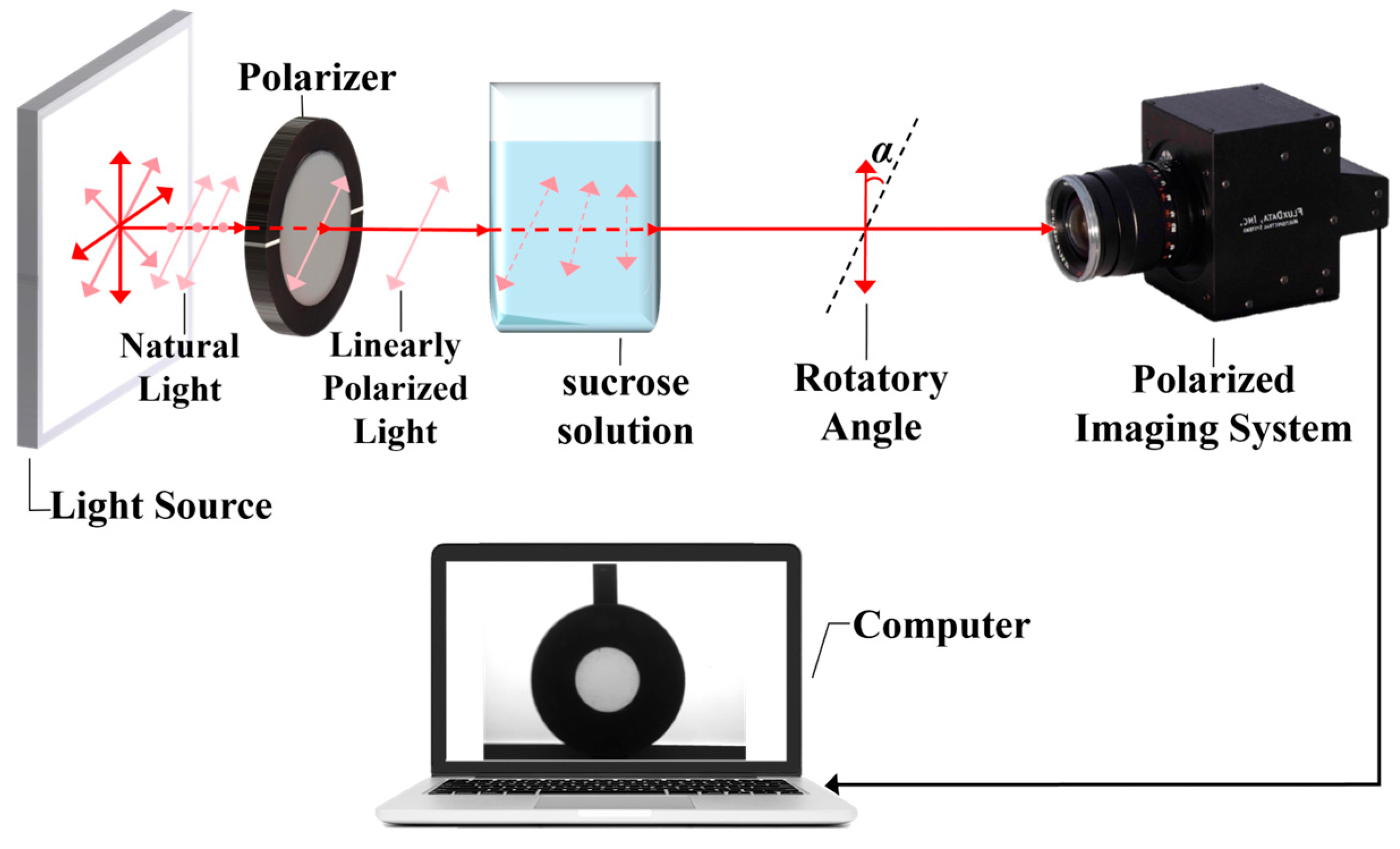
2.1. Simultaneous Division-of-Amplitude Polarization Imaging System
2.2. Experimental Principle
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Experimental Setup
2.5. Experimental Methods
2.6. Modeling
3. Results and Discussions
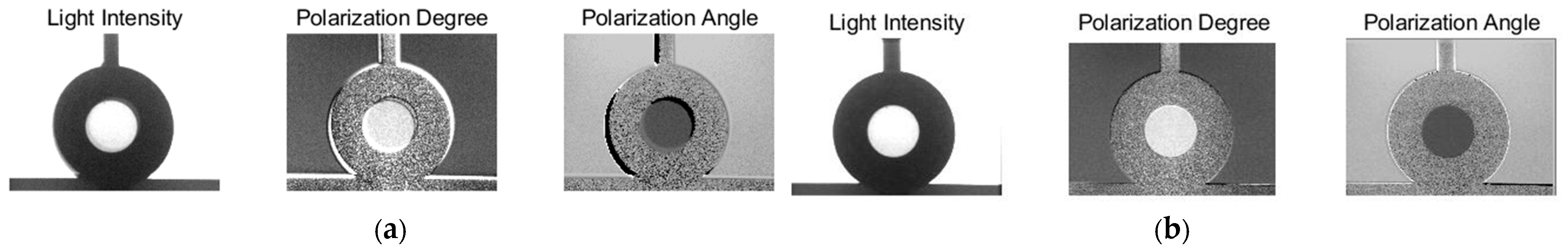
3.1. Image Alignment
3.2. Value Calculation
3.3. Linear Fitting
3.4. Interaction Linear Effect Regression Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.-R.; Mo, F.-Z.; Niu, X.-W.; Min, T. Accurate sugar concentration measurements based on optical inspection technology. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2006, 46, 477–479,487. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Fan, S.; Huang, W. Optimization of online detection model for whole apple sugar concentration using full transmission near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 6, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtczak, M.; Antczak, A.; Lisik, K. Starch concentration in various types of cane sugars as a criterion of quality and authenticity. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozana, N.; Arbel, N.; Beiderman, Y.; Mico, V.; Sanz, M.; Garcia, J.; Anand, A.; Javidi, B.; Epstein, Y.; Zalevsky, Z. Improved noncontact optical sensor for detection of glucose concentration and indication of dehydration level. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 1926–1940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emily, E.V.; Jaimie, N.D.; Michael, I.G. Sugar Concentration of Popular Sweetened Beverages Based on Objective Laboratory Analysis: Focus on Fructose Concentration. Obesity 2011, 19, 868–874. [Google Scholar]
- Jindahra, P.; Phumpradab, P. Label copresence for healthier choices: How sugar concentration per daily limit and sugar warning labels balance out the health halos of nutrient-concentration claim. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 107, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasiunas, B.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric sensing strategy for the determination of reducing sugars. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.-H.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wang, C.; Zheng, G. The measurement of the concentration of glucose solution by using optical low coherence interferometry. Opt. Tech. 2018, 44, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Aksorn, J.; Teepoo, S. Development of the simultaneous colorimetric enzymatic detection of sucrose, fructose and glucose using a microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Talanta 2020, 207, 120302. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, S.J.; Bialkowski, K.S. Dielectric spectroscopy based determination of sugar concentration in solution. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaulaniya, A.S.; Balan, B.; Yadav, A.; Jamwal, R.; Kelly, S.; Cannavan, A.; Singh, D.K. Development of an FTIR based chemometric model for the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of cane sugar as an added sugar adulterant in apple fruit juices. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 539–551. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-L.; Lo, Y.-L.; Liao, C.-C.; Phan, Q.-H. Noninvasive measurement of glucose concentration on human fingertip by optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, P.; Hernandez, C. High-accuracy universal polarimeter measurement of optical activity and birefringence of α-quartz in the presence of multiple reflections. JOSA B 1998, 15, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, R.N.; Mahurin, S.M.; Zare, R.N. Demonstration of Optical Rotatory Dispersion of Sucrose. J. Chem. Educ. 1999, 76, 1234. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.-F.; Qiu, Q.; Guo, Y. Dual modulation optical polarimetry for glucose monitoring. Acta Opt. Sin. 2016, 36, 0117001. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Peng, Y.-F.; Han, X.-Y. Research on glucose concentration sensing based on Faraday rotation effect. J. Optoelectron.·Laser 2021, 32, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Sun, X.; Hao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J. Principle and implementation of stokes vector polarization imaging technology. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Wang, Z.-B.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, S. Highly efficient measurement technology based on hyper-spectropolarimetric imaging. Chin. J. Lasers 2016, 43, 107–128. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, D.; Goldstein, D.H. Stokes Polarization Parameters: 5.3 Stokes Vector. In Polarized Light, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Chapter 5; pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Li, S.; Wang, X.-Q.; Wang, F.-Y. Research on camouflage target recognition method based on polarization fusion. Laser J. 2020, 10, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.-Y.; Liang, J.; Qu, E.-S.; Zhang, W.-F.; Du, B.-J.; Ma, F.-Y.; Guo, S.-B.; Zhang, J. Polarimetric optical imaging: Devices, technologies, and applications (Invited). Acta Photonica Sin. 2022, 51, 0851505. [Google Scholar]
- Paternina-Arboleda, C.D.; Agudelo-Castañeda, D.; Voß, S.; Das, S. Towards cleaner ports: Predictive modeling of sulfur dioxide shipping emissions in maritime facilities using machine learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, K.D.; Vaithiyanathan, V. Image registration techniques based on the scale invariant feature transform. IETE Tech. Rev. 2017, 34, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mize, T.D. Best practices for estimating, interpreting, and presenting nonlinear interaction effects. Sociol. Sci. 2019, 6, 81–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Deng, Y.-J. Spatiotemporal pattern evolution and driving factors of brucellosis in China, 2003–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

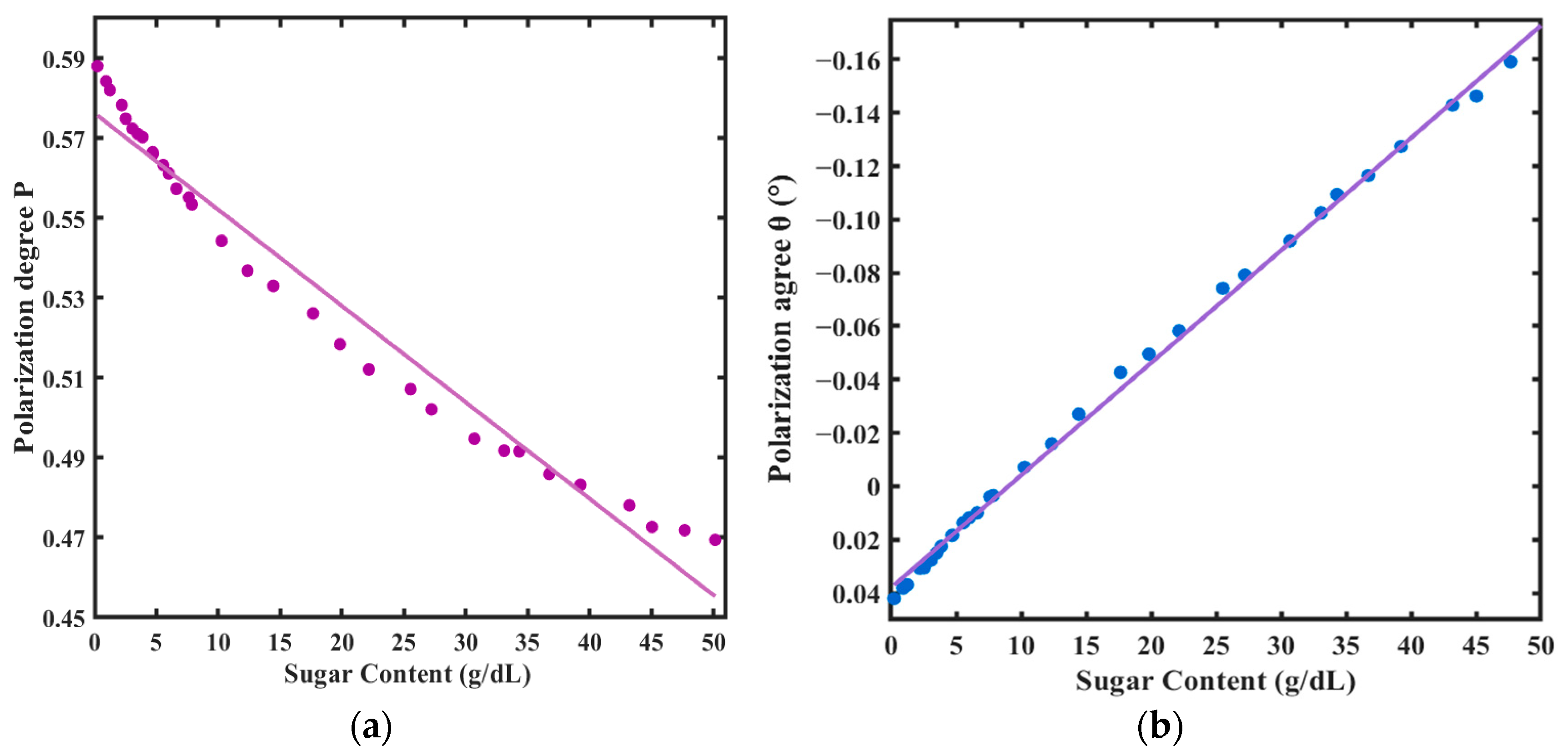

| Variable | Regression Equation | Uncertainty SE () | R2 | Covariance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polarization Degree P | −0.0024 ± 0.0002 | 0.9677 | −0.6277 | |
| 0.5762 ± 0.0019 | ||||
| Polarization Angle θ (°) | 0.0042 ± 0.0001 | 0.9980 | −1.0880 | |
| 0.0380 ± 0.0008 |
| Indicator Parameters | Validation | Test | Error Metrics (<±5%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (g/dL) | 0.37982 | 0.36934 | −3% |
| MSE (g/dL)2 | 0.14431 | 0.14095 | −2% |
| R2 | 0.99826 | 0.98331 | −2% |
| MAE (g/dL) | 0.27724 | 0.27523 | −1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Q.; Lyu, T.; Ye, S.; Wang, X. Research on Sugar Concentration Sensing Based on Real-Time Polarization and Interaction Effects. Photonics 2025, 12, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040308
Gong Q, Lyu T, Ye S, Wang X. Research on Sugar Concentration Sensing Based on Real-Time Polarization and Interaction Effects. Photonics. 2025; 12(4):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040308
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Qiong, Tongxiao Lyu, Song Ye, and Xinqiang Wang. 2025. "Research on Sugar Concentration Sensing Based on Real-Time Polarization and Interaction Effects" Photonics 12, no. 4: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040308
APA StyleGong, Q., Lyu, T., Ye, S., & Wang, X. (2025). Research on Sugar Concentration Sensing Based on Real-Time Polarization and Interaction Effects. Photonics, 12(4), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040308




