On Optically Modulated Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern-Dependent Overshoot Mitigation Using a Birefringent Fiber Loop
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- The basic metric employed to quantify the performance of the BFL-assisted RSOA, i.e., the overshoot (), has not been adopted or investigated for this purpose before, at least to the best of our knowledge. In fact, the has not been considered either for RSOA optical modulation or for investigating the possibility of improving the performance of RSOA using BFL filtering. However, this metric is critical for properly characterizing the behavior of active devices [10], such as the RSOA, both alone and with the aid of the BFL. This means that other experimental and theoretical studies that have exploited optical filtering technologies to compensate for the pattern effects in semiconductor optical amplifiers and their modified versions may be incomplete, as they have not fully captured the severity of the single (R)SOA performance degradation, on one hand, and the extent of performance improvement enabled by frequency-discrimination-based optical equalization, on the other hand.
- (b)
- The suitability of the reduced model employed to describe the operation of the optically modulated RSOA has been tested either for electrical modulation [11], which from a physical perspective is a totally different function of the RSOA than that considered in our work, or for a train of consecutive input pulses [9], which is a much more relaxed condition for driving the RSOA than ours. In fact, after a couple of repetitive pulses, the RSOA is brought into an equilibrium that prevents pattern effects from manifesting, whilst when subject to pulses of alternating binary content, the RSOA response is not uniform, which provokes the pattern effects.
2. Setup and Modeling
2.1. Setup
2.2. Modeling
2.2.1. RSOA Input
2.2.2. RSOA Response
2.2.3. BFL Response
2.2.4. RSOA-BFL Output
2.2.5. Numerical Solution
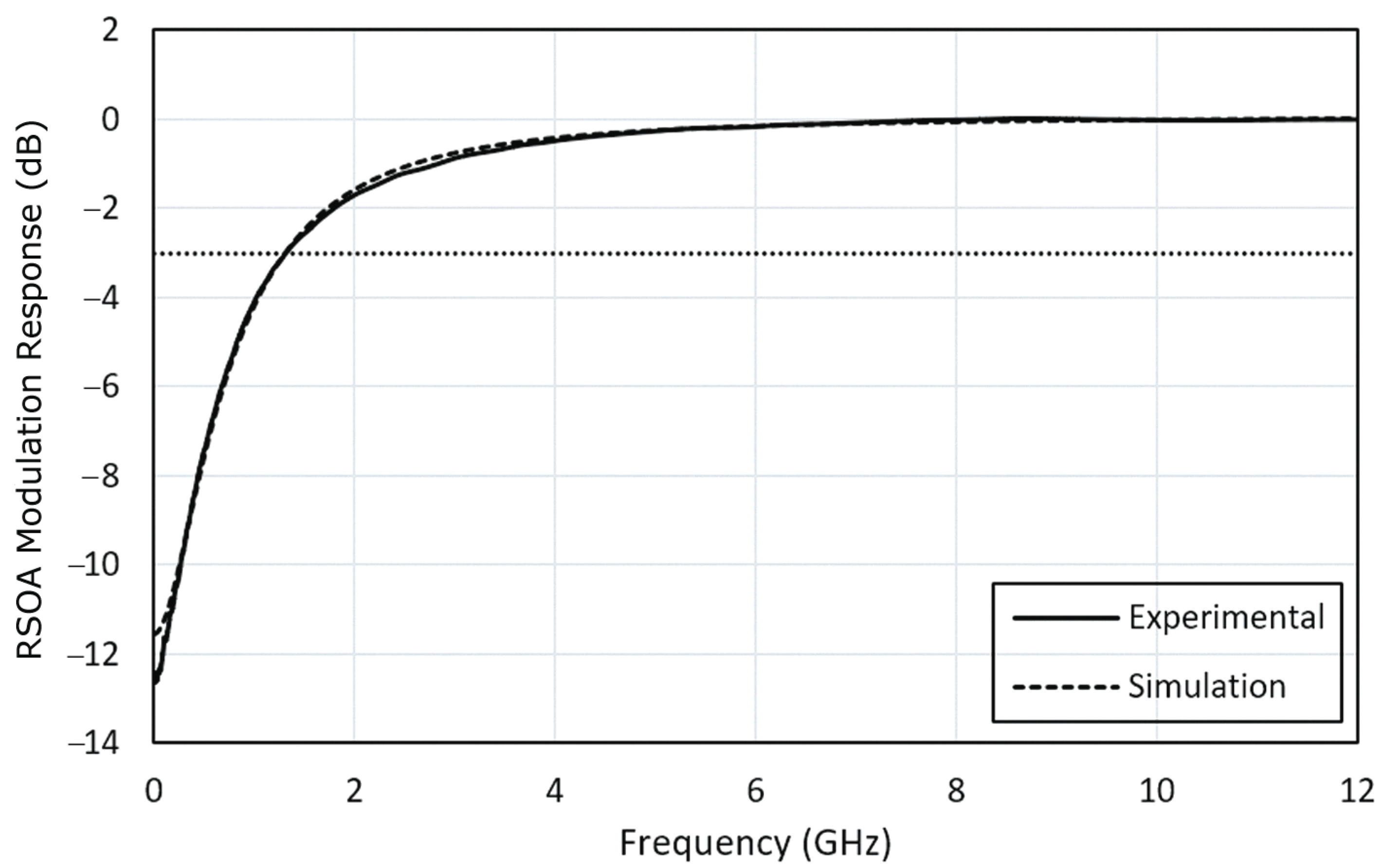
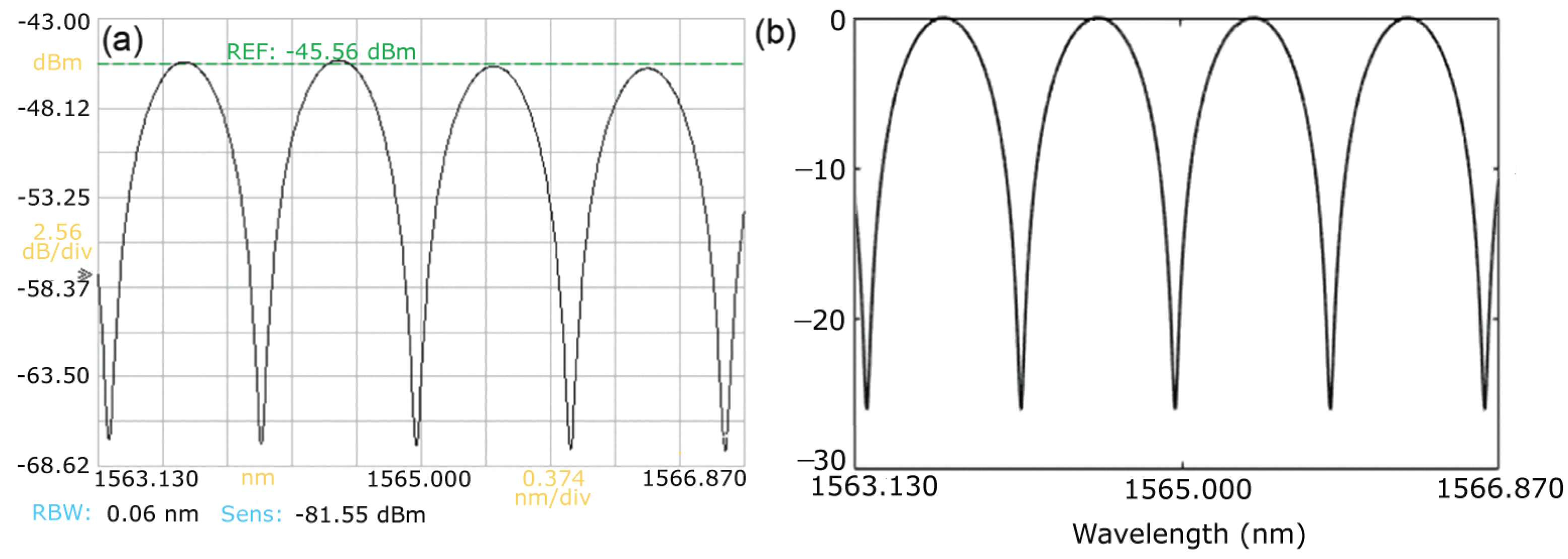
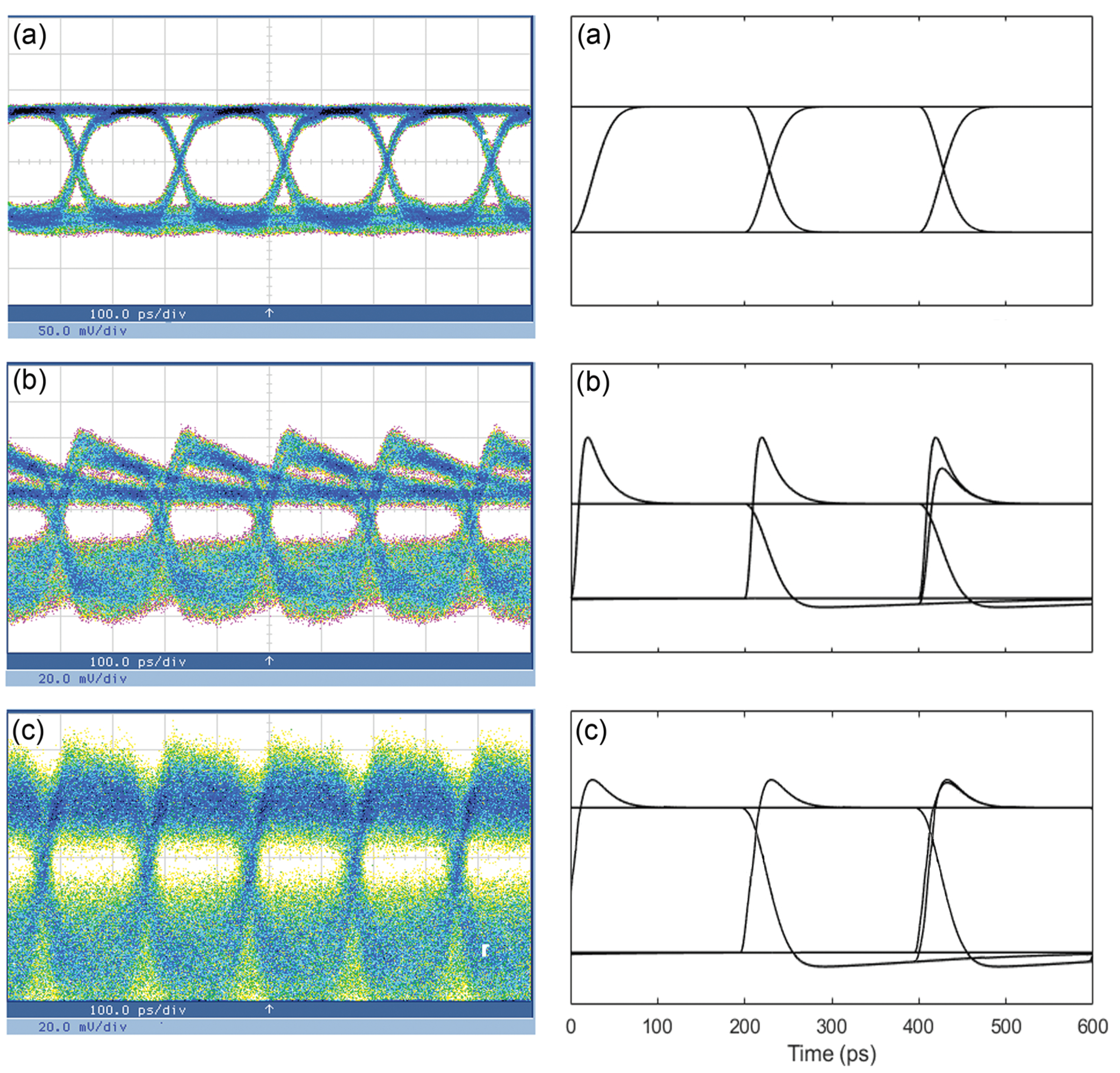
3. Model Validation
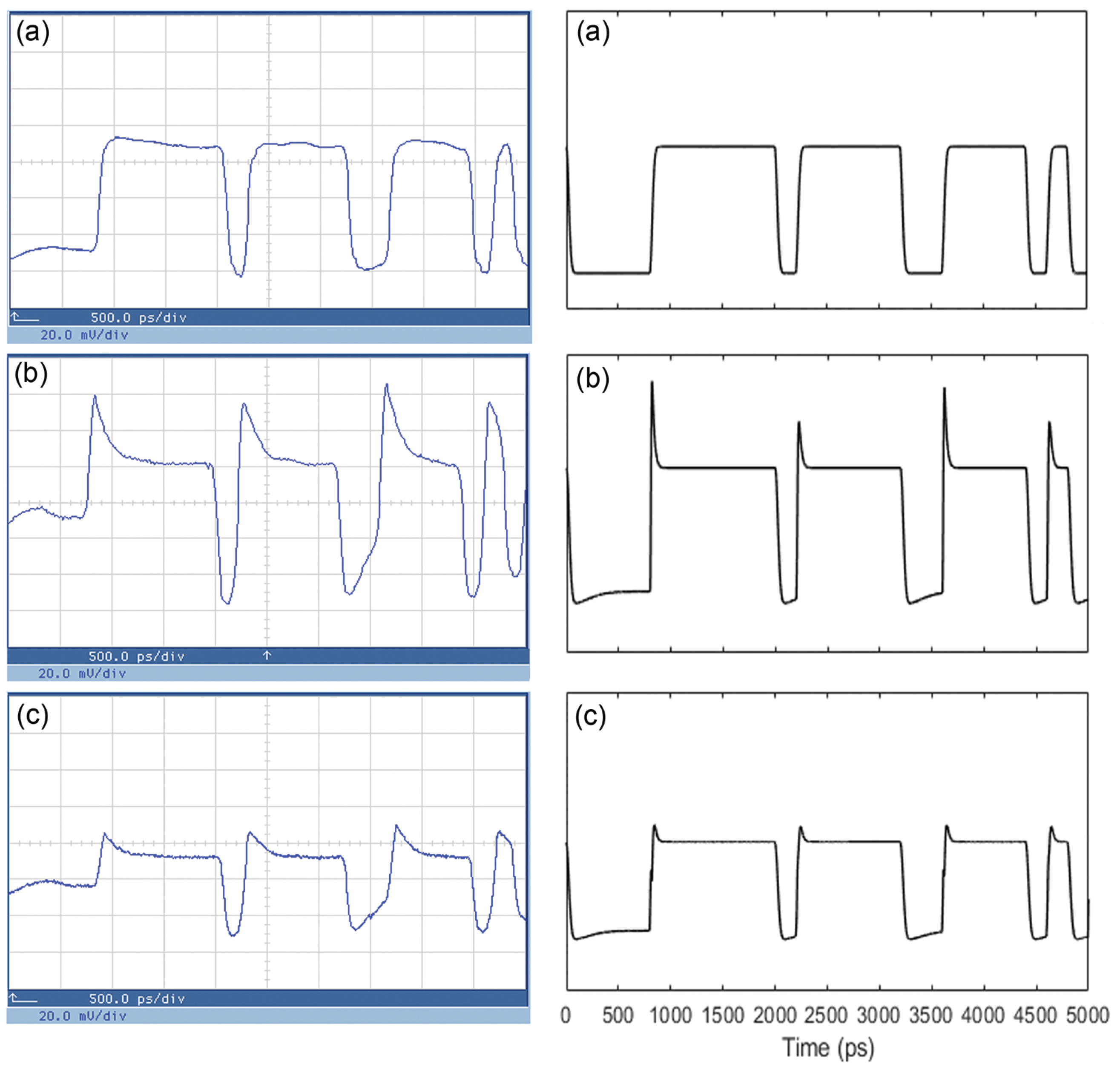
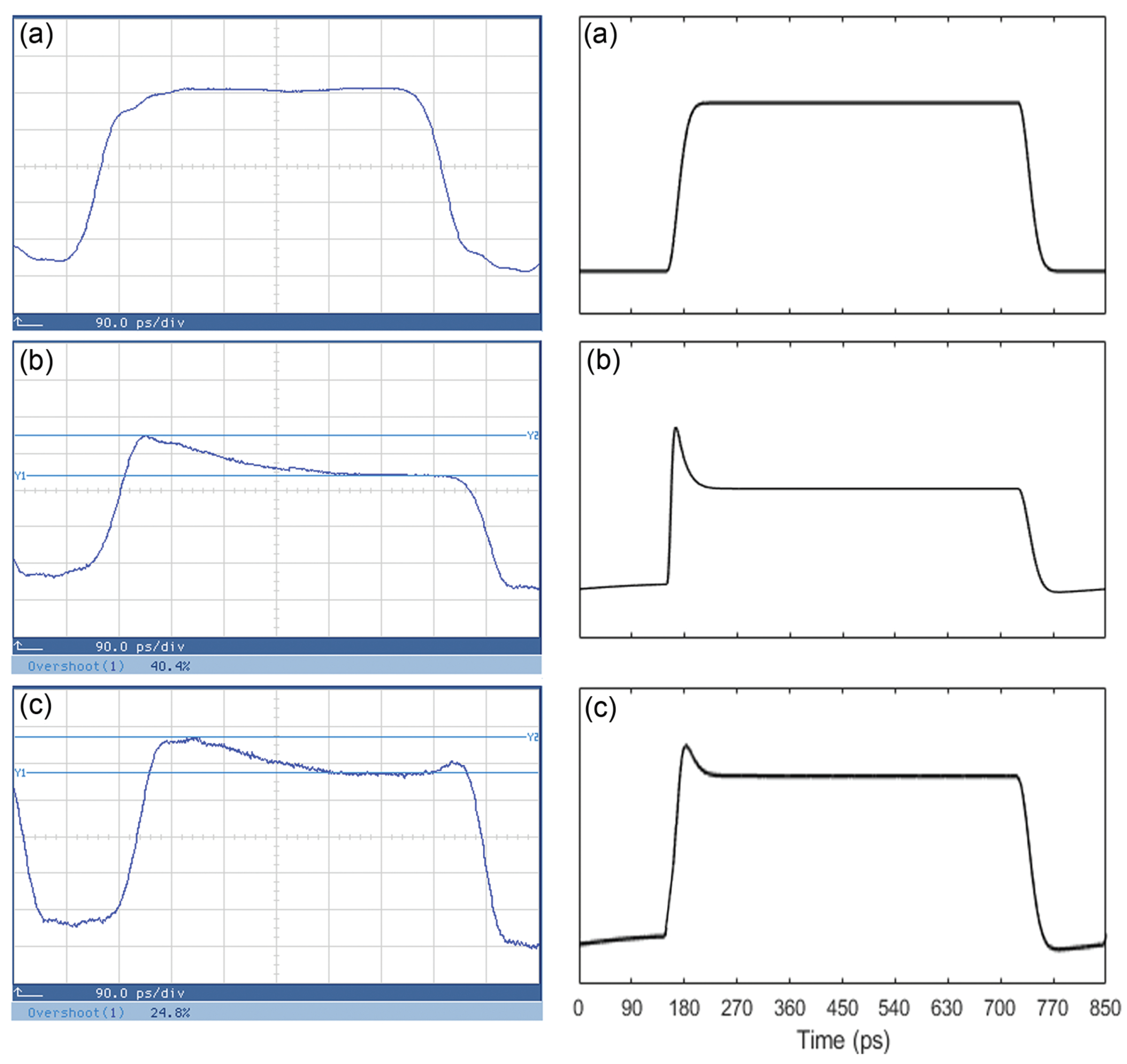
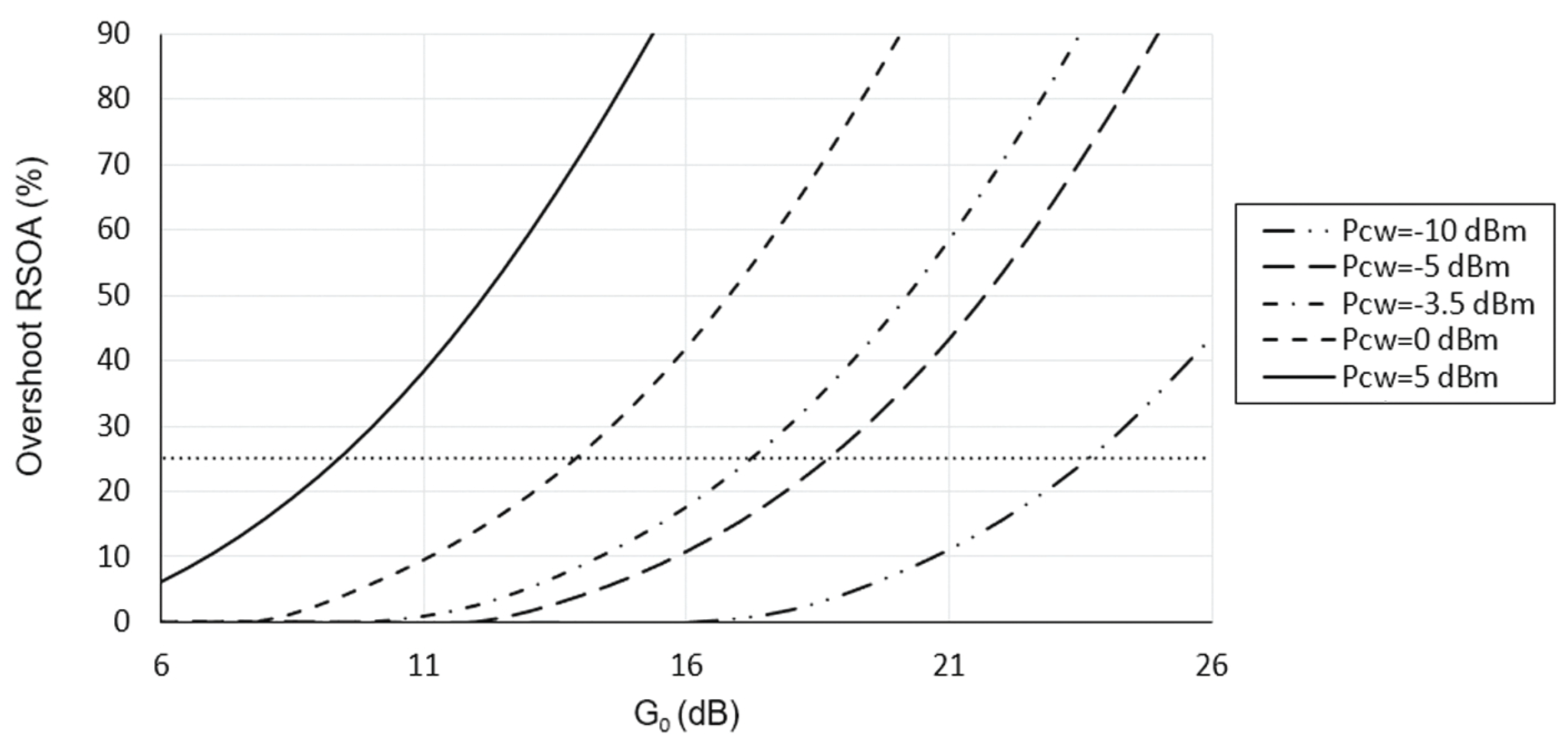
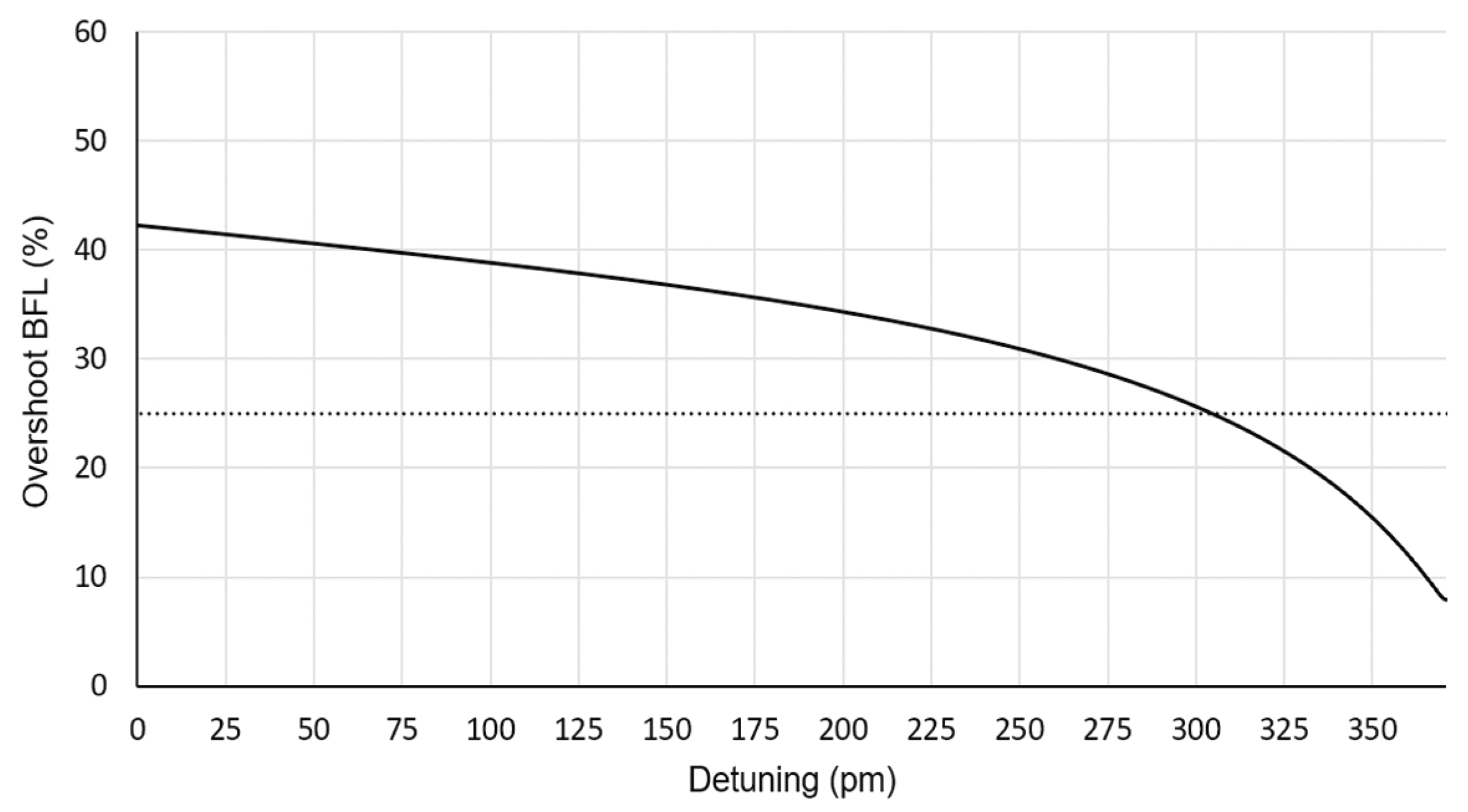
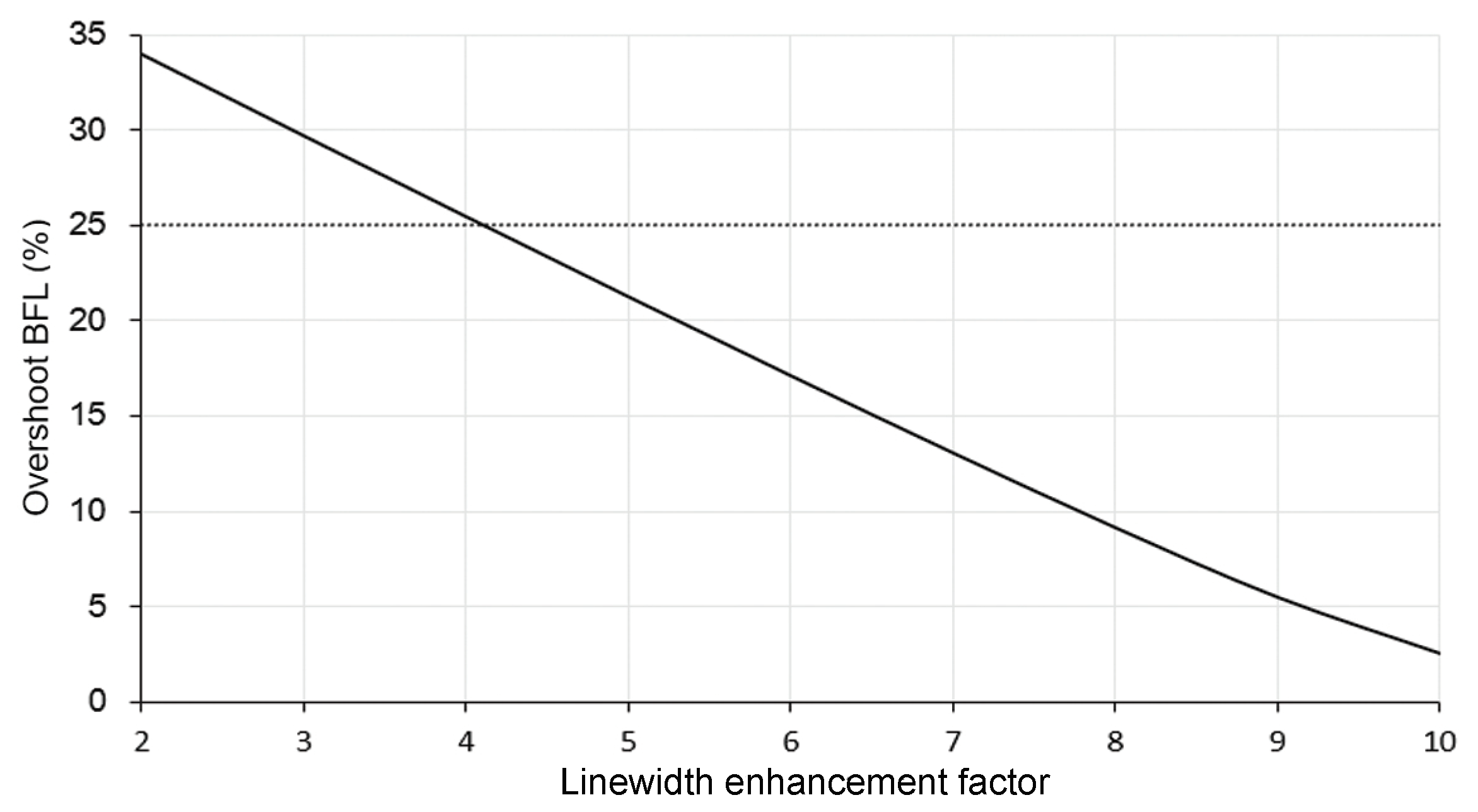
4. Performance Investigation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gebrewold, S.A. Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (RSOAs) as Colorless Sources in Access Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, J. (Ed.) Next-Generation FTTH Passive Optical Networks; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, M.J. Reflective semiconductor optical amplifier pulse propagation model. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 24, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dúill, S.Ó.; Marazzi, L.; Parolari, P.; Brenot, R.; Koos, C.; Freude, W.; Leuthold, J. Efficient modulation cancellation using reflective SOAs. Opt. Express 2012, 20, B587–B594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K. Optical filtering technique to suppress waveform distortion induced in a gain-saturated semiconductor optical amplifier. Electron. Lett. 1997, 33, 885–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Castrejón, R.; Fernández-Segura, O.; Torres-Ferrera, P.; Ceballos-Herrera, D.E. Performance analysis of a directly modulated semiconductor optical amplifiers using non-return-to-zero, duobinary and quaternary pulse amplitude modulation signalling. IET Optoelectron. 2021, 15, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoiros, K.E.; Kastritsis, D.; Rampone, T.; Sharaiha, A. Reflective semiconductor optical amplifier pattern effect compensation with birefringent fiber loop. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, Z.; Zoiros, K.; Connelly, M. Semiconductor optical amplifier pattern effect suppression using optical notch filtering. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2016, 9, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, C.; Mecozzi, A. Reduced model for the nonlinear response of reflective semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEEPhotonics Technol. Lett. 2013, 25, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.L.; Tsuruoka, K.; Kato, T.; Morimoto, T.; Sudo, S.; Okamoto, T.; Mizutani, K.; Sakuma, H.; Sato, K.; Kudo, K. SOA-booster integrated Mach–Zehnder modulator: Investigation of SOA position. J. Light. Technol. 2010, 28, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, C.; Mecozzi, A.; Hu, Z.; Santagiustina, M. Analytic study of the modulation response of reflective semiconductor optical amplifiers. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 4367–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patent, E.; van der Tol, J.; Calabretta, N.; Liu, Y. Compensation of the pattern effect in SOAs. In International Workshop on Optical Signal Processing (COST 276 and SCOOP); Citeseer: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.; Tsang, H. Reduction of bit-pattern dependent errors from a semiconductor optical amplifier using an optical delay interferometer. Opt. Commun. 2004, 232, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K. Waveform distortion in a gain-saturated semiconductor optical amplifier for NRZ and Manchester formats. IEE Proc.-Optoelectron. 1997, 144, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujičić, Z.; Dionísio, R.P.; Shahpari, A.; Pavlović, N.B.; Teixeira, A. Efficient dynamic modeling of the reflective semiconductor optical amplifier. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2013, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Hong, W.; Huang, D. Experimental study of SOA-based NRZ-to-PRZ conversion and distortion elimination of amplified NRZ signal using spectral filtering. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 5618–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, Z.V.; Zoiros, K.E.; Hatziefremidis, A.; Connelly, M.J. Performance tolerance analysis of birefringent fiber loop for semiconductor optical amplifier pattern effect suppression. Appl. Phys. B 2015, 119, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, Z.V.; Zoiros, K.E.; Rampone, T.; Sharaiha, A. Reflective semiconductor optical amplifier direct modulation capability enhancement using birefringent fiber loop. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamze, M. Study of Different SOA Structures Impact on the Transmission of IMDD OOFDM Signals. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bretagne Occidentale (UBO), Brest, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L. Analysis of the phase noise in saturated SOAs for DPSK applications. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2005, 41, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Toba, H. Reduction of mode partition noise by using semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2001, 7, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, D.R.; Spiekman, L.H. Amplifiers for the masses: EDFA, EDWA, and SOA amplets for metro and access applications. J. Light. Technol. 2004, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valicourt, G.; Make, D.; Landreau, J.; Lamponi, M.; Duan, G.; Chanclou, P.; Brenot, R. High gain (30 dB) and high saturation power (11 dBm) RSOA devices as colorless ONU sources in long-reach hybrid WDM/TDM-PON architecture. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2010, 22, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Castrejón, R.; Occhi, L.; Schares, L.; Guekos, G. Recovery dynamics of cross-modulated beam phase in semiconductor amplifiers and applications to all-optical signal processing. Opt. Commun. 2001, 195, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, Z.V.; Zoiros, K.E.; Hatziefremidis, A.; Connelly, M.J. Design analysis and performance optimization of a Lyot filter for semiconductor optical amplifier pattern effect suppression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2013, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M. Information Transmission, Modulation and Noise. A Unified Approach to Communication Systems; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]




| Symbol | Definition | Value | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data pulse average (CW) power | −3.5 | dBm | [7] | |
| Data pulse repetition period | 200 | ps | [7] | |
| Data pulse rise time | 17% of repetition period | ps | [7] | |
| RSOA confinement factor | 0.21 | - | [19] | |
| a | RSOA differential gain | m | [19] | |
| RSOA carrier density at transparency | m | [19] | ||
| RSOA linewidth enhancement factor | 5 | - | [19] | |
| RSOA semiconductor material group refractive index | 3.6 | - | [19] | |
| RSOA active region length | 713 | um | [19] | |
| RSOA dc bias current | 70 | mA | [7] | |
| RSOA transparency current | 45 | mA | [18] | |
| RSOA carrier lifetime | 248.9 | ps | Specified by fitting to experiment [7] | |
| RSOA semiconductor material saturation power | 17 | dBm | Specified by fitting to experiment [7] | |
| B | BFL birefringence | - | [7] | |
| BFL PMF total length | 8.5 | m | [7] | |
| BFL detuning | 325 | pm | [7] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avgenos, N.; Zoiros, K.E.; Rizou, Z.V. On Optically Modulated Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern-Dependent Overshoot Mitigation Using a Birefringent Fiber Loop. Photonics 2022, 9, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040248
Avgenos N, Zoiros KE, Rizou ZV. On Optically Modulated Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern-Dependent Overshoot Mitigation Using a Birefringent Fiber Loop. Photonics. 2022; 9(4):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040248
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvgenos, Nikolaos, Kyriakos E. Zoiros, and Zoe V. Rizou. 2022. "On Optically Modulated Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern-Dependent Overshoot Mitigation Using a Birefringent Fiber Loop" Photonics 9, no. 4: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040248
APA StyleAvgenos, N., Zoiros, K. E., & Rizou, Z. V. (2022). On Optically Modulated Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern-Dependent Overshoot Mitigation Using a Birefringent Fiber Loop. Photonics, 9(4), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040248






