Maritime Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Refined Features Fusion and Sobel Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a framework for the maritime infrared and visible image fusion task that is very important for ship navigation and human rescue at sea;
- We measure the gradients of each pair of feature maps and fuse the refined features;
- We develop a loss function based on Sobel edge detection to reduce hyperparameters in the loss function. As far as we know, this is the first time that Sobel edge is used as a loss function for multimodal image fusion;
- We test the proposed method on public datasets. The qualitative and quantitative results validate the effectiveness of our method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Maritime Computer Vision
2.2. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
2.3. Loss Function
3. Method
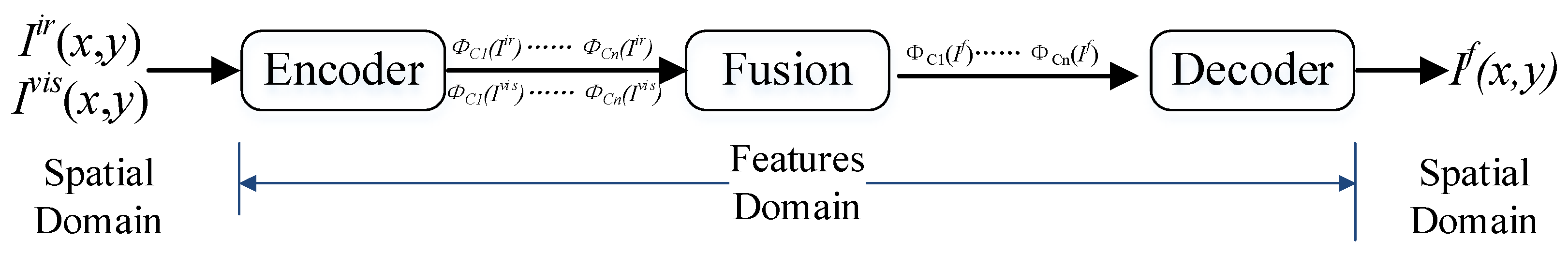
3.1. Domain Transform
3.2. Refined Features Fusion
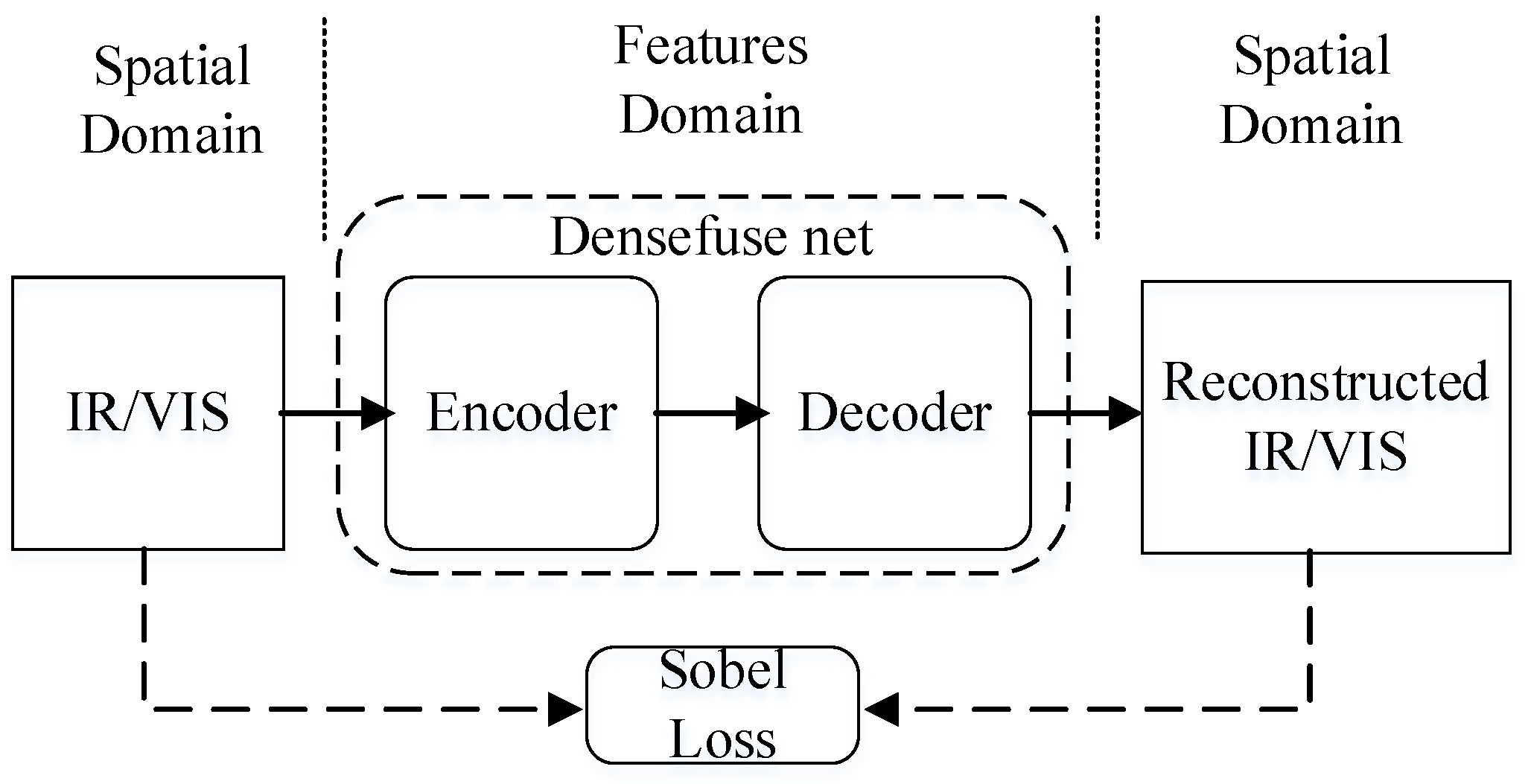
3.3. Sobel Loss
4. Results and Discussion
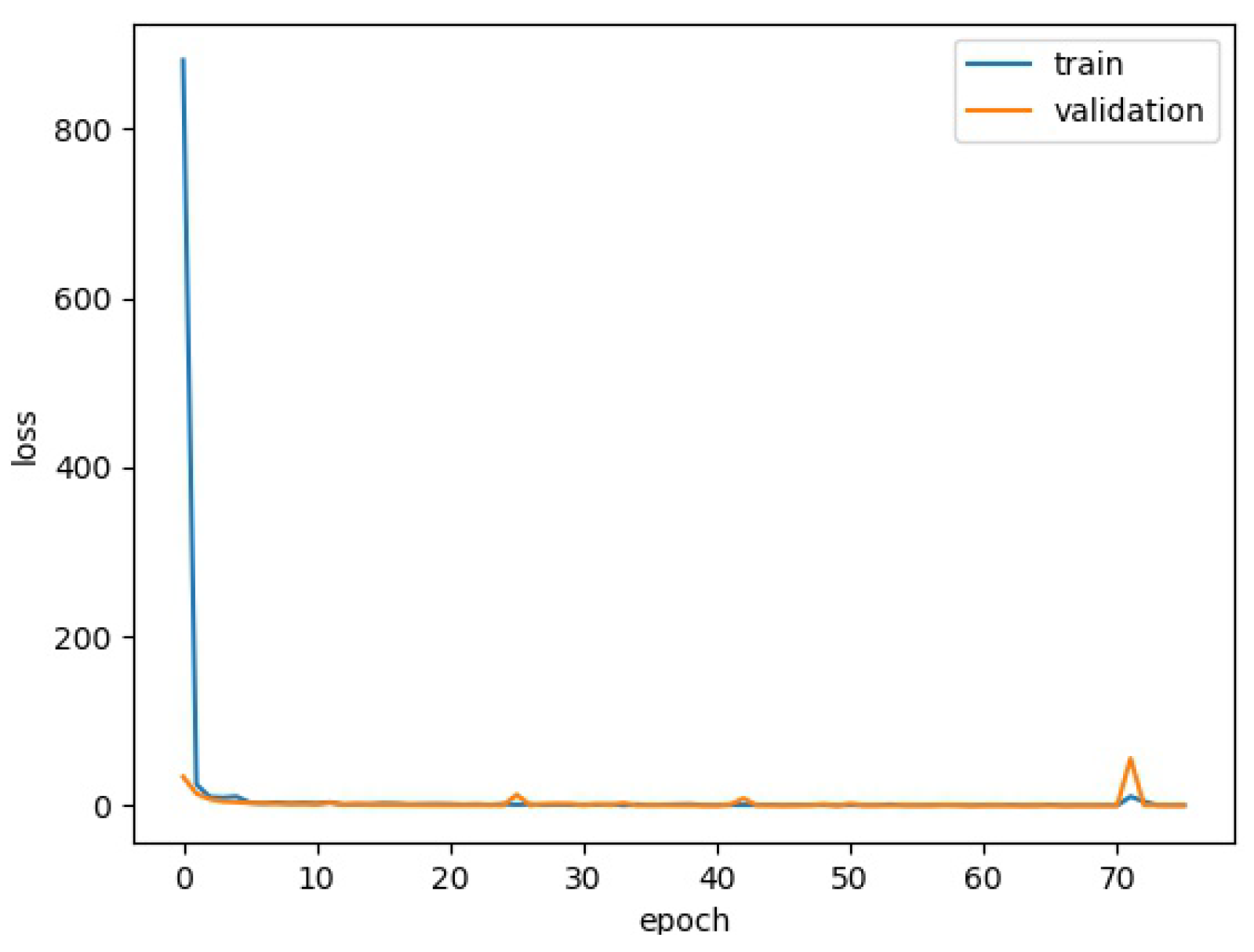
4.1. Training Details
4.2. Refined Feature Fusion
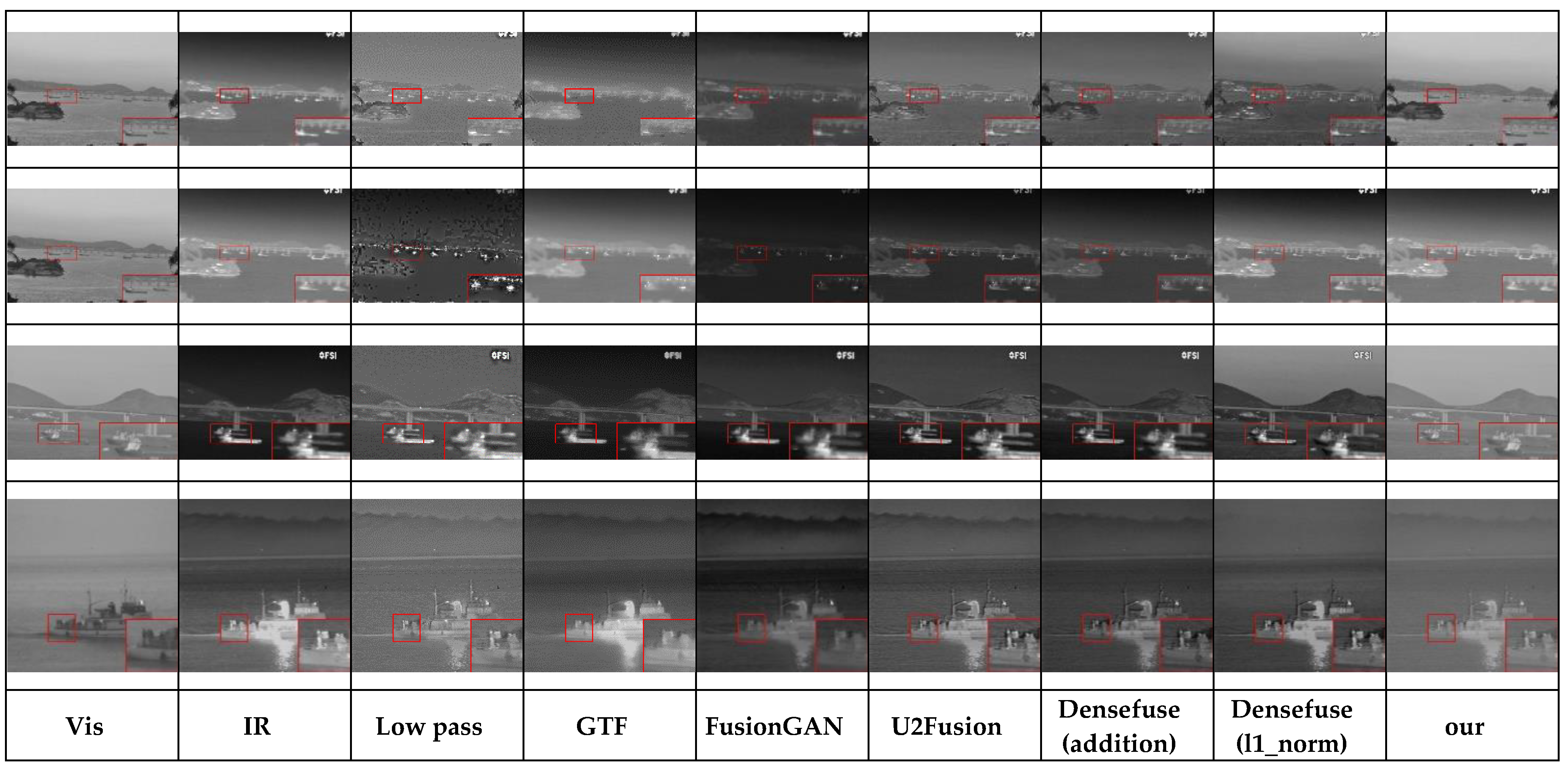
4.3. Performance Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion meets deep learning: A survey and perspective. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, S.; Zhou, D.; Nie, R.; Hai, J.; He, K. A survey of infrared and visual image fusion methods. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 85, 478–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødseth, Ø.J.; Tjora, Å. A System Architecture for an Unmanned Ship. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer and IT Applications in the Maritime Industries (COMPIT), Redworth, UK, 12–14 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Wróbel, K.; Montewka, J.; Gil, M.; Wan, C.; Zhang, D. A framework to identify factors influencing navigational risk for Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships. Ocean Eng. 2020, 202, 107–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls-Royce. Remote and Autonomous Ships the Next Steps, London, UK. 2016. Available online: https://www.rolls-royce.com/~/media/Files/R/Rolls-Royce/documents/%20customers/marine/ship-intel/rr-ship-intel-aawa-8pg.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- China Classification Soc. Smart Ship Specification 2020, Beijing, China. December 2019. Available online: https://www.ccs.org.cn/ccswz/articleDetail?id=201900001000009739 (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Toet, A. Image fusion by a ratio of low-pass pyramid. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1989, 9, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Qu, X.D. An infrared and visible image fusion method based on multi-scale transformation and norm optimization. Inf. Fusion 2021, 71, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image Fusion With Convolutional Sparse Representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y. Self-supervised feature adaption for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A Unified Unsupervised Image Fusion Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Qi, Y.; Ding, W.R. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, D. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment with Convolutional Neural Networks and Decision Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmanis, D.; Datcu, M.; Esch, T.; Stilla, U. Deep learning earth observation classification using ImageNet pretrained networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 13, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, J.; Boots, B. Improving image clustering with multiple pretrained cnn feature extractors. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.07760. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.P. DDcGAN: A Dual-Discriminator Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Multi-Resolution Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Le, Z.; Shao, Z.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. MFF-GAN: An unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gallo, O.; Frosio, I.; Kautz, J. Loss Functions for Image Restoration with Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2017, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Li, F.-F. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales, R.; Woods, R. Digital Image Processing, 4th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.; Fowlkes, C.; Tal, D.; Malik, J. A Database of Human Segmented Natural Images and Its Application to Evaluating Segmentation Algorithms and Measuring Ecological Statistics. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; pp. 416–423. [Google Scholar]
- Arbeláez, P.; Maire, M.; Fowlkes, C.; Malik, J. Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. TNO Image Fusion Dataset. 2014. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/TNO_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029 (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Zhang, Y. Handbook of Image Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Y.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xydeas, C.S.; Petrovic, V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMT/COPPE/Poli/UFRJ and IME-Instituto Militar de Engenharia, Visible-Infrared Data. 2016. Available online: http://www02.smt.ufrj.br/∼fusion/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).



| Layer | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature gradient | 269.2 | 48.3 | 42.8 | 4.8 | 74.2 | 140.1 | 10.3 | 39.6 | |
| 142.3 | 52 | 43.2 | 4.5 | 92.4 | 122.2 | 9.4 | 34.3 | ||
| Weight | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.54 | |
| 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.46 | ||
| EN | Qabf | SCD | FMIw | FMIdct | SSIM | MS_SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low pass | 6.470 | 0.468 | 1.634 | 0.401 | 0.283 | 0.689 | 0.858 | |
| GTF | 6.637 | 0.425 | 1.028 | 0.437 | 0.420 | 0.704 | 0.814 | |
| FusionGAN | 6.355 | 0.219 | 1.472 | 0.371 | 0.361 | 0.655 | 0.731 | |
| U2Fusion | 6.745 | 0.424 | 1.810 | 0.362 | 0.339 | 0.695 | 0.925 | |
| Densefuse | Addition | 6.665 | 0.442 | 1.849 | 0.427 | 0.416 | 0.732 | 0.930 |
| l1_norm | 6.846 | 0.474 | 1.712 | 0.431 | 0.381 | 0.720 | 0.860 | |
| ours | 6.341 | 0.496 | 1.627 | 0.440 | 0.423 | 0.765 | 0.894 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Ma, B. Maritime Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Refined Features Fusion and Sobel Loss. Photonics 2022, 9, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080566
Gao Z, Zhu F, Chen H, Ma B. Maritime Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Refined Features Fusion and Sobel Loss. Photonics. 2022; 9(8):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080566
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zongjiang, Feixiang Zhu, Haili Chen, and Baoshan Ma. 2022. "Maritime Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Refined Features Fusion and Sobel Loss" Photonics 9, no. 8: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080566
APA StyleGao, Z., Zhu, F., Chen, H., & Ma, B. (2022). Maritime Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Refined Features Fusion and Sobel Loss. Photonics, 9(8), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080566





