Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
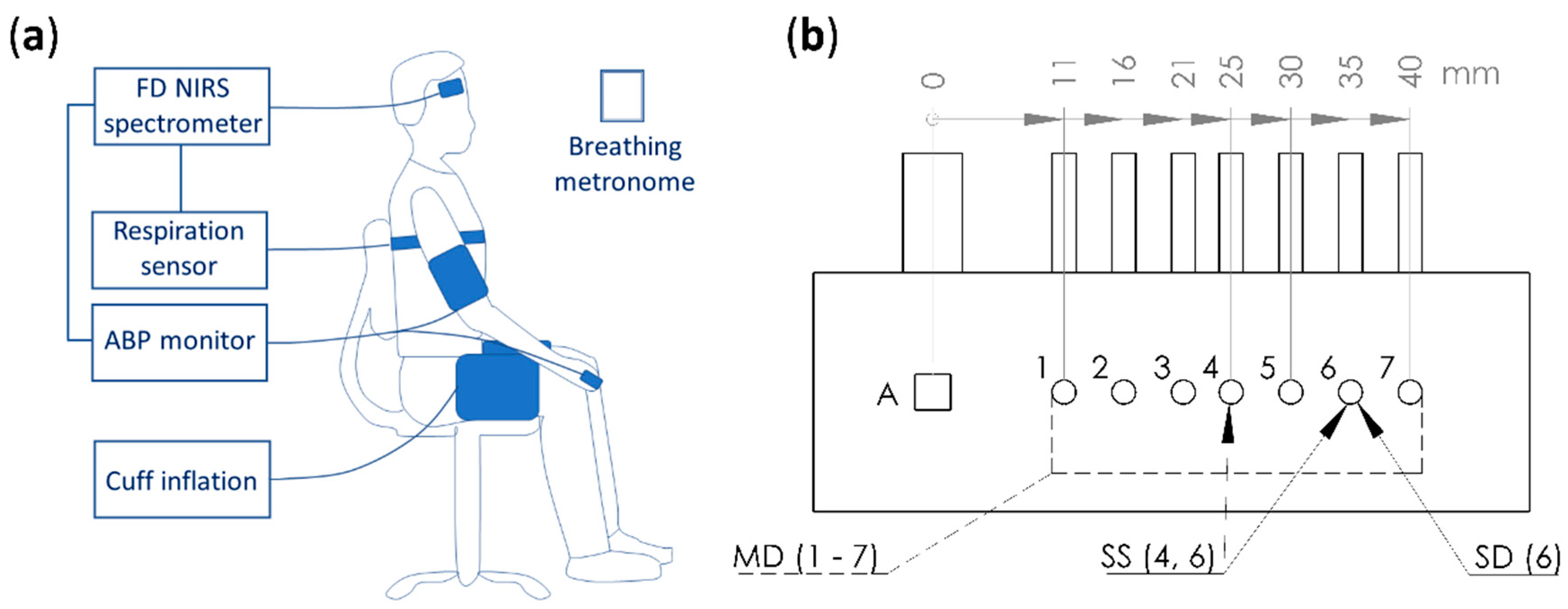
2.1. Human Subjects, Near-InfraRed Spectroscopy (NIRS) Instrument, and Measurement Protocol
2.2. Measurement of Tissue Optical Properties and Hemoglobin Concentrations
2.2.1. Absolute Measurements with Multi-Distance (MD) Intensity (I) and Phase (ϕ)
2.2.2. Relative Measurements with Single-Distance Intensity (SDI)
2.2.3. Relative Measurements with Single-Distance Phase (SDϕ)
2.2.4. Relative Measurements with Single-Slope Intensity (SSI)
2.3. Coherence and Phasor Analysis
2.4. Amplitude and Phase of Oscillatory Hemodynamics that are Coherent with Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP)
2.5. Diffusion Theory Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Absolute Optical Properties
3.2. Coherence between Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) and One of Oxyhemoglobin (ΔO), Deoxyhemoglobin (ΔD), and Total Hemoglobin (ΔT) Changes
3.3. Deoxyhemoglobin and Oxyhemoglobin Phasor Ratio (D/O) as a Function of Source-Detector Distance for Different Measurement Methods
- A top layer (10 mm thick) featuring arterial volume oscillations represented by D = 0.05∠20° µM and O = 0.95∠20° µM.
- An intermediate layer (at depths of 10–15 mm) featuring no hemodynamic oscillations.
- A bottom layer (at depths of 15–30 mm) featuring blood flow oscillations represented by D = 3∠180° µM and O = 3∠0° µM.
3.4. Deoxyhemoglobin and Oxyhemoglobin Phasor Ratio (D/O) Measured at Long Source-Detector Distances with Different Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fantini, S.; Frederick, B.; Sassaroli, A. Perspective: Prospects of non-invasive sensing of the human brain with diffuse optical imaging. APL Photonics 2018, 3, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, F.; Wiegel, P.; Scholkmann, F.; Müller, N. Applications of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) Neuroimaging in Exercise–Cognition Science: A Systematic, Methodology—Focused Review. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.B. Systematic review of near-infrared spectroscopy determined cerebral oxygenation during non-cardiac surgery. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Cour, A.; Greisen, G.; Hyttel-Sørensen, S. In vivo validation of cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy: A review. Neurophotonics 2018, 5, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Brown, E.N.; Strangman, G.E. Adaptive filtering for global interference cancellation and real-time recovery of evoked brain activity: A Monte Carlo simulation study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saager, R.; Berger, A. Measurement of layer-like hemodynamic trends in scalp and cortex: Implications for physiological baseline suppression in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 034017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, L.; Yücel, M.A.; Boas, D.A.; Cooper, R.J. Further improvement in reducing superficial contamination in NIRS using double short separation measurements. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funane, T.; Atsumori, H.; Katura, T.; Obata, A.N.; Sato, H.; Tanikawa, Y.; Okada, E.; Kiguchi, M. Quantitative evaluation of deep and shallow tissue layers contribution to fNIRS signal using multi-distance optodes and independent component analysis. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, M.A.; Fantini, S.; Paunescu, L.A.; Maier, J.S.; Gratton, E. Influence of a superficial layer in the quantitative spectroscopic study of strongly scattering media. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulgerakis-Kontoudis, M.; Eggebrecht, A.T.; Dehghani, H. Information rich phase content of frequency domain functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Neural Imaging and Sensing 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1 March 2019; Luo, Q., Ding, J., Fu, L., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, F.; Tachtsidis, I. Clinical Brain Monitoring with Time Domain NIRS: A Review and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, G.; Konishi, Y.; Maki, A.; Tachibana, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Koizumi, H. Spontaneous oscillation of oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin changes with a phase difference throughout the occipital cortex of newborn infants observed using non-invasive optical topography. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 282, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrig, H.; Neufang, M.; Wenzel, R.; Kohl, M.; Steinbrink, J.; Einhäupl, K.; Villringer, A. Spontaneous Low Frequency Oscillations of Cerebral Hemodynamics and Metabolism in Human Adults. Neuroimage 2000, 12, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Niu, H.; Khan, B.; Alexandrakis, G.; Behbehani, K.; Liu, H. Enhanced Functional Brain Imaging by Using Adaptive Filtering and a Depth Compensation Algorithm in Diffuse Optical Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierro, M.L.; Sassaroli, A.; Bergethon, P.R.; Ehrenberg, B.L.; Fantini, S. Phase-amplitude investigation of spontaneous low-frequency oscillations of cerebral hemodynamics with near-infrared spectroscopy: A sleep study in human subjects. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sassaroli, A.; Pierro, M.; Bergethon, P.R.; Fantini, S. Low-Frequency Spontaneous Oscillations of Cerebral Hemodynamics Investigated with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2012, 18, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Shitara, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tsuchida, S.; Takahashi, N.; Taga, G. Hemoglobin phase of oxygenation and deoxygenation in early brain development measured using fNIRS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1737–E1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinhard, M.; Wehrle-Wieland, E.; Grabiak, D.; Roth, M.; Guschlbauer, B.; Timmer, J.; Weiller, C.; Hetzel, A. Oscillatory cerebral hemodynamics—The macro- vs. microvascular level. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 250, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, G.R.; Graber, H.L.; Voelbel, G.T.; Kohl, A.D.; DeLuca, J.; Pei, Y.; Xu, Y.; Barbour, R.L. Using co-variations in the Hb signal to detect visual activation: A near infrared spectroscopic imaging study. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Kato, T. Vector-based phase classification of initial dips during word listening using near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroreport 2012, 23, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, S. Dynamic model for the tissue concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in relation to blood volume, flow velocity, and oxygen consumption: Implications for functional neuroimaging and coherent hemodynamics spectroscopy (CHS). Neuroimage 2014, 85, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierro, M.L.; Hallacoglu, B.; Sassaroli, A.; Kainerstorfer, J.M.; Fantini, S. Validation of a novel hemodynamic model for coherent hemodynamics spectroscopy (CHS) and functional brain studies with fNIRS and fMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassaroli, A.; Blaney, G.; Fantini, S. Dual-slope method for enhanced depth sensitivity in diffuse optical spectroscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2019. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham, T.; Fernandez, C.; Fantini, S. Enhanced sensitivity to brain tissue with dual-slope cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biophotonics 2019. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bigio, I.J.; Fantini, S. Quantitative Biomedical Optics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-521-87656-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fantini, S.; Franceschini, M.A.; Fishkin, J.B.; Barbieri, B.; Gratton, E. Quantitative determination of the absorption spectra of chromophores in strongly scattering media: A light-emitting-diode based technique. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantini, S.; Hueber, D.; Franceschini, M.A.; Gratton, E.; Rosenfeld, W.; Stubblefield, P.G.; Maulik, D.; Stankovic, M.R. Non-invasive optical monitoring of the newborn piglet brain using continuous-wave and frequency-domain spectroscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 1543–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Comment on the modified Beer–Lambert law for scattering media. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N255–N257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Algorithm for Determination of Thresholds of Significant Coherence in Time-Frequency Analysis. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2019. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Hallacoglu, B.; Sassaroli, A.; Guerrero-Berroa, E.; Schnaider Beeri, M.; Haroutunian, V.; Shaul, M.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Toren, A.; Fantini, S. Absolute measurement of cerebral optical coefficients, hemoglobin concentration and oxygen saturation in old and young adults with near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 081406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, G.P.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham, T.T.; Fantini, S. Comparison of spontaneous and induced coherent hemodynamics in the human brain. In Proceedings of the Optical Tomography and Spectroscopy of Tissue XIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1 March 2019; Fantini, S., Taroni, P., Tromberg, B.J., Sevick-Muraca, E.M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Khaksari, K.; Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Pham, T.; Fantini, S. Depth dependence of coherent hemodynamics in the human head. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Lu, H.; Ye, F.Q.; Stein, E.A.; Yang, Y. Noninvasive quantification of cerebral blood volume in humans during functional activation. Neuroimage 2006, 30, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Liu, P.; Kim, T.; Donahue, M.; Rane, S.; Chen, J.J.; Qin, Q.; Kim, S.-G. MRI techniques to measure arterial and venous cerebral blood volume. Neuroimage 2019, 187, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, S.N.; Streicher, M.N.; Trampel, R.; Turner, R. Cerebral Blood Volume Changes during Brain Activation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Subject | Gender | Age (Years) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (μM) | (μM) | (μM) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 25 | 0.098(6) | 0.106(6) | 9.0(5) | 7.5(4) | 22(3) | 18(2) | 40(3) | 55(4) |
| 2 | Female | 29 | 0.10(1) | 0.104(5) | 10.5(8) | 8.9(3) | 19(3) | 18(2) | 37(3) | 51(5) |
| 3 | Male | 29 | 0.11(1) | 0.125(8) | 10.0(4) | 8.0(1) | 28(3) | 18(2) | 46(4) | 60(4) |
| 4 | Female | 34 | 0.095(9) | 0.092(3) | 8.9(5) | 6.9(3) | 18(2) | 17(1) | 35(2) | 51(3) |
| 5 | Male | 53 | 0.12(1) | 0.13(1) | 10.7(6) | 8.6(5) | 31(4) | 20(3) | 51(6) | 61(2) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham, T.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Fantini, S. Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics. Photonics 2019, 6, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6030083
Blaney G, Sassaroli A, Pham T, Krishnamurthy N, Fantini S. Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics. Photonics. 2019; 6(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaney, Giles, Angelo Sassaroli, Thao Pham, Nishanth Krishnamurthy, and Sergio Fantini. 2019. "Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics" Photonics 6, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6030083
APA StyleBlaney, G., Sassaroli, A., Pham, T., Krishnamurthy, N., & Fantini, S. (2019). Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics. Photonics, 6(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6030083






