Reduction of Compton Background Noise for X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography with Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
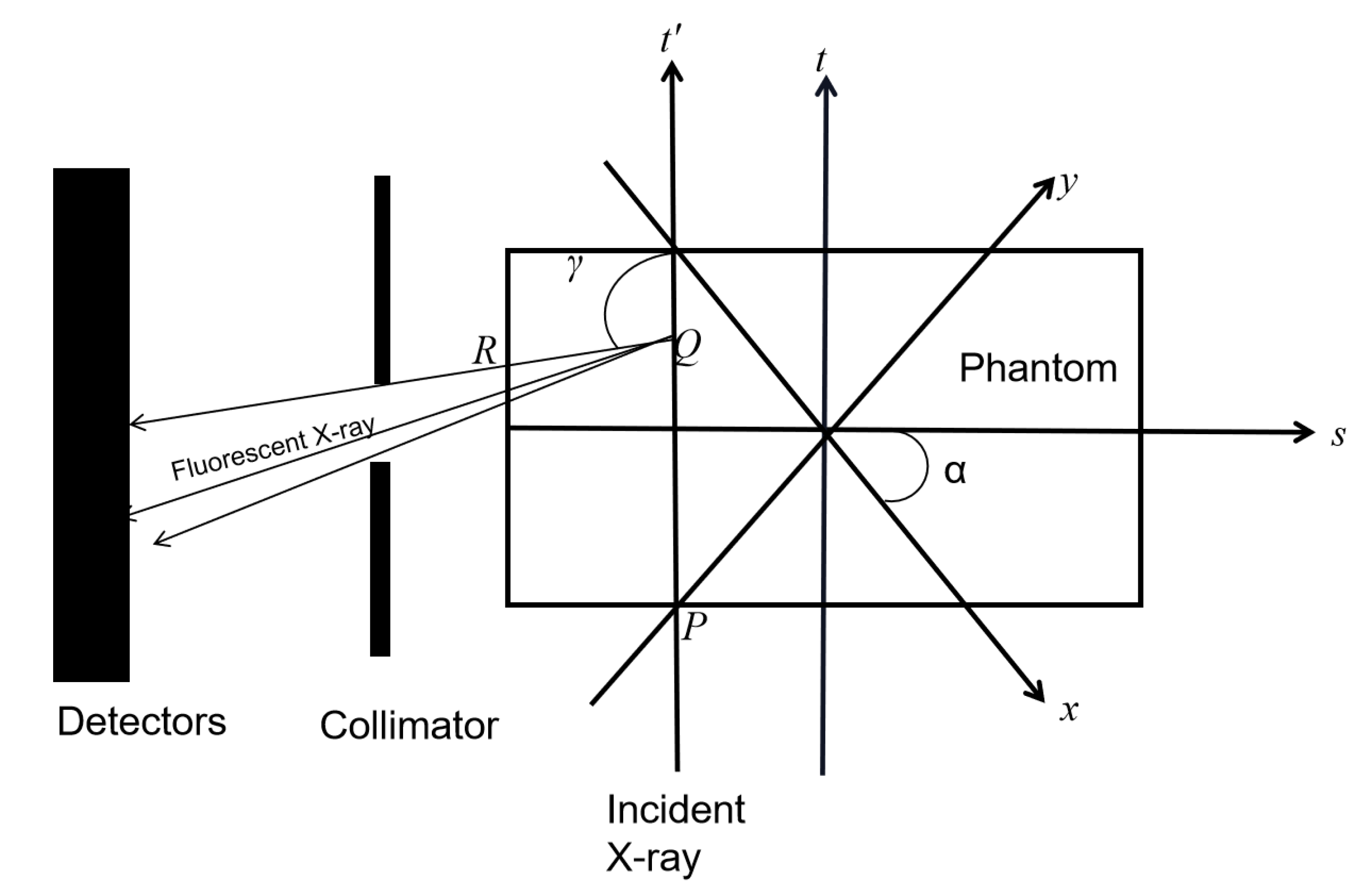
2.1. XFCT Theory
2.2. Noise2noise Model
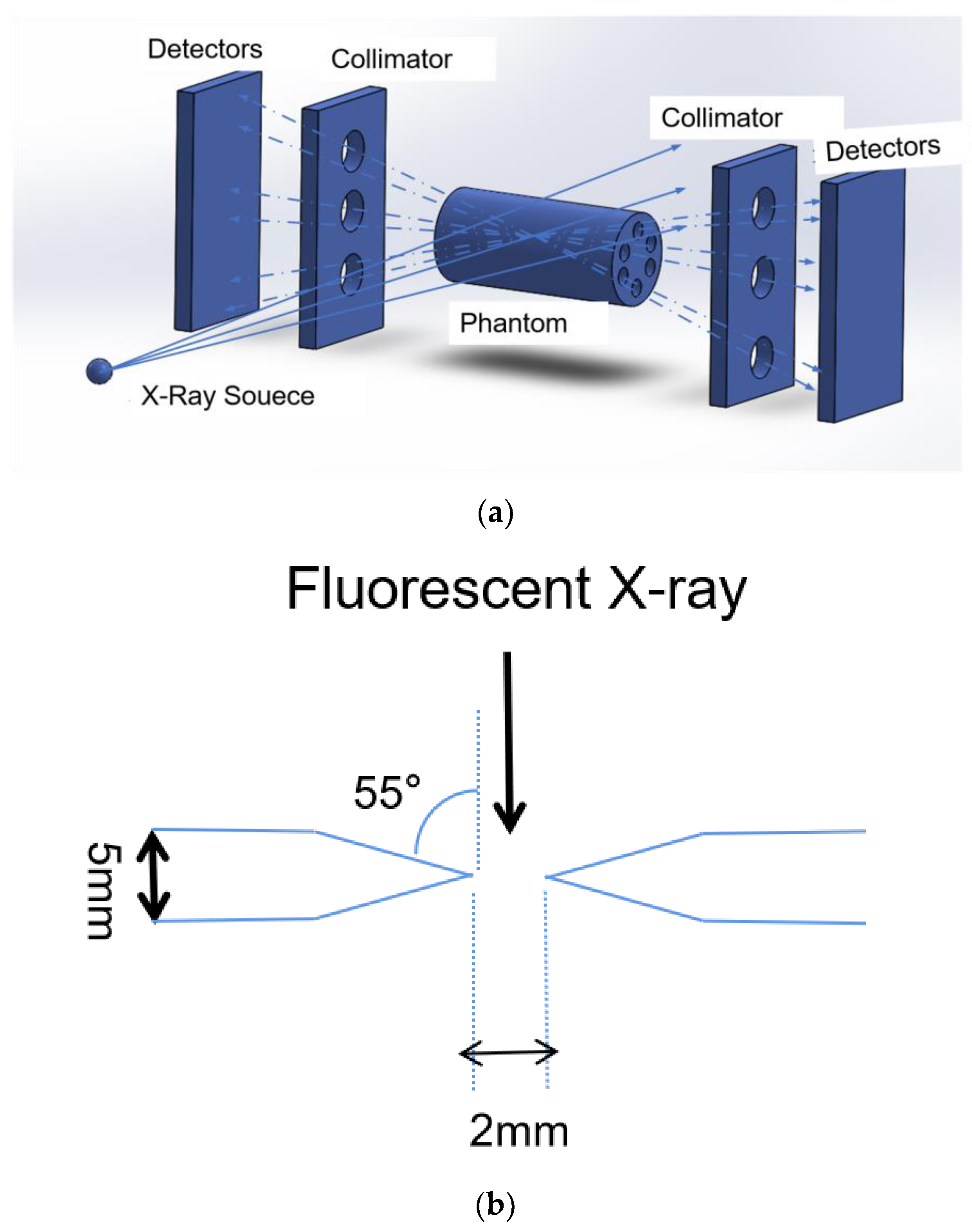
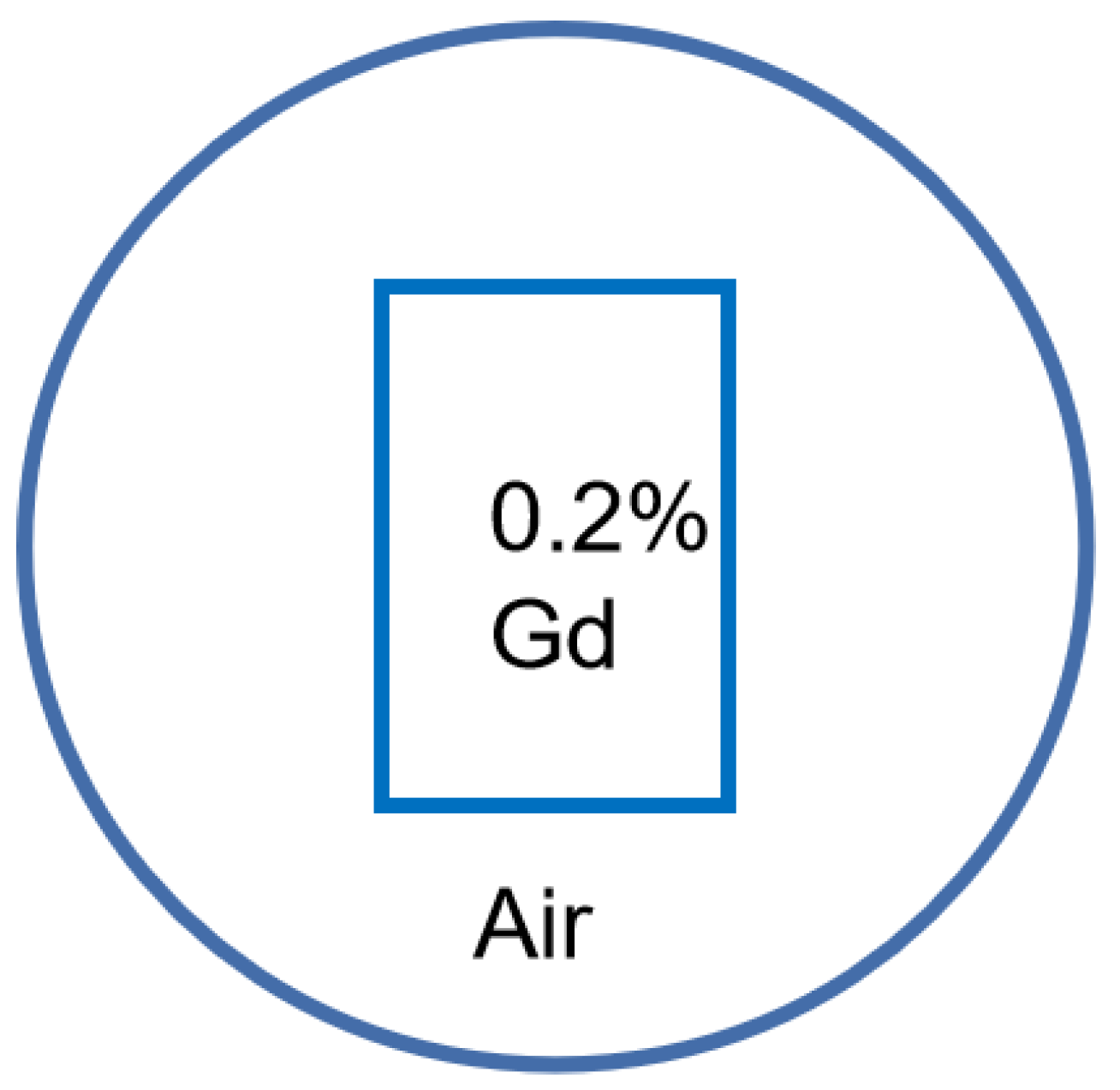
2.3. Datasets
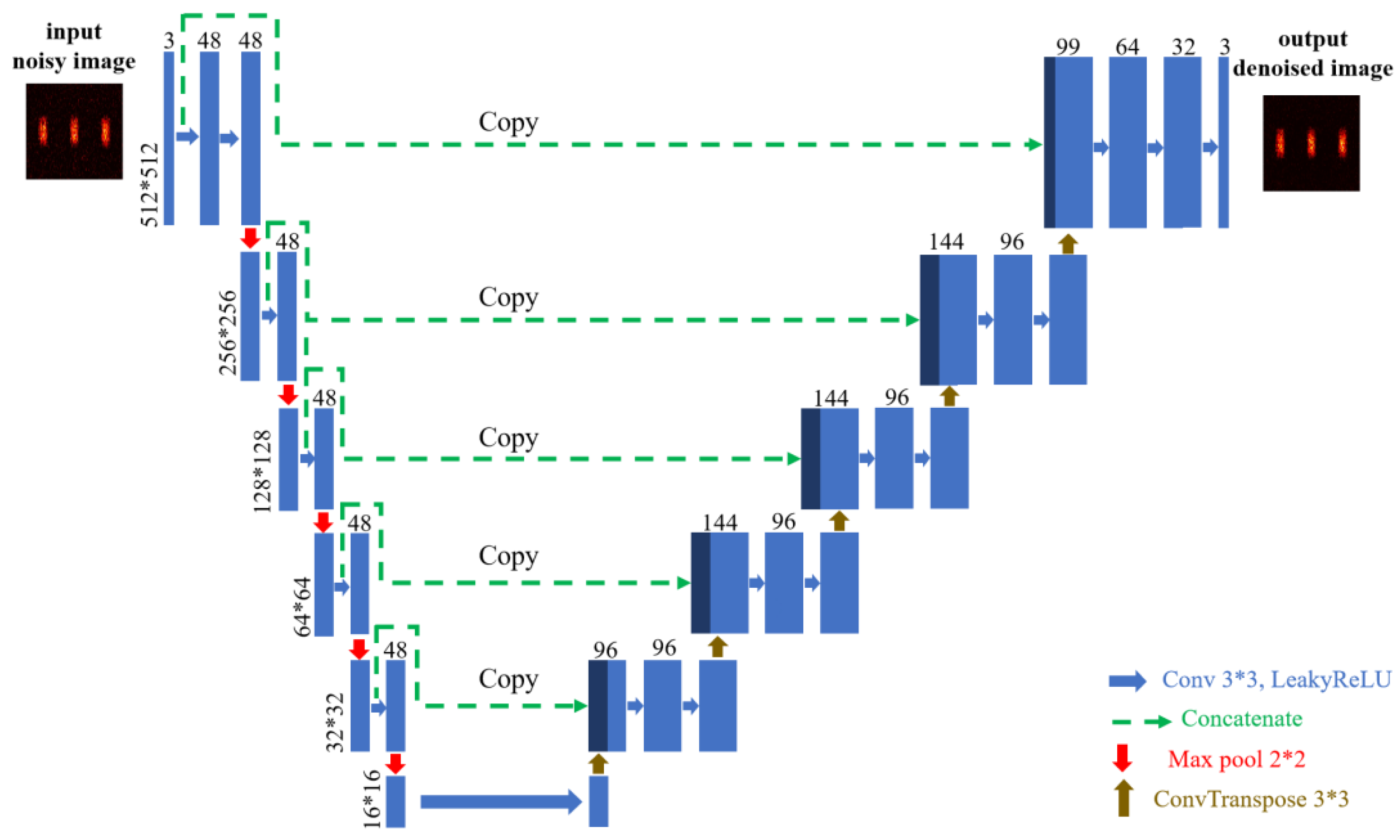
2.4. Network Architecture
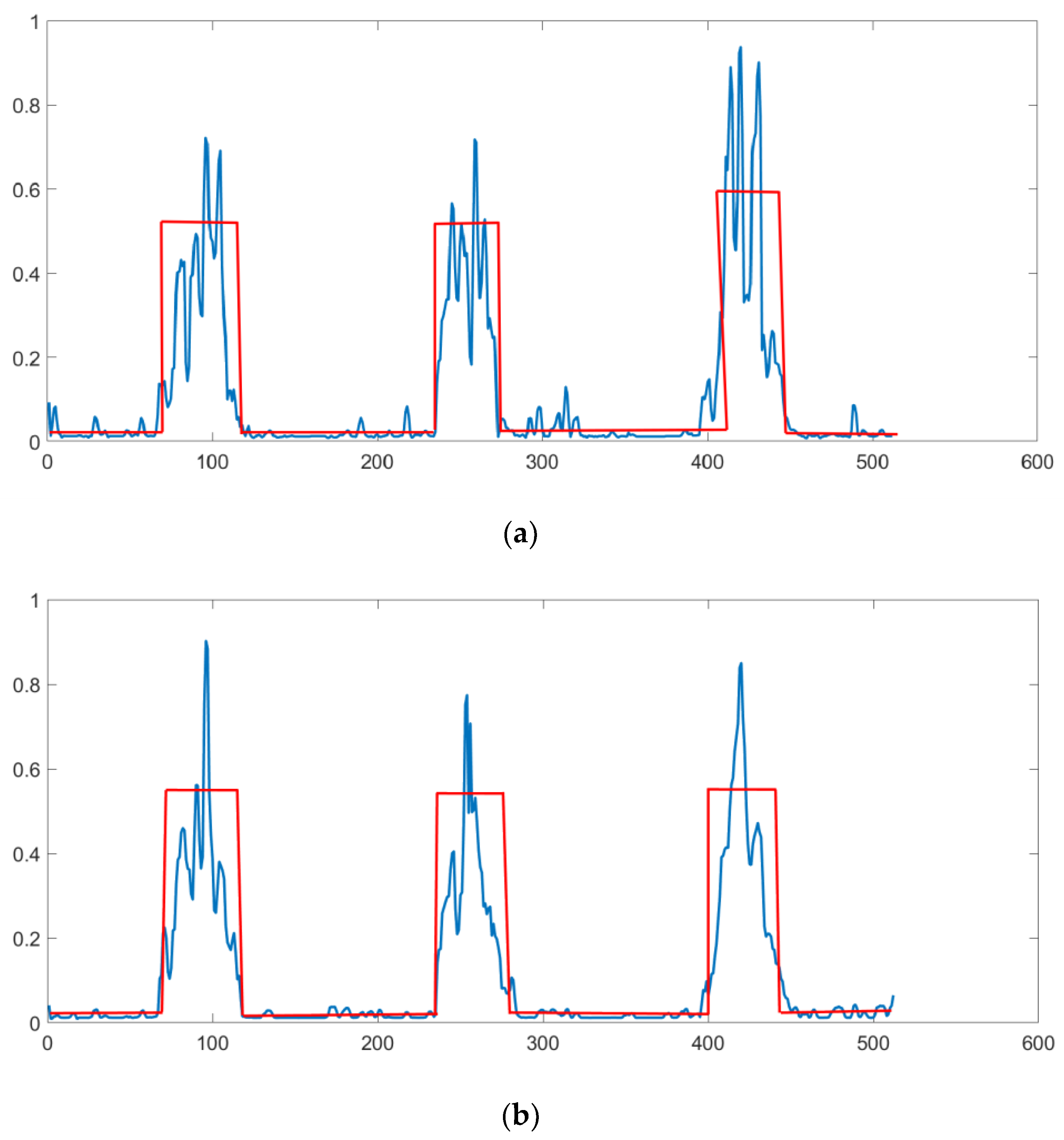
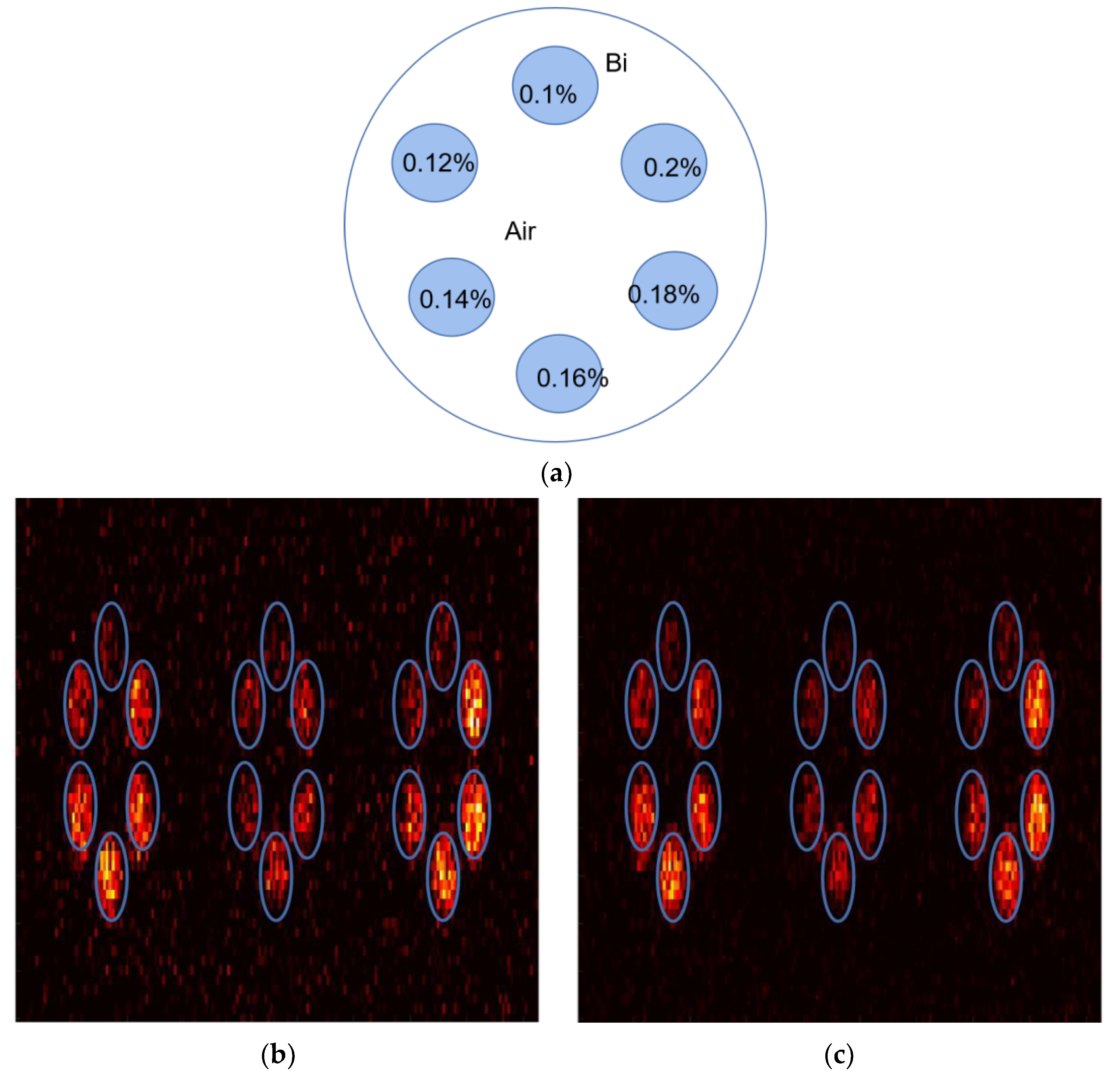
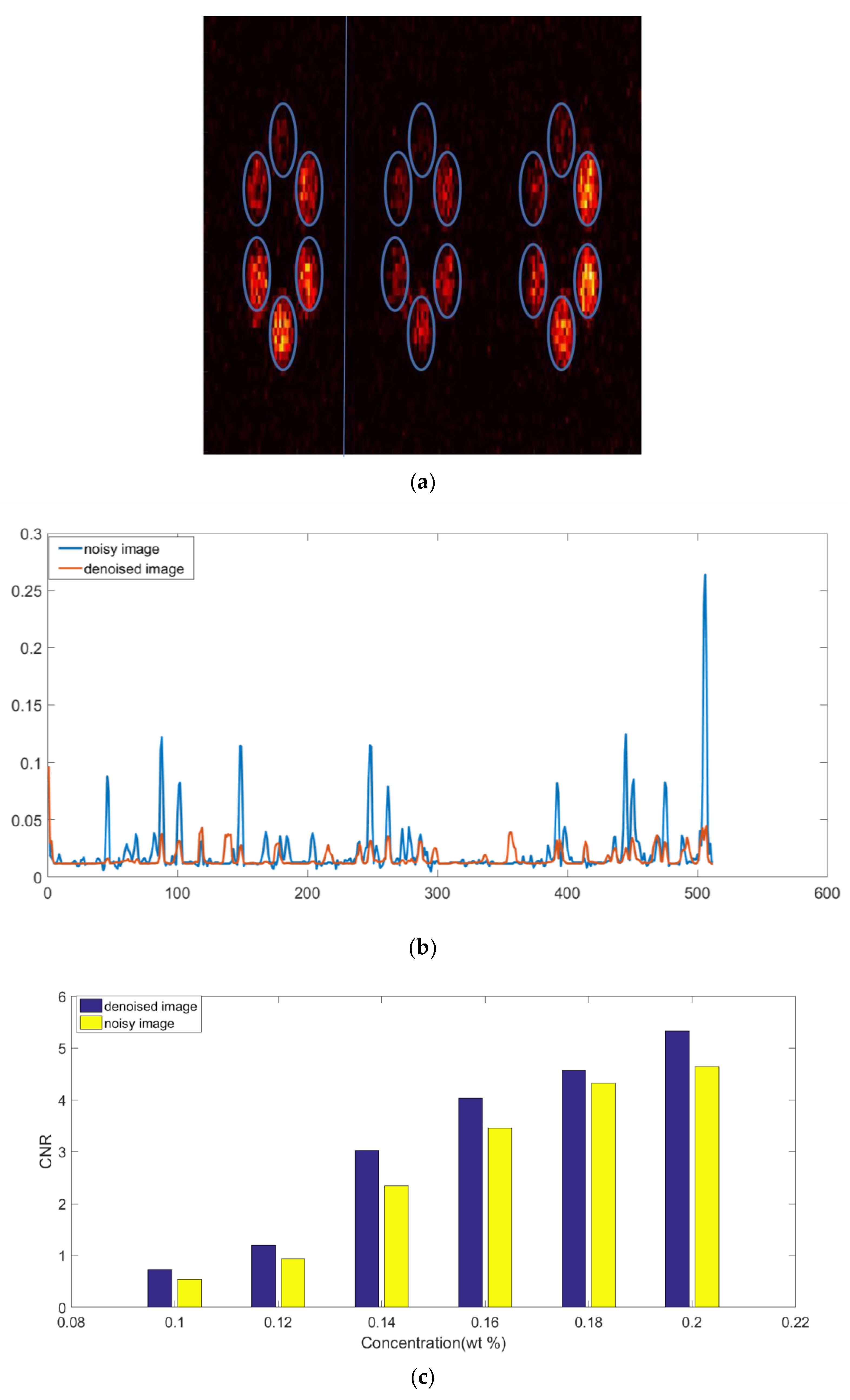
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siyuan, Z.; Liang, L. Quantitative Imaging of Gd Nanoparticles in Mice Using Benchtop Cone-Beam X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, J.; Vogt, C. High-spatial-resolution X-ray fluorescence tomography with spectrally matched nanoparticles. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 164001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, N.; Reynoso, F. Quantitative imaging of gold nanoparticle distribution in a tumor-bearing mouse using benchtop X-ray fluorescence computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grodzins, L.; Boisseau, P. Ion Induced X-rays for X-ray Fluorescence Analysis. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1983, 30, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Yuasa, T. Iodine imaging in thyroid by fluorescent X-ray CT with 0. 05 mm spatial resolution. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2001, 467, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.; Jones, B. X-ray fluorescence computed tomography (XFCT) imaging of gold nanoparticle-loaded objects using 110 kVp X-rays. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.; Shen, H. X-ray fluorescence tomographic system design and image reconstruction. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzhen, D.; Md, F. A detector’s eye view (DEV)-based OSEM algorithm for benchtop X-ray fluorescence computed tomography (XFCT) image reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 64, 08NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, J. Compton Background Elimination for in Vivo X-ray Fluorescence Imaging of Gold Nanoparticles Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Cong, W. Analytic comparison between X-ray fluorescence CT and K-edge CT. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Peng, F. Simulation Research of Multi-Pinhole Collimated L-Shell XFCT Imaging System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 180273–180279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Hasan, M. Hybrid Collaborative Noise2Noise Denoiser for Low-dose CT Images. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020, 5, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawna, G.; Ayush, D. BM3D Outperforms Major Benchmarks in Denoising: An Argument in Favor. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 16, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Peng, F. Simulation Research of Potential Contrast Agents for X ray Fluorescence CT with Photon Counting Detector. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, N.; Morales, H. Contrast/Noise ratio on conventional MRI and choline/creatine ratio on proton MRI spectroscopy accurately discriminate low-grade from high-grade cerebral gliomas. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, P.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, R.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; He, P.; Tang, B.; Zhao, X. Reduction of Compton Background Noise for X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography with Deep Learning. Photonics 2022, 9, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020108
Feng P, Luo Y, Zhao R, Huang P, Li Y, He P, Tang B, Zhao X. Reduction of Compton Background Noise for X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography with Deep Learning. Photonics. 2022; 9(2):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Peng, Yan Luo, Ruge Zhao, Pan Huang, Yonghui Li, Peng He, Bin Tang, and Xiansheng Zhao. 2022. "Reduction of Compton Background Noise for X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography with Deep Learning" Photonics 9, no. 2: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020108
APA StyleFeng, P., Luo, Y., Zhao, R., Huang, P., Li, Y., He, P., Tang, B., & Zhao, X. (2022). Reduction of Compton Background Noise for X-ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography with Deep Learning. Photonics, 9(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020108





