Photoacoustic Imaging in Visualization of Acupuncture Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
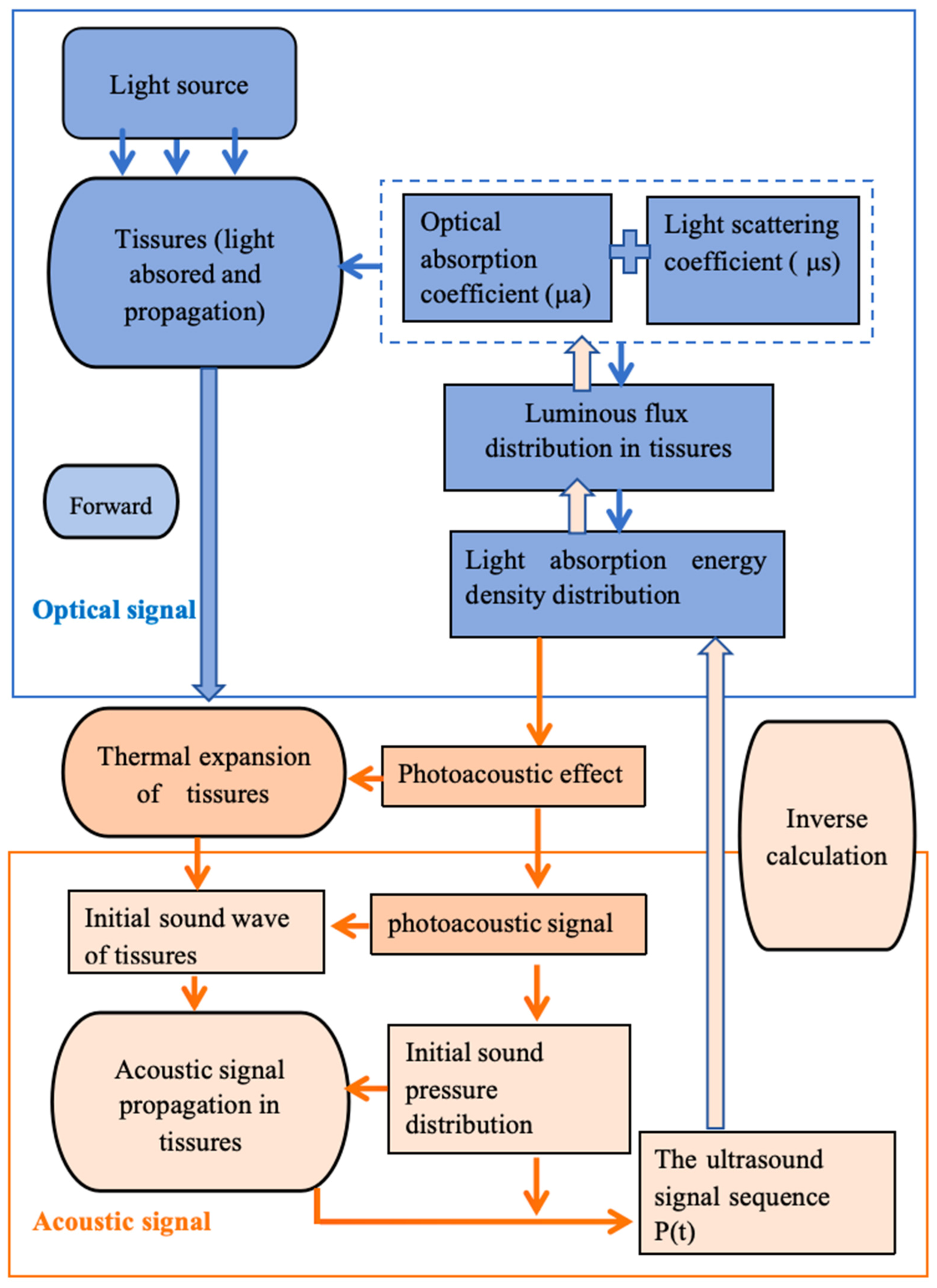
2. Photoacoustic Imaging (PAI)
- Stress confinement condition: This condition mandates that the laser pulse duration (τp) be shorter than the acoustic transit time across the irradiated volume:where d denotes the characteristic dimension of the irradiated region (m), and Vs represents the speed of sound in the medium (m·s−1). Stress confinement ensures localized energy deposition by restricting acoustic wave propagation beyond the thermal source region, thereby enabling efficient thermoelastic pressure generation.τp < d/Vs
- Thermal confinement condition: This requires the laser pulse duration to be shorter than the thermal relaxation time (τth):where αth is the thermal diffusivity (m2·s−1), and corresponds to the thermal diffusion length, empirically approximated as dth ≈ 1 μm in biological tissues. Compliance with this criterion minimizes thermal conduction losses (<5% energy dissipation) during irradiation, preserving spatial resolution.τth < dth2/αth
3. PAI in Acupuncture
3.1. Central Nervous System Modulation via Acupuncture
3.2. Local Effects of Acupoints—Microcirculation Sensitization
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAI | Photoacoustic imaging |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| NEI | Neuro-endocrine-immunity |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PA | Photoacoustic effect |
| HB | Hemoglobin |
| PAT | Photoacoustic tomography |
| PAM | Photoacoustic microscopy |
| PAE | Photoacoustic endoscopy |
| EA | Electronic acupuncture |
| ST36 | Zusanli |
| CBV | Cerebral blood volume |
| BL23 | Shenyu |
| KN12 | Zhongwan |
| GB30 | Huantiao |
| Sp6 | Sanyinjiao |
| HbT | Hemoglobin |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| KOA | Knee osteoarthritis |
| GB34 | Yanglingquan |
| CCM | Curvature count metric |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CV12 | Zhongwan |
References
- Ondrejkovicova, A.; Petrovics, G.; Svitkova, K.; Bajtekova, B.; Bangha, O. Why acupuncture in pain treatment? Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2016, 37, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Acupuncture theory in Huangdi Neijing and launching the natural history of the body. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2024, 44, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. The effect of acupuncture in the acute phase of intracerebral hemorrhage on prognosis and serum BDNF: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1167620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Minakawa, Y.; Kitakoji, H. The effect of acupuncture depth on muscle pain. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Efficacy and safety evaluation of acupuncture therapy for patients with salpingitis undergoing IVF-ET: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Wei, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhou, J. Acupuncture for adult lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-reported outcomes. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 921151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. Application of Photoacoustic Imaging Technology in Acupuncture Therapy. Master’s Thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, Y. Progress in the application of medical imaging in the study of acupuncture mechanisms. Mod. Med. Health 2016, 32, 2359–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Nie, L. Progress in the application of optical imaging technology in the study of acupuncture in Chinese medicine. China Laser 2023, 50, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, K.; Jing, M.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Yin, S.; Lan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Gao, F.; et al. The status of quality control in acupuncture-neuroimaging studies. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 3685785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, M.; Fan, L.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. Optimized acupuncture treatment (acupuncture and intradermal needling) for cervical spondylosis-related neck pain: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Pain 2021, 162, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Thomas, S. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. BMJ 2006, 332, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.S.; Zang, Z.W.; Wu, J.N.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z. Efficacy of acupuncture for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndromes: Study protocol for a randomized. 2016, sham acupuncture-controlled trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, T.; Shen, W.; Huang, F.Y.; Liu, C.R. Effect of Fu’s subcutaneous needling on thickness and elasticity of affected muscles in shoulder neck pain based on ultrasonic elastography. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2020, 40, 939–941. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D. Optoacoustic Imaging of Brain Function and Acupuncture Brain Mapping. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.Y.; Han, S.; Huang, Q.; He, S.Q.; Ford, N.C.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Dong, X.; Guan, Y. Calcium imaging in population of dorsal root ganglion neurons unravels novel mechanisms of visceral pain sensitization and referred somatic hypersensitivity. Pain 2021, 162, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhang, S.S.; Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Gan, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Lin, Y.; et al. Electroacupuncture of the trigeminal nerve causes N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors to mediate blood-brain barrier opening and induces neuronal excitatory changes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1020644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, W.; Xu, W.J.; Xu, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Cui, X.; Zhu, B.; Gao, X.Y. Perspective of calcium imaging technology applied to acupuncture research. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 30, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Tang, Y.S.; Li, Y.J.; Gao, K.; Shi, X.; Li, Z. Behavioral changes, and hippocampus glucose metabolism in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via electro-acupuncture at governor vessel acupoints. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.D.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, E.J. Electroacupuncture attenuates cognition impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Lin, Y.S.; Tan, Y.H.; Shen, X.; Liao, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, N.; Han, F.; Xu, N.; Tang, C.; et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cerebrovascular impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mice via melatonin signaling. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yao, S.Q.; Wu, C.X.; Yao, L.; Huang, P.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Xu, N. Electroacupuncture involved in motor cortex and hypoglossal neural control to improve voluntary swallowing of poststroke dysphagia mice. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 8857543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; Yang, J.G.; Wu, D.; Zeng, D.W.; Yi, Y.; Yang, N.; Jiang, H.B. Photoacoustic imaging of cerebral hypoperfusion during acupuncture. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.G.; Wu, D.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, H. Photoacoustic microscopy of electronic acupuncture (EA) effect in small animals. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jia, J.; Yan, X. Efficacy of needling Baihui (GV20), Neiguan (PC6), Shenmen (HT7) and Taichong (LR3) on cerebral cortical blood oxygen level in rats with insomnia. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 43, 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, B. Evaluation of the recovery outcome of poststroke cognitive impairment after cluster needling of scalp acupuncture therapy based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.X.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, B.B.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S.; Tao, J. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging analysis of brain functional activity in rats with ischemic stroke treated by electro-acupuncture. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Fan, X.W.; Chen, K.Y.; Yu, X.; Gao, J. Effects of three kinds of head acupuncture therapies on regulation of brain microenvironment and rehabilitation of nerve function in rats with cerebral palsy. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.Y.; Chen, K.; Cheng, T.; Lai, P.T.; Zhang, L.; So, K.F.; Yang, E.S. In vivo neuronal and astrocytic activation in somatosensory cortex by acupuncture stimuli. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2526–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Leow, M.Q.; Lee, S.H.; Mohamed-Shah, M.T.; Cao, T.; Cui, S.L.; Tay, S.C.; Ooi, C.C. Exploring the physiological and physical effects of acupuncture using ultrasound. Acupunct. Med. 2016, 35, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Tao, X.X.; Wang, M.; Yu, C.; Liu, S.R.; Li, M.; Tian, X.; Qi, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Multimodal photoacoustic/ultrasonic imaging system: A promising imaging method for the evaluation of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3542–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, I.; Huland, D.M.; Vermesh, O.; Frostig, H.E.; Tummers, W.S.; Gambhir, S.S. Photoacoustic clinical imaging. Photoacoustics 2019, 14, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, H.H.; Liu, H.; Shou, K.Q.; Zheng, X.; Fan, Q.L.; Yu, A.; Hu, X. Quantitative photoacoustic imaging for early detection of muscle ischemia injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.G.; Zhang, G.; Chang, W.; Chi, Z.H.; Shang, Q.Q.; Wu, M.; Pan, T.; Huang, L.; Jiang, H. Photoacoustic imaging of hemodynamic changes in forearm skeletal muscle during cuff occlusion. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 4560–4570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liba, O.; de la Zerda, A. Photoacoustic tomography: Breathtaking whole-body imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0075. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbaran, S.M.; Aghamiry, H.S.; Gholami, A.; Operto, S.; Avanaki, K. Quantitative photoacoustic tomography using iteratively refined wavefield reconstruction inversion: A simulation study. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 43, 874–885. [Google Scholar]
- Tarvainen, T.; Cox, B. Quantitative photoacoustic tomography: Modeling and inverse problems. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29 (Suppl. 1), S11509. [Google Scholar]
- Pattyn, A.; Mumm, Z.; Alijabbari, N.; Duric, N.; Anastasio, M.A.; Mehrmohammadi, M. Model-based optical and acoustical compensation for photoacoustic tomography of heterogeneous media. Photoacoustics 2021, 23, 100275. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, C. High-resolution functional photoacoustic monitoring of vascular dynamics in human fingers. Photoacoustics 2021, 23, 100282. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, M.; An, L.; Beard, P.; Cox, B. Sulfates as chromophores for multiwavelength photoacoustic imaging phantoms. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 125007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Wu, D.; Jiang, H. Photoacoustic imaging and Chinese medicine research. World Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: In vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Kneipp, M.; Turner, J.; Hambauer, S.; Krieg, S.M.; Lehmberg, J.; Lindauer, U.; Razansky, D. Functional real-time optoacoustic imaging of middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean-Ben, X.L.; Sela, G.; Lauri, A.; Kneipp, M.; Ntziachristos, V.; Westmeyer, G.G.; Shoham, S.; Razansky, D. Functional optoacoustic neuro-tomography for scalable whole-brain monitoring of calcium indicators. Light Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, 16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, H.; Huang, X.; Rebling, J.; Zwack, M.; Gottschalk, S.; Razansky, D. Virtual craniotomy for high-resolution optoacoustic brain microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heywang-Kobrunner, S.H.; Hacker, A. Advantages and disadvantages of mammography screening. Breast Care 2011, 6, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hu, P.; Shi, J.; Appleton, C.M.; Maslov, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.V. Single-breath-hold photoacoustic computed tomography of the breast. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijblom, M.; Piras, D.; van den Engh, F.M.; van der Schaaf, M.; Klaase, J.M.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. The state of the art in breast imaging using the Twente Photoacoustic Mammoscope: Results from 31 measurements on malignancies. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3874–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toi, M.; Asao, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sekiguchi, H.; Yoshikawa, A.; Takada, M.; Kataoka, M.; Endo, T.; Kawaguchi-Sakita, N.; Kawashima, M.; et al. Visualization of tumor-related blood vessels in the human breast using a photoacoustic imaging system with a hemispherical detector array. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.B.E.; Balasundaram, G.; Moothanchery, M.; Dinish, U.S.; Bi, R.; Ntziachristos, V.; Olivo, M. A review of clinical photoacoustic imaging: Current and future trends. Photoacoustics 2019, 16, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Zhou, G.; Qian, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H. Molecular photoacoustic tomography of breast cancer using receptor-targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Li, X.; Yao, L.; Grobmyer, S.; Jiang, H. Design and evaluation of a hybrid photoacoustic tomography and diffuse optical tomography system for breast cancer detection. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2584–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Heldermon, C.D.; Yao, L.; Xi, L.; Jiang, H. High-resolution functional photoacoustic tomography of breast cancer. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 5321–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Tian, C.; Xu, G.; Sarazin, J.; Schiopu, E.; Gandikota, G.; Wang, X. Photoacoustic tomography for human musculoskeletal imaging and inflammatory arthritis detection. Photoacoustics 2018, 12, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, T.; Lu, T.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Gao, F.; Ntziachristos, V. Deep learning-based quantitative optoacoustic tomography of deeptissues in the absence of labeled experimental data. Optica 2022, 9, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, B.; Rong, J.; Jiang, H. Photoacoustic imaging of acupuncture effects in small animals. J. Biophotonics 2015, 6, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S. Experimental Study of Acupuncture at Different Acupoints Based on a Photoacoustic Tomography Imaging System. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, R. PAT In Vivo Study of Monitoring the Response of Different Acupuncture Methods on the Cerebral Cortex. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. Monitoring of Cerebral Cortex Response to Acupuncture Under Different Anaesthetic States. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Q. Photoacoustic Imaging Study of Organism Response to Needling. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Jiang, J.; Qin, P.; Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Prospects for the application of photoacoustic imaging in microcirculation sensitization imaging study of acupoints. Acupunct. Res. 2017, 42, 454–458. [Google Scholar]
- Mirg, S.; Turner, K.L.; Chen, H.; Drew, P.J.; Kothapalli, S.R. Photoacoustic imaging for microcirculation. Microcirculation 2022, 29, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.V. In vivo photoacoustic microscopy of human cuticle microvasculature with single-cell resolution. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Yang, L.; Jia, S.; Mu, X.; Wu, M.; Ye, H.; Liu, W.; Cheng, X. Capillary blood flow in patients with dysmenorrhea treated with acupuncture. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 757–760. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Photoacoustic Imaging Study of Acupoint Sensitization in a Mouse Model of Knee Osteoarthritis. Doctoral Dissertation, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C. Lack of association between acupoint sensitization and microcirculatory structural changes in a mouse model of knee osteoarthritis: A pilot study. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.H.; Liu, C.B.; Li, Z.G. Photoacoustic imaging study of microvascular spatial structure of relevant acupoints in mice with acute myocardial ischemia. Acupunct. Res. 2021, 46, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Visualization of microvascular dynamics in response to acupuncture intervention in a mouse model. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Wen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chi, Z.; Sun, M.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, H.B. Photoacoustic image guidance for acupuncture. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Harbin, China, 12–15 August 2022; Volume 1, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Li, J.; Ning, B.; Sun, N.; Wang, T.; Zuo, Z.; Hu, S. Functional and oxygen-metabolic photoacoustic microscopy of the awake mouse brain. NeuroImage 2017, 150, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirg, S.; Chen, H.; Turner, K.L.; Gheres, K.W.; Liu, J.; Gluckman, B.J.; Drew, P.J.; Kothapalli, S.R. Awake mouse brain photoacoustic and optical imaging through a transparent ultrasound cranial window. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, H.; Klippel, P.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H.S.; Jing, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yao, J. Deep thrombosis characterization using photoacoustic imaging with intravascular light delivery. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2022, 12, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic tomography of neural systems. In Neural Engineering; He, B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 349–378. [Google Scholar]
| Imaging Method | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Expensive | Portable | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable Areas | Application in Acupuncture Research |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Imaging | <1 μm | 10–100 ms | No | No | High resolution, large field of view, long-term monitoring | Shallow observation depth | Observing activity of neurons and glial cells | Acupoint–brain function relationship, acupuncture–neural circuit research [16,17,18] |
| PET | 4 mm | 30–60 s | Yes | No | High sensitivity | Low spatial resolution | Dynamic observation of physiological, chemical reactions, and metabolic processes | Acupoint specificity, acupoint–brain system research [19,20] |
| Laser Speckle | 2~3 μm | 10–100 ms | No | Yes | High image resolution, large monitoring area, non-invasive | Shallow imaging depth | Contrast imaging (LSCI)real-time monitoring of local tissue blood perfusion | Acupuncture–microcirculation research [21,22] |
| Photoacoustic Imaging | 50–500 μm | 1–100 ms | No | Yes | High resolution, high contrast, strong penetration | Requires coupling medium | Monitoring cerebral hemodynamics and blood oxygen levels | Acupuncture–brain effects research [23,24] |
| Near Infrared Spectroscopy (f-NIRS) | 10–30 mm | 0.1–10 Hz | No | Yes | Real-time measurement of hemodynamics, non-invasive | Accuracy slightly reduced when penetrating skull | Provides metabolic, physiological, molecular, and anatomical information | Acupoint–brain function relationship research [25,26] |
| fMRI | 2–3 mm | 1–3 s | Yes | No | Three-dimensional data acquisition, non-invasive | Long imaging time, slightly lower sensitivity | Cellular, tissue, and in vivo imaging | Acupoint–brain function relationship, acupoint–organ connection research [27,28] |
| Two-Photon In Vivo Imaging | <1 μm | 1–100 ms | No | Yes | High sensitivity, low light toxicity | Only fluorescent imaging, invasive | Used for vascular and neural diseases | Acupoint–brain microcirculation research [29] |
| US | 100–500 μm | 10–100 Hz | No | Yes | Non-invasive, high contrast, strong penetration. | Limited spatial resolution | Used for vascular and structures | Monitoring the effects of acupuncture on blood flow and soft tissue [30] |
| References | Time | Imaging System | Method | Acupuncture Effect on the Brain | Acupoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li Tingting et al. [56] | 2015 | PAT | Comparison of before acupuncture vs. after acupuncture | The blood flow in the mouse brain increased after acupuncture | Yongquan |
| Chen et al. [23] | 2015 | PAT | Comparison of before acupuncture vs. after in a mouse model of cerebral hypoperfusion | promoting the generation of new blood vessels and increasing the diameter of the blood vessels in the hypoperfusion area by acupuncture | Yanglingquan |
| Jinge Yang et al. [24] | 2016 | PAM | Comparison of real acupuncture vs. sham acupuncture | Remarkable cerebral blood volume (CBV) and hemoglobin concentration changes in sensorimotor and retro splenial agranular cortex by delayed effect and accumulated effect of acupuncture. | Zusanli (ST36) |
| Jiang Shuhua et al. [57] | 2016 | PAT | Comparison of acupuncture effects among different acupoints in different periods | Semi-quantitative analysis of acupoint-specific hemodynamic differentiation among different acupoints | Yongquan, Yanglingquan and Taichong |
| Cui Ruihuan et al. [58] | 2019 | PAT | Comparison of different acupuncture methods | Different changes in cerebral hemodynamics for different method | Yongquan |
| Guo Xiuyun [59] | 2019 | PAT | Comparison of different anesthetic states | Cerebral cortical response to acupuncture under different anesthetic states | Zusanli (ST36) |
| Wu, Dan [15] | 2019 | PAT | Comparison of multiple acupoints | (1) Built comprehensive mapping of acupuncture-induced cerebral hemodynamic responses (e.g., oxygen saturation, hemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentration); (2) Monitoring and evaluating the efficacy and mechanisms of acupuncture in stroke management | 17 acupoints |
| Shang Qiquan [60] | 2020 | PAT | Comparison of immediate and aftereffects of acupuncture | Eliciting a positive response from specific regions for different acupoints | Shenyu(BL23), Zhongjiao (KN12), Huanjiao (GB30), and Sanyinjiao (Sp6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Wu, D.; Wen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chi, Z.; Jiang, H. Photoacoustic Imaging in Visualization of Acupuncture Mechanisms. Photonics 2025, 12, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040365
Wu Y, Wu D, Wen Y, Yang Y, Zhang J, Chi Z, Jiang H. Photoacoustic Imaging in Visualization of Acupuncture Mechanisms. Photonics. 2025; 12(4):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040365
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yun, Dan Wu, Yanting Wen, Ying Yang, Jing Zhang, Zihui Chi, and Huabei Jiang. 2025. "Photoacoustic Imaging in Visualization of Acupuncture Mechanisms" Photonics 12, no. 4: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040365
APA StyleWu, Y., Wu, D., Wen, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Chi, Z., & Jiang, H. (2025). Photoacoustic Imaging in Visualization of Acupuncture Mechanisms. Photonics, 12(4), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040365





